Every organization is unique. Every organization’s sales process has unique aspects. Despite that, however, the overall sales process structure across different companies and industries is quite similar. The YPS Methodical Sales Process (MSP) was designed to exploit this overall similarity and to provide a well-organized, intuitive, logical framework. Because of this, it can serve as not only as a “stake-in-the-ground-starting-point” for a Sales Process Engineering (SPE) effort; it can also provide a basis for sales process quality benchmarking.
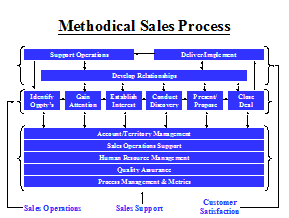
The MSP architecture includes fourteen sales sub-processes that are grouped into three main categories… Sales Operations, the starting point and “guts” of the whole selling process; Customer Satisfaction, concerned with maintaining/enhancing the satisfaction of the current customer base and building credibility with prospects; and Sales Support, the activities performed by field reps, staff and management to make the sales operation as productive as possible.
Each of the fourteen sub-processes is further broken down into four parts; Completion Criteria, Metrics, Best Practices and Tools. Completion Criteria unambiguously define conditions that exist when a sub-process has been completed. For example, you might define completion of the “Identity Opportunities” sub-process as having the decision maker’s name and contact information.
 Metrics provide a means to keep score. They are the quantitative, non-debatable aspect of how well a sub-process is being executed. For example, you may decide that for your business, each sales rep must have a minimum of 50 opportunities that meet the completion criteria for the “Identify Opportunities” sub-process.
Metrics provide a means to keep score. They are the quantitative, non-debatable aspect of how well a sub-process is being executed. For example, you may decide that for your business, each sales rep must have a minimum of 50 opportunities that meet the completion criteria for the “Identify Opportunities” sub-process.
Sales Best Practices are the most effective activities and tasks that must be executed to complete a sub-process. Note that “best” is a relative term. It may be helpful to think in terms of practices, good practices, better practices and ultimately best practices. Start by documenting what you and your team actually do. Over time, you can eliminate the time spent executing “good” practices and focus on only the “best” ones. As you would expect, the list of practices for any sub-process continuously changes as your customers, competitors and market conditions change.
Tools are exactly what they sound like, prospect lists, sample value propositions, product samples, brochures, pricing tools, proposal boilerplate, references… All those things that can be used to help advance a sale.
Send an e-mail to info@ypsgroup.com to get a blank MSP in MS Word format.
What follows is a brief description of each of the fourteen sub-processes in the YPS MSP. Sample completion criteria, metrics and practices are provided. Note that while the sub-processes are applicable to companies in virtually all industries, the completion criteria, metrics and best practices may vary by industry.
Sales Operations
Identify Opportunities
- Completion Criteria
- Opportunity information entered into the CRM data base
- Decision maker’s contact information entered into CRM data base
- Metrics
- Number of opportunities at this stage
- Identified potential revenue
- % of Identify stage prospects moved to “Gain Attention”
- Days to move “Identify” stage prospects moved to “Gain Attention”
- Best Practices
- Segment current customer base by industry, size, growth rate, profitability, etc. to determine likely characteristics of a “good” prospect
- Ask current customers about potential future requirements
- Use internet tools & data bases to identity account names and individual prospects
- Call prospect companies to identify decision makers
- Ask current contacts for references inside and outside his/her company
- Tools
- Hoovers.com
- EDGAR
- Chamber of Commerce listings
Gain Attention
- Completion Criteria
- First face-to-face call with the decision maker is scheduled
- Metrics
- Number of opportunities at this stage
- Potential revenue at this stage by prospect
- % of “Gain Attention” stage prospects moved to “Establish Interest”
- Days to move “Gain Attention” stage prospects moved to “Establish Interest”
- Best Practices
- Carefully script and rehearse, rehearse, rehearse the following:
- One sentence value statement (Why they should meet with you)
- For each target market segment – “Elevator Pitch” (90 second statement of your value and why they should meet with you)
- Telephone version
- Voice Mail version
- Face-To-Face version
- Cold call the prospect
- Send direct mail or e-mail piece with applicable reference and quantified value to decision maker, then call for appointment
- Get a reference (or someone who knows the decision maker) to call the decision maker to recommend a meeting. Follow-up to schedule
- Publish articles in appropriate trade magazines, web sites, etc. Include your contact information
- Speak at local events
- Attend “networking” meetings regularly
- Carefully script and rehearse, rehearse, rehearse the following:
- Tools
- Scripted cold calls
- Value Statement samples
Establish Interest
- Completion Criteria
- Decision maker is committed to DO SOMETHING (e.g., follow-up meeting, reference site visit, set up meeting with subordinates or other executive)
- Action plan with dates is entered into the CRM data base
- Metrics
- Number of opportunities at this stage
- Potential revenue at this stage by prospect
- % of “Establish Interest” stage prospects moved to “Discovery”
- Days to move “Establish Interest” stage prospects moved to “Discovery”
- Best Practices
- Carefully script and rehearse, rehearse, rehearse a standardized version of a “Killer Introductory Sales Call” for each target market segment and level of executive
- Use specific references
- Use verifiable, quantified value statements
- Document a “Call Plan” for every call that customizes the standard call as needed
- Use a set of high-quality sales aids & tools
- Be prepared with appropriate “leave behind” material
- Always make the first call with a partner (e.g., tech support rep, sales manager)
- Document the call results including all “TODOs” and due dates– get it to the decision maker within 24 hours
- Carefully script and rehearse, rehearse, rehearse a standardized version of a “Killer Introductory Sales Call” for each target market segment and level of executive
- Tools
- Key questions to ask
- Sample action plans – Best/2nd Best/Minimal
Conduct Discovery
- Completion Criteria
- Customer requirements document is complete and confirmed by customer
- Internal “Solution Phase Quality Assurance review is completed
- Client Decision Process & Criteria Identified, Documented and Agreed to
- Decision Maker Committed to Attend Proposal Presentation
- CRM data base updated
- Metrics
- Number of opportunities at this stage
- Potential revenue at this stage by prospect
- % of “Discovery” stage prospects moved to “Present/Propose”
- Days to move “Discovery” stage prospects moved to “Present/Propose”
- Best Practices
- Conduct requirements study – verify results with decision maker
- Conduct customer executive briefing(s)
- Conduct product/service education session(s) for decision influencers
- Determine and document the customer’s decision process and criteria, including identity of decision-maker and influencers
- Verify “conditional” or “preliminary” support from decision-maker and influencers
- Tools
- Total Cost of Ownership data collection & calculation spreadsheet
- Proposal content checklist
- Common decision criteria & calculator
Present/Propose
- Completion Criteria
- Formal or informal proposal submitted and/or formal presentation of recommendations to decision maker completed
- CRM data base updated
- Metrics
- Number of opportunities at this stage
- Potential revenue at this stage by prospect
- % of “Present/Propose” stage prospects moved to “Close”
- Days to move “Present/Propose” stage prospects moved to “Close”
- Best Practices
- Always submit a written proposal for ALL opportunities
- Use standardized proposal format and boilerplate – ALWAYS include a customer signoff/commitment page
- Hand deliver the proposal to the decision maker and key decision influencers
- Ensure that the decision maker is available and attends entire proposal presentation – reschedule if necessary
- Tools
- Boilerplate
- Product/service spec sheets
Close
- Completion Criteria
- Customer has paid the first invoice in full
- Metrics
- Number of opportunities at this stage
- Potential revenue at this stage by prospect
- % Closed
- Days to Close
- Best Practices
- Ask for the order at the beginning (and if necessary, the close) of the formal proposal presentation
- Fully document all objections, their background and how they are resolved (or not resolved)
- Send a “decision announcement” to all involved customer personnel with 24 hours of the “go-ahead”
Customer Satisfaction
Deliver/Implement
- Completion Criteria
- Customer has signed off on delivery/implementation
- Metrics – Obtain customer signoff for 100% of implementations
- Best Practices
- Formally review delivery/implementation checklist with customer
- Develop and review “Implementation Issues” document – take appropriate action to prevent future problems
Support Customer Operations
- Completion Criteria
- KAPS review submitted to customer annually (Key Account Performance Summary – see http://www.ypsgroup.com/december2002.htm)
- Customer Satisfaction review/survey completed annually
- Metrics – 100% of customers rated at “Good” or better customer satisfaction
- Best Practices
- Prepare and submit an annual KAPS report (Key Account Performance Summary – see http://www.ypsgroup.com/december2002.htm)
- Conduct a customer satisfaction survey at least annually
- Conduct a Customer Focus survey
- Conduct monthly/quarterly performance reviews with customer
- Jointly with each customer, develop key performance metrics and continuously monitor them
Develop Relationships
- Completion Criteria
- Quality of all key contacts at all key customers are rated as “A” (see http://www.ypsgroup.com/december2001.htm)
- Metrics
- 33% of contacts rated as “A”
- 25% of all “C” contacts upgraded to “B” annually
- 25% of all “B” contacts upgraded to “A” annually
- Best Practices
- Formally rate your relationships with contacts at least annually
- Implement and execute a process to ensure 100% follow-up on your commitments to customers
- Provide a continuous stream of relevant, useful information to contacts
- Use a variety of “touch base” techniques (e-mail, voice mail, drop by, etc.) – use them all, but predominantly the one each contact prefers
- Conduct monthly “no surprises” reviews with key contacts
- Regularly attend social, sporting and other events with key customers
- Take a customer to breakfast/lunch/dinner
- Operate a Customer Advisory Council
Sales Support
NOTE: Sales Support consists of a series of back-office/staff functions. There is great variability by industry in the types and priorities of required activities. For the most part therefore, only sample Best Practices are listed. As these are developed for your own company, specific completion criteria, metrics and tools should be defined for each Sales Support Best Practice.
Account & Territory Management
- Best Practices
- Maintain a rolling 12 month forecast of business by segment, customer/prospect and opportunity – update it monthly
- Conduct formal, annual Account Planning sessions with monthly or quarterly informal updates (Each Rep must have a documented Account/Territory plan that has been formally updated within 90 days)
- Develop and implement a coverage strategy to ensure consistent contact with key decision makers and influencers
- Keep the CRM data base updated constantly – use it consistently
- Consistently use a Sales Force Automation (SFA) system to ensure follow-up on all commitments
- Be aware of and use all available support resources – Keep track of what you use, where and how well it worked
- Track “Customer Share” for all key accounts (Customer Share is like market share, but focused on a single customer)
- Maintain a formal customer retention strategy and tactical plan
- Formally review performance against all key metrics monthly
- Use various sales channels for some/all of the sales process
Field Operations Support
- Best Practices
- Segment the market
- Classify all accounts and prospects according to appropriate criteria (e.g., industry, revenue, potential revenue, growth, profitability, etc.)
- Collect & analyze both internal sales data & public data bases
- Identify business issues and requirements for each segment
- Maintain a “Product/Service to Customer Matrix” (to identify cross-selling opportunities)
- Conduct Product Marketing
- Provide for easy access to product/service sales support personnel that are both technically and application knowledgeable
- Maintain a library of references
- Maintain a library of product/services application descriptions
- Collect, maintain and prioritize product requirements based on customer & sales rep feedback
- Provide proposal boilerplate and preparation support
- Maintain library of company and product/service information (electronic and paper)
- Company value statement(s)
- Company differentiators
- Brochures – Somewhat detailed product/service descriptions – Highly detailed technical specifications
- Develop a clear pricing strategy along with an exception-handling process
- Conduct competitive research and analysis
- Provide Information Technology Support
- Operate a CRM/SFA system (Customer Relationship Management/Sales Force Automation)
- Maintain a high quality web site
- Provide cell phones, laptops and other tools
- Conduct regular/periodic promotional campaigns
- Segment the market
Human Resources
- Best Practices
- Formalize the recruiting/screening/hiring process
- Develop, maintain and use a “new sales rep” training curriculum
- Conduct product, service and professional sales training regularly
- Conduct job and employee profiling – ensure a match between job requirements and individuals
- Develop a sales compensation plan that matches closely with company requirements – administer it fairly and consistently
- Implement written performance plans for each sales rep – Conduct informal quarterly and formal annual performance reviews
Quality Assurance
- Best Practices
- Conduct “War Room Meetings” for all significant opportunities at appropriate checkpoints including pre-proposal – All affected sales and support personnel and management should attend
- Conduct regular Win & Loss Reviews to identify what does and does not work
- Conduct a “CPA” (Customer Perception Audit) for all key accounts annually (see http://www.ypsgroup.com/cpa.htm)
Process Management & Metrics
- Best Practices
- Appoint a “SPE Czar” – i.e., an individual with responsibility for documentation of, training/education on and continuous improvement of your sales process
- Involve top sales performers in the continuous improvement & development of the sales process
- Develop and maintain quantitative measurements for all significant sales activities
- Funnel
- Account Importance (how well it fits the definition of the “perfect’ customer/prospect)
- Relationship Quality
- Integrate automated tracking and analysis of these metrics in the CRM system
