42
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Taunton And Somerset NHS
- Miscellaneous dental conditions tauntonmaxfax.net
- maxfax sho.co.uk
- Oral Health Rural Health West au
- Centre for Rural and Remote Oral Health University of Western Australia
- youtu.be/RLYhVe5Cp14
- youtu.be/pl3jnDRr9f4
Mouth examination
Perioral Dermatitis
hacking-medschool/perioral-dermatitis
Angular cheilitis / stomatitis
Herpes simplex stomatitis
Apthous ulcers
- Apthous ulcers medscape
- Paediatric apthous ulcers medscape
- Apthous Ulcers AAFP
- Apthae dermnetnz
- tauntonmaxfax.net oral ulceration
Behcets syndrome
Oral thrush
C. albicans yeast infection of the oral mucous membrane and tongue
3 types
acute pseudomembranous – newborn and impaired immunity including inhaled steroids – use a spacer and gargle with water afterwards
chronic atrophic
chronic hyperplastic
- tauntonmaxfax.net oral candida infections
- youtube.com/watch?v=x1orHYpV0kc
- youtube.com/watch?v=ijk855MLDvg
DD – Consider leukoplakia oral lichen planus
1st line Rx Nystatin suspension 100,000 units/mL, 1mL 6 hourly for 7 days or 48 hours after lesions have resolved
Increase dose to 500,000 units if extensive in terminal illness and immuno-compromised adults.
Miconazole gel in babies and small children.
2nd line Fluconazole 50-100mg daily for 7-14 days or itraconazole 100mg daily for 15 days. (200mg daily in immuno-compromised).
Leukoplakia
- youtu.be/bn1NNFMRde4
- tauntonmaxfax.net white patches leukoplakia and oral lichen planus
- Leukoplakia NHS choices
- Leukoplakia medlineplus
- cancerresearchuk.org mouth and oropharyngeal cancers
- skincancer-survivor.com leukoplakia
Oral Lichen Planus
Geographic Tongue
Smooth patches due to loss of papillae. Not clinically significant.
tauntonmaxfax.net geographic tongue
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_QJ2jho_8d0
Pale smooth tongue
with atrophy of filiform papillae – iron/B12 deficiency
Giant black hairy tongue
Benign condition due to overgrowth/elongation of dermal papillae.
?? May be due to candida secondary to smoking, antibiotics or steroids.
Enlarged tongue
Amyloidosis, acromegaly, myxoedema
Neurological Conditions
fasiculations and wasting – LMN lesions eg progressive bulbar palsy
spastic tongue + dysarthria and increased jaw jerk – pseudobulbar palsy
Glossodynia
- tauntonmaxfax.net burning tongue
- mayoclinic.com burning mouth syndrome
- emedicinezone.com glossodynia
Xerostomia dry mouth
- http://youtu.be/FIFgYuP6dqE
- Xerostomia PUK
- Xerostomia uic.edu
- macmillan.org.uk Mouthcare/Radiotherapy
Halitosis
Facial pain
TMJ disorders
http://youtu.be/wOAtErs0yR8
TMJ tauntonmaxfax.net
Salivary gland disease
Parotid swelling
Mumps, DM, debilitated alkies, TB sarcoid, Sjorjens lymphoma and syphilis.
Unilateral swelling – mised parotid tumour
Intermittent swelling – salivary calculi
Submandibular swelling
Whartonns submandibular duct obstruction
hacking-medschool/parotid-salivary-glands
tauntonmaxfax.net salivary glands
Teeth
Dentition naming systems
Dental arch – Visual Dictionary ©2005-2011 – All rights reserved
Tooth numbering system Web dental office
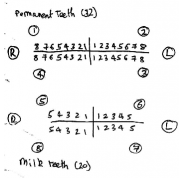
Teeth are numbered from 1 to 8 from the midline.
Permanent teeth (n =32)
Deciduous teeth (n = 20)
World Dental Federation International 2 digit notation
Each of the four quadrants are numbered
Palmer’s notation
A cross is drawn to represent quadrants, but the numerals are used as above for permanent teeth. Deciduous teeth are represented by the letters A-E.
Wisdom teeth
Lower third molars.
upper (maxillary) right
upper (maxillary) left
Lower (mandibular) right
Lower (mandibular) left
Teething and tooth eruption
Teeth eruption charts medicinenet.com
Dental problems and toothache
Dental abcess
- Dental abcess medscape
- Dental abcess journal of medical microbiology
- youtu.be/TKjxpStUdDY
- youtu.be/uBfpUQkvw6U
- youtube.com/watch?v=YDCbiG9cZBA
Dental caries
Periodontitis periodental disease
Dental Plaque and Gum Disease PUK
youtube.com/watch?v=7fx7ixe3X6Q
Gum disease
Dry dental socket
- dry sockets medicinenet.com
- dentalguide.co.uk dry sockets
- tauntonmaxfax.net Oral surgery complications
- youtube.com/watch?v=G44GOArVAjg
Tooth extraction 1-3 days earlier.
Very severe pain. unrelieved by analgesics.
Continuous pain on the side of the face.
Foetid odour.
Mainly in the lower molars. especially the third (wisdom teeth).
Examination shows a socket with few or no blood clots. and sensitive bone surfaces covered by a greyish-yellow layer of necrotic tissue.
Wisdom teeth (3rd Molars)
Dento-alveolar surgery for Third Molars tauntonmaxfax.net
Orofacial and dental trauma
Maxfax trauma Cork Emergency medicine
Knocked-out tooth
Paediatric Orofacial Trauma New York partners in oral health
If a permanent (second) tooth is knocked out (in an accident or fight) but is intact, it can be saved by the following, immediate procedure.
1. Replace the tooth in its original position,preferably immediately; if dirty, put it in milk, before replacement or place it under the tongue
Note: Do not use water, and do not wipe it or touch the root.
2. Fix the tooth by moulding strong silver foil (e.g.a milk bottle top or cooking foil) over it and the adjacent teeth.
3. Refer the patient to his/her dentist or dental hospital as soon as possible.
Note: Teeth replaced within half an hour have a 90% chance of successful re-implantation.
(source Murtagh)
