158
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Analyze the growth policies of low-income countries seeking to improve standards of living
- Analyze the growth policies of middle-income countries, particularly the East Asian Tigers with their focus on technology and market-oriented incentives
- Analyze the struggles facing economically-challenged countries wishing to enact growth policies
- Evaluate the success of sending aid to low-income countries
Jobs are created in economies that grow. Where does economic growth come from? According to most economists who believe in the growth consensus, economic growth (as discussed in Economic Growth) is built on a foundation of productivity improvements. In turn, productivity increases are the result of greater human and physical capital and technology, all interacting in a market-driven economy. In the pursuit of economic growth, however, some countries and regions start from different levels, as illustrated by the differences in per capita GDP presented earlier in Table 2.
Growth Policies for the High-Income Countries
For the high-income countries, the challenge of economic growth is to push continually for a more educated workforce that can create, invest in, and apply new technologies. In effect, the goal of their growth-oriented public policy is to shift their aggregate supply curves to the right (refer to The Aggregate Demand/Aggregate Supply Model). The main public policies targeted at achieving this goal are fiscal policies focused on investment, including investment in human capital, in technology, and in physical plant and equipment. These countries also recognize that economic growth works best in a stable and market-oriented economic climate. For this reason, they use monetary policy to keep inflation low and stable, and to minimize the risk of exchange rate fluctuations, while also encouraging domestic and international competition.
However, early in the second decade of the 2000s, many high-income countries found themselves more focused on the short term than on the long term. The United States, Western Europe, and Japan all experienced a combination of financial crisis and deep recession, and the after-effects of the recession—like high unemployment rates—seemed likely to linger for several years. Most of these governments took aggressive, and in some cases controversial, steps to jump-start their economies by running very large budget deficits as part of expansionary fiscal policy. These countries must adopt a course that combines lower government spending and higher taxes.
Similarly, many central banks ran highly expansionary monetary policies, with both near-zero interest rates and unconventional loans and investments. For example, in 2012, Shinzo Abe (see Figure 1), then newly-elected Prime Minister of Japan, unveiled a plan to get his country out of its two-decade-long slump in economic growth. It included both fiscal stimulus and an increase in the money supply. The plan was quite successful in the short run. However, according to the Economist, with public debt “expected to approach 240% of GDP,” (as of 2012 it was 226% of GDP) printing money and public-works spending were only short-term solutions.

As other chapters discuss, macroeconomics needs to have both a short-run and a long-run focus. The challenge for many of the developed countries in the next few years will be to exit from the short-term policies that were used to correct the 2008–2009 recession. Since the return to growth has been sluggish, it has been politically challenging for these governments to refocus their efforts on new technology, education, and physical capital investment.
Growth Policies for the Middle-Income Economies
The world’s great economic success stories in the last few decades began in the 1970s with that group of nations sometimes known as the East Asian Tigers: South Korea, Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia, and Singapore. The list sometimes includes Hong Kong and Taiwan, although these are often treated under international law as part of China, rather than as separate countries. The economic growth of the Tigers has been phenomenal, typically averaging 5.5% real per capita growth for several decades. In the 1980s, other countries began to show signs of convergence. China began growing rapidly, often at annual rates of 8% to 10% per year. India began growing rapidly, first at rates of about 5% per year in the 1990s, but then higher still in the first decade of the 2000s.
The underlying causes of these rapid growth rates are known:
- China and the East Asian Tigers, in particular, have been among the highest savers in the world, often saving one-third or more of GDP as compared to the roughly one-fifth of GDP, which would be a more typical saving rate in Latin America and Africa. These higher savings were harnessed for domestic investment to build physical capital.
- These countries had policies that supported heavy investments in human capital, first building up primary-level education and then expanding secondary-level education. Many focused on encouraging math and science education, which is useful in engineering and business.
- Governments made a concerted effort to seek out applicable technology, by sending students and government commissions abroad to look at the most efficient industrial operations elsewhere. They also created policies to support innovative companies that wished to build production facilities to take advantage of the abundant and inexpensive human capital.
- China and India in particular also allowed far greater freedom for market forces, both within their own domestic economies and also in encouraging their firms to participate in world markets.
This combination of technology, human capital, and physical capital, combined with the incentives of a market-oriented economic context, proved an extremely powerful stimulant to growth. Challenges faced by these middle-income countries are a legacy of government economic controls that for political reasons can be dismantled only slowly over time. In many of them, the banking and financial sector is heavily regulated. Governments have also sometimes selected certain industries to receive low-interest loans or government subsidies. These economies have found that an increased dose of market-oriented incentives for firms and workers has been a critical ingredient in the recipe for faster growth. To learn more about measuring economic growth, read the following Clear It Up feature.
What is the rule of 72?
It is worth pausing a moment to marvel at the growth rates of the East Asian Tigers. If per capita GDP grows at, say, 6% per year, then you can apply the formula for compound growth rates—that is (1 + 0.06)30—meaning a nation’s level of per capita GDP will rise by a multiple of almost six over 30 years. Another strategy is to apply the rule of 72. The rule of 72 is an approximation to figure out doubling time. The rule number, 72, is divided by the annual growth rate to obtain the approximate number of years it will take for income to double. So if we have a 6% growth rate, it will take 72/6, or 12 years, for incomes to double. Using this rule here suggests that a Tiger that grows at 6% will double its GDP every 12 years. In contrast, a technological leader, chugging along with per capita growth rates of about 2% per year, would double its income in 36 years.
Growth Policies for Economically-Challenged Countries
Many economically-challenged or low-income countries are geographically located in Sub-Saharan Africa. Other pockets of low income are found in the former Soviet Bloc, and in parts of Central America and the Caribbean.
There are macroeconomic policies and prescriptions that might alleviate the extreme poverty and low standard of living. However, many of these countries lack the economic and legal stability, along with market-oriented institutions, needed to provide a fertile climate for domestic economic growth and to attract foreign investment. Thus, macroeconomic policies for low income economies are vastly different from those of the high income economies. The World Bank has made it a priority to combat poverty and raise overall income levels through 2030. One of the key obstacles to achieving this is the political instability that seems to be a common feature of low-income countries.
Figure 2 shows the ten lowest income countries as ranked by The World Bank in 2013. These countries share some common traits, the most significant of which is the recent failures of their governments to provide a legal framework for economic growth. Ethiopia and Eritrea recently ended a long-standing war in 2000. Civil and ethnic wars have plagued countries such as Burundi and Liberia. Command economies, corruption, as well as political factionalism and infighting are commonly adopted elements in these low-income countries. The Democratic Republic of the Congo (often referred to as “Congo”) is a resource-wealthy country that has not been able to increase its subsistence standard of living due to the political environment.
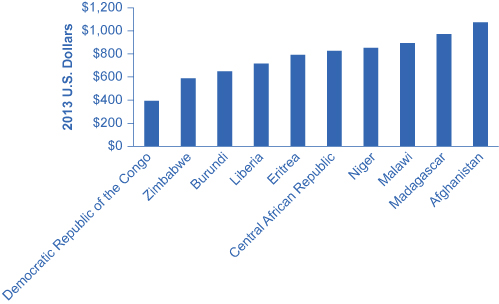
Low-income countries are at a disadvantage because any incomes received are spent immediately on necessities such as food. People in these countries live on less than $1,035 per year, which is less than $100 per month. Lack of saving means a lack of capital accumulation and a lack of loanable funds for investment in physical and human capital. Recent research by two MIT economists, Abhijit Bannerjee and Esther Duflo, has confirmed that the households in these economies are trapped in low incomes because they cannot muster enough investment to push themselves out of poverty.
For example, the average citizen of Burundi, the lowest-income country, subsists on $150 per year (adjusted to 2005 dollars). According to data collected by the Central Intelligence Agency in its CIA Factbook, as of 2013, 90% of Burundi’s population is agrarian, with coffee and tea as the main income producing crop. Only one in two children attends school and, as shown in Figure 3, many are not in schools comparable to what is found in developed countries. The CIA Factbook also estimates that 15% of Burundi’s population suffers from HIV/AIDS. Political instability has made it difficult for Burundi to make significant headway toward growth, as verified by the electrification of only 2% of households and 42% of its national income coming from foreign aid.

The World Factbook website is loaded with maps, flags, and other information about countries across the globe.

Other low-income countries share similar stories. These countries have found it difficult to generate investments for themselves or to find foreign investors willing to put up the money for more than the basic needs. Foreign aid and external investment comprise significant portions of the income in these economies, but are not sufficient to allow for the capital accumulation necessary to invest in physical and human capital. But is foreign aid always a contributor to economic growth? It can be a controversial issue, as the next Clear it Up feature points out.
Does foreign aid to low-income countries work?
According to the Organization of Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), about $134 billion per year in foreign aid flows from the high-income countries of the world to the low-income ones. Relative to the size of their populations or economies, this is not a large amount for either donors or recipients. For low-income countries, aid averages about 1.3 percent of their GDP. But even this relatively small amount has been highly controversial.
Supporters of additional foreign aid point to the extraordinary human suffering in the low-and middle-income countries of the world. They see opportunities all across Africa, Asia, and Latin America to set up health clinics and schools. They want to help with the task of building economic infrastructure: clean water, plumbing, electricity, and roads. Supporters of this aid include formal state-sponsored institutions like the United Kingdom’s Department for International Development (DFID) or independent non-governmental organizations (NGOs) like CARE International that also receive donor government funds. For example, because of an outbreak of meningitis in Ethiopia in 2010, DFID channeled significant funds to the Ethiopian Ministry of Health to train rural health care workers and also for vaccines. These monies helped the Ministry offset shortfalls in their budget.
Opponents of increased aid do not quarrel with the goal of reducing human suffering, but they suggest that foreign aid has often proved a poor tool for advancing that goal. For example, according to an article in the Attaché Journal of International Affairs, the Canadian foreign aid organization (CIDA) provided $100 million to Tanzania to grow wheat. The project did produce wheat, but nomadic pastoralists and other villagers who had lived on the land were driven off 100,000 acres of land to make way for the project. The damage in terms of human rights and lost livelihoods was significant. Villagers were beaten and killed because some refused to leave the land. At times, the unintended collateral damage from foreign aid can be significant.
William Easterly, professor of economics at New York University and author of The White Man’s Burden, argues that aid is often given for political reasons and ends up doing more harm than good. If the government of a country creates a reasonably stable and market-oriented macroeconomic climate, then foreign investors will be likely to provide funds for many profitable activities. For example, according to The New York Times, Facebook is partnering with multiple organizations in a project called Internet.org to provide access in remote and low-income areas of the world, and Google began its own initiative called Project Loon. Facebook’s first forays into providing Internet access via mobile phones began in stable, market-oriented countries like India, Brazil, Indonesia, Turkey, and the Philippines.
Policymakers are now wiser about the limitations of foreign aid than they were a few decades ago. In targeted and specific cases, especially if foreign aid is channeled to long-term investment projects, foreign aid can have a modest role to play in reducing the extreme levels of deprivation experienced by hundreds of millions of people around the world.
Watch this video on the complexities of providing economic aid in Africa.

Key Concepts and Summary
The fundamentals of growth are the same in every country: improvements in human capital, physical capital, and technology interacting in a market-oriented economy. Countries that are high-income tend to focus on developing and using new technology. Countries that are middle-income focus on increasing human capital and becoming more connected to technology and global markets. They have charted unconventional paths by relying more on state-led support rather than relying solely on markets. Low-income, economically-challenged countries have many health and human development needs, but they are also challenged by the lack of investment and foreign aid to develop infrastructure like roads. There are some bright spots when it comes to financial development and mobile communications, which suggest that low-income countries can become technology leaders in their own right, but it is too early to claim victory. These countries must do more to connect to the rest of the global economy and find the technologies that work best for them.
Self-Check Questions
- Create a table that identifies the macroeconomic policies for a high-income country, a middle-income country, and a low-income country.
- Use the data in the text to contrast the policy prescriptions of the high-income, middle-income, and low-income countries.
Review Questions
- What other factors, aside from labor productivity, capital investment, and technology, impact the economic growth of a country? How?
- What strategies were employed by the East Asian Tigers to stimulate economic growth?
Critical Thinking Questions
- Explain why is it difficult to set aside funds for investment when you are in poverty.
- Why do you think it is difficult for high-income countries to achieve high growth rates?
Problems
- Use the Rule of 72 to estimate how long it will take for India, Spain, and South Africa to double their standards of living.
- Using the research skills you have acquired, retrieve the following data from The World Bank database (http://databank.worldbank.org/data/home.aspx) for India, Spain, and South Africa for 2008–2013, if available:
- Telephone lines
- Mobile cellular subscriptions
- Secure Internet servers (per one million people)
- Electricity production (kWh)
Prepare a chart that compares these three countries. Describe the key differences between the countries.
References
“Shinzo Abe’s Government Looks Likely to Disappoint on Fiscal Consolidation.” The Economist, May 4, 2013. http://www.economist.com/news/finance-and-economics/21577080-shinzo-abes-government-looks-likely-disappoint-fiscal-consolidation-dont.
Banerjee, Abhijit V., and Esther Duflo. Poor Economics. “About the Book: Overview.” http://pooreconomics.com/about-book.
CARE International. “About Us.” Accessed January 14, 2014. http://www.care-international.org/about-us.aspx.
Central Intelligence Agency. “The World Factbook: Africa, Burundi.” Last modified November 12, 2013. https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/by.html.
Central Intelligence Agency. “The World Factbook: Africa, Democratic Republic of the Congo.” Last modified November 12, 2013. https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/cg.html.
Easterly, William. The White Man’s Burden: Why the West’s Efforts to Aid the Rest Have Done So Much Ill and So Little Good. Penguin Group (USA), 2006.
Goel, Vindu. “Facebook Leads an Effort to Lower Barriers to Internet Access,” The New York Times. Last modified August 20, 2013.
Google. “Project Loon.” http://www.google.com/loon/.
GOV.UK. “Department for International Development.” https://www.gov.uk/government/organisations/department-for-international-development.
The World Bank. “Millennium Development Goals.” http://www.worldbank.org/mdgs/.
Todaro, Michael P., and Stephen C Smith. Economic Development (11th Edition). Boston, MA: Addison-Wesley: Pearson, 2011, chap. 3.
Vercillo, Siera. “The Failures of Canadian Foreign Aid: Tied, Mismanaged and Uncoordinated.” The Attaché Journal of International Affairs. (2010). http://theattachejia.files.wordpress.com/2013/10/the-attache-2010-issue.pdf.
Glossary
- East Asian Tigers
- the economies of Taiwan, Singapore, Hong Kong, and South Korea, which maintained high growth rates and rapid export-led industrialization between the early 1960s and 1990 allowing them to converge with the technological leaders in high-income countries
- growth consensus
- a series of studies that show, statistically, that 70% of the differences in income per person across the world is explained by differences in physical capital (savings/investment)
- high-income country
- nation with a per capita income of $12,475 or more; typically has high levels of human and physical capital
- low-income country
- a nation that has a per capita income of less than $1,025; a third of the world’s population
- middle-income country
- a nation with per capita income between $1,025 and $12, 475 and that has shown some ability, even if not always sustained, to catch up to the technology leaders in high-income countries
Solutions
Answers to Self-Check Questions
- The following table provides a summary of possible answers.
High-Income Countries Middle-Income Countries Low-Income Countries - Foster a more educated workforce
- Create, invest in, and apply new technologies
- Adopt fiscal policies focused on investment, including investment in human capital, in technology, and in physical plant and equipment
- Create stable and market-oriented economic climate
- Use monetary policy to keep inflation low and stable
- Minimize the risk of exchange rate fluctuations, while also encouraging domestic and international competition
- Invest in technology, human capital, and physical capital
- Provide incentives of a market-oriented economic context
- Work to reduce government economic controls on market activities
- Deregulate the banking and financial sector
- Reduce protectionist policies
- Eradicate poverty and extreme hunger
- Achieve universal primary education
- Promote gender equality
- Reduce child mortality rates
- Improve maternal health
- Combat HIV/AIDS, malaria, and other diseases
- Ensure environmental sustainability
- Develop global partnerships for development
Table 6. - Low-income countries must adopt government policies that are market-oriented and that educate the workforce and population. After this is done, low-income countries should focus on eradicating other social ills that inhibit their growth. The economically challenged are stuck in poverty traps. They need to focus more on health and education and create a stable macroeconomic and political environment. This will attract foreign aid and foreign investment. Middle-income countries strive for increases in physical capital and innovation, while higher-income countries must work to maintain their economies through innovation and technology.