Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Identify the classes of cells that make up nervous tissue
- Discuss how nervous tissue mediates perception and response
Nervous tissue is characterised as being excitable and capable of sending and receiving electrochemical signals that provide the body with information. Two main classes of cells make up nervous tissue: the neuron and neuroglia (Figure 3.5.1). Neurons propagate information via electrochemical impulses, called action potentials, which are biochemically linked to the release of chemical signals. Neuroglia play an essential role in supporting neurons and modulating their information propagation.
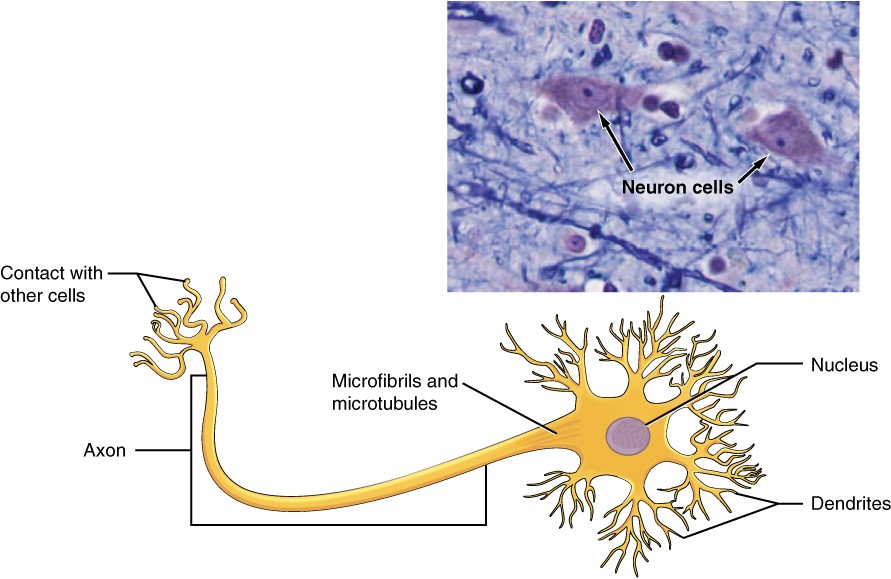
Neurons display distinctive morphology, well suited to their role as conducting cells, with three main parts. The cell body includes most of the cytoplasm, the organelles, and the nucleus. Dendrites branch off the cell body and appear as thin extensions. A long “tail,” the axon, extends from the neuron body and can be wrapped in an insulating layer known as myelin, which is formed by accessory cells. The synapse is the gap between nerve cells, or between a nerve cell and its target, for example, a muscle or a gland, across which the impulse is transmitted by chemical compounds known as neurotransmitters. Neurons categorised as multipolar neurons have several dendrites and a single prominent axon. Bipolar neurons possess a single dendrite and axon with the cell body, while unipolar neurons have only a single process extending out from the cell body, which divides into a functional dendrite and into a functional axon. When a neuron is sufficiently stimulated, it generates an action potential that propagates down the axon towards the synapse. If enough neurotransmitters are released at the synapse to stimulate the next neuron or target, a response is generated.
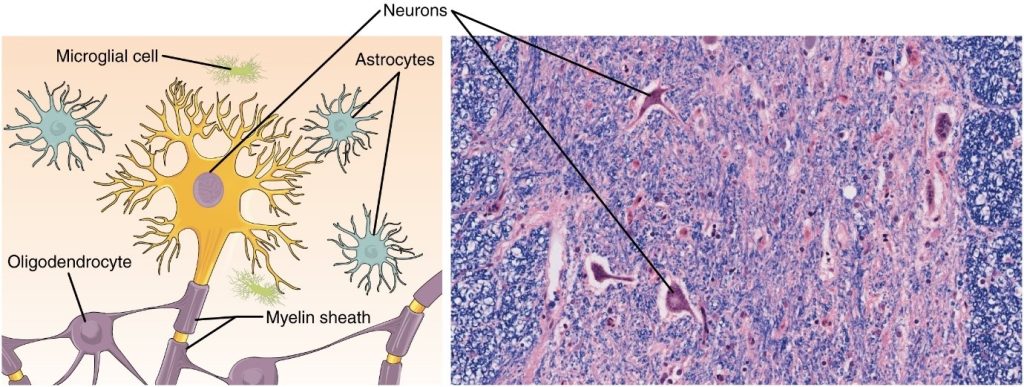
The second class of neural cells comprises the neuroglia or glial cells, which have been characterised as having a simple support role. The word “glia” comes from the Greek word for glue. Recent research is shedding light on the more complex role of neuroglia in the function of the brain and nervous system. Astrocyte cells, named for their distinctive star shape, are abundant in the central nervous system. The astrocytes have many functions, including regulation of ion concentration in the intercellular space, uptake and/or breakdown of some neurotransmitters, and formation of the blood-brain barrier, the membrane that separates the circulatory system from the brain. Microglia protect the nervous system against infection but are not nervous tissue because they are related to macrophages. Oligodendrocyte cells produce myelin in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) while the Schwann cell produces myelin in the peripheral nervous system (Figure 3.5.2).
Section Review
The most prominent cell of the nervous tissue, the neuron, is characterised mainly by its ability to receive stimuli and respond by generating an electrical signal, known as an action potential, which can travel rapidly over great distances in the body. A typical neuron displays a distinctive morphology: a large cell body branches out into short extensions called dendrites, which receive chemical signals from other neurons, and a long tail called an axon, which relays signals away from the cell to other neurons, muscles, or glands. Many axons are wrapped by a myelin sheath, a lipid derivative that acts as an insulator and speeds up the transmission of the action potential. Other cells in the nervous tissue, the neuroglia, include the astrocytes, microglia, oligodendrocytes, and Schwann cells.
