Articles links:
“What Is ‘Academic’ Writing?” by L. Lennie Irvin
“What is an Essay?” provided by Candela Open Courses
“Critical Thinking in College Writing: From the Personal to the Academic” by Gita DasBender
Chapter Preview
- Explore academic writing myths.
- Identify characteristics of academic writing.
- Describe what first-year writing courses are designed to teach.

What Is “Academic” Writing?
by L. Lennie Irvin
Introduction: The Academic Writing Task
As a new college student, you may have a lot of anxiety and questions about the writing you’ll do in college.* That word “academic,” especially, may turn your stomach or turn your nose. However, with this first year composition class, you begin one of the only classes in your entire college career where you will focus on learning to write. Given the importance of writing as a communication skill, I urge you to consider this class as a gift and make the most of it. But writing is hard, and writing in college may resemble playing a familiar game by completely new rules (that often are unstated). This chapter is designed to introduce you to what academic writing is like, and hopefully ease your transition as you face these daunting writing challenges.
So here’s the secret. Your success with academic writing depends upon how well you understand what you are doing as you write and then how you approach the writing task. Early research done on college writers discovered that whether students produced a successful piece of writing depended largely upon their representation of the writing task. The writers’ mental model for picturing their task made a huge difference. Most people as they start college have wildly strange ideas about what they are doing when they write an essay, or worse—they have no clear idea at all. I freely admit my own past as a clueless freshman writer, and it’s out of this sympathy as well as twenty years of teaching college writing that I hope to provide you with something useful. So grab a cup of coffee or a diet coke, find a comfortable chair with good light, and let’s explore together this activity of academic writing you’ll be asked to do in college. We will start by clearing up some of those wild misconceptions people often arrive at college possessing. Then we will dig more deeply into the components of the academic writing situation and nature of the writing task.
Myths about Writing
Though I don’t imagine an episode of MythBusters will be based on the misconceptions about writing we are about to look at, you’d still be surprised at some of the things people will believe about writing. You may find lurking within you viral elements of these myths—all of these lead to problems in writing.
Myth #1: The “Paint by Numbers” myth
Some writers believe they must perform certain steps in a particular order to write “correctly.” Rather than being a lock-step linear process, writing is “recursive.” That means we cycle through and repeat the various activities of the writing process many times as we write.
Myth #2: Writers only start writing when they have everything figured out
Writing is not like sending a fax! Writers figure out much of what they want to write as they write it. Rather than waiting, get some writing on the page—even with gaps or problems. You can come back to patch up rough spots.
Myth #3: Perfect first drafts
We put unrealistic expectations on early drafts, either by focusing too much on the impossible task of making them perfect (which can put a cap on the development of our ideas), or by making too little effort because we don’t care or know about their inevitable problems. Nobody writes perfect first drafts; polished writing takes lots of revision.
Myth #4: Some got it; I don’t—the genius fallacy
When you see your writing ability as something fixed or out of your control (as if it were in your genetic code), then you won’t believe you can improve as a writer and are likely not to make any efforts in that direction. With effort and study, though, you can improve as a writer. I promise.
Myth #5: Good grammar is good writing
When people say “I can’t write,” what they often mean is they have problems with grammatical correctness. Writing, however, is about more than just grammatical correctness. Good writing is a matter of achieving your desired effect upon an intended audience. Plus, as we saw in myth #3, no one writes perfect first drafts.
Myth #6: The Five Paragraph Essay
Some people say to avoid it at all costs, while others believe no other way to write exists. With an introduction, three supporting paragraphs, and a conclusion, the five paragraph essay is a format you should know, but one which you will outgrow. You’ll have to gauge the particular writing assignment to see whether and how this format is useful for you.
Myth #7: Never use “I”
Adopting this formal stance of objectivity implies a distrust (almost fear) of informality and often leads to artificial, puffed-up prose. Although some writing situations will call on you to avoid using “I” (for example, a lab report), much college writing can be done in a middle, semi-formal style where it is ok to use “I.”
The Academic Writing Situation
Now that we’ve dispelled some of the common myths that many writers have as they enter a college classroom, let’s take a moment to think about the academic writing situation. The biggest problem I see in freshman writers is a poor sense of the writing situation in general. To illustrate this problem, let’s look at the difference between speaking and writing.
When we speak, we inhabit the communication situation bodily in three dimensions, but in writing we are confined within the two-dimensional setting of the flat page (though writing for the web—or multimodal writing—is changing all that). Writing resembles having a blindfold over our eyes and our hands tied behind our backs: we can’t see exactly whom we’re talking to or where we are. Separated from our audience in place and time, we imaginatively have to create this context. Our words on the page are silent, so we must use punctuation and word choice to communicate our tone. We also can’t see our audience to gauge how our communication is being received or if there will be some kind of response. It’s the same space we share right now as you read this essay. Novice writers often write as if they were mumbling to themselves in the corner with no sense that their writing will be read by a reader or any sense of the context within which their communication will be received.
What’s the moral here? Developing your “writer’s sense” about communicating within the writing situation is the most important thing you should learn in freshman composition.
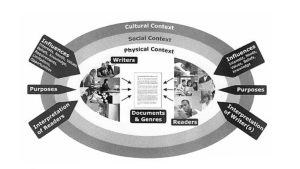
Looking More Closely at the “Academic Writing” Situation
Writing in college is a fairly specialized writing situation, and it has developed its own codes and conventions that you need to have a keen awareness of if you are going to write successfully in college. Let’s break down the writing situation in college:
| Who’s your audience? | Primarily the professor and possibly your classmates (though you may be asked to include a secondary outside audience). |
| What’s the occasion or context? | An assignment given by the teacher within a learning context and designed to have you learn and demonstrate your learning. |
| What’s your message? | It will be your learning or the interpretation gained from your study of the subject matter. |
| What’s your purpose? | To show your learning and get a good grade (or to accomplish the goals of the writing assignment). |
| What documents/genres are used? | The essay is the most frequent type of document used. |
So far, this list looks like nothing new. You’ve been writing in school toward teachers for years. What’s different in college? Lee Ann Carroll, a professor at Pepperdine University, performed a study of student writing in college and had this description of the kind of writing you will be doing in college:
What are usually called ‘writing assignments’ in college might more accurately be called ‘literacy tasks’ because they require much more than the ability to construct correct sentences or compose neatly organized paragraphs with topic sentences Projects calling for high levels of critical literacy in college typically require knowledge of research skills, ability to read complex texts, understanding of key disciplinary concepts, and strategies for synthesizing, analyzing, and responding critically to new information, usually within a limited time frame. (3–4)
Academic writing is always a form of evaluation that asks you to demonstrate knowledge and show proficiency with certain disciplinary skills of thinking, interpreting, and presenting. Writing the paper is never “just” the writing part. To be successful in this kind of writing, you must be completely aware of what the professor expects you to do and accomplish with that particular writing task. For a moment, let’s explore more deeply the elements of this college writing “literacy task.”
Knowledge of Research Skills
Perhaps up to now research has meant going straight to Google and Wikipedia, but college will require you to search for and find more in-depth information. You’ll need to know how to find information in the library, especially what is available from online databases which contain scholarly articles. Researching is also a process, so you’ll need to learn how to focus and direct a research project and how to keep track of all your source information. Realize that researching represents a crucial component of most all college writing assignments, and you will need to devote lots of work to this researching.
The Ability to Read Complex Texts
Whereas your previous writing in school might have come generally from your experience, college writing typically asks you to write on unfamiliar topics. Whether you’re reading your textbook, a short story, or scholarly articles from research, your ability to write well will be based upon the quality of your reading. In addition to the labor of close reading, you’ll need to think critically as you read. That means separating fact from opinion, recognizing biases and assumptions, and making inferences. Inferences are how we as readers connect the dots: an inference is a belief (or statement) about something unknown made on the basis of something known. You smell smoke; you infer fire. They are conclusions or interpretations that we arrive at based upon the known factors we discover from our reading. When we, then, write to argue for these interpretations, our job becomes to get our readers to make the same inferences we have made.
The Understanding of Key Disciplinary Concepts
Each discipline whether it is English, Psychology, or History has its own key concepts and language for describing these important ways of understanding the world. Don’t fool yourself that your professors’ writing assignments are asking for your opinion on the topic from just your experience. They want to see you apply and use these concepts in your writing. Though different from a multiple-choice exam, writing similarly requires you to demonstrate your learning. So whatever writing assignment you receive, inspect it closely for what concepts it asks you to bring into your writing.
Strategies for Synthesizing, Analyzing, and Responding Critically to New Information
You need to develop the skill of a seasoned traveler who can be dropped in any city around the world and get by. Each writing assignment asks you to navigate through a new terrain of information, so you must develop ways for grasping new subject matter in order, then, to use it in your writing. We have already seen the importance of reading and research for these literacy tasks, but beyond laying the information out before you, you will need to learn ways of sorting and finding meaningful patterns in this information.
In College, Everything’s an Argument: A Guide for Decoding College Writing Assignments
Let’s restate this complex “literacy task” you’ll be asked repeatedly to do in your writing assignments. Typically, you’ll be required to write an “essay” based upon your analysis of some reading(s). In this essay you’ll need to present an argument where you make a claim (i.e. present a “thesis”) and support that claim with good reasons that have adequate and appropriate evidence to back them up. The dynamic of this argumentative task often confuses first-year writers, so let’s examine it more closely.
Academic Writing Is an Argument
To start, let’s focus on argument. What does it mean to present an “argument” in college writing? Rather than a shouting match between two disagreeing sides, argument instead means a carefully arranged and supported presentation of a viewpoint. Its purpose is not so much to win the argument as to earn your audience’s consideration (and even approval) of your perspective. It resembles a conversation between two people who may not hold the same opinions, but they both desire a better understanding of the subject matter under discussion. My favorite analogy, however, to describe the nature of this argumentative stance in college writing is the courtroom. In this scenario, you are like a lawyer making a case at trial that the defendant is not guilty, and your readers are like the jury who will decide if the defendant is guilty or not guilty. This jury (your readers) won’t just take your word that he’s innocent; instead, you must convince them by presenting evidence that proves he is not guilty. Stating your opinion is not enough—you have to back it up too. I like this courtroom analogy for capturing two importance things about academic argument: 1) the value of an organized presentation of your “case,” and 2) the crucial element of strong evidence.
Academic Writing Is an Analysis
We now turn our attention to the actual writing assignment and that confusing word “analyze.” Your first job when you get a writing assignment is to figure out what the professor expects. This assignment may be explicit in its expectations, but often built into the wording of the most defined writing assignments are implicit expectations that you might not recognize. First, we can say that unless your professor specifically asks you to summarize, you won’t write a summary. Let me say that again: don’t write a summary unless directly asked to. But what, then, does the professor want? We have already picked out a few of these expectations: You can count on the instructor expecting you to read closely, research adequately, and write an argument where you will demonstrate your ability to apply and use important concepts you have been studying. But the writing task also implies that your essay will be the result of an analysis. At times, the writing assignment may even explicitly say to write an analysis, but often this element of the task remains unstated.
So what does it mean to analyze? One way to think of an analysis is that it asks you to seek How and Why questions much more than What questions. An analysis involves doing three things:
- Engage in an open inquiry where the answer is not known at first (and where you leave yourself open to multiple suggestions)
- Identify meaningful parts of the subject
- Examine these separate parts and determine how they relate to each other
An analysis breaks a subject apart to study it closely, and from this inspection, ideas for writing emerge. When writing assignments call on you to analyze, they require you to identify the parts of the subject (parts of an ad, parts of a short story, parts of Hamlet’s character), and then show how these parts fit or don’t fit together to create some larger effect or meaning. Your interpretation of how these parts fit together constitutes your claim or thesis, and the task of your essay is then to present an argument defending your interpretation as a valid or plausible one to make. My biggest bit of advice about analysis is not to do it all in your head. Analysis works best when you put all the cards on the table, so to speak. Identify and isolate the parts of your analysis, and record important features and characteristics of each one. As patterns emerge, you sort and connect these parts in meaningful ways. For me, I have always had to do this recording and thinking on scratch pieces of paper. Just as critical reading forms a crucial element of the literacy task of a college writing assignment, so too does this analysis process. It’s built in.
Three Common Types of College Writing Assignments
We have been decoding the expectations of the academic writing task so far, and I want to turn now to examine the types of assignments you might receive. From my experience, you are likely to get three kinds of writing assignments based upon the instructor’s degree of direction for the assignment. We’ll take a brief look at each kind of academic writing task.
The Closed Writing Assignment
- Is Creon a character to admire or condemn?
- Does your advertisement employ techniques of propaganda, and if so what kind?
- Was the South justified in seceding from the Union?
- In your opinion, do you believe Hamlet was truly mad?
These kinds of writing assignments present you with two counter claims and ask you to determine from your own analysis the more valid claim. They resemble yes-no questions. These topics define the claim for you, so the major task of the writing assignment then is working out the support for the claim. They resemble a math problem in which the teacher has given you the answer and now wants you to “show your work” in arriving at that answer.
Be careful with these writing assignments, however, because often these topics don’t have a simple yes/no, either/or answer (despite the nature of the essay question). A close analysis of the subject matter often reveals nuances and ambiguities within the question that your eventual claim should reflect. Perhaps a claim such as, “In my opinion, Hamlet was mad” might work, but I urge you to avoid such a simplistic thesis. This thesis would be better: “I believe Hamlet’s unhinged mind borders on insanity but doesn’t quite reach it.”
The Semi-Open Writing Assignment
- Discuss the role of law in Antigone.
- Explain the relationship between character and fate in Hamlet.
- Compare and contrast the use of setting in two short stories.
- Show how the Fugitive Slave Act influenced the Abolitionist Movement.
Although these topics chart out a subject matter for you to write upon, they don’t offer up claims you can easily use in your paper. It would be a misstep to offer up claims such as, “Law plays a role in Antigone” or “In Hamlet we can see a relationship between character and fate.” Such statements express the obvious and what the topic takes for granted. The question, for example, is not whether law plays a role in Antigone, but rather what sort of role law plays. What is the nature of this role? What influences does it have on the characters or actions or theme? This kind of writing assignment resembles a kind of archaeological dig. The teacher cordons off an area, hands you a shovel, and says dig here and see what you find. Be sure to avoid summary and mere explanation in this kind of assignment. Despite using key words in the assignment such as “explain,” “illustrate,” analyze,” “discuss,” or “show how,” these topics still ask you to make an argument. Implicit in the topic is the expectation that you will analyze the reading and arrive at some insights into patterns and relationships about the subject. Your eventual paper, then, needs to present what you found from this analysis—the treasure you found from your digging. Determining your own claim represents the biggest challenge for this type of writing assignment.
The Open Writing Assignment
- Analyze the role of a character in Dante’s The Inferno.
- What does it mean to be an “American” in the 21st Century?
- Analyze the influence of slavery upon one cause of the Civil War.
- Compare and contrast two themes within Pride and Prejudice.
These kinds of writing assignments require you to decide both your writing topic and you claim (or thesis). Which character in the Inferno will I pick to analyze? What two themes in Pride and Prejudice will I choose to write about? Many students struggle with these types of assignments because they have to understand their subject matter well before they can intelligently choose a topic. For instance, you need a good familiarity with the characters in The Inferno before you can pick one. You have to have a solid understanding defining elements of American identity as well as 21st century culture before you can begin to connect them. This kind of writing assignment resembles riding a bike without the training wheels on. It says, “You decide what to write about.” The biggest decision, then, becomes selecting your topic and limiting it to a manageable size.
Picking and Limiting a Writing Topic
Let’s talk about both of these challenges: picking a topic and limiting it. Remember how I said these kinds of essay topics expect you to choose what to write about from a solid understanding of your subject? As you read and review your subject matter, look for things that interest you. Look for gaps, puzzling items, things that confuse you, or connections you see. Something in this pile of rocks should stand out as a jewel: as being “do-able” and interesting. (You’ll write best when you write from both your head and your heart.) Whatever topic you choose, state it as a clear and interesting question. You may or may not state this essay question explicitly in the introduction of your paper (I actually recommend that you do), but it will provide direction for your paper and a focus for your claim since that claim will be your answer to this essay question. For example, if with the Dante topic you decided to write on Virgil, your essay question might be: “What is the role of Virgil toward the character of Dante in The Inferno?” The thesis statement, then, might be this: “Virgil’s predominant role as Dante’s guide through hell is as the voice of reason.” Crafting a solid essay question is well worth your time because it charts the territory of your essay and helps you declare a focused thesis statement.
Many students struggle with defining the right size for their writing project. They chart out an essay question that it would take a book to deal with adequately. You’ll know you have that kind of topic if you have already written over the required page length but only touched one quarter of the topics you planned to discuss. In this case, carve out one of those topics and make your whole paper about it. For instance, with our Dante example, perhaps you planned to discuss four places where Virgil’s role as the voice of reason is evident. Instead of discussing all four, focus your essay on just one place. So your revised thesis statement might be: “Close inspection of Cantos I and II reveal that Virgil serves predominantly as the voice of reason for Dante on his journey through hell.” A writing teacher I had in college said it this way: A well tended garden is better than a large one full of weeds. That means to limit your topic to a size you can handle and support well.
Three Characteristics of Academic Writing
I want to wrap up this section by sharing in broad terms what the expectations are behind an academic writing assignment. Chris Thaiss and Terry Zawacki conducted research at George Mason University where they asked professors from their university what they thought academic writing was and its standards. They came up with three characteristics:
- Clear evidence in writing that the writer(s) have been persistent, open-minded, and disciplined in study. (5)
- The dominance of reason over emotions or sensual perception. (5)
- An imagined reader who is coolly rational, reading for information, and intending to formulate a reasoned response. (7)
Your professor wants to see these three things in your writing when they give you a writing assignment. They want to see in your writing the results of your efforts at the various literacy tasks we have been discussing: critical reading, research, and analysis. Beyond merely stating opinions, they also want to see an argument toward an intelligent audience where you provide good reasons to support your interpretations.
The Format of the Academic Essay
Your instructors will also expect you to deliver a paper that contains particular textual features. The following list contains the characteristics of what I have for years called the “critical essay.” Although I can’t claim they will be useful for all essays in college, I hope that these features will help you shape and accomplish successful college essays. Be aware that these characteristics are flexible and not a formula, and any particular assignment might ask for something different.
Characteristics of the Critical Essay
“Critical” here is not used in the sense of “to criticize” as in find fault with. Instead, “critical” is used in the same way “critical thinking” is used. A synonym might be “interpretive” or “analytical.”
- It is an argument, persuasion essay that in its broadest sense MAKES A POINT and SUPPORTS IT. (We have already discussed this argumentative nature of academic writing at length.)
- The point (“claim” or “thesis”) of a critical essay is interpretive in nature. That means the point is debatable and open to interpretation, not a statement of the obvious. The thesis statement is a clear, declarative sentence that often works best when it comes at the end of the introduction.
- Organization: Like any essay, the critical essay should have a clear introduction, body, and conclusion. As you support your point in the body of the essay, you should “divide up the proof,” which means structuring the body around clear primary supports (developed in single paragraphs for short papers or multiple paragraphs for longer papers).
- Support: (a) The primary source for support in the critical essay is from the text (or sources). The text is the authority, so using quotations is required. (b) The continuous movement of logic in a critical essay is “assert then support; assert then support.” No assertion (general statement that needs proving) should be left without specific support (often from the text(s)). (c) You need enough support to be convincing. In general, that means for each assertion you need at least three supports. This threshold can vary, but invariably one support is not enough.
- A critical essay will always “document” its sources, distinguishing the use of outside information used inside your text and clarifying where that information came from (following the rules of MLA documentation style or whatever documentation style is required).
- Whenever the author moves from one main point (primary support) to the next, the author needs to clearly signal to the reader that this movement is happening. This transition sentence works best when it links back to the thesis as it states the topic of that paragraph or section.
- A critical essay is put into an academic essay format such as the MLA or APA document format.
- Grammatical correctness: Your essay should have few if any grammatical problems. You’ll want to edit your final draft carefully before turning it in.
Conclusion
As we leave this discussion, I want to return to what I said was the secret for your success in writing college essays: Your success with academic writing depends upon how well you understand what you are doing as you write and then how you approach the writing task. Hopefully, you now have a better idea about the nature of the academic writing task and the expectations behind it. Knowing what you need to do won’t guarantee you an “A” on your paper—that will take a lot of thinking, hard work, and practice—but having the right orientation toward your college writing assignments is a first and important step in your eventual success.
Discussion
- How did what you wrote in high school compare to what you have/will do in your academic writing in college?
- Think of two different writing situations you have found yourself in. What did you need to do the same in those two situations to place your writing appropriately? What did you need to do differently?
- Think of a writing assignment that you will need to complete this semester. Who’s your audience? What’s the occasion or context? What’s your message? What’s your purpose? What documents/genres are used? How does all that compare to the writing you are doing in this class?
Works Cited
Carroll, Lee Ann. Rehearsing New Roles: How College Students Develop as Writers. Carbondale: Southern Illinois UP, 2002. Print.
Thaiss, Chris, and Terry Zawacki. Engaged Writers & Dynamic Disciplines: Research on the Academic Writing Life. Portsmouth: Boynton/Cook, 2006. Print.

What is an Essay?
provided by Candela Open Courses
If you were asked to describe an essay in one word, what would that one word be?
Okay, well, in one word, an essay is an idea.
No idea; no essay.
But more than that, the best essays have original and insightful ideas.
Okay, so the first thing we need to begin an essay is an insightful idea that we wish to share with the reader.
But original and insightful ideas do not just pop up every day. Where does one find original and insightful ideas?
Let’s start here: an idea is an insight gained from either a) our personal experiences, or b) in scholarship, from synthesizing the ideas of others to create a new idea.
In this class (except for the last essay) we write personal essays; therefore, we will focus mostly on a) personal experience as a source for our ideas.
Life teaches us lessons. We learn from our life experiences. This is how we grow as human beings. So before you start on your essays, reflect on your life experiences by employing one or more of the brainstorming strategies described in this course. Your brainstorming and prewriting assignments are important assignments because remember: no idea; no essay. Brainstorming can help you discover an idea for your essay. So, ask yourself: What lessons have I learned? What insights have I gained that I can write about and share with my reader? Your reader can learn from you.
Why do we write?
We write to improve our world; it’s that simple. We write personal essays to address the most problematic and fundamental question of all: What does it mean to be a human being? By sharing the insights and lessons we have learned from our life experiences we can add to our community’s collective wisdom.
We respect the writings of experts. And, guess what; you are an expert! You are the best expert of all on one subject—your own life experiences. So when we write personal essays, we research our own life experiences and describe those experiences with rich and compelling language to convince our reader that our idea is valid.
For example:
For your Narrative essay: do more than simply relate a series of events. Let the events make a point about the central idea you are trying to teach us.
For your Example essay: do more than tell us about your experience. Show us your experience. Describe your examples in descriptive details so that your reader actually experiences for themselves the central idea you wish to teach them.
For the Comparison Contrast essay: do more than simply tell us about the differences and similarities of two things. Evaluate those differences and similarities and draw an idea about them, so that you can offer your reader some basic insight into the comparison.
Okay, one last comment. Often students say to me: “I am so young; I do not have any  meaningful insights in to life.” Okay, well, you may not be able to solve the pressing issues of the day, but think of it this way. What if a younger brother or sister came to you and in an anxious voice said; “I’ve got to do X. I’ve never had to do X. You’ve had some experience with X. Can you give me some advice?” You may have some wisdom and insights from your own life experience with X to share with that person. Don’t worry about solving the BIG issues in this class. You can serve the world as well by simply addressing, and bringing to life in words, the problems and life situations that you know best, no matter how mundane. Please notice that with rare exception the essays you will read in this class do not cite outside sources. They are all written from the author’s actual life experiences. So think of your audience as someone who can learn from your life experiences and write to them and for them.
meaningful insights in to life.” Okay, well, you may not be able to solve the pressing issues of the day, but think of it this way. What if a younger brother or sister came to you and in an anxious voice said; “I’ve got to do X. I’ve never had to do X. You’ve had some experience with X. Can you give me some advice?” You may have some wisdom and insights from your own life experience with X to share with that person. Don’t worry about solving the BIG issues in this class. You can serve the world as well by simply addressing, and bringing to life in words, the problems and life situations that you know best, no matter how mundane. Please notice that with rare exception the essays you will read in this class do not cite outside sources. They are all written from the author’s actual life experiences. So think of your audience as someone who can learn from your life experiences and write to them and for them.

Critical Thinking in College Writing: From the Personal to the Academic
by Gita DasBender
There is something about the term “critical thinking” that makes you draw a blank every time you think about what it means.* It seems so fuzzy and abstract that you end up feeling uncomfortable, as though the term is thrust upon you, demanding an intellectual effort that you may not yet have. But you know it requires you to enter a realm of smart, complex ideas that others have written about and that you have to navigate, understand, and interact with just as intelligently. It’s a lot to ask for. It makes you feel like a stranger in a strange land.
As a writing teacher I am accustomed to reading and responding to difficult texts. In fact, I like grappling with texts that have interesting ideas no matter how complicated they are because I understand their value. I have learned through my years of education that what ultimately engages me, keeps me enthralled, is not just grammatically pristine, fluent writing, but writing that forces me to think beyond the page. It is writing where the writer has challenged herself and then offered up that challenge to the reader, like a baton in a relay race. The idea is to run with the baton.
You will often come across critical thinking and analysis as requirements for assignments in writing and upper-level courses in a variety of disciplines. Instructors have varying explanations of what they actually require of you, but, in general, they expect you to respond thoughtfully to texts you have read. The first thing you should remember is not to be afraid of critical thinking. It does not mean that you have to criticize the text, disagree with its premise, or attack the writer simply because you feel you must. Criticism is the process of responding to and evaluating ideas, argument, and style so that readers understand how and why you value these items.
Critical thinking is also a process that is fundamental to all disciplines. While in this essay I refer mainly to critical thinking in composition, the general principles behind critical thinking are strikingly similar in other fields and disciplines. In history, for instance, it could mean examining and analyzing primary sources in order to understand the context in which they were written. In the hard sciences, it usually involves careful reasoning, making judgments and decisions, and problem solving. While critical thinking may be subject-specific, that is to say, it can vary in method and technique depending on the discipline, most of its general principles such as rational thinking, making independent evaluations and judgments, and a healthy skepticism of what is being read, are common to all disciplines. No matter the area of study, the application of critical thinking skills leads to clear and flexible thinking and a better understanding of the subject at hand.
To be a critical thinker you not only have to have an informed opinion about the text but also a thoughtful response to it. There is no doubt that critical thinking is serious thinking, so here are some steps you can take to become a serious thinker and writer.
Attentive Reading: A Foundation for Critical Thinking
A critical thinker is always a good reader because to engage critically with a text you have to read attentively and with an open mind, absorbing new ideas and forming your own as you go along. Let us imagine you are reading an essay by Annie Dillard, a famous essayist, called “Living like Weasels.” Students are drawn to it because the idea of the essay appeals to something personally fundamental to all of us: how to live our lives. It is also a provocative essay that pulls the reader into the argument and forces a reaction, a good criterion for critical thinking.
So let’s say that in reading the essay you encounter a quote that gives you pause. In describing her encounter with a weasel in Hollins Pond, Dillard says, “I would like to learn, or remember, how to live . . . I don’t think I can learn from a wild animal how to live in particular . . . but I might learn something of mindlessness, something of the purity of living in the physical senses and the dignity of living without bias or motive” (220). You may not be familiar with language like this. It seems complicated, and you have to stop ever so often (perhaps after every phrase) to see if you understood what Dillard means. You may ask yourself these questions:
- What does “mindlessness” mean in this context?
- How can one “learn something of mindlessness?”
- What does Dillard mean by “purity of living in the physical senses?”
- How can one live “without bias or motive?”
These questions show that you are an attentive reader. Instead of simply glossing over this important passage, you have actually stopped to think about what the writer means and what she expects you to get from it. Here is how I read the quote and try to answer the questions above: Dillard proposes a simple and uncomplicated way of life as she looks to the animal world for inspiration. It is ironic that she admires the quality of “mindlessness” since it is our consciousness, our very capacity to think and reason, which makes us human, which makes us beings of a higher order. Yet, Dillard seems to imply that we need to live instinctually, to be guided by our senses rather than our intellect. Such a “thoughtless” approach to daily living, according to Dillard, would mean that our actions would not be tainted by our biases or motives, our prejudices. We would go back to a primal way of living, like the weasel she observes. It may take you some time to arrive at this understanding on your own, but it is important to stop, reflect, and ask questions of the text whenever you feel stumped by it. Often such questions will be helpful during class discussions and peer review sessions.
Listing Important Ideas
When reading any essay, keep track of all the important points the writer makes by jotting down a list of ideas or quotations in a notebook. This list not only allows you to remember ideas that are central to the writer’s argument, ideas that struck you in some way or the other, but it also you helps you to get a good sense of the whole reading assignment point by point. In reading Annie Dillard’s essay, we come across several points that contribute toward her proposal for better living and that help us get a better understanding of her main argument. Here is a list of some of her ideas that struck me as important:
- “The weasel lives in necessity and we live in choice, hating necessity and dying at the last ignobly in its talons” (220).
- “And I suspect that for me the way is like the weasel’s: open to time and death painlessly, noticing everything, remembering nothing, choosing the given with a fierce and pointed will” (221).
- “We can live any way we want. People take vows of poverty, chastity, and obedience—even of silence—by choice. The thing is to stalk your calling in a certain skilled and supple way, to locate the most tender and live spot and plug into that pulse” (221).
- “A weasel doesn’t ‘attack’ anything; a weasel lives as he’s meant to, yielding at every moment to the perfect freedom of single necessity” (221).
- “I think it would be well, and proper, and obedient, and pure, to grasp your one necessity and not let it go, to dangle from it limp wherever it takes you” (221).
These quotations give you a cumulative sense of what Dillard is trying to get at in her essay, that is, they lay out the elements with which she builds her argument. She first explains how the weasel lives, what she learns from observing the weasel, and then prescribes a lifestyle she admires—the central concern of her essay.
Noticing Key Terms and Summarizing Important Quotes
Within the list of quotations above are key terms and phrases that are critical to your understanding of the ideal life as Dillard describes it. For instance, “mindlessness,” “instinct,” “perfect freedom of a single necessity,” “stalk your calling,” “choice,” and “fierce and pointed will” are weighty terms and phrases, heavy with meaning, that you need to spend time understanding. You also need to understand the relationship between them and the quotations in which they appear. This is how you might work on each quotation to get a sense of its meaning and then come up with a statement that takes the key terms into account and expresses a general understanding of the text:
Quote 1: Animals (like the weasel) live in “necessity,” which means that their only goal in life is to survive. They don’t think about how they should live or what choices they should make like humans do. According to Dillard, we like to have options and resist the idea of “necessity.” We fight death—an inevitable force that we have no control over—and yet ultimately surrender to it as it is the necessary end of our lives.
Quote 2: Dillard thinks the weasel’s way of life is the best way to live. It implies a pure and simple approach to life where we do not worry about the passage of time or the approach of death. Like the weasel, we should live life in the moment, intensely experiencing everything but not dwelling on the past. We should accept our condition, what we are “given,” with a “fierce and pointed will.” Perhaps this means that we should pursue our one goal, our one passion in life, with the same single-minded determination and tenacity that we see in the weasel.
Quote 3: As humans, we can choose any lifestyle we want. The trick, however, is to go after our one goal, one passion like a stalker would after a prey.
Quote 4: While we may think that the weasel (or any animal) chooses to attack other animals, it is really only surrendering to the one thing it knows: its need to live. Dillard tells us there is “the perfect freedom” in this desire to survive because to her, the lack of options (the animal has no other option than to fight to survive) is the most liberating of all.
Quote 5: Dillard urges us to latch on to our deepest passion in life (the “one necessity”) with the tenacity of a weasel and not let go. Perhaps she’s telling us how important it is to have an unwavering focus or goal in life.
Writing a Personal Response: Looking Inward
Dillard’s ideas will have certainly provoked a response in your mind, so if you have some clear thoughts about how you feel about the essay this is the time to write them down. As you look at the quotes you have selected and your explanation of their meaning, begin to create your personal response to the essay. You may begin by using some of these strategies:
- Tell a story. Has Dillard’s essay reminded you of an experience you have had? Write a story in which you illustrate a point that Dillard makes or hint at an idea that is connected to her essay.
- Focus on an idea from Dillard’s essay that is personally important to you. Write down your thoughts about this idea in a first-person narrative and explain your perspective on the issue.
- If you are uncomfortable writing a personal narrative or using “I” (you should not be), reflect on some of her ideas that seem important and meaningful in general. Why were you struck by these ideas?
- Write a short letter to Dillard in which you speak to her about the essay. You may compliment her on some of her ideas by explaining why you like them, ask her a question related to her essay and explain why that question came to you, and genuinely start up a conversation with her.
This stage in critical thinking is important for establishing your relationship with a text. What do I mean by this “relationship,” you may ask? Simply put, it has to do with how you feel about the text. Are you amazed by how true the ideas seem to be, how wise Dillard sounds? Or are you annoyed by Dillard’s let-me-tell-you-how-to-live approach and disturbed by the impractical ideas she so easily prescribes? Do you find Dillard’s voice and style thrilling and engaging or merely confusing? No matter which of the personal response options you select, your initial reaction to the text will help shape your views about it.
Making an Academic Connection: Looking Outward
First year writing courses are designed to teach a range of writing— from the personal to the academic—so that you can learn to express advanced ideas, arguments, concepts, or theories in any discipline. While the example I have been discussing pertains mainly to college writing, the method of analysis and approach to critical thinking I have demonstrated here will serve you well in a variety of disciplines. Since critical thinking and analysis are key elements of the reading and writing you will do in college, it is important to understand how they form a part of academic writing. No matter how intimidating the term “academic writing” may seem (it is, after all, associated with advanced writing and becoming an expert in a field of study), embrace it not as a temporary college requirement but as a habit of mind.
To some, academic writing often implies impersonal writing, writing that is detached, distant, and lacking in personal meaning or relevance. However, this is often not true of the academic writing you will do in a composition class. Here your presence as a writer—your thoughts, experiences, ideas, and therefore who you are—is of much significance to the writing you produce. In fact, it would not be far-fetched to say that in a writing class academic writing often begins with personal writing. Let me explain. If critical thinking begins with a personal view of the text, academic writing helps you broaden that view by going beyond the personal to a more universal point of view. In other words, academic writing often has its roots in one’s private opinion or perspective about another writer’s ideas but ultimately goes beyond this opinion to the expression of larger, more abstract ideas. Your personal vision—your core beliefs and general approach to life— will help you arrive at these “larger ideas” or universal propositions that any reader can understand and be enlightened by, if not agree with. In short, academic writing is largely about taking a critical, analytical stance toward a subject in order to arrive at some compelling conclusions.
Let us now think about how you might apply your critical thinking skills to move from a personal reaction to a more formal academic response to Annie Dillard’s essay. The second stage of critical thinking involves textual analysis and requires you to do the following:
- Summarize the writer’s ideas the best you can in a brief paragraph. This provides the basis for extended analysis since it contains the central ideas of the piece, the building blocks, so to speak.
- Evaluate the most important ideas of the essay by considering their merits or flaws, their worthiness or lack of worthiness. Do not merely agree or disagree with the ideas but explore and explain why you believe they are socially, politically, philosophically, or historically important and relevant, or why you need to question, challenge, or reject them.
- Identify gaps or discrepancies in the writer’s argument. Does she contradict herself? If so, explain how this contradiction forces you to think more deeply about her ideas. Or if you are confused, explain what is confusing and why.
- Examine the strategies the writer uses to express her ideas. Look particularly at her style, voice, use of figurative language, and the way she structures her essay and organizes her ideas. Do these strategies strengthen or weaken her argument? How?
- Include a second text—an essay, a poem, lyrics of a song— whose ideas enhance your reading and analysis of the primary text. This text may help provide evidence by supporting a point you’re making, and further your argument.
- Extend the writer’s ideas, develop your own perspective, and propose new ways of thinking about the subject at hand.
Crafting the Essay
Once you have taken notes and developed a thorough understanding of the text, you are on your way to writing a good essay. If you were asked to write an exploratory essay, a personal response to Dillard’s essay would probably suffice. However, an academic writing assignment requires you to be more critical. As counter-intuitive as it may sound, beginning your essay with a personal anecdote often helps to establish your relationship to the text and draw the reader into your writing. It also helps to ease you into the more complex task of textual analysis. Once you begin to analyze Dillard’s ideas, go back to the list of important ideas and quotations you created as you read the essay. After a brief summary, engage with the quotations that are most important, that get to the heart of Dillard’s ideas, and explore their meaning. Textual engagement, a seemingly slippery concept, simply means that you respond directly to some of Dillard’s ideas, examine the value of Dillard’s assertions, and explain why they are worthwhile or why they should be rejected. This should help you to transition into analysis and evaluation. Also, this part of your essay will most clearly reflect your critical thinking abilities as you are expected not only to represent Dillard’s ideas but also to weigh their significance. Your observations about the various points she makes, analysis of conflicting viewpoints or contradictions, and your understanding of her general thesis should now be synthesized into a rich new idea about how we should live our lives. Conclude by explaining this fresh point of view in clear, compel- ling language and by rearticulating your main argument.
Modeling Good Writing
When I teach a writing class, I often show students samples of really good writing that I’ve collected over the years. I do this for two reasons: first, to show students how another freshman writer understood and responded to an assignment that they are currently working on; and second, to encourage them to succeed as well. I explain that although they may be intimidated by strong, sophisticated writing and feel pressured to perform similarly, it is always helpful to see what it takes to get an A. It also helps to follow a writer’s imagination, to learn how the mind works when confronted with a task involving critical thinking. The following sample is a response to the Annie Dillard essay. Figure 1 includes the entire student essay and my comments are inserted into the text to guide your reading.
Though this student has not included a personal narrative in his essay, his own world-view is clear throughout. His personal point of view, while not expressed in first person statements, is evident from the very beginning. So we could say that a personal response to the text need not always be expressed in experiential or narrative form but may be present as reflection, as it is here. The point is that the writer has traveled through the rough terrain of critical thinking by starting out with his own ruminations on the subject, then by critically analyzing and responding to Dillard’s text, and finally by developing a strong point of view of his own about our responsibility as human beings. As readers, we are engaged by clear, compelling writing and riveted by critical thinking that produces a movement of ideas that give the essay depth and meaning. The challenge Dillard set forth in her essay has been met and the baton passed along to us.
Figure 1:





Discussion
- Write about your experiences with critical thinking assignments. What seemed to be the most difficult? What approaches did you try to overcome the difficulty?
- Respond to the list of strategies on how to conduct textual analysis. How well do these strategies work for you? Add your own tips to the list.
- Evaluate the student essay by noting aspects of critical thinking that are evident to you. How would you grade this essay? What other qualities (or problems) do you notice?
Works Cited
Dillard, Annie. “Living Like Weasels.” One Hundred Great Essays. Ed. Robert DiYanni. New York: Longman, 2002. 217-221. Print.
Important Concepts
recursive
critical literacy
essay
critical thinking
Licenses and Attributions
CC LICENSED CONTENT, ORIGINAL
Composing Ourselves and Our World, Provided by: the authors. License: Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0)
CC LICENSED CONTENT INCLUDED
This chapter contains an adaptation of What Is Academic Writing?: by Lenny L Irvin, and is used under an Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 United States (CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 US) license.
The chapter also contains an adaptation of English Composition 1 Provided by: Lumen Learning. Located at: http://lumenlearning.com/. License: CC BY: Attribution Authored by: Paul Powell. Provided by: Central Community College. Project: Kaleidoscope Open Course Initiative. License: CC BY: Attribution
This chapter contains an excerpt from Critical Thinking in College Writing: From the Personal to the Academic by Gita DasBender.
MULTIMEDIA CONTENT INCLUDED
- Video 1: 7 Tips for Effective Academic Writing by KeeleStudentLearning. Licensed: Creative Commons Attribution license (reuse allowed)
- Image 1: License: CC0 “No Rights Reserved”
- Image of blank journal. Authored by: Sembazuru. Located at: https://flic.kr/p/BKeN. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Image of Idea. Authored by: Mike Linksvayer. Located at: https://flic.kr/p/bD6jZH. License: Public Domain: No Known Copyright
