35
alexandria.healthlibrary.ca Electrophysiology and ECG
ECG recording and lead placement
Electrodes, leads & wires mikecowley.co.uk
ECG reading and reporting |
|
|---|---|
| Calibration | Time measured on horizontal axis, Voltage on vertical axis1 large sq = 0.2s or 5 mv1 small sq = 0.04s or 1mvRate = 300 / number of large squares between two R waves |
| Rate | Ventricular Rate = 300/no large squares between adjacent r waves |
| Rhythm | Sinus rhythmSlow & RegularFast & RegularSlow & IrregularFast & Irregular |
| P wave | atrial contraction |
| PR interval | should be less tha 0.2s (5 small squares) |
| QRS complex | ventricular contraction shoiuld be less than 0.12s (3 small squares) |
| ST segment | |
| T wave | resting phase/repolarisation |
| Axis | |
ECG tutorials
Alan Lindsay ECG learning centre med.utah.edu
ABC Clinical Cardiology BMJ 2002 Acute MI
ECG rate
ECG Heart Rate
Ventricular Rate = 300/no large squares between adjacent r waves
| no big squares between QRS | rate |
| 1 | 300 bpm |
| 2 | 150 bpm |
| 3 | 100 bpm |
| 4 | 75 bpm |
| 5 | 60 bpm |
| 6 | 50 bpm |
mcgill.ca ekg heart rate rhythm
ECG rythm
ECG rythm lifeinthefastlane.com
QRS complex / waveform and intervals
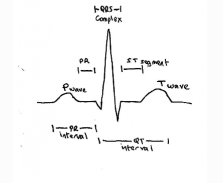
ECG Basics lifeinthefastlane.com
ambulancetechnicianstudy.co.uk ecg basics
ECG axis
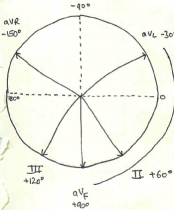
ECG axis lifeinthefastlane.com
Common pathological conditions on ECG
ECG Interpretation A to Z by diagnosis lifeinthefastlane.com
| ECG Conduction Abnormalities (see also under pulse) | |
|---|---|
| Heart block | impaired conduction through AV node |
| 1° HB | prolonged conduction through AV nodePR interval >0.2sasymptomatic – no treatment |
| 2° HBMobitz type 1Wenkebach | PR increases progressively then dropped QRSusually asymptomatic – observe |
| 2° HBMobitz type 2 | occasional intermittent or regular (eg 2:1, 3:1) dropped beats not preceded by progressive PR prolongation |
| 3° HB / CHB | no relationship between P waves and (wide slow) QRS complexes- failure of conduction through AV node with venticular escape beatsM type 2 and CHB may cause stokes adams, dizyness, palpitations, chest pain, HF – Rx pacing |
| IntraventricularConduction Defects | Bundle Branch Block BBB QRS > 0.12soften incidental and asymptomaticno treatment unless post MI |
| RBBB | RIGHT BBB MaRRoW m shaped v1 sometimes w in V6rSR with wide R in V1: QRS with wide s in V6 |
| LBBB | LEFT BBB WiLLiamW in V1 with occassional M shaped in V6wide negative QS in V1 Wide R without Q in V6 |
ECG hypertrophy
Atrial Hypertrophy
left atrial enlargement lifeinthefastlane.com
right atrial enlargement lifeinthefastlane.com
biatrial enlargement lifeinthefastlane.com
Ventricular hypertrophy
Left Ventricle Hypertrophy lifeinthefastlane.com
| Locating Myocardial Damage from the ECG | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Site | Leads | Artery Involved | Reciprocal Changes |
| Anterior | v3-v4 | ||
| Anterolateral | v5-v6 | ||
| Anteroseptal | v1-v2 | ||
| Inferior | II III avF | ||
| Lateral | I avL | ||
| Posterior | Tall R wave and ST depression in V1-v3 | ||
| Right Ventricular | |||
ECG ischaemia and ACSMI Localisation lifeinthefastlane.com
ECG arrythmias
ECG learning centre med.utah.edu
ECG bradycardias
ECG bradycardias – see heart blocks
ECG atrial fibrillation and flutter
Atrial Fibrillation 3 Ps – paroxysmal persistant and permanant but no p on ECG
ECG supra ventricular tachycardia SVT
VT versus SVT with aberrancy lifeinthefastlane.com
ECG ventricular tachycardia
Ventricular tachycardia medscape
Ventricular Rhythms and Tachycardias ECG library med.utah.edu