Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Distinguish between systolic pressure, diastolic pressure, pulse pressure, and mean arterial pressure
- Describe the clinical measurement of pulse and blood pressure
- Identify and discuss five variables affecting arterial blood flow and blood pressure
- Discuss several factors affecting blood flow in the venous system
Blood flow refers to the movement of blood through a vessel, tissue, or organ, and is usually expressed in terms of volume of blood per unit of time. It is initiated by the contraction of the ventricles of the heart. Ventricular contraction ejects blood into the major arteries, resulting in flow from regions of higher pressure to regions of lower pressure, as blood encounters smaller arteries and arterioles, then capillaries, then the venules and veins of the venous system. This section discusses a number of critical variables that contribute to blood flow throughout the body. It also discusses the factors that impede or slow blood flow, a phenomenon known as resistance.
As noted earlier, hydrostatic pressure is the force exerted by a fluid due to gravitational pull, usually against the wall of the container in which it is located. One form of hydrostatic pressure is blood pressure, the force exerted by blood upon the walls of the blood vessels or the chambers of the heart. Blood pressure may be measured in capillaries and veins, as well as the vessels of the pulmonary circulation; however, the term blood pressure without any specific descriptors typically refers to systemic arterial blood pressure—that is, the pressure of blood flowing in the arteries of the systemic circulation. In clinical practice, this pressure is measured in mm Hg and is usually obtained using the brachial artery of the arm.
Components of Arterial Blood Pressure
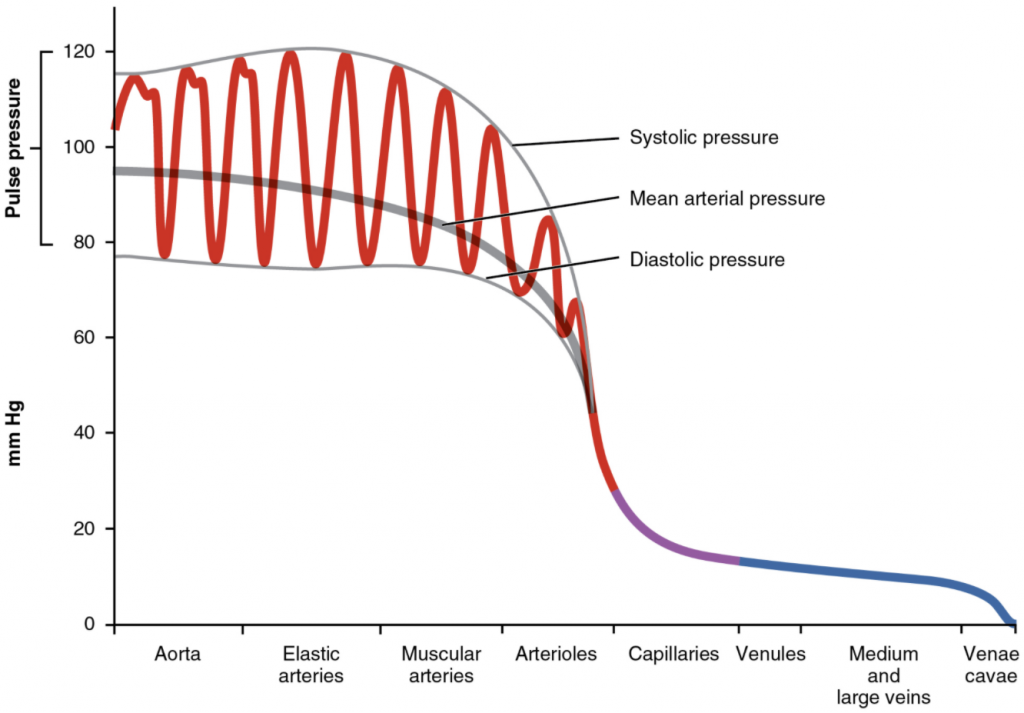
Arterial blood pressure in the larger vessels consists of several distinct components (Figure 11.6.1): systolic and diastolic pressures, pulse pressure, and mean arterial pressure.
Systolic and Diastolic Pressure
When systemic arterial blood pressure is measured, it is recorded as a ratio of two numbers (e.g., 120/80 is a normal adult blood pressure), expressed as systolic pressure over diastolic pressure. The systolic pressure is the higher value (typically around 120 mm Hg) and reflects the arterial pressure resulting from the ejection of blood during ventricular contraction, or systole. The diastolic pressure is the lower value (usually about 80 mm Hg) and represents the arterial pressure of blood during ventricular relaxation, or diastole.
Pulse Pressure
As shown in Figure 11.6.1, the difference between the systolic pressure and the diastolic pressure is the pulse pressure. For example, an individual with a systolic pressure of 120 mm Hg and a diastolic pressure of 80 mm Hg would have a pulse pressure of 40 mmHg.
Generally, a pulse pressure should be at least 25 percent of the systolic pressure. A pulse pressure below this level is described as low or narrow. This may occur, for example, in patients with a low stroke volume, which may be seen in congestive heart failure, stenosis of the aortic valve, or significant blood loss following trauma. In contrast, a high or wide pulse pressure is common in healthy people following strenuous exercise, when their resting pulse pressure of 30–40 mm Hg may increase temporarily to 100 mm Hg as stroke volume increases. A persistently high pulse pressure at or above 100 mm Hg may indicate excessive resistance in the arteries and can be caused by a variety of disorders. Chronic high resting pulse pressures can degrade the heart, brain, and kidneys, and warrant medical treatment.
Mean Arterial Pressure
Mean arterial pressure (MAP) represents the “average” pressure of blood in the arteries, that is, the average force driving blood into vessels that serve the tissues. Mean is a statistical concept and is calculated by taking the sum of the values divided by the number of values. Although complicated to measure directly and complicated to calculate, MAP can be approximated by adding the diastolic pressure to one-third of the pulse pressure or systolic pressure minus the diastolic pressure:
MAP = diastolic BP + ((systolic-diastolic BP) / 3)
In Figure 6.7.1, this value is approximately 80 + (120 − 80) / 3, or 93.33. Normally, the MAP falls within the range of 70–110 mm Hg. If the value falls below 60 mm Hg for an extended time, blood pressure will not be high enough to ensure circulation to and through the tissues, which results in ischemia, or insufficient blood flow. A condition called hypoxia, inadequate oxygenation of tissues, commonly accompanies ischemia. The term hypoxemia refers to low levels of oxygen in systemic arterial blood. Neurons are especially sensitive to hypoxia and may die or be damaged if blood flow and oxygen supplies are not quickly restored.
Pulse
After blood is ejected from the heart, elastic fibers in the arteries help maintain a high-pressure gradient as they expand to accommodate the blood, then recoil. This expansion and recoiling effect, known as the pulse, can be palpated manually or measured electronically. Although the effect diminishes over distance from the heart, elements of the systolic and diastolic components of the pulse are still evident down to the level of the arterioles.
Because pulse indicates heart rate, it is measured clinically to provide clues to a patient’s state of health. It is recorded as beats per minute. Both the rate and the strength of the pulse are important clinically. A high or irregular pulse rate can be caused by physical activity or other temporary factors, but it may also indicate a heart condition. The pulse strength indicates the strength of ventricular contraction and cardiac output. If the pulse is strong, then systolic pressure is high. If it is weak, systolic pressure has fallen, and medical intervention may be warranted.
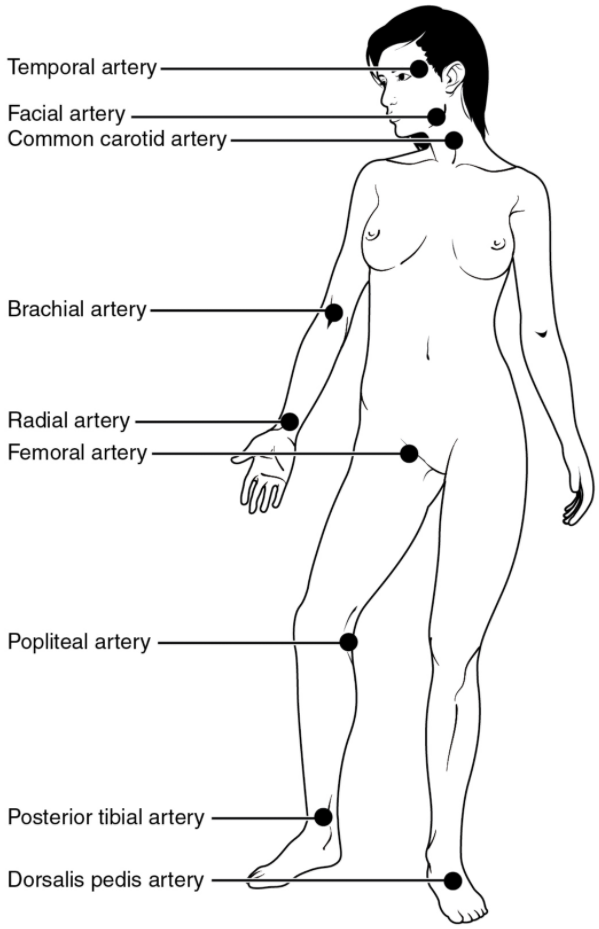
Pulse can be palpated manually by placing the tips of the fingers across an artery that runs close to the body surface and pressing lightly. While this procedure is normally performed using the radial artery in the wrist or the common carotid artery in the neck, any superficial artery that can be palpated may be used (Figure 11.6.2). Common sites to find a pulse include temporal and facial arteries in the head, brachial arteries in the upper arm, femoral arteries in the thigh, popliteal arteries behind the knees, posterior tibial arteries near the medial tarsal regions, and dorsalis pedis arteries in the feet. A variety of commercial electronic devices are also available to measure pulse.
Measurement of Blood Pressure
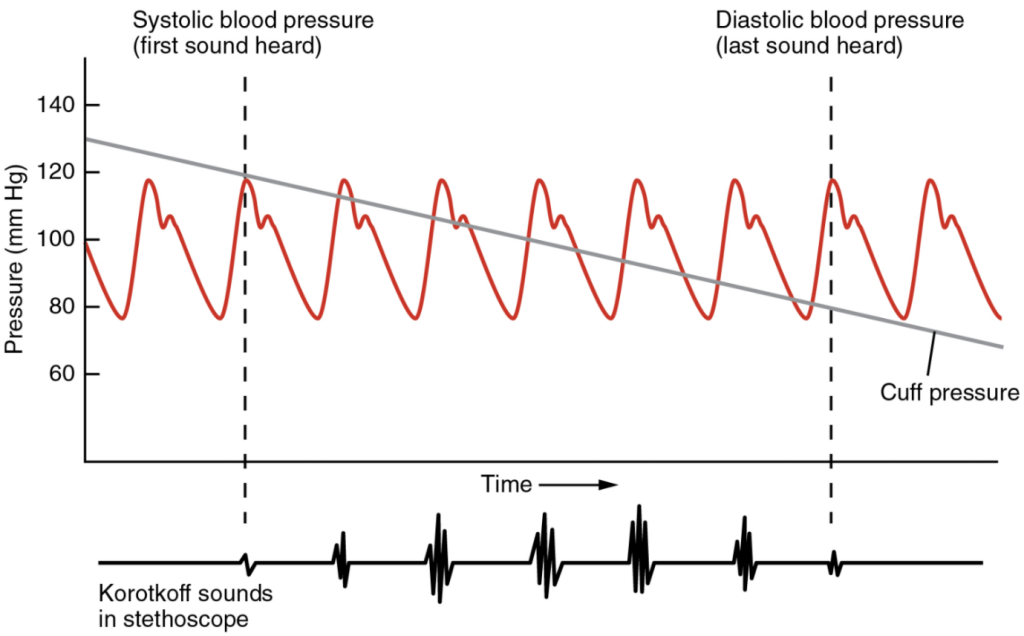
Blood pressure is one of the critical parameters measured on virtually every patient in every healthcare setting. The technique used today was developed more than 100 years ago by a pioneering Russian physician, Dr. Nikolai Korotkoff. Turbulent blood flow through the vessels can be heard as a soft ticking while measuring blood pressure; these sounds are known as Korotkoff sounds. The technique of measuring blood pressure requires the use of a sphygmomanometer (a blood pressure cuff attached to a measuring device) and a stethoscope. The technique is as follows:
- The clinician wraps an inflatable cuff tightly around the patient’s arm at about the level of the heart.
- The clinician squeezes a rubber pump to inject air into the cuff, raising pressure around the artery and temporarily cutting off blood flow into the patient’s arm.
- The clinician places the stethoscope on the patient’s antecubital region and, while gradually allowing air within the cuff to escape, listens for the Korotkoff sounds.
Although there are five recognised Korotkoff sounds, only two are normally recorded. Initially, no sounds are heard since there is no blood flow through the vessels, but as air pressure drops, the cuff relaxes, and blood flow returns to the arm. As shown in Figure 11.6.3, the first sound heard through the stethoscope—the first Korotkoff sound—indicates systolic pressure. As more air is released from the cuff, blood is able to flow freely through the brachial artery and all sounds disappear. The point at which the last sound is heard is recorded as the patient’s diastolic pressure.
The majority of hospitals and clinics have automated equipment for measuring blood pressure that work on the same principles. An even more recent innovation is a small instrument that wraps around a patient’s wrist. The patient then holds the wrist over the heart while the device measures blood flow and records pressure.
Variables Affecting Blood Flow and Blood Pressure
Five variables influence blood flow and blood pressure:
- Cardiac output
- Compliance
- Volume of the blood
- Viscosity of the blood
- Blood vessel length and diameter
Recall that blood moves from higher pressure to lower pressure. It is pumped from the heart into the arteries at high pressure. If you increase pressure in the arteries (afterload), and cardiac function does not compensate, blood flow will actually decrease. In the venous system, the opposite relationship is true. Increased pressure in the veins does not decrease flow as it does in arteries, but actually increases flow. Since pressure in the veins is normally relatively low, for blood to flow back into the heart, the pressure in the atria during atrial diastole must be even lower. It normally approaches zero, except when the atria contract (see Figure 11.6.1).
Cardiac Output
Cardiac output is the measurement of blood flow from the heart through the ventricles and is usually measured in liters per minute. Any factor that causes cardiac output to increase, by elevating heart rate or stroke volume or both, will elevate blood pressure and promote blood flow. These factors include sympathetic stimulation, the catecholamines epinephrine and norepinephrine, thyroid hormones, and increased calcium ion levels. Conversely, any factor that decreases cardiac output, by decreasing heart rate or stroke volume or both, will decrease arterial pressure and blood flow. These factors include parasympathetic stimulation, elevated or decreased potassium ion levels, decreased calcium levels, anoxia, and acidosis.
Compliance
Compliance is the ability of any compartment to expand to accommodate increased content. A metal pipe, for example, is not compliant, whereas a balloon is. The greater the compliance of an artery, the more effectively it is able to expand to accommodate surges in blood flow without increased resistance or blood pressure. Veins are more compliant than arteries and can expand to hold more blood. When vascular disease causes stiffening of arteries, compliance is reduced and resistance to blood flow is increased. The result is more turbulence, higher pressure within the vessel, and reduced blood flow. This increases the work of the heart.
Blood Volume
The relationship between blood volume, blood pressure, and blood flow is intuitively obvious. Water may merely trickle along a creek bed in a dry season but rush quickly and under great pressure after a heavy rain. Similarly, as blood volume decreases, pressure and flow decrease. As blood volume increases, pressure and flow increase.
Under normal circumstances, blood volume varies little. Low blood volume, called hypovolemia, may be caused by bleeding, dehydration, vomiting, severe burns, or some medications used to treat hypertension. It is important to recognize that other regulatory mechanisms in the body are so effective at maintaining blood pressure that an individual may be asymptomatic until 10–20 percent of the blood volume has been lost. Treatment typically includes intravenous fluid replacement.
Hypervolemia, excessive fluid volume, may be caused by retention of water and sodium, as seen in patients with heart failure, liver cirrhosis, some forms of kidney disease, hyperaldosteronism, and some glucocorticoid steroid treatments. Restoring homeostasis in these patients depends upon reversing the condition that triggered the hypervolemia.
Blood Viscosity
Viscosity is the thickness of fluids that affects their ability to flow. Clean water, for example, is less viscous than mud. The viscosity of blood is directly proportional to resistance and inversely proportional to flow; therefore, any condition that causes viscosity to increase will also increase resistance and decrease flow. For example, imagine sipping milk, then a milkshake, through the same size straw. You experience more resistance and therefore less flow from the milkshake. Conversely, any condition that causes viscosity to decrease (such as when the milkshake melts) will decrease resistance and increase flow.
Normally the viscosity of blood does not change over short periods of time. The two primary determinants of blood viscosity are the formed elements and plasma proteins. Since most formed elements are erythrocytes, any condition affecting erythropoiesis, such as polycythemia or anemia, can alter viscosity. Since most plasma proteins are produced by the liver, any condition affecting liver function can also change the viscosity slightly and therefore decrease blood flow. Liver abnormalities include hepatitis, cirrhosis, alcohol damage, and drug toxicities. While leukocytes and platelets are normally a small component of the formed elements, there are some rare conditions in which severe overproduction can impact viscosity as well.
Vessel Length and Diameter
The length of a vessel is directly proportional to its resistance: the longer the vessel, the greater the resistance and the lower the flow. As with blood volume, this makes intuitive sense, since the increased surface area of the vessel will impede the flow of blood. Likewise, if the vessel is shortened, the resistance will decrease and flow will increase.
The length of our blood vessels increases throughout childhood as we grow, of course, but is unchanging in adults under normal physiological circumstances. Further, the distribution of vessels is not the same in all tissues. Adipose tissue does not have an extensive vascular supply. One pound of adipose tissue contains approximately 200 miles of vessels, whereas skeletal muscle contains more than twice that. Overall, vessels decrease in length only during loss of mass or amputation. An individual weighing 68kg has approximately 96,560km of vessels in the body. Gaining about 4.5km adds from 3218 to 6437 kilometers of vessels, depending upon the nature of the gained tissue. One of the great benefits of weight reduction is the reduced stress to the heart, which does not have to overcome the resistance of as many miles of vessels.
In contrast to length, the diameter of blood vessels changes throughout the body, according to the type of vessel, as we discussed earlier. The diameter of any given vessel may also change frequently throughout the day in response to neural and chemical signals that trigger vasodilation and vasoconstriction. The vascular tone of the vessel is the contractile state of the smooth muscle and the primary determinant of diameter, and thus of resistance and flow. The effect of vessel diameter on resistance is inverse: Given the same volume of blood, an increased diameter means there is less blood contacting the vessel wall, thus lower friction and lower resistance, subsequently increasing flow. A decreased diameter means more of the blood contacts the vessel wall, and resistance increases, subsequently decreasing flow.
The influence of lumen diameter on resistance is dramatic: A slight increase or decrease in diameter causes a huge decrease or increase in resistance. This is because resistance is inversely proportional to the radius of the blood vessel (one-half of the vessel’s diameter) raised to the fourth power (R = 1/r4). This means, for example, that if an artery or arteriole constricts to one-half of its original radius, the resistance to flow will increase 16 times. And if an artery or arteriole dilates to twice its initial radius, then resistance in the vessel will decrease to 1/16 of its original value and flow will increase 16 times.
The Roles of Vessel Diameter and Total Area in Blood Flow and Blood Pressure
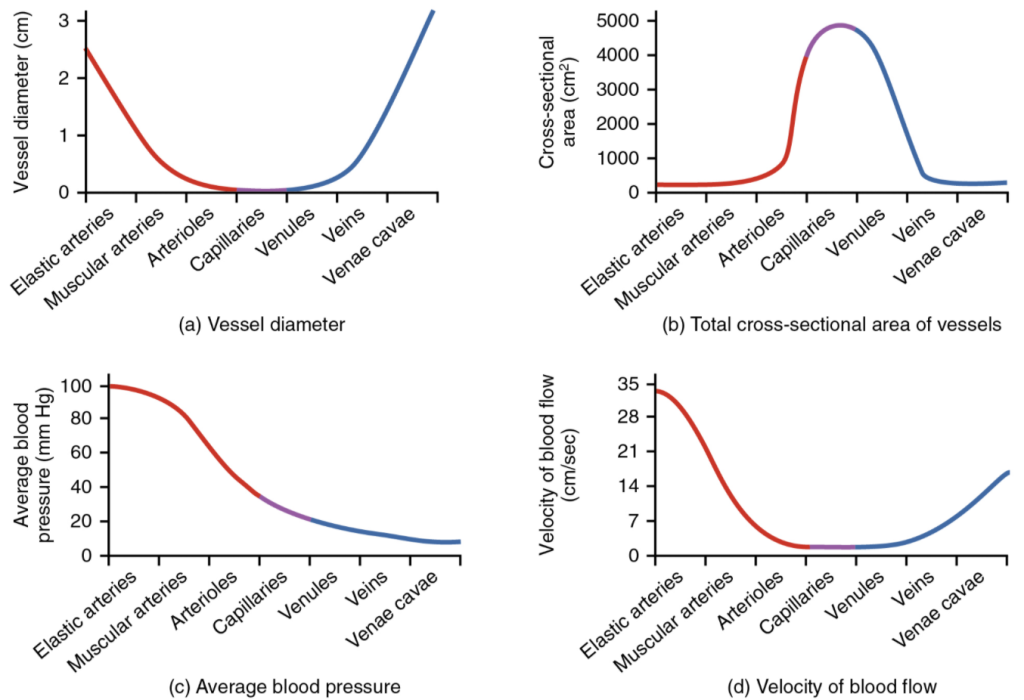
Recall that we classified arterioles as resistance vessels, because given their small lumen, they dramatically slow the flow of blood from arteries. In fact, arterioles are the site of greatest resistance in the entire vascular network. This may seem surprising, given that capillaries have a smaller size. How can this phenomenon be explained?
Figure 11.6.4 compares vessel diameter, total cross-sectional area, average blood pressure, and blood velocity through the systemic vessels. Notice in parts (a) and (b) that the total cross-sectional area of the body’s capillary beds is far greater than any other type of vessel. Although the diameter of an individual capillary is significantly smaller than the diameter of an arteriole, there are vastly more capillaries in the body than there are other types of blood vessels. Part (c) shows that blood pressure drops unevenly as blood travels from arteries to arterioles, capillaries, venules, and veins, and encounters greater resistance. However, the site of the most precipitous drop, and the site of greatest resistance, is the arterioles. This explains why vasodilation and vasoconstriction of arterioles play more significant roles in regulating blood pressure than do the vasodilation and vasoconstriction of other vessels.
Part (d) shows that the velocity (speed) of blood flow decreases dramatically as the blood moves from arteries to arterioles to capillaries. This slow flow rate allows more time for exchange processes to occur. As blood flows through the veins, the rate of velocity increases, as blood is returned to the heart.
Disorders of the Cardiovascular System: Arteriosclerosis
Compliance allows an artery to expand when blood is pumped through it from the heart, and then to recoil after the surge has passed. This helps promote blood flow. In arteriosclerosis, compliance is reduced, and pressure and resistance within the vessel increase. This is a leading cause of hypertension and coronary heart disease, as it causes the heart to work harder to generate a pressure great enough to overcome the resistance.
Arteriosclerosis begins with injury to the endothelium of an artery, which may be caused by irritation from high blood glucose, infection, tobacco use, excessive blood lipids, and other factors. Artery walls that are constantly stressed by blood flowing at high pressure are also more likely to be injured—which means that hypertension can promote arteriosclerosis, as well as result from it.
Recall that tissue injury causes inflammation. As inflammation spreads into the artery wall, it weakens and scars it, leaving it stiff (sclerotic). As a result, compliance is reduced. Moreover, circulating triglycerides and cholesterol can seep between the damaged lining cells and become trapped within the artery wall, where they are frequently joined by leukocytes, calcium, and cellular debris. Eventually, this build-up, called plaque, can narrow arteries enough to impair blood flow. The term for this condition, atherosclerosis (athero- = “porridge”) describes the mealy deposits (Figure 11.6.5).
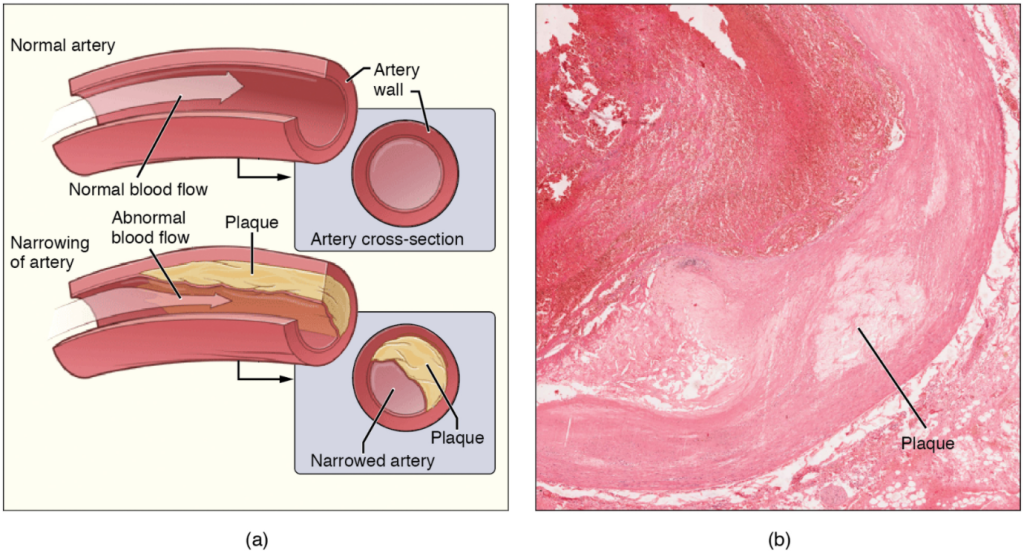
Sometimes a plaque can rupture, causing microscopic tears in the artery wall that allow blood to leak into the tissue on the other side. When this happens, platelets rush to the site to clot the blood. This clot can further obstruct the artery and—if it occurs in a coronary or cerebral artery—cause a sudden heart attack or stroke. Alternatively, plaque can break off and travel through the bloodstream as an embolus until it blocks a more distant, smaller artery.
Even without total blockage, vessel narrowing leads to ischemia—reduced blood flow—to the tissue region “downstream” of the narrowed vessel. Ischemia in turn leads to hypoxia—decreased supply of oxygen to the tissues. Hypoxia involving cardiac muscle or brain tissue can lead to cell death and severe impairment of brain or heart function.
A major risk factor for both arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis is advanced age, as the conditions tend to progress over time. Arteriosclerosis is normally defined as the more generalized loss of compliance, “hardening of the arteries,” whereas atherosclerosis is a more specific term for the build-up of plaque in the walls of the vessel and is a specific type of arteriosclerosis. There is also a distinct genetic component, and pre-existing hypertension and/or diabetes also greatly increase the risk. However, obesity, poor nutrition, lack of physical activity, and tobacco use all are major risk factors.
Treatment includes lifestyle changes, such as weight loss, smoking cessation, regular exercise, and adoption of a diet low in sodium and saturated fats. Medications to reduce cholesterol and blood pressure may be prescribed. For blocked coronary arteries, surgery is warranted. In angioplasty, a catheter is inserted into the vessel at the point of narrowing, and a second catheter with a balloon-like tip is inflated to widen the opening. To prevent subsequent collapse of the vessel, a small mesh tube called a stent is often inserted. In an endarterectomy, plaque is surgically removed from the walls of a vessel. This operation is typically performed on the carotid arteries of the neck, which are a prime source of oxygenated blood for the brain. In a coronary bypass procedure, a non-vital superficial vessel from another part of the body (often the great saphenous vein) or a synthetic vessel is inserted to create a path around the blocked area of a coronary artery.
Venous System
The pumping action of the heart propels the blood into the arteries, from an area of higher pressure toward an area of lower pressure. If blood is to flow from the veins back into the heart, the pressure in the veins must be greater than the pressure in the atria of the heart. Two factors help maintain this pressure gradient between the veins and the heart. First, the pressure in the atria during diastole is very low, often approaching zero when the atria are relaxed (atrial diastole). Second, two physiologic “pumps” increase pressure in the venous system. The use of the term “pump” implies a physical device that speeds flow. These physiological pumps are less obvious.
Skeletal Muscle Pump
In many body regions, the pressure within the veins can be increased by the contraction of the surrounding skeletal muscle. This mechanism, known as the skeletal muscle pump (Figure 11.6.6), helps the lower-pressure veins counteract the force of gravity, increasing pressure to move blood back to the heart. As leg muscles contract, for example during walking or running, they exert pressure on nearby veins with their numerous one-way valves. This increased pressure causes blood to flow upward, opening valves superior to the contracting muscles so blood flows through. Simultaneously, valves inferior to the contracting muscles close; thus, blood should not seep back downward toward the feet. Military recruits are trained to flex their legs slightly while standing at attention for prolonged periods. Failure to do so may allow blood to pool in the lower limbs rather than returning to the heart. Consequently, the brain will not receive enough oxygenated blood, and the individual may lose consciousness.
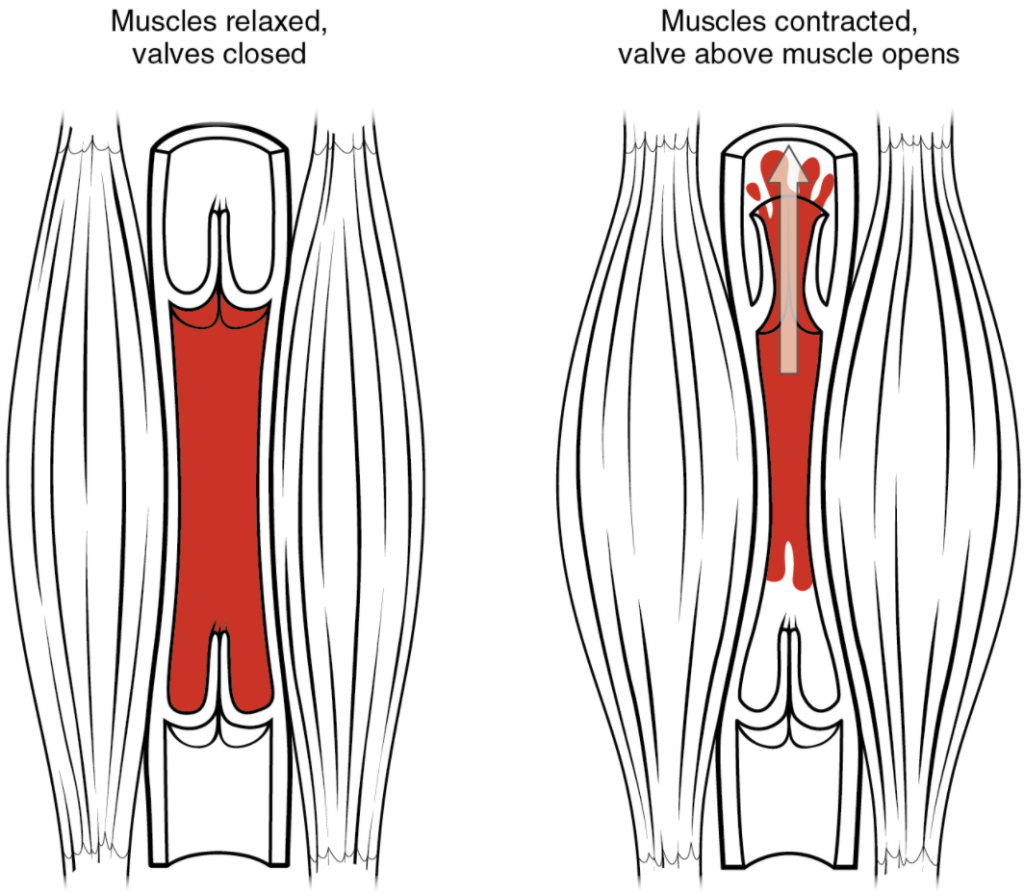
Respiratory Pump
The respiratory pump aids blood flow through the veins of the thorax and abdomen. During inhalation, the volume of the thorax increases, largely through the contraction of the diaphragm, which moves downward and compresses the abdominal cavity. The elevation of the chest caused by the contraction of the external intercostal muscles also contributes to the increased volume of the thorax. The volume increase causes air pressure within the thorax to decrease, allowing us to inhale. Additionally, as air pressure within the thorax drops, blood pressure in the thoracic veins also decreases, falling below the pressure in the abdominal veins. This causes blood to flow along its pressure gradient from veins outside the thorax, where pressure is higher, into the thoracic region, where pressure is now lower. This in turn promotes the return of blood from the thoracic veins to the atria. During exhalation, when air pressure increases within the thoracic cavity, pressure in the thoracic veins increases, speeding blood flow into the heart while valves in the veins prevent blood from flowing backward from the thoracic and abdominal veins.
Pressure Relationship in the Venous System
Although vessel diameter increases from the smaller venules to the larger veins and eventually to the venae cavae (singular = vena cava), the total cross-sectional area actually decreases (see Figure 11.6.4a and 11.6.4b). The individual veins are larger in diameter than the venules, but their total number is much lower, so their total cross-sectional area is also lower.
Also notice that, as blood moves from venules to veins, the average blood pressure drops (see Figure 6.7.4c), but the blood velocity actually increases (see Figure 11.6.4d). This pressure gradient drives blood back toward the heart. Again, the presence of one-way valves and the skeletal muscle and respiratory pumps contribute to this increased flow. Since approximately 64 percent of the total blood volume resides in systemic veins, any action that increases the flow of blood through the veins will increase venous return to the heart. Maintaining vascular tone within the veins prevents the veins from merely distending, dampening the flow of blood, and as you will see, vasoconstriction actually enhances the flow.
The Role of Venoconstriction in Resistance, Blood Pressure and Flow
As previously discussed, vasoconstriction of an artery or arteriole decreases the radius, increasing resistance and pressure, but decreasing flow. Venoconstriction, on the other hand, has a very different outcome. The walls of veins are thin but irregular; thus, when the smooth muscle in those walls constricts, the lumen becomes more rounded. The more rounded the lumen, the less surface area the blood encounters, and the less resistance the vessel offers. Vasoconstriction increases pressure within a vein as it does in an artery, but in veins, the increased pressure increases flow. Recall that the pressure in the atria, into which the venous blood will flow, is very low, approaching zero for at least part of the relaxation phase of the cardiac cycle. Thus, venoconstriction increases the return of blood to the heart. Another way of stating this is that venoconstriction increases the preload or stretch of the cardiac muscle and increases contraction.
Section Review
Blood flow is the movement of blood through a vessel, tissue, or organ. The slowing or blocking of blood flow is called resistance. Blood pressure is the force that blood exerts upon the walls of the blood vessels or chambers of the heart. The components of blood pressure include systolic pressure, which results from ventricular contraction, and diastolic pressure, which results from ventricular relaxation. Pulse pressure is the difference between systolic and diastolic measures, and mean arterial pressure is the “average” pressure of blood in the arterial system, driving blood into the tissues. Pulse, the expansion and recoiling of an artery, reflects the heartbeat. The variables affecting blood flow and blood pressure in the systemic circulation are cardiac output, compliance, blood volume, blood viscosity, and the length and diameter of the blood vessels. In the arterial system, vasodilation and vasoconstriction of the arterioles is a significant factor in systemic blood pressure: Slight vasodilation greatly decreases resistance and increases flow, whereas slight vasoconstriction greatly increases resistance and decreases flow. In the arterial system, as resistance increases, blood pressure increases and flow decreases. In the venous system, constriction increases blood pressure as it does in arteries; the increasing pressure helps to return blood to the heart. In addition, constriction causes the vessel lumen to become more rounded, decreasing resistance and increasing blood flow. Venoconstriction, while less important than arterial vasoconstriction, works with the skeletal muscle pump, the respiratory pump, and their valves to promote venous return to the heart.
