Writing Thesis Statements
CHAPTER DESCRIPTION
Discusses weak thesis statements and ways to revise
To be effective, all support in an essay must work together to convey a central point; otherwise, an essay can fall into the trap of being out of order and confusing. Just as a topic sentence focuses and unifies a single paragraph, the thesis statement focuses and unifies an entire essay. This statement is like a signpost that signals the essay’s destination; it tells the reader the point you want to make in your essay, while the essay itself supports that point.
Because writing is not a linear process, you may find that the best thesis statement develops near the end of your first draft. However, creating a draft or working thesis early in the writing project helps give the drafting process clear direction. You should form your thesis before you begin to organize an essay, but you may find that it needs revision as the essay develops.
A thesis is not just a topic, but rather the writer’s comment or interpretation of the question or subject. For whatever topic you select (for example, school uniforms, social networking), you must ask yourself, “What do I want to say about it?” Asking and then answering this question is vital to forming a thesis that is precise, forceful, and confident.
In the majority of essays, a thesis is one sentence long and appears toward the end of the introductory paragraph. It is specific and focuses on one to three points of a single idea—points that are able to be demonstrated in the body paragraphs. It forecasts the content of the essay and suggests how you will organize your information. Remember that a thesis statement does not summarize an issue but rather dissects it.
Working Thesis Statements
A strong thesis statement must have the following qualities:
- It must be arguable. A thesis statement must state a point of view or judgment about a topic. An established fact is not considered arguable.
- It must be supportable. The thesis statement must contain a point of view that can be supported with evidence (reasons, facts, examples).
- It must be specific. A thesis statement must be precise enough to allow for a coherent argument and remain focused on the topic.
Examples of Appropriate Thesis Statements
- Closing all American borders for a period of five years is one solution that will tackle illegal immigration.
- Compared to an absolute divorce, no-fault divorce is less expensive, promotes fairer settlements, and reflects a more realistic view of the causes for marital breakdown.
- Exposing children from an early age to the dangers of drug abuse is a sure method of preventing future drug addicts.
- In today’s crumbling job market, a high school diploma is not significant enough education to land a stable, lucrative job.
- The societal and personal struggles of Troy Maxson in the play Fences symbolize the challenges of black males who lived through segregation and integration in the United States.
Pitfalls to Avoid
A thesis is weak when it is simply a declaration of your subject or a description of what you will discuss in your essay.
Weak Thesis Statement Example
My paper will explain why imagination is more important than knowledge.
A thesis is weak when it makes an unreasonable or outrageous claim or insults the opposing side.
Weak Thesis Statement Example
Religious radicals across America are trying to legislate their Puritanical beliefs by banning required high school books.
A thesis is weak when it contains an obvious fact or something that no one can disagree with or provides a dead end.
Weak Thesis Statement Example
Advertising companies use sex to sell their products.
A thesis is weak when the statement is too broad.
Weak Thesis Statement Example
The life of Abraham Lincoln was long and challenging.
Ways to Revise Your Thesis
Your thesis statement begins as a working thesis statement, an indefinite statement that you make about your topic early in the writing process for the purpose of planning and guiding your writing. Working thesis statements often become stronger as you gather information and develop new ideas and reasons for those ideas. Revision helps you strengthen your thesis so that it matches what you have expressed in the body of the paper.
You can cut down on irrelevant aspects and revise your thesis by taking the following steps:
- Pinpoint and replace all non specific words, such as people, everything, society, or life, with more precise words in order to reduce any vagueness.
Pinpoint and Replace Example
Working thesis: Young people have to work hard to succeed in life.
Revised thesis: Recent college graduates must have discipline and persistence in order to find and maintain a stable job in which they can use, and be appreciated for, their talents.
Explanation: The original includes too broad a range of people and does not define exactly what success entails. By replacing those general words like people and work hard, the writer can better focus their research and gain more direction in their writing. The revised thesis makes a more specific statement about success and what it means to work hard.
- Clarify ideas that need explanation by asking yourself questions that narrow your thesis.
Clarify Example
Working thesis: The welfare system is a joke.
Revised thesis: The welfare system keeps a socioeconomic class from gaining employment by alluring members of that class with unearned income, instead of programs to improve their education and skill sets.
Explanation: A joke means many things to many people. Readers bring all sorts of backgrounds and perspectives to the reading process and would need clarification for a word so vague. This expression may also be too informal for the selected audience. By asking questions, the writer can devise a more precise and appropriate explanation for joke and more accurately defines their stance, which will better guide the writing of the essay.
- Replace any linking verbs with action verbs. Linking verbs are forms of the verb to be, a verb that simply states that a situation exists.
Replace with Action Verbs Example
Working thesis: Kansas City school teachers are not paid enough.
Revised thesis: The Kansas City legislature cannot afford to pay its educators, resulting in job cuts and resignations in a district that sorely needs highly qualified and dedicated teachers.
Explanation: The linking verb in this working thesis statement is the word are. Linking verbs often make thesis statements weak because they do not express action. Rather, they connect words and phrases to the second half of the sentence. Readers might wonder, “Why are they not paid enough?” But this statement does not compel them to ask many more questions.
-
- Asking questions will help you replace the linking verb with an action verb, thus forming a stronger thesis statement that takes a more definitive stance on the issue:
- Who is not paying the teachers enough?
- How much is considered “enough”?
- What is the problem?
- What are the results?
- Asking questions will help you replace the linking verb with an action verb, thus forming a stronger thesis statement that takes a more definitive stance on the issue:
- Omit any general claims that are hard to support.
Omit General Claims Example
Working thesis: Today’s teenage girls are too sexualized.
Revised thesis: Teenage girls who are captivated by the sexual images on the internet and social media are conditioned to believe that a woman’s worth depends on her sensuality, a feeling that harms their self-esteem and behavior.
Explanation: It is true that some young women in today’s society are more sexualized than in the past, but that is not true for all girls. Many girls have strict parents, dress appropriately, and do not engage in sexual activity while in middle school and high school. The writer of this thesis should ask the following questions:
- Which teenage girls?
- What constitutes “too” sexualized?
- Why are they behaving that way?
- Where does this behavior show up?
- What are the repercussions?
Practice Activity
[h5p id=”12″]
This section contains material from:
Crowther, Kathryn, Lauren Curtright, Nancy Gilbert, Barbara Hall, Tracienne Ravita, and Kirk Swenson. Successful College Composition. 2nd ed. Book 8. Georgia: English Open Textbooks, 2016. http://oer.galileo.usg.edu/english-textbooks/8. Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. Archival link: https://web.archive.org/web/20230711203012/https://oer.galileo.usg.edu/english-textbooks/8/
Content Description
Graphic organizer that helps students understand a writing assignment
https://uclalibrary.github.io/research-tips/handouts/Breaking-Down-Your-Prompt/
CHAPTER DESCRIPTION
- Discusses the elements that shape an essay
Once you have determined the assignment parameters, it’s time to begin drafting. While doing so, it is important to remain focused on your topic and thesis in order to guide your reader through the essay. Imagine reading one long block of text with each idea blurring into the next. Even if you are reading a thrilling novel or an interesting news article, you will likely lose interest in what the author has to say very quickly. During the writing process, it is helpful to position yourself as a reader. Ask yourself whether you can focus easily on each point you make. Keep in mind that three main elements shape the content of each essay (see Figure 2.4.1).[1]
- Purpose: The reason the writer composes the essay.
- Audience: The individual or group whom the writer intends to address.
- Tone: The attitude the writer conveys about the essay’s subject.
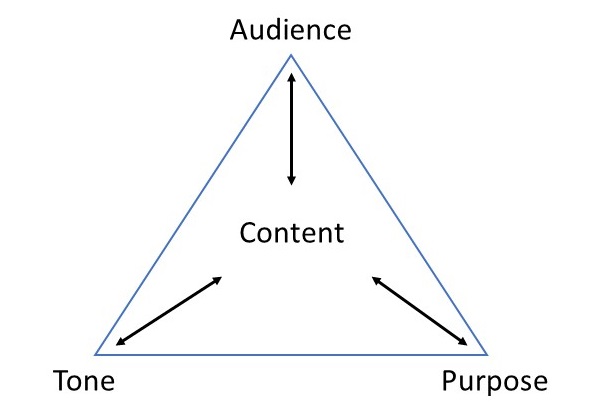
The assignment’s purpose, audience, and tone dictate what each paragraph of the essay covers and how the paragraph supports the main point or thesis.
Identifying Common Academic Purposes
The purpose for a piece of writing identifies the reason you write it by, basically, answering the question “Why?” For example, why write a play? To entertain a packed theater. Why write instructions to the babysitter? To inform him or her of your schedule and rules. Why write a letter to your congressman? To persuade him to address your community’s needs.
In academic settings, the reasons for writing typically fulfill four main purposes:
- to classify
- to analyze
- to synthesize
- to evaluate
A classification shrinks a large amount of information into only the essentials, using your own words; although shorter than the original piece of writing, a classification should still communicate all the key points and key support of the original document without quoting the original text. Keep in mind that classification moves beyond simple summary to be informative.
An analysis, on the other hand, separates complex materials into their different parts and studies how the parts relate to one another. In the sciences, for example, the analysis of simple table salt would require a deconstruction of its parts—the elements sodium (Na) and chloride (Cl). Then, scientists would study how the two elements interact to create the compound NaCl, or sodium chloride: simple table salt.
In an academic analysis, instead of deconstructing compounds, the essay takes apart a primary source (an essay, a book, an article, etc.) point by point. It communicates the main points of the document by examining individual points and identifying how the points relate to one another.
The third type of writing—synthesis—combines two or more items to create an entirely new item. Take, for example, the electronic musical instrument aptly named the synthesizer. It looks like a simple keyboard but displays a dashboard of switches, buttons, and levers. With the flip of a few switches, a musician may combine the distinct sounds of a piano, a flute, or a guitar—or any other combination of instruments—to create a new sound. The purpose of an academic synthesis is to blend individual documents into a new document by considering the main points from one or more pieces of writing and linking the main points together to create a new point, one not replicated in either document.
Finally, an evaluation judges the value of something and determines its worth. Evaluations in everyday life are often not only dictated by set standards but also influenced by opinion and prior knowledge such as a supervisor’s evaluation of an employee in a particular job. Academic evaluations, likewise, communicate your opinion and its justifications about a particular document or a topic of discussion. They are influenced by your reading of the document as well as your prior knowledge and experience with the topic or issue. Evaluations typically require more critical thinking and a combination of classifying, analysis, and synthesis skills.
You will encounter these four purposes not only as you read for your classes but also as you read for work or pleasure and, because reading and writing work together, your writing skills will improve as you read. Remember that the purpose for writing will guide you through each part of your paper, helping you make decisions about content and style.
When reviewing directions for assignments, look for the verbs that ask you to classify, analyze, synthesize, or evaluate. Instructors often use these words to clearly indicate the assignment’s purpose. These words will cue you on how to complete the assignment because you will know its exact purpose.
Identifying the Audience
Imagine you must give a presentation to a group of executives in an office. Weeks before the big day, you spend time creating and rehearsing the presentation. You must make important, careful decisions not only about the content but also about your delivery. Will the presentation require technology to project figures and charts? Should the presentation define important words, or will the executives already know the terms? Should you wear your suit and dress shirt? The answers to these questions will help you develop an appropriate relationship with your audience, making them more receptive to your message.
Now imagine you must explain the same business concepts from your presentation to a group of high school students. Those important questions you previously answered may now require different answers. The figures and charts may be too sophisticated, and the terms will certainly require definitions. You may even reconsider your outfit and sport a more casual look. Because the audience has shifted, your presentation and delivery will shift as well to create a new relationship with the new audience.
In these two situations, the audience—the individuals who will watch and listen to the presentation—plays a role in the development of presentation. As you prepare the presentation, you visualize the audience to anticipate their expectations and reactions. What you imagine affects the information you choose to present and how you will present it. Then, during the presentation, you meet the audience in person and discover immediately how well you perform.
Although the audience for writing assignments—your readers—may not appear in person, they play an equally vital role. Even in everyday writing activities, you identify your readers’ characteristics, interests, and expectations before making decisions about what you write. In fact, thinking about the audience has become so common that you may not even detect the audience-driven decisions. For example, you update your status on a social networking site with the awareness of who will digitally follow the post. If you want to brag about a good grade, you may write the post to please family members. If you want to describe a funny moment, you may write with your friends’ senses of humor in mind. Even at work, you send emails with an awareness of an unintended receiver who could intercept the message.
In other words, being aware of “invisible” readers is a skill you most likely already possess and one you rely on every day. Consider the following paragraphs. Which one would the author send to her parents? Which one would she send to her best friend?
Example A
Last Saturday, I volunteered at a local hospital. The visit was fun and rewarding. I even learned how to do cardiopulmonary resuscitation, or CPR. Unfortunately, I think I caught a cold from one of the patients. This week, I will rest in bed and drink plenty of clear fluids. I hope I am well by next Saturday to volunteer again.
Example B
OMG! You won’t believe this! My advisor forced me to do my community service hours at this hospital all weekend! We learned CPR but we did it on dummies, not even real peeps. And some kid sneezed on me and got me sick! I was so bored and sniffling all weekend; I hope I don’t have to go back next week. I def do NOT want to miss the basketball tournament!
Most likely, you matched each paragraph to its intended audience with little hesitation. Because each paragraph reveals the author’s relationship with the intended readers, you can identify the audience fairly quickly. When writing your own essays, you must engage with your audience to build an appropriate relationship given your subject.
Imagining your readers during each stage of the writing process will help you make decisions about your writing. Ultimately, the people you visualize will affect what and how you write.
While giving a speech, you may articulate an inspiring or critical message, but if you left your hair a mess and laced up mismatched shoes, your audience might not take you seriously. They may be too distracted by your appearance to listen to your words.
Similarly, grammar and sentence structure serve as the appearance of a piece of writing. Polishing your work using correct grammar will impress your readers and allow them to focus on what you have to say.
Because focusing on your intended audience will enhance your writing, your process, and your finished product, you must consider the specific traits of your audience members. Use your imagination to anticipate the readers’ demographics, education, prior knowledge, and expectations.
Demographics
These measure important data about a group of people such as their age range, their ethnicity, their religious beliefs, or their gender. Certain topics and assignments will require these kinds of considerations about your audience. For other topics and assignments, these measurements may not influence your writing in the end. Regardless, it is important to consider demographics when you begin to think about your purpose for writing.
Education
Education considers the audience’s level of schooling. If audience members have earned a doctorate degree, for example, you may need to elevate your style and use more formal language. Or, if audience members are still in college, you could write in a more relaxed style. An audience member’s major or emphasis may also dictate your writing.
Prior Knowledge
This refers to what the audience already knows about your topic. If your readers have studied certain topics, they may already know some terms and concepts related to the topic. You may decide whether to define terms and explain concepts based on your audience’s prior knowledge. Although you cannot peer inside the brains of your readers to discover their knowledge, you can make reasonable assumptions. For instance, a nursing major would presumably know more about health-related topics than a business major would.
Expectations
These indicate what readers will look for while reading your assignment. Readers may expect consistencies in the assignment’s appearance such as correct grammar and traditional formatting like double-spaced lines and legible font. Readers may also have content-based expectations given the assignment’s purpose and organization. In an essay titled “The Economics of Enlightenment: The Effects of Rising Tuition,” for example, audience members may expect to read about the economic repercussions of college tuition costs.
Selecting an Appropriate Tone
Tone identifies a speaker’s attitude toward a subject or another person. You may pick up a person’s tone of voice fairly easily in conversation. A friend who tells you about her weekend may speak excitedly about a fun skiing trip. An instructor who means business may speak in a low, slow voice to emphasize her serious mood. Or, a coworker who needs to let off some steam after a long meeting may crack a sarcastic joke.
Just as speakers transmit emotion through voice, writers can transmit a range of attitudes and emotions through prose--from excited and humorous to somber and critical. These emotions create connections among the audience, the author, and the subject, ultimately building a relationship between the audience and the text. To stimulate these connections, writers convey their attitudes and feelings with useful devices such as sentence structure, word choice, punctuation, and formal or informal language. Keep in mind that the writer’s attitude should always appropriately match the audience and the purpose.
Exercise
Read the following paragraph and consider the writer’s tone. How would you describe the writer’s attitude toward wildlife conservation?
"Many species of plants and animals are disappearing right before our eyes. If we don’t act fast, it might be too late to save them. Human activities, including pollution, deforestation, hunting, and overpopulation, are devastating the natural environment. Without our help, many species will not survive long enough for our children to see them in the wild. Take the tiger, for example. Today, tigers occupy just seven percent of their historical range, and many local populations are already extinct. Hunted for their beautiful pelts and other body parts, the tiger population has plummeted from one hundred thousand in 1920 to just a few thousand. Contact your local wildlife conservation society today to find out how you can stop this terrible destruction."
Choosing Appropriate, Interesting Content
Content refers to all the written substance in a document. After selecting an audience and a purpose, you must choose what information will make it to the page. Content may consist of examples, statistics, facts, anecdotes, testimonies, and observations, but no matter the type, the information must be appropriate and interesting for the audience and purpose. An essay written for third graders that summarizes the legislative process, for example, would have to contain succinct and simple content.
Content is also shaped by tone. When the tone matches the content, the audience will be more engaged, and you will build a stronger relationship with your readers. When applied to that audience of third graders, you would choose simple content that the audience would easily understand, and you would express that content through an enthusiastic tone.
The same considerations apply to all audiences and purposes.
Practice Activity
[h5p id="6"]
Practice Activity
[h5p id="7"]
This section contains material from:
Crowther, Kathryn, Lauren Curtright, Nancy Gilbert, Barbara Hall, Tracienne Ravita, and Kirk Swenson. Successful College Composition. 2nd edition. Book 8. Georgia: English Open Textbooks, 2016. http://oer.galileo.usg.edu/english-textbooks/8. Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. Archival link: https://web.archive.org/web/20230711203012/https://oer.galileo.usg.edu/english-textbooks/8/

Introduction
Reflecting on your work is an important step in your growth as a writer. Reflection allows you to recognize the ways in which you have mastered some skills and have addressed instances when your intention and execution fail to match. By recognizing previous challenges and applying learned strategies for addressing them, you demonstrate improvement and progress as a writer. This kind of reflection is an example of recursive. At this point in the semester, you know that writing is a recursive process: you prewrite, you write, you revise, you edit, you reflect, you revise, and so on. In working through a writing assignment, you learn and understand more about particular sections of your draft, and you can go back and revise them. The ability to return to your writing and exercise objectivity and honesty about it is one of skills you have practiced during this journey. You are now able to evaluate your own work, accept another’s critique of your writing, and make meaningful revisions.
In this chapter, you will review your work from earlier chapters and write a reflection that captures your growth, feelings, and challenges as a writer. In your reflection, you will apply many of the writing, reasoning, and evidentiary strategies you have already used in other papers—for example, analysis, evaluation, comparison and contrast, problem and solution, cause and effect, examples, and anecdotes.
When looking at your earlier work, you may find that you cringe at those papers and wonder what you were thinking when you wrote them. If given that same assignment, you now would know how to produce a more polished paper. This response is common and is evidence that you have learned quite a bit about writing.
14.1 Thinking Critically about Your Semester
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Reflect on and write about the development of composing processes and how those processes affect your work.
- Demonstrate honesty and objectivity in reflecting on written work.
You have written your way through a long semester, and the journey is nearly complete. Now is the time to step back and reflect on what you have written, what you have mastered, what skill gaps remain, and what you will do to continue growing and improving as a communicator. This reflection will be based on the work you have done and what you have learned during the semester. Because the subject of this reflection is you and your work, no further research is required. The information you need is in the work you have done in this course and in your head. Now, you will work to organize and transfer this information to an organized written text. Every assignment you have completed provides you with insight into your writing process as you think about the assignment’s purpose, its execution, and your learning along the way. The skill of reflection requires you to be critical and honest about your habits, feelings, skills, and writing. In the end, you will discover that you have made progress as a writer, perhaps in ways not yet obvious.
14.2 Glance at Genre: Purpose and Structure
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Identify conventions of reflection regarding structure, paragraphing, and tone.
- Articulate how genre conventions are shaped by purpose, culture, and expectation.
- Adapt composing processes for a variety of technologies and modalities.
Reflective writing is the practice of thinking about an event, an experience, a memory, or something imagined and expressing its larger meaning in written form. Reflective writing comes from the author’s specific perspective and often contemplates the way an event (or something else) has affected or even changed the author’s life.
Areas of Exploration
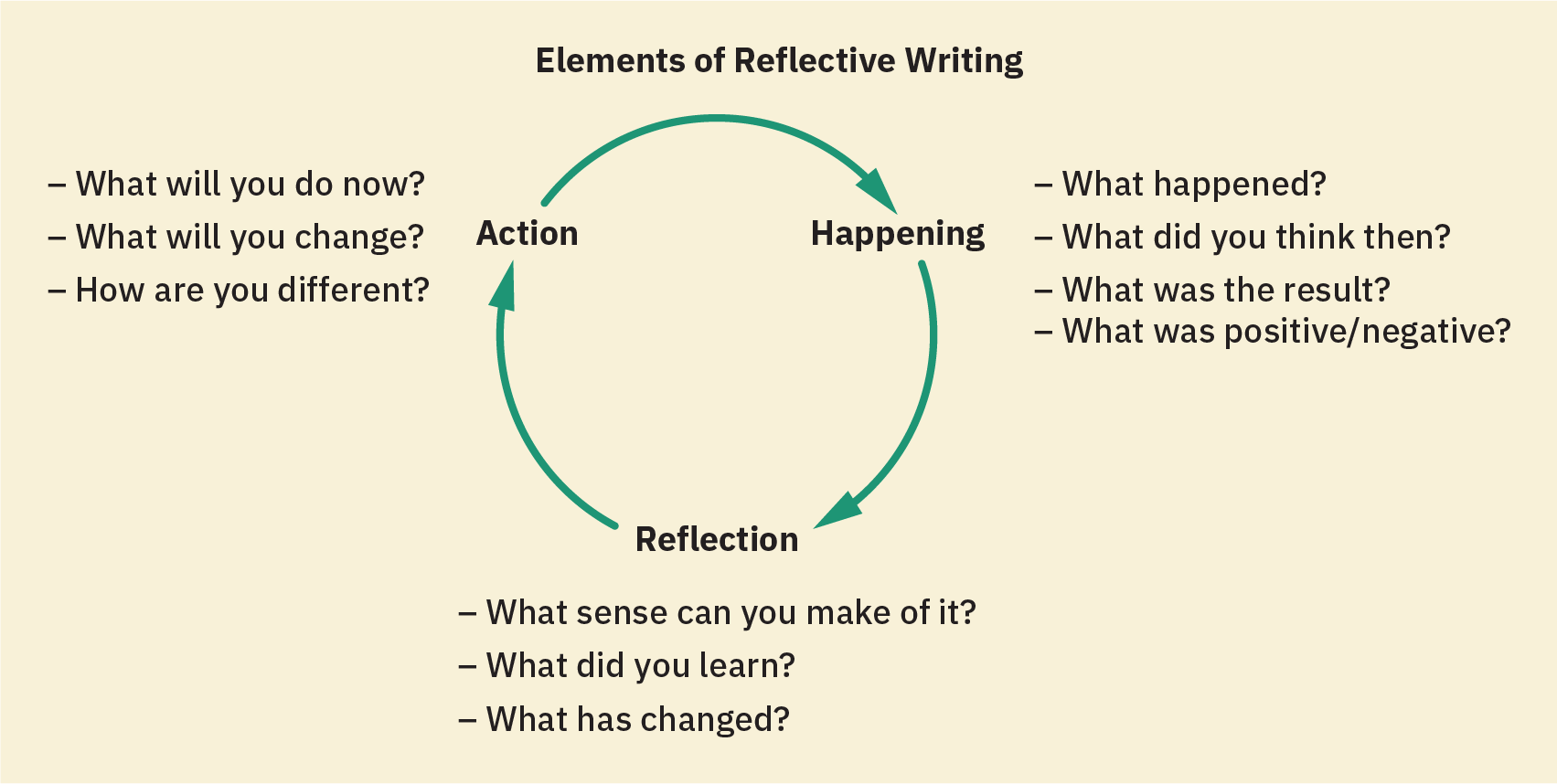
When you write a reflective piece, consider three main areas of exploration as shown in Figure 14.3. The first is the happening. This area consists of the events included in the reflection. For example, you will be examining writing assignments from this course. As you describe the assignments, you also establish context for the reflection so that readers can understand the circumstances involved. For each assignment, ask yourself these questions: What was the assignment? How did I approach the assignment? What did I do to start this assignment? What did I think about the assignment? If you think of other questions, use them. Record your answers because they will prove useful in the second area.
The second area is reflection. When you reflect on the happening, you go beyond simply writing about the specific details of the assignment; you move into the writing process and an explanation of what you learned from doing the work. In addition, you might recognize—and note—a change in your skills or way of thinking. Ask yourself these questions: What works effectively in this text? What did I learn from this assignment? How is this assignment useful? How did I feel when I was working on this assignment? Again, you can create other questions, and note your responses because you will use them to write a reflection.
The third area is action. Here, you decide what to do next and plan the steps needed to reach that goal. Ask yourself: What does (and does not) work effectively in this text? How can I continue to improve in this area? What should I do now? What has changed in my thinking? How would I change my approach to this assignment if I had to do another one like it? Base your responses to these questions on what you have learned, and implement these elements in your writing.
Figure 14.3 Elements of reflective writing (attribution: Copyright Rice University, OpenStax, under CC BY 4.0 license)
Format of Reflective Writing
Unlike thesis statements, which often come at the beginning of an essay, the main point of a piece of reflective writing may be conveyed only indirectly and nearly always emerges at the end, almost like an epiphany, or sudden realization. With this structure, readers are drawn into the act of reflecting and become more curious about what the writer is thinking and feeling. ln other words, reflective writers are musing, exploring, or wondering rather than arguing. In fact, reflective essays are most enlightening when they are not obviously instructive or assertive. However, even though reflective writing does not present an explicit argument, it still includes evidence and cohesion and provides lessons to be learned. As such, elements of persuasion or argument often appear in reflective essays.
Discovery through Writing
Keep in mind, too, that when you start to reflect on your growth as a writer, you may not realize what caused you to explore a particular memory. In other words, writers may choose to explore an idea, such as why something got their attention, and only by recalling the details of that event do they discover the reason it first drew their attention.
When you tell the story of your writing journey this semester, you may find that more was on your mind than you realized. The writing itself is one thing, but the meaning of what you learned becomes something else, and you may deliberately share how that second level, or deeper meaning or feeling, emerged through the act of storytelling. For example, in narrating a writing experience, you may step back, pause, and let readers know, “Wait a minute, something else is going on here.” An explanation of the new understanding, for both you and your readers, can follow this statement. Such pauses are a sign that connections are being made—between the present and the past, the concrete and the abstract, the literal and the symbolic. They signal to readers that the essay or story is about to move in a new and less predictable direction. Yet each idea remains connected through the structure of happenings, reflections, and actions.
Sometimes, slight shifts in voice or tone accompany reflective pauses as a writer moves closer to what is really on their mind. The exact nature of these shifts will, of course, be determined by the writer’s viewpoint. Perhaps one idea that you, as the writer, come up with is the realization that writing a position argument was useful in your history class. You were able to focus more on the material than on how to write the paper because you already knew how to craft a position argument. As you work through this process, continue to note these important little discoveries.
Your Writing Portfolio
As you recall, each chapter in this book has included one or more assignments for a writing portfolio. In simplest terms, a writing portfolio is a collection of your writing contained within a single binder or folder. A portfolio may contain printed copy, or it may be completely digital. Its contents may have been created over a number of weeks, months, or even years, and it may be organized chronologically, thematically, or qualitatively. A portfolio assigned for a class will contain written work to be shared with an audience to demonstrate your writing, learning, and skill progression. This kind of writing portfolio, accumulated during a college course, presents a record of your work over a semester and may be used to assign a grade. Many instructors now offer the option of, or even require, digital multimodal portfolios, which include visuals, audio, and/or video in addition to written texts. Your instructor will provide guidelines on how to create a multimodal portfolio, if applicable. You can also learn more about creating a multimodal portfolio and view one by a first-year student.
Key Terms
As you begin crafting your reflection, consider these elements of reflective writing.
Analysis: When you analyze your own writing, you explain your reasoning or writing choices, thus showing that you understand your progress as a writer.
Context: The context is the circumstances or situation in which the happening occurred. A description of the assignment, an explanation of why it was given, and any other relevant conditions surrounding it would be its context.
Description: Providing specific details, using figurative language and imagery, and even quoting from your papers helps readers visualize and thus share your reflection. When describing, writers may include visuals if applicable.
Evaluation: An effective evaluation points out where you faltered and where you did well. With that understanding, you have a basis to return to your thoughts and speculate about progress you will continue to make in the future.
Observation: Observation is a close look at the writing choices you made and the way you managed the rhetorical situations you encountered. When observing, be objective, and pay attention to the more and less effective parts of your writing.
Purpose: By considering the goals of these previous assignments, you will be better equipped to look at them critically and objectively to understand their larger use in academia.
Speculation: Speculation encourages you to think about your next steps: where you need to improve and where you need to stay sharp to avoid recurring mistakes.
Thoughts: Your thoughts (and feelings) before, during, and after an assignment can provide you with descriptive material. In a reflective essay, writers may choose to indicate their thoughts in a different tense from the one in which they write the essay itself.
When you put these elements together, you will be able to reflect objectively on your own writing. This reflection might include identifying areas of significant improvement and areas that still need more work. In either case, focus on describing, analyzing, and evaluating how and why you did or did not improve. This is not an easy task for any writer, but it proves valuable for those who aim to improve their skills as communicators.