Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the external structure of the kidney, including its location, support structures and covering
- Identify the major internal divisions and structures of the kidney
- Identify the major blood vessels associated with the kidney and trace the path of blood through the kidney
- Compare and contrast the cortical and juxtamedullary nephrons
- Name structures found in the cortex and medulla
- Describe the physiological characteristics of the cortex and medulla
The kidneys lie on either side of the spine in the retroperitoneal space between the parietal peritoneum and the posterior abdominal wall, well protected by muscle, fat, and ribs. They are roughly the size of your fist, and the male kidney is typically a bit larger than the female kidney. The kidneys are well vascularised, receiving about 25 percent of the cardiac output at rest.
External Anatomy
In humans, the left kidney is located at about the T12 to L3 vertebrae, whereas the right is lower due to slight displacement by the liver. Upper portions of the kidneys are somewhat protected by the eleventh and twelfth ribs (Figure 14.3.1). Each kidney weighs about 125–175 g in males and 115–155 g in females. They are about 11–14 cm in length, 6 cm wide, and 4 cm thick and are directly covered by a fibrous capsule composed of dense, irregular connective tissue that helps to hold their shape and protect them. This capsule is covered by a shock-absorbing layer of adipose tissue called the renal fat pad, which in turn is encompassed by a tough renal fascia. The fascia and, to a lesser extent, the overlying peritoneum serve to firmly anchor the kidneys to the posterior abdominal wall in a retroperitoneal position.
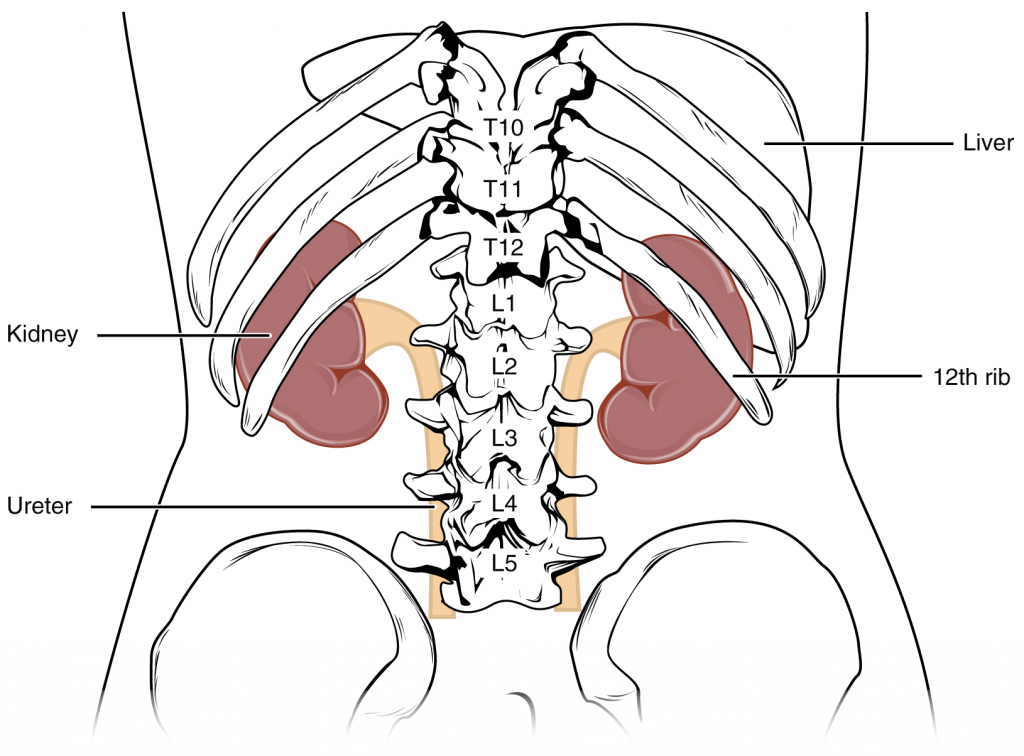
On the superior aspect of each kidney is the adrenal gland. The adrenal cortex directly influences renal function through the production of the hormone aldosterone to stimulate sodium reabsorption.
Internal Anatomy
A frontal section through the kidney reveals an outer region called the renal cortex and an inner region called the medulla (Figure 14.3.2). The renal columns are connective tissue extensions that radiate downward from the cortex through the medulla to separate the most characteristic features of the medulla, the renal pyramids and renal papillae. The papillae are bundles of collecting ducts that transport urine made by nephrons to the calyces of the kidney for excretion. The renal columns also serve to divide the kidney into six-eight lobes and provide a supportive framework for vessels that enter and exit the cortex. The pyramids and renal columns taken together constitute the kidney lobes.
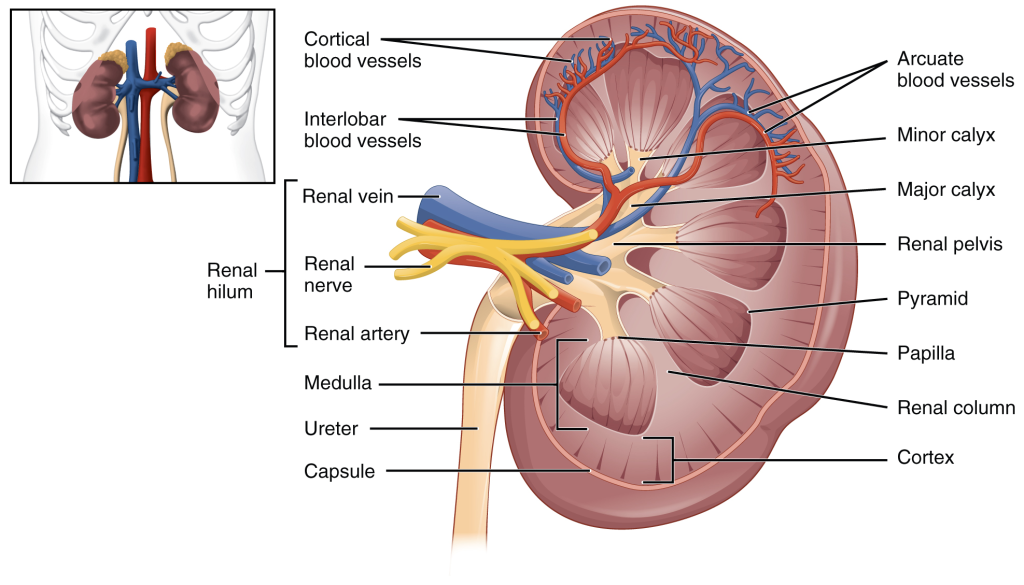
Renal Hilum
The renal hilum is the entry and exit site for structures servicing the kidneys: vessels, nerves, lymphatics and ureters. The medial-facing hila are tucked into the sweeping convex outline of the cortex. Emerging from the hilum is the renal pelvis, which is formed from the major and minor calyxes in the kidney. The smooth muscle in the renal pelvis funnels urine, via peristalsis, into the ureter. The renal arteries form directly from the descending aorta, whereas the renal veins return ‘cleansed’ blood directly to the inferior vena cava. The artery, vein and renal pelvis are arranged in an anterior-to-posterior order.
Nephrons and Vessels
The renal artery first divides into segmental arteries, followed by further branching to form interlobar arteries that pass through the renal columns to reach the cortex (Figure 14.3.3). The interlobar arteries, in turn, branch into arcuate arteries, cortical radiate arteries and then into afferent arterioles. The afferent arterioles service about 1.3 million nephrons in each kidney.
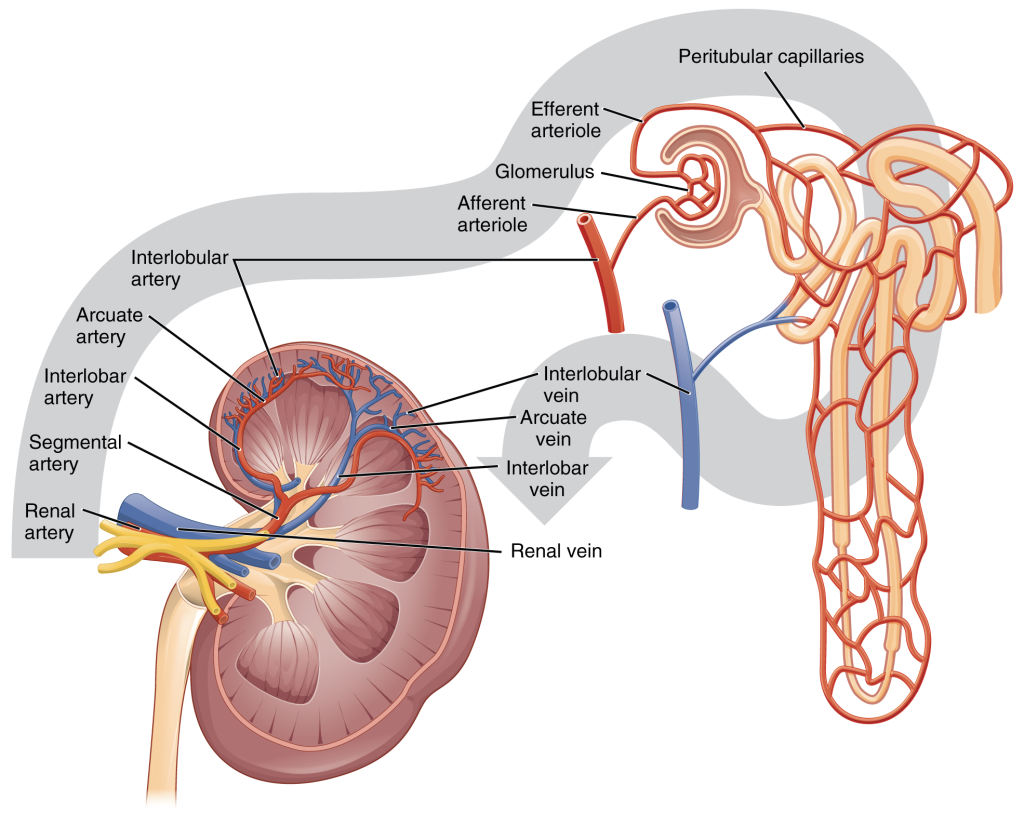
Nephrons are the “functional units” of the kidney; they cleanse the blood and balance the constituents of the circulation. The afferent arterioles form a tuft of high-pressure capillaries about 200 µm in diameter, the glomerulus. The rest of the nephron consists of a continuous sophisticated tubule whose proximal end surrounds the glomerulus in an intimate embrace—this is Bowman’s (or glomerular) capsule. The glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule together form the renal corpuscle. As mentioned earlier, these glomerular capillaries filter the blood based on particle size. After passing through the renal corpuscle, the capillaries form a second arteriole, the efferent arteriole (Figure 14.3.4). These will next form a capillary network around the more distal portions of the nephron tubule, the peritubular capillaries and vasa recta, before returning to the venous system. As the glomerular filtrate progresses through the nephron, these capillary networks recover most of the solutes and water and return them to the circulation. Since a capillary bed (the glomerulus) drains into a vessel that in turn forms a second capillary bed, the definition of a portal system is met. This is the only portal system in which an arteriole is found between the first and second capillary beds. (Portal systems also link the hypothalamus to the anterior pituitary, and the blood vessels of the digestive viscera to the liver.)
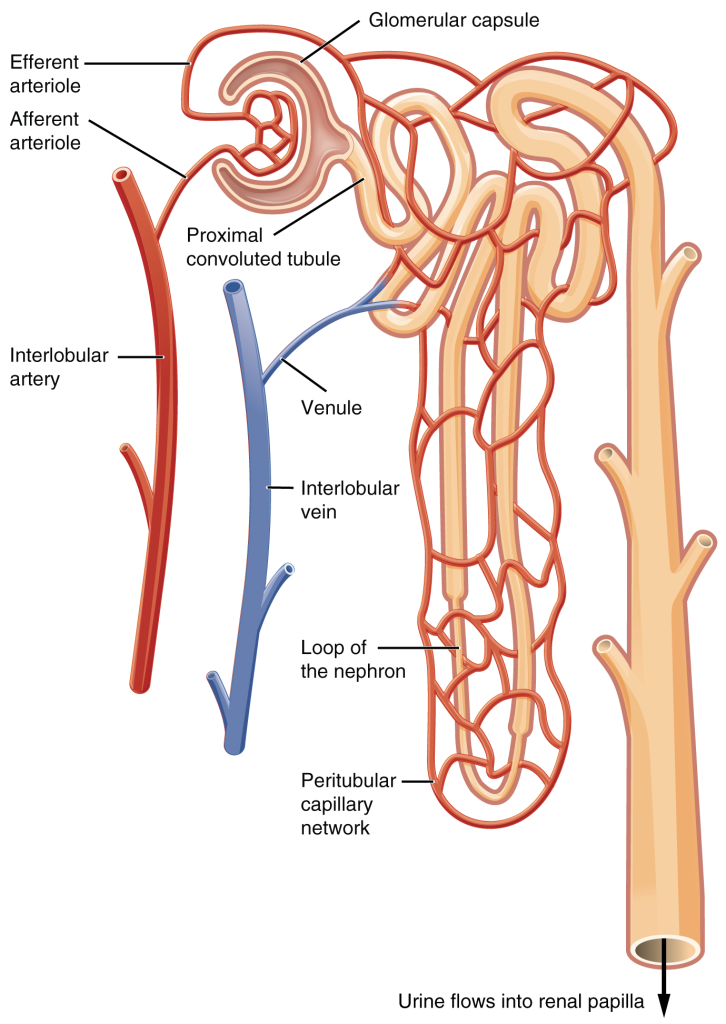
Cortex
In a dissected kidney, it is easy to identify the cortex; it appears lighter in colour compared to the rest of the kidney. All of the renal corpuscles as well as both the proximal convoluted tubules (PCTs) and distal convoluted tubules are found here. Some nephrons have a short loop of Henle that does not dip beyond the cortex. These nephrons are called cortical nephrons. About 15 percent of nephrons have long loops of Henle that extend deep into the medulla and are called juxtamedullary nephrons.
Section Review
As noted previously, the structure of the kidney is divided into two principal regions—the peripheral rim of cortex and the central medulla. The two kidneys receive about 25 percent of cardiac output. They are protected in the retroperitoneal space by the renal fat pad and overlying ribs and muscle. Ureters, blood vessels, lymph vessels and nerves enter and leave at the renal hilum. The renal arteries arise directly from the aorta, and the renal veins drain directly into the inferior vena cava. Kidney function is derived from the actions of about 1.3 million nephrons per kidney; these are the “functional units.” A capillary bed, the glomerulus, filters blood and the filtrate is captured by Bowman’s capsule. A portal system is formed when the blood flows through a second capillary bed surrounding the proximal and distal convoluted tubules and the loop of Henle. Most water and solutes are recovered by this second capillary bed. This filtrate is processed and finally gathered by collecting ducts that drain into the minor calyces, which merge to form major calyces; the filtrate then proceeds to the renal pelvis and finally the ureters.
