What Is Lifespan Development?
This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the
Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0y
Welcome to the story of your life. In this chapter we explore the fascinating tale of how you have grown and developed into the person you are today. We also look at some ideas about who you will grow into tomorrow. Yours is a story of lifespan development, from the start of life to the end.
The process of human growth and development is more obvious in infancy and childhood, yet your development is happening this moment and will continue, minute by minute, for the rest of your life. Who you are today and who you will be in the future depends on a blend of genetics, environment, culture, relationships, and more, as you continue through each phase of life. You have experienced firsthand much of what is discussed in this chapter. Now consider what psychological science has to say about your physical, cognitive, and psychosocial development, from the womb to the tomb.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Define and distinguish between the three domains of development: physical, cognitive, and psychosocial
- Discuss the normative approach to development
- Understand the three major issues in development: continuity and discontinuity, one common course of development or many unique courses of development, and nature versus nurture
My heart leaps up when I behold
A rainbow in the sky:
So was it when my life began;
So is it now I am a man;
So be it when I shall grow old,
Or let me die!
The Child is father of the Man;
I could wish my days to be
Bound each to each by natural piety. (Wordsworth, 1802)
In this poem, William Wordsworth writes, the child is father of the man. What does this seemingly incongruous statement mean, and what does it have to do with lifespan development? Wordsworth might be suggesting that the person he is as an adult depends largely on the experiences he had in childhood.
Consider the following questions: To what extent is the adult you are today influenced by the child you once were? To what extent is a child fundamentally different from the adult he grows up to be?
These are the types of questions developmental psychologists try to answer, by studying how humans change and grow from conception through childhood, adolescence, adulthood, and death. They view development as a lifelong process that can be studied scientifically across three developmental domains physical, cognitive, and psychosocial development. Physical development involves growth and changes in the body and brain, the senses, motor skills, and health and wellness. Cognitive development involves learning, attention, memory, language, thinking, reasoning, and creativity. Psychosocial development involves emotions, personality, and social relationships. We refer to these domains throughout the chapter.
CONNECT THE CONCEPTS: RESEARCH METHODS IN DEVELOPMENTAL PSYCHOLOGYDevelopmental psychologists use many approaches in order to better understand how individuals change mentally and physically over time. These methods include naturalistic observations, case studies, surveys, and experiments, among others. Naturalistic observations involve observing behavior in its natural context. A developmental psychologist might observe how children behave on a playground, at a daycare center, or in the child’s own home. While this research approach provides a glimpse into how children behave in their natural settings, researchers have very little control over the types and/or frequencies of displayed behavior. In a case study, developmental psychologists collect a great deal of information from one individual in order to better understand physical and psychological changes over the lifespan. This particular approach is an excellent way to better understand individuals, who are exceptional in some way, but it is especially prone to researcher bias in interpretation, and it is difficult to generalize conclusions to the larger population. In one classic example of this research method being applied to a study of lifespan development Sigmund Freud analyzed the development of a child known as “Little Hans” (Freud, 1909/1949). Freud’s findings helped inform his theories of psychosexual development in children, which you will learn about later in this chapter. Little Genie, the subject of a case study discussed in the chapter on thinking and intelligence, provides another example of how psychologists examine developmental milestones through detailed research on a single individual. In Genie’s case, her neglectful and abusive upbringing led to her being unable to speak until, at age 13, she was removed from that harmful environment. As she learned to use language, psychologists were able to compare how her language acquisition abilities differed when occurring in her late-stage development compared to the typical acquisition of those skills during the ages of infancy through early childhood (Fromkin, Krashen, Curtiss, Rigler, & Rigler, 1974; Curtiss, 1981). The survey method asks individuals to self-report important information about their thoughts, experiences, and beliefs. This particular method can provide large amounts of information in relatively short amounts of time; however, validity of data collected in this way relies on honest self-reporting, and the data is relatively shallow when compared to the depth of information collected in a case study. Experiments involve significant control over extraneous variables and manipulation of the independent variable. As such, experimental research allows developmental psychologists to make causal statements about certain variables that are important for the developmental process. Because experimental research must occur in a controlled environment, researchers must be cautious about whether behaviors observed in the laboratory translate to an individual’s natural environment. Later in this book, you will learn about several experiments in which toddlers and young children observe scenes or actions so that researchers can determine at what age specific cognitive abilities develop. For example, children may observe a quantity of liquid poured from a short, fat glass into a tall, skinny glass. As the experimenters question the children about what occurred, the subjects’ answers help psychologists understand at what age a child begins to comprehend that the volume of liquid remained the same although the shapes of the containers differs. |
Across these three domains physical, cognitive, and psychosocial the normative approach to development is also discussed. This approach asks, What is normal development? In the early decades of the 20th century, normative psychologists studied large numbers of children at various ages to determine norms (i.e., average ages) of when most children reach specific developmental milestones in each of the three domains (Gesell, 1933, 1939, 1940; Gesell & Ilg, 1946; Hall, 1904). Although children develop at slightly different rates, we can use these age-related averages as general guidelines to compare children with same-age peers to determine the approximate ages they should reach specific normative events called developmental milestones (e.g., crawling, walking, writing, dressing, naming colors, speaking in sentences, and starting puberty).
Not all normative events are universal, meaning they are not experienced by all individuals across all cultures. Biological milestones, such as puberty, tend to be universal, but social milestones, such as the age when children begin formal schooling, are not necessarily universal; instead, they affect most individuals in a particular culture (Gesell & Ilg, 1946). For example, in developed countries children begin school around 5 or 6 years old, but in developing countries, like Nigeria, children often enter school at an advanced age, if at all (Huebler, 2005; United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization [UNESCO], 2013).
To better understand the normative approach, imagine two new mothers, Louisa and Kimberly, who are close friends and have children around the same age. Louisa’s daughter is 14 months old, and Kimberly’s son is 12 months old. According to the normative approach, the average age a child starts to walk is 12 months. However, at 14 months Louisa’s daughter still isn’t walking. She tells Kimberly she is worried that something might be wrong with her baby. Kimberly is surprised because her son started walking when he was only 10 months old. Should Louisa be worried? Should she be concerned if her daughter is not walking by 15 months or 18 months?
Link to Learning: The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) describes the developmental milestones for children from 2 months through 5 years old. After reviewing the information, take this quiz to see how well you recall what you’ve learned. If you are a parent with concerns about your child’s development, contact your pediatrician.
ISSUES IN DEVELOPMENTAL PSYCHOLOGY
There are many different theoretical approaches regarding human development. As we evaluate them in the following chapter, recall that developmental psychology focuses on how people change, and keep in mind that all the approaches that we present in this chapter address questions of change: Is the change smooth or uneven (continuous versus discontinuous)? Is this pattern of change the same for everyone, or are there many different patterns of change (one course of development versus many courses)? How do genetics and environment interact to influence development (nature versus nurture)?
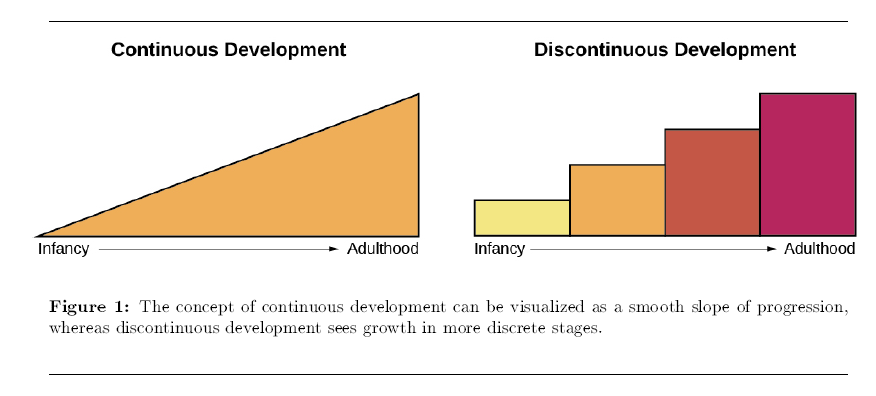
Is Development Continuous or Discontinuous?
Continuous development views development as a cumulative process, gradually improving on existing skills (Figure 1). With this type of development, there is gradual change. Consider, for example, a child’s physical growth: adding inches to her height year by year. In contrast, theorists who view development as discontinuous believe that development takes place in unique stages: It occurs at specific times or ages. With this type of development, the change is more sudden, such as an infant’s ability to conceive object permanence.
Is there One Course of Development or Many?
Is development essentially the same, or universal, for all children (i.e., there is one course of development) or does development follow a different course for each child, depending on the child’s specific genetics and environment (i.e., there are many courses of development)? Do people across the world share more similarities or more differences in their development? How much do culture and genetics influence a child’s behavior?
Stage theories hold that the sequence of development is universal. For example, in cross-cultural studies of language development, children from around the world reach language milestones in a similar sequence (Gleitman & Newport, 1995). Infants in all cultures coo before they babble. They begin babbling at about the same age and utter their first word around 12 months old. Yet we live in diverse contexts that have a unique effect on each of us. For example, researchers once believed that motor development follows one course for all children regardless of culture. However, child care practices vary by culture, and different practices have been found to accelerate or inhibit achievement of developmental milestones such as sitting, crawling, and walking (Karasik, Adolph, Tamis-LeMonda, & Bornstein, 2010).
For instance, let’s look at the Aché society in Paraguay. They spend a significant amount of time foraging in forests. While foraging, Aché mothers carry their young children, rarely putting them down in order to protect them from getting hurt in the forest. Consequently, their children walk much later: They walk around 23–25 months old, in comparison to infants in Western cultures who begin to walk around 12 months old. However, as Aché children become older, they are allowed more freedom to move about, and by about age 9, their motor skills surpass those of U.S. children of the same age: Aché children are able to climb trees up to 25 feet tall and use machetes to chop their way through the forest (Kaplan & Dove, 1987). As you can see, our development is influenced by multiple contexts, so the timing of basic motor functions may vary across cultures. However, the functions themselves are present in all societies.
Figure 2. All children across the world love to play. Whether in (a) Florida or (b) South Africa, children enjoy exploring sand, sunshine, and the sea. (credit a: modification of work by “Visit St. Pete/Clearwater”/Flickr; credit b: modification of work by “stringer_bel”/Flickr)
How Do Nature and Nurture Influence Development?
Are we who we are because of nature (biology and genetics), or are we who we are because of nurture (our environment and culture)? This longstanding question is known in psychology as the nature versus nurture debate. It seeks to understand how our personalities and traits are the product of our genetic makeup and biological factors, and how they are shaped by our environment, including our parents, peers, and culture. For instance, why do biological children sometimes act like their parents—is it because of genetics or because of early childhood environment and what the child has learned from the parents? What about children who are adopted—are they more like their biological families or more like their adoptive families? And how can siblings from the same family be so different?
We are all born with specific genetic traits inherited from our parents, such as eye color, height, and certain personality traits. Beyond our basic genotype, however, there is a deep interaction between our genes and our environment: Our unique experiences in our environment influence whether and how particular traits are expressed, and at the same time, our genes influence how we interact with our environment (Diamond, 2009; Lobo, 2008). This book will show that there is a reciprocal interaction between nature and nurture as they both shape who we become, but the debate continues as to the relative contributions of each.
|
DIG DEEPER: THE ACHIEVEMENT GAP: HOW DOES SOCIOECONOMIC STATUS AFFECT DEVELOPMENT?
The achievement gap refers to the persistent difference in grades, test scores, and graduation rates that exist among students of different ethnicities, races, and—in certain subjects—sexes (Winerman, 2011). Research suggests that these achievement gaps are strongly influenced by differences in socioeconomic factors that exist among the families of these children. While the researchers acknowledge that programs aimed at reducing such socioeconomic discrepancies would likely aid in equalizing the aptitude and performance of children from different backgrounds, they recognize that such large-scale interventions would be difficult to achieve. Therefore, it is recommended that programs aimed at fostering aptitude and achievement among disadvantaged children may be the best option for dealing with issues related to academic achievement gaps (Duncan & Magnuson, 2005). Low-income children perform significantly more poorly than their middle- and high-income peers on a number of educational variables: They have significantly lower standardized test scores, graduation rates, and college entrance rates, and they have much higher school dropout rates. There have been attempts to correct the achievement gap through state and federal legislation, but what if the problems start before the children even enter school? Psychologists Betty Hart and Todd Risley (2006) spent their careers looking at early language ability and progression of children in various income levels. In one longitudinal study, they found that although all the parents in the study engaged and interacted with their children, middle- and high-income parents interacted with their children differently than low-income parents. After analyzing 1,300 hours of parent-child interactions, the researchers found that middle- and high-income parents talk to their children significantly more, starting when the children are infants. By 3 years old, high-income children knew almost double the number of words known by their low-income counterparts, and they had heard an estimated total of 30 million more words than the low-income counterparts (Hart & Risley, 2003). And the gaps only become more pronounced. Before entering kindergarten, high-income children score 60% higher on achievement tests than their low-income peers (Lee & Burkam, 2002). There are solutions to this problem. At the University of Chicago, experts are working with low-income families, visiting them at their homes, and encouraging them to speak more to their children on a daily and hourly basis. Other experts are designing preschools in which students from diverse economic backgrounds are placed in the same classroom. In this research, low-income children made significant gains in their language development, likely as a result of attending the specialized preschool (Schechter & Byeb, 2007). What other methods or interventions could be used to decrease the achievement gap? What types of activities could be implemented to help the children of your community or a neighboring community? |
Summary
Lifespan development explores how we change and grow from conception to death. This field of psychology is studied by developmental psychologists. They view development as a lifelong process that can be studied scientifically across three developmental domains: physical, cognitive development, and psychosocial. There are several theories of development that focus on the following issues: whether development is continuous or discontinuous, whether development follows one course or many, and the relative influence of nature versus nurture on development.
References
Ainsworth, M. D. S., & Bell, S. M. (1970). Attachment, exploration, and separation: Illustrated by the behavior of one-year-olds in a strange situation. Child Development, 41, 49–67.
Ainsworth, M. D. S., Blehar, M. C., Waters, E., & Wall, S. (1978). Patterns of attachment: A psychological study of the strange situation. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
American Academy of Pediatrics. (2007). The importance of play in promoting healthy child development and maintaining strong parent-child bonds. Pediatrics, 199(1), 182–191.
Amsterdam, B. (1972). Mirror image reactions before age two. Developmental Psychobiology, 5, 297–305.
Archer, J. (1992). Ethology and human development. New York, NY: Harvester Wheatsheaf.
Arnett, J. (2000). Emerging adulthood: A theory of development from the late teens through the twenties. American Psychologist, 55(5), 469–480.
Ashley, S. J., Magnuson, S. I., Omnell, L. M., & Clarren, S. K. (1999). Fetal alcohol syndrome: Changes in craniofacial form with age, cognition, and timing of ethanol exposure in the macaque. Teratology, 59(3), 163–172.
Bahr, S. J., & Hoffman, J. P. (2010). Parenting style, religiosity, peers, and adolescent heavy drinking. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, 71, 539–543.
Baillargeon, R. (2004). Infants’ reasoning about hidden objects: Evidence for event-general and event-specific expectations.Developmental Science, 7(4), 391–424.
Baillargeon, R. (1987). Young infants’ reasoning about the physical and spatial properties of a hidden object. Cognitive Development, 2(3), 179–200.
Baillargeon, R., Li, J., Gertner, Y., & Wu, D. (2011). How do infants reason about physical events. The Wiley-Blackwell handbook of childhood cognitive development, 2, 11–48.
Barber, B. K. (1994). Cultural, family, and person contexts of parent-adolescent conflict. Journal of Marriage and the Family, 56, 375–386.
Basseches, M. (1984). Dialectical thinking as metasystematic form of cognitive organization. In M. L. Commons, F. A. Richards, & C. Armon (Eds.), Beyond formal operations: Late adolescent and adult cognitive development (pp. 216–238). New York, NY: Praeger.
Baumrind, D. (1971). Current patterns of parental authority. Developmental Psychology, 4(1, Pt. 2), 1–103. doi:10.1037/h0030372
Baumrind, D. (1991). The influence of parenting style on adolescent competence and substance use. Journal of Early Adolescence, 11(1), 56–95.
Bayley, N., & Oden, M. H. (1955). The maintenance of intellectual ability in gifted adults. Journal of Gerontology, 10, 91–107.
Bjorklund, D. F. (1987). A note on neonatal imitation. Developmental Review, 7, 86–92.
Blossom, M., & Morgan, J.L. (2006). Does the face say what the mouth says? A study of infants’ sensitivity to visual prosody. In 30th anuual Boston University conference on language development, Somerville, MA.
Bogartz, R. S., Shinskey, J. L., & Schilling, T. (2000). Infancy, 1(4), 403–428.
Bowlby, J. (1969). Attachment and loss: Attachment (Vol. 1). New York, NY: Basic Books.
Bowlby, J. (1988). A secure base: Parent-child attachment and health human development. New York, NY: Basic Books.
Brumley, R., Enquidanos, S., Jamison, P., Seitz, R., Morgenstern, N., Saito, S., . . . Gonzalez, J. (2007). Increased satisfaction with care and lower costs: Results of a randomized trial of in-home palliative care. Journal of the American Geriatric Society, 55(7), 993–1000.
Brumley, R. D., Enquidanos, S., & Cherin, D. A. (2003). Effectiveness of a home-based palliative care program for end-of-life.Journal of Palliative Medicine, 6(5), 715–724.
Callaghan, T. C., Rochat, P., Lillard, A., Claux, M.L., Odden, H., Itakura, S., . . . Singh, S. (2005). Synchrony in the onset of mental-state reasoning. Psychological Science, 16, 378–384.
Carel, J-C., Lahlou, N., Roger, M., & Chaussain, J. L. (2004). Precocious puberty and statural growth. Human Reproduction Update, 10(2), 135–147.
Carstensen, L. L. (1992). Social and emotional patterns in adulthood: Support for socioemotional selectivity. Psychology and Aging, 7(3), 331–338.
Case, R. (1985). Intellectual development: Birth to Adulthood. New York, NY: Academic.
Casey, B. J., Tottenham, N., Liston, C., & Durston, S. (2005). Imaging the developing brain: What have we learned about cognitive development? TRENDS in Cognitive Sciences, 19(3), 104–110.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2013). Smoking during pregnancy. Retrieved from http://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/basic_information/health_effects/pregnancy/
Chick, K., Heilman-Houser, R., & Hunter, M. (2002). The impact of child care on gender role development and gender stereotypes.Early Childhood Education Journal, 29(3), 149–154.
Chomsky, N. (1957). Syntactic structures. The Hague, Netherlands: Mouton.
Clements, R. (2004). An investigation of the status of outdoor play. Contemporary Issues in Early Childhood, 5(1), 68–80.
Commons, M. L., & Bresette, L. M. (2006). Illuminating major creative scientific innovators with postformal stages. In C. Hoare (Ed.),Handbook of adult development and learning (pp. 255–280). New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
Connor, S. R., Pyenson, B., Fitch, K., Spence, C., & Iwasaki, K. (2007). Comparing hospice and nonhospice patient survival among patients who die within a three-year window. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management, 33(3), 238–246.
Courage, M. L., & Howe, M. L. (2002). From infant to child: The dynamics of cognitive change in the second year of life.Psychological Bulletin, 128, 250–277.
Curtiss, S. (1981). Dissociations between language and cognition: Cases and implications. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 11(1), 15–30.
Darling, N. (1999). Parenting style and its correlates. Retrieved from ERIC database (EDO-PS-99-3) http://ecap.crc.illinois.edu/eecearchive/digests/1999/darlin99.pdf
de Hevia, M. D., & Spelke, E. S. (2010). Number-space mapping in human infants. Psychological Science, 21(5), 653–660.
Dennett, D. (1987). The intentional stance. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Diamond, A. (2009). The interplay of biology and the environment broadly defined. Developmental Psychology, 45(1), 1–8.
Donenberg, G. R., Wilson, H. W., Emerson, E., Bryant, F. B. (2002). Holding the line with a watchful eye: The impact of perceived parental permissiveness and parental monitoring on risky sexual behavior among adolescents in psychiatric care. AIDS Education Prevention, 14(2), 138–157.
Dornbusch, S. M., Ritter, P. L., Leiderman, P. H., Roberts, D. F., & Fraleigh, M. J. (1987). The relation of parenting style to adolescent school performance. Child Development, 58(5), 1244–1257.
Duncan, G. J., & Magnuson, K. A. (2005). Can family socioeconomic resources account for racial and ethnic test score gaps? The Future of Children, 15(1), 35–54.
Erikson, E. H. (1963). Childhood and Society (2nd ed.). New York, NY: Norton.
Erikson, E. H. (1968). Identity: Youth and crisis. New York, NY: Norton.
Ferrer, M., & Fugate, A. (2003). Helping your school-age child develop a healthy self-concept. Retrieved from http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fy570#FOOTNOTE_2
Figdor, E., & Kaeser, L. (1998). Concerns mount over punitive approaches to substance abuse among pregnant women. The Guttmacher Report on Public Policy 1(5), 3–5.
Fischer, K. W., Yan, Z., & Stewart, J. (2003). Adult cognitive development: Dynamics in the developmental web. In J. Valsiner & K Connolly (Eds.), Handbook of developmental psychology (pp. 491–516). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
Flannery, D. J., Rowe, D. C., & Gulley, B. L. (1993). Impact of pubertal status, timing, and age on adolescent sexual experience and delinquency. Journal of Adolescent Research, 8, 21–40.
Freud, S. (1909). Analysis of a phobia in a five-year-old boy. In Collected Papers: Volume 111, Case Histories (1949) (pp. 149–289). Hogarth Press: London.
Fromkin, V., Krashen, S., Curtiss, S., Rigler, D., & Rigler, M. (1974). The development of language in Genie: A case of language acquisition beyond the critical period. Brain and Language, 1, 81–107.
Galambos, N. L., & Almeida, D. M. (1992). Does parent-adolescent conflict increase in early adolescence? Journal of Marriage and the Family, 54, 737–747.
Ganger, J., & Brent, M.R. (2004). Reexamining the vocabulary spurt. Developmental Psychology, 40(4), 621–632.
Ge, X., Conger, R. D., & Elder, G. H. (2001). Pubertal transition, stressful life events, and the emergence of gender differences in adolescent depressive symptoms. Developmental Psychology, 37, 404–417.
Gervai, J. (2009). Environmental and genetic influences on early attachment. Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and Mental Health, 3, 25.
Gesell, A. (1933). Maturation and the patterning of behavior. In C. Murchison (Ed.), A handbook of child psychology (2nd ed., pp. 209–235). Worcester, MA: Clark University Press.
Gesell, A. (1939). Biographies of child development. New York, NY: Paul B. Hoeber.
Gesell, A. (1940). The first five years of life. New York, NY: Harper.
Gesell, A., & Ilg, F. L. (1946). The child from five to ten. New York, NY: Harper.
Gilligan, C. (1982). In a different voice: Psychological theory and women’s development. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Gleitman, L.R., & Newport, E. L. (1995). The invention of language by children: Environmental and biological influences on the acquisition of language. In D.N. Osherson , L.R. Gleitman, & M. Liberman (Eds.), An invitation to cognitive science: Language (pp. 1–24). Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press.
Gleitman, L. R., & Newport, E. L. (1995). The invention of language by children: Environmental and biological influences on the acquisition of language. In L. R. Gleitman & M. Liberman (Eds.), An invitation to cognitive science, Vol. 1: Language. (2nd ed.) (pp. 1–24). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Godkin, M., Krant, M., & Doster, N. (1984). The impact of hospice care on families. International Journal of Psychiatry in Medicine, 13, 153–165.
Graber, J. A., Lewinsohn, P. M., Seeley, J. R., & Brooks-Gunn, J. (1997). Is psychopathology associated with the timing of pubertal development? Journal of the Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 36, 1768–1776.
Hair, E. C., Moore, K. A., Garrett, S. B., Kinukawa, A., Lippman, L., & Michelson, E. (2005). The parent-adolescent relationship scale. In L. Lippman (Ed.), Conceptualizing and Measuring Indicators of Positive Development: What Do Children Need to Fluorish? (pp. 183–202). New York, NY: Kluwer Academic/Plenum Press.
Hall, S. S. (2004, May). The good egg. Discover, 30–39.
Hall, G. S. (1904). Adolescence. New York, NY: Appleton.
Harlow, H. (1958). The nature of love. American Psychologist, 13, 673–685.
Harris, J. R. (2009). The nurture assumption: Why children turn out the way they do (2nd ed.). New York, NY: Free Press.
Hart, B., & Risley, T. R. (2003). The early catastrophe: The 30 million word gap. American Educator, 27(1), 4–9.
Hatch, E. (1983). Psycholinguistics: A second language perspective. Rowley, MA: Newbury House.
Hertzog, C., Kramer, A. F., Wilson, R. S., & Lindenberger, U. (2009). Enrichment effects on adult cognitive development.Psychological Science in the Public Interest, 9(1), 1–65.
Hood, R. W., Jr., Spilka, B., Hunsberger, B., & Corsuch, R. (1996). The psychology of religion: An empirical approach (2nd ed.). New York, NY: Guilford.
Huebler, F. (2005, December 14). International education statistics [Web log post]. Retrieved from http://huebler.blogspot.com/2005/12/age-and-level-of-education-in-nigeria.html
Hutchinson, N. (2011). A geographically informed vision of skills development. Geographical Education, 24, 15.
Huttenlocher, P. R., & Dabholkar, A. S. (1997). Regional differences in synaptogenesis in human cerebral cortex. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 387(2), 167–178.
Iverson, J.M., & Goldin-Meadow, S. (2005). Gesture paves the way for language development. Psychological Science, 16(5), 367–71.
Iyengar, S. S., Wells, R. E., & Schwartz, B. (2006). Doing better but feeling worse: Looking for the best job undermines satisfaction.Psychological Science, 17, 143–150.
Jos, P. H., Marshall, M. F., & Perlmutter, M. (1995). The Charleston policy on cocaine use during pregnancy: A cautionary tale. The Journal of Law, Medicine & Ethics, 23(2), 120–128.
Kaltiala-Heino, R. A., Rimpela, M., Rissanen, A., & Rantanen, P. (2001). Early puberty and early sexual activity are associated with bulimic-type eating pathology in middle adolescence. Journal of Adolescent Health, 28, 346–352.
Kaplan, H., & Dove, H. (1987). Infant development among the Aché of Eastern Paraguay. Developmental Psychology, 23, 190–198.
Karasik, L. B., Adolph, K. E., Tamis-LeMonda, C. S., & Bornstein, M. H. (2010). WEIRD Walking: Cross-cultural research on motor development. Behavioral & Brain Sciences, 33(2-3), 95–96.
Karnik, S., & Kanekar, A. (2012). Childhood obesity: A global public health crisis. International Journal of Preventive Medicine, 3(1), 1–7.
Kohlberg, L. (1969). Stage and sequence: The cognitive-developmental approach to socialization. In D. A. Goslin (Ed.), Handbook of socialization theory and research (p. 379). Chicago, IL: Rand McNally.
Kolb, B., & Whishaw, I. Q. (2009). Fundamentals of human neuropsychology. New York, NY: Worth.
Kübler-Ross, E. (1969). On death and dying. New York, NY: Macmillan.
Labouvie-Vief, G., & Diehl, M. (1999). Self and personality development. In J. C. Cavanaugh & S. K. Whitbourne (Eds.), Gerontology: An interdisciplinary perspective (pp. 238–268). New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
Larson, E. B., Wang, L., Bowen, J. D., McCormick, W. C., Teri, L., Crane, P., & Kukull, W. (2006). Exercise is associated with reduced risk for incident dementia among persons 65 years of age or older. Annals of Internal Medicine, 144, 73–81.
Lee, V. E., & Burkam, D. T. (2002). Inequality at the starting gate: Social background differences in achievement as children begin school. Washington, DC: Economic Policy Institute.
Lobo, I. (2008) Environmental influences on gene expression. Nature Education 1(1), 39.
Loop, E. (2013). Major milestones in cognitive development in early childhood. Retrieved from http://everydaylife.globalpost.com/major-milestones-cognitive-development-early-childhood-4625.html
Maccoby, E. (1980). Social development: Psychological growth and the parent-child relationship. New York, NY: Harcourt Brace Jovanovich.
MacFarlane, A. (1978, February). What a baby knows. Human Nature, 74–81.
Maier, S. E., & West, J. R. (2001). Drinking patterns and alcohol-related birth defects. Alcohol Research & Health, 25(3), 168–174.
Main, M., & Solomon, J. (1990). Procedures for identifying infants as disorganized/disoriented during the Ainsworth Strange Situation. In M. T. Greenberg, D. Cicchetti, & E. M. Cummings (Eds.), Attachment in the Preschool Years (pp. 121–160). Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Markus, H. R., Ryff, C. D., Curan, K., & Palmersheim, K. A. (2004). In their own words: Well-being at midlife among high school-educated and college-educated adults. In O. G. Brim, C. D. Ryff, & R. C. Kessler (Eds.), How healthy are we? A national study of well-being at midlife (pp. 273–319). Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
McIntosh, D. N., Silver, R. C., & Wortman, C. B. (1993). Religion’s role in adjustment to a negative life event: Coping with the loss of a child. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 65, 812–821.
McMillan, S. C., Small, B. J., Weitzner, M., Schonwetter, R., Tittle, M., Moody, L., & Haley, W. E. (2006). Impact of coping skills intervention with family caregivers of hospice patients with cancer. Cancer, 106(1), 214-222.
Miklikowska, M., Duriez, B., & Soenens, B. (2011). Family roots of empathy-related characteristics: The role of perceived maternal and paternal need support in adolescence. Developmental Psychology, 47(5), 1342–1352.
Mills, M., & Melhuish, E. (1974). Recognition of mother’s voice in early infancy. Nature, 252, 123–124.
Mohr, R. D., & Zoghi, C. (2006). Is job enrichment really enriching? (U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics Working Paper 389). Washington, DC: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Retrieved from http://www.bls.gov/ore/pdf/ec060010.pdf
Moore, K. A., Guzman, L., Hair, E. C., Lippman, L., & Garrett, S. B. (2004). Parent-teen relationships and interactions: Far more positive than not. Child Trends Research Brief, 2004-25. Washington, DC: Child Trends.
National Institutes of Health. (2013). What is prenatal care and why is it important? Retrieved from http://www.nichd.nih.gov/health/topics/pregnancy/conditioninfo/Pages/prenatal-care.aspx
Nolen-Hoeksema, S., & Larson, J. (1999). Coping with loss. Mahweh, NJ: Erlbaum.
Overman, W. H., Bachevalier, J., Turner, M., & Peuster, A. (1992). Object recognition versus object discrimination: Comparison between human infants and infant monkeys. Behavioral Neuroscience, 106, 15–29.
Paloutzian, R. F. (1996). Invitation to the psychology of religion. Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon.
Parent, J., Forehand, R., Merchant, M. J., Edwards, M. C., Conners-Burrow, N. A., Long, N., & Jones, D. J. (2011). The relation of harsh and permissive discipline with child disruptive behaviors: Does child gender make a difference in an at-risk sample? Journal of Family Violence, 26, 527–533.
Piaget, J. (1954). The construction of reality in the child. New York: Basic Books.
Pickens, J. (1994). Full-term and preterm infants’ perception of face-voice synchrony. Infant Behavior and Development, 17, 447–455.
Piaget, J. (1930). The child’s conception of the world. New York, NY: Harcourt, Brace & World.
Piaget, J. (1932). The moral judgment of the child. New York, NY: Harcourt, Brace & World.
Podewils, L. J., Guallar, E., Kuller, L. H., Fried, L. P., Lopez, O. L., Carlson, M., & Lyketsos, C. G. (2005). Physical activity, APOE genotype, and dementia risk: Findings from the Cardiovascular Health Cognition Study. American Journal of Epidemiology, 161, 639–651.
Pollack, W., & Shuster, T. (2000). Real boys’ voices. New York, NY: Random House.
Rhodes, R. L., Mitchell, S. L., Miller, S. C., Connor, S. R., & Teno, J. M. (2008). Bereaved family members’ evaluation of hospice care: What factors influence overall satisfaction with services? Journal of Pain and Symptom Management, 35, 365–371.
Risley, T. R., & Hart, B. (2006). Promoting early language development. In N. F. Watt, C. Ayoub, R. H. Bradley, J. E. Puma, & W. A. LeBoeuf (Eds.), The crisis in youth mental health: Early intervention programs and policies (Vol. 4, pp. 83–88). Westport, CT: Praeger.
Rothbaum, R., Weisz, J., Pott, M., Miyake, K., & Morelli, G. (2000). Attachment and culture: Security in the United States and Japan.American Psychologist, 55, 1093–1104.
Russell, S. T., Crockett, L. J., & Chao, R. (Eds.). (2010). Asian American parenting and parent-adolescent relationships. In R. Levesque (Series Ed.), Advancing responsible adolescent development. New York, NY: Springer.
Ryff, C. D., & Singer, B. (2009). Understanding healthy aging: Key components and their integration. In V. L. Bengtson, D. Gans., N. M. Putney, & M. Silverstein. (Eds.), Handbook of theories of aging (2nd ed., pp. 117–144). New York, NY: Springer.
Samarel, N. (1991). Caring for life after death. Washington, DC: Hemisphere.
Sanson, A., & Rothbart, M. K. (1995). Child temperament and parenting. In M. Bornstein (Ed.), Applied and practical parenting (Vol. 4, pp. 299–321). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Schechter, C., & Byeb, B. (2007). Preliminary evidence for the impact of mixed-income preschools on low-income children’s language growth. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 22, 137–146.
Shamay-Tsoory, S. G., Tomer, R., & Aharon-Peretz, J. (2005). The neuroanatomical basis of understanding sarcasm and its relationship to social cognition. Neuropsychology, 19(3), 288–300.
Shanahan, L., McHale, S. M., Osgood, D. W., & Crouter, A. C. (2007). Conflict frequency with mothers and fathers from middle childhood to late adolescence: Within and between family comparisons. Developmental Psychology, 43, 539–550.
Siegler, R. S. (2005). Children’s thinking (4th ed). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
Siegler, R. S. (2006). Microgenetic analyses of learning. In D. Kuhn & R. S. Siegler (Eds.), Handbook of child psychology: Cognition, perception, and language (6th ed., Vol. 2). New York: Wiley.
Sinnott, J. D. (1998). The development of logic in adulthood: Postformal thought and its applications. New York, NY: Springer.
Small, M. F. (1999). Our babies, ourselves: How biology and culture shape the way we parent. New York, NY: Anchor Books.
Spelke, E.S., & Cortelyou, A. (1981). Perceptual aspects of social knowing: Looking and listening in infancy. In M.E. Lamb & L.R. Sherrod (Eds.), Infant social cognition: Empirical and theoretical considerations (pp. 61–83). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Steinberg, L., & Morris, A. S. (2001). Adolescent development. Annual Review of Psychology, 52, 83–110.
Sterns, H. L., & Huyck, M. H. (2001). The role of work in midlife. In M. Lachman (Ed.), The handbook of midlife development (pp. 447–486). New York, NY:Wiley.
Steven L. Youngentob, et. al. (2007). Experience-induced fetal plasticity: The effect of gestational ethanol exposure on the behavioral and neurophysiologic olfactory response to ethanol odor in early postnatal and adult rats. Behavioral Neuroscience, 121(6), 1293–1305.
Stork, F. C., & Widdowson, D. A. (1974). Learning about linguistics. London, UK: Hutchinson Ltd.
Streissguth, A. P., Bookstein, F. L., Barr, H. M., Sampson, P. D., O’Malley, K., & Young, J. K. (2004). Risk factors for adverse life outcomes in fetal alcohol syndrome and fetal alcohol effects. Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics, 25(4), 228–238.
Striegel-Moore, R. H., & Cachelin, F. M. (1999). Body image concerns and disordered eating in adolescent girls: Risk and protective factors. In N. G. Johnson, M. C. Roberts, & J. Worell (Eds.), Beyond appearance: A new look at adolescent girls. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association
Tanner, J. M. (1978). Fetus into man: Physical growth from conception to maturity. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Temel, J. S., Greer, J. A., Muzikansky, A., Gallagher, E. R., Admane, S., Jackson, V. A. . . . Lynch, T. J. (2010). Early palliative care for patients with metastic non-small-cell lung cancer. New England Journal of Medicine, 363, 733–742.
Thomas, A. (1984). Temperament research: Where we are, where we are going. Merrill-Palmer Quarterly, 30(2), 103–109.
Tran, T. D., & Kelly, S. J. (2003). Critical periods for ethanol-induced cell loss in the hippocampal formation. Neurotoxicology and Teratology, 25(5), 519–528.
Umberson, D., Pudrovska, T., & Reczek, C. (2010). Parenthood, childlessness, and well-being: A life course perspective. Journal of Marriage and the Family, 72(3), 612–629.
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization. (2013, June). UIS Fact Sheet: Schooling for millions of children jeopardized by reductions in aid. Montreal, Canada: UNESCO Institute for Statistics.
Vaillant, G. E. (2002). Aging well. New York, NY: Little Brown & Co.
Van der Graaff, J., Branje, S., De Wied, M., Hawk, S., Van Lier, P., & Meeus, W. (2013). Perspective taking and empathetic concern in adolescence: Gender differences in developmental changes. Developmental Psychology, 50(3), 881.
van Ijzendoorn, M. H., & Sagi-Schwartz, A. (2008). Cross-cultural patterns of attachment: Universal and contextual dimensions. In J. Cassidy & P. R. Shaver (Eds.), Handbook of attachment. New York, NY: Guilford.
Vouloumanos, A., & Werker, J. F. (2004). Tuned to the signal: The privileged status of speech for young infants. Developmental Science, 7, 270–276.
WHO Multicentre Growth Reference Study Group. (2006). WHO Child growth standards: Methods and development: Length/height-for-age, weight-for-age, weight-for-length, weight-for-height and body mass index-for-age. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization.
Winerman, L. (2011). Closing the achievement gap. Monitor of Psychology, 42(8), 36.
Wortman, J. H., & Park, C. L. (2008). Religion and spirituality in adjustment following bereavement: An integrative review. Death Studies