Learning Objectives
- Use strategies for managing time effectively as a college student.
- Identify and apply strategies for taking notes efficiently.
- Determine the specific time-management, study, and note-taking strategies that work best for you individually.
By now, you have a general idea of what to expect from your college courses. You have probably received course syllabi, started on your first few assignments, and begun applying the strategies you learned about in Section 1.1 “Reading and Writing in College”.
At the beginning of the semester, your work load is relatively light. This is the perfect time to brush up on your study skills and establish good habits. When the demands on your time and energy become more intense, you will have a system in place for handling them.
This section covers specific strategies for managing your time effectively. You will also learn about different note-taking systems that you can use to organize and record information efficiently.
As you work through this section, remember that every student is different. The strategies presented here are tried and true techniques that work well for many people. However, you may need to adapt them slightly to develop a system that works well for you personally. If your friend swears by her smartphone, but you hate having to carry extra electronic gadgets around, then using a smartphone will not be the best organizational strategy for you.
Read with an open mind, and consider what techniques have been effective (or ineffective) for you in the past. Which habits from your high school years or your work life could help you succeed in college? Which habits might get in your way? What changes might you need to make?
Understanding Yourself as a Learner
To succeed in college—or any situation where you must master new concepts and skills—it helps to know what makes you tick. For decades, educational researchers and organizational psychologists have examined how people take in and assimilate new information, how some people learn differently than others, and what conditions make students and workers most productive. Here are just a few questions to think about:
- What is your learning style? For the purposes of this chapter, learning style refers to the way you prefer to take in new information, by seeing, by listening, or through some other channel. For more information, see the section on learning styles.
- What times of day are you most productive? If your energy peaks early, you might benefit from blocking out early morning time for studying or writing. If you are a night owl, set aside a few evenings a week for schoolwork.
- How much clutter can you handle in your work space? Some people work fine at a messy desk and know exactly where to find what they need in their stack of papers; however, most people benefit from maintaining a neat, organized space.
- How well do you juggle potential distractions in your environment? If you can study at home without being tempted to turn on the television, check your e-mail, fix yourself a snack, and so on, you may make home your work space. However, if you need a less distracting environment to stay focused, you may be able to find one on your college’s campus or in your community.
- Does a little background noise help or hinder your productivity? Some people work better when listening to background music or the low hum of conversation in a coffee shop. Others need total silence.
- When you work with a partner or group, do you stay on task? A study partner or group can sometimes be invaluable. However, working this way takes extra planning and effort, so be sure to use the time productively. If you find that group study sessions turn into social occasions, you may study better on your own.
- How do you manage stress? Accept that at certain points in the semester, you will feel stressed out. In your day-to-day routine, make time for activities that help you reduce stress, such as exercising, spending time with friends, or just scheduling downtime to relax.
Learning Styles
Most people have one channel that works best for them when it comes to taking in new information. Knowing yours can help you develop strategies for studying, time management, and note taking that work especially well for you.
To begin identifying your learning style, think about how you would go about the process of assembling a piece of furniture. Which of these options sounds most like you?
- You would carefully look over the diagrams in the assembly manual first so you could picture each step in the process.
- You would silently read the directions through, step by step, and then look at the diagrams afterward.
- You would read the directions aloud under your breath. Having someone explain the steps to you would also help.
- You would start putting the pieces together and figure out the process through trial and error, consulting the directions as you worked.
Now read the following explanations. Again, think about whether each description sounds like you.
- If you chose (a), you may be a visual learner. You understand ideas best when they are presented in a visual format, such as a flowchart, a diagram, or text with clear headings and many photos or illustrations.
- If you chose (b), you may be a verbal learner. You understand ideas best through reading and writing about them and taking detailed notes.
- If you chose (c), you may be an auditory learner. You understand ideas best through listening. You learn well from spoken lectures or books on tape.
- If you chose (d), you may be a kinesthetic learner. You learn best through doing and prefer hands-on activities. In long lectures, fidgeting may help you focus.
Your learning style does not completely define you as a student. Auditory learners can comprehend a flow chart, and kinesthetic learners can sit still long enough to read a book. However, if you do have one dominant learning style, you can work with it to get the most out of your classes and study time. Table 1.3 “Learning Style Strategies” lists some tips for maximizing your learning style.
Table 1.3 Learning Style Strategies
| Learning Style | Strategies |
|---|---|
| Visual |
|
| Verbal |
|
| Auditory |
|
| Kinesthetic |
|
Tip
The material presented here about learning styles is just the tip of the iceberg. There are numerous other variations in how people learn. Some people like to act on information right away while others reflect on it first. Some people excel at mastering details and understanding concrete, tried and true ideas while others enjoy exploring abstract theories and innovative, even impractical ideas. For more information about how you learn, visit your school’s academic resource center.
Time Management
In college you have increased freedom to structure your time as you please. With that freedom comes increased responsibility. High school teachers often take it upon themselves to track down students who miss class or forget assignments. College instructors, however, expect you to take full responsibility for managing yourself and getting your work done on time.
Getting Started: Short- and Long-Term Planning
At the beginning of the semester, establish a weekly routine for when you will study and write. A general guideline is that for every hour spent in class, students should expect to spend another two to three hours on reading, writing, and studying for tests. Therefore, if you are taking a biology course that meets three times a week for an hour at a time, you can expect to spend six to nine hours per week on it outside of class. You will need to budget time for each class just like an employer schedules shifts at work, and you must make that study time a priority.
That may sound like a lot when taking multiple classes, but if you plan your time carefully, it is manageable. A typical full-time schedule of fifteen credit hours translates into thirty to forty-five hours per week spent on schoolwork outside of class. All in all, a full-time student would spend about as much time on school each week as an employee spends on work. Balancing school and a job can be more challenging, but still doable.
In addition to setting aside regular work periods, you will need to plan ahead to handle more intense demands, such as studying for exams and writing major papers. At the beginning of the semester, go through your course syllabi and mark all major due dates and exam dates on a calendar. Use a format that you check regularly, such as your smartphone or the calendar feature in your e-mail. (In Section 1.3 “Becoming a Successful College Writer” you will learn strategies for planning out major writing assignments so you can complete them on time.)
Tip
The two- to three-hour rule may sound intimidating. However, keep in mind that this is only a rule of thumb. Realistically, some courses will be more challenging than others, and the demands will ebb and flow throughout the semester. You may have trouble-free weeks and stressful weeks. When you schedule your classes, try to balance introductory-level classes with more advanced classes so that your work load stays manageable.
Crystal knew that to balance a job, college classes, and a family, it was crucial for her to get organized. For the month of September, she drew up a week-by-week calendar that listed not only her own class and work schedules but also the days her son attended preschool and the days her husband had off from work. She and her husband discussed how to share their day-to-day household responsibilities so she would be able to get her schoolwork done. Crystal also made a note to talk to her supervisor at work about reducing her hours during finals week in December.
Exercise 1
Now that you have learned some time-management basics, it is time to apply those skills. For this exercise, you will develop a weekly schedule and a semester calendar.
- Working with your class schedule, map out a week-long schedule of study time. Try to apply the “two- to three-hour” rule. Be sure to include any other nonnegotiable responsibilities, such as a job or child care duties.
- Use your course syllabi to record exam dates and due dates for major assignments in a calendar (paper or electronic). Use a star, highlighting, or other special marking to set off any days or weeks that look especially demanding.
Staying Consistent: Time Management Dos and Don’ts
Setting up a schedule is easy. Sticking with it, however, may create challenges. A schedule that looked great on paper may prove to be unrealistic. Sometimes, despite students’ best intentions, they end up procrastinating or pulling all-nighters to finish a paper or study for an exam.
Keep in mind, however, that your weekly schedule and semester calendar are time-management tools. Like any tools, their effectiveness depends on the user: you. If you leave a tool sitting in the box unused (e.g., if you set up your schedule and then forget about it), it will not help you complete the task. And if, for some reason, a particular tool or strategy is not getting the job done, you need to figure out why and maybe try using something else.
With that in mind, read the list of time-management dos and don’ts. Keep this list handy as a reference you can use throughout the semester to “troubleshoot” if you feel like your schoolwork is getting off track.
Dos
- Set aside time to review your schedule or calendar regularly and update or adjust them as needed.
- Be realistic when you schedule study time. Do not plan to write your paper on Friday night when everyone else is out socializing. When Friday comes, you might end up abandoning your plans and hanging out with your friends instead.
- Be honest with yourself about where your time goes. Do not fritter away your study time on distractions like e-mail and social networking sites.
- Accept that occasionally your work may get a little off track. No one is perfect.
- Accept that sometimes you may not have time for all the fun things you would like to do.
- Recognize times when you feel overextended. Sometimes you may just need to get through an especially demanding week. However, if you feel exhausted and overworked all the time, you may need to scale back on some of your commitments.
- Have a plan for handling high-stress periods, such as final exam week. Try to reduce your other commitments during those periods—for instance, by scheduling time off from your job. Build in some time for relaxing activities, too.
Don’ts
- Do not procrastinate on challenging assignments. Instead, break them into smaller, manageable tasks that can be accomplished one at a time.
- Do not fall into the trap of “all-or-nothing” thinking: “There is no way I can fit in a three-hour study session today, so I will just wait until the weekend.” Extended periods of free time are hard to come by, so find ways to use small blocks of time productively. For instance, if you have a free half hour between classes, use it to preview a chapter or brainstorm ideas for an essay.
- Do not fall into the trap of letting things slide and promising yourself, “I will do better next week.” When next week comes, the accumulated undone tasks will seem even more intimidating, and you will find it harder to get them done.
- Do not rely on caffeine and sugar to compensate for lack of sleep. These stimulants may temporarily perk you up, but your brain functions best when you are rested.
Exercise 2
The key to managing your time effectively is consistency. Completing the following tasks will help you stay on track throughout the semester.
- Establish regular times to “check in” with yourself to identify and prioritize tasks and plan how to accomplish them. Many people find it is best to set aside a few minutes for this each day and to take some time to plan at the beginning of each week.
- For the next two weeks, focus on consistently using whatever time-management system you have set up. Check in with yourself daily and weekly, stick to your schedule, and take note of anything that interferes. At the end of the two weeks, review your schedule and determine whether you need to adjust it.
- Review the preceeding list of dos and don’ts.
Writing at Work
If you are part of the workforce, you have probably established strategies for accomplishing job-related tasks efficiently. How could you adapt these strategies to help you be a successful student? For instance, you might sync up your school and work schedules on an electronic calendar. Instead of checking in with your boss about upcoming work deadlines, establish a buddy system where you check in with a friend about school projects. Give school the same priority you give to work.
Note-Taking Methods
One final valuable tool to have in your arsenal as a student is a good note-taking system. Just the act of converting a spoken lecture to notes helps you organize and retain information, and of course, good notes also help you review important concepts later. Although taking good notes is an essential study skill, many students enter college without having received much guidance about note taking.
These sections discuss different strategies you can use to take notes efficiently. No matter which system you choose, keep the note-taking guidelines in mind.
General Note-Taking Guidelines
- Before class, quickly review your notes from the previous class and the assigned reading. Fixing key terms and concepts in your mind will help you stay focused and pick out the important points during the lecture.
- Come prepared with paper, pens, highlighters, textbooks, and any important handouts.
- Come to class with a positive attitude and a readiness to learn. During class, make a point of concentrating. Ask questions if you need to. Be an active participant.
- During class, capture important ideas as concisely as you can. Use words or phrases instead of full sentences and abbreviate when possible.
- Visually organize your notes into main topics, subtopics, and supporting points, and show the relationships between ideas. Leave space if necessary so you can add more details under important topics or subtopics.
- Record the following:
- Review your notes regularly throughout the semester, not just before exams.
Organizing Ideas in Your Notes
A good note-taking system needs to help you differentiate among major points, related subtopics, and supporting details. It visually represents the connections between ideas. Finally, to be effective, your note-taking system must allow you to record and organize information fairly quickly. Although some students like to create detailed, formal outlines or concept maps when they read, these may not be good strategies for class notes, because spoken lectures may not allow time for elaborate notes.
Instead, focus on recording content simply and quickly to create organized, legible notes. Try one of the following techniques.
Modified Outline Format
A modified outline format uses indented spacing to show the hierarchy of ideas without including roman numerals, lettering, and so forth. Just use a dash or bullet to signify each new point unless your instructor specifically presents a numbered list of items.
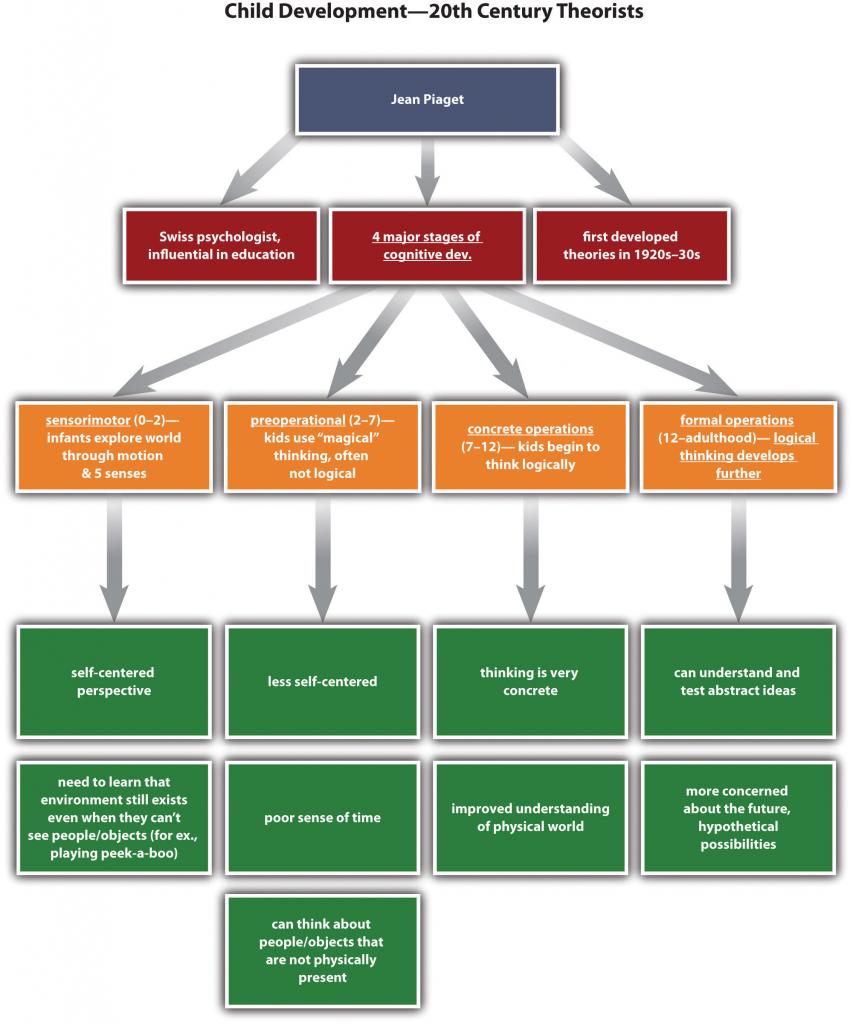
The first example shows Crystal’s notes from a developmental psychology class about an important theorist in this field. Notice how the line for the main topic is all the way to the left. Subtopics are indented, and supporting details are indented one level further. Crystal also used abbreviations for terms like development and example.
Idea Mapping
If you discovered in this section that you learn best with visual presentations, you may prefer to use a more graphic format for notes, such as an idea map. The next example shows how Crystal’s lecture notes could be set up differently. Although the format is different, the content and organization are the same.
Charting
If the content of a lecture falls into a predictable, well-organized pattern, you might choose to use a chart or table to record your notes. This system works best when you already know, either before class or at the beginning of class, which categories you should include. The next figure shows how this system might be used.
| THEORIST | COUNTRY OF ORIGIN | YEARS ACTIVE | STAGES OF CHILD DEVELOPMENT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jean Piaget | Switzerland |
1920s through 1970s |
|
| Erik Erikson | Denmark (studied in Austria, emigrated to US in 1930s) |
1930s through 1980s |
***See also stages of adult development |
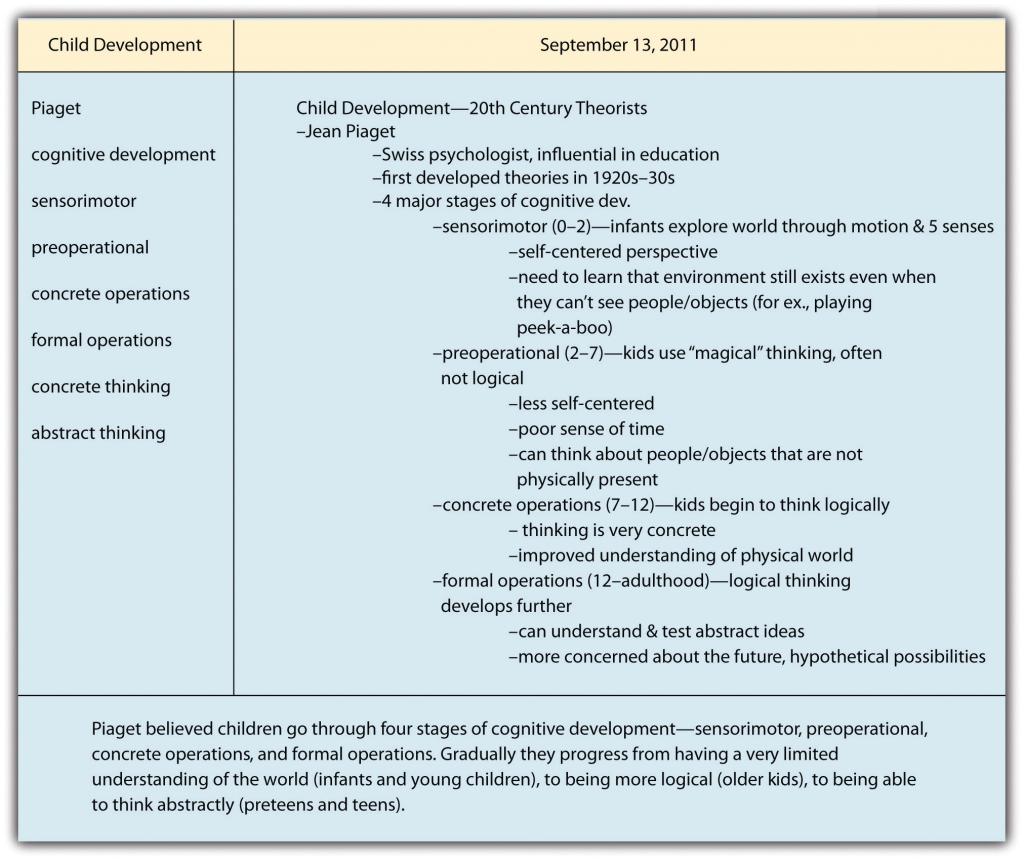
The Cornell Note-Taking System
In addition to the general techniques already described, you might find it useful to practice a specific strategy known as the Cornell note-taking system. This popular format makes it easy not only to organize information clearly but also to note key terms and summarize content.
To use the Cornell system, begin by setting up the page with these components:
- The course name and lecture date at the top of the page
- A narrow column (about two inches) at the left side of the page
- A wide column (about five to six inches) on the right side of the page
- A space of a few lines marked off at the bottom of the page
During the lecture, you record notes in the wide column. You can do so using the traditional modified outline format or a more visual format if you prefer.
Then, as soon as possible after the lecture, review your notes and identify key terms. Jot these down in the narrow left-hand column. You can use this column as a study aid by covering the notes on the right-hand side, reviewing the key terms, and trying to recall as much as you can about them so that you can mentally restate the main points of the lecture. Uncover the notes on the right to check your understanding. Finally, use the space at the bottom of the page to summarize each page of notes in a few sentences.
Using the Cornell system, Crystal’s notes would look like the following:
Writing at Work
Often, at school or in the workplace, a speaker will provide you with pre-generated notes summarizing electronic presentation slides. You may be tempted not to take notes at all because much of the content is already summarized for you. However, it is a good idea to jot down at least a few notes. Doing so keeps you focused during the presentation, allows you to record details you might otherwise forget, and gives you the opportunity to jot down questions or reflections to personalize the content.
Exercise 3
Over the next few weeks, establish a note-taking system that works for you.
- If you are not already doing so, try using one of the aforementioned techniques. (Remember that the Cornell system can be combined with other note-taking formats.)
- It can take some trial and error to find a note-taking system that works for you. If you find that you are struggling to keep up with lectures, consider whether you need to switch to a different format or be more careful about distinguishing key concepts from unimportant details.
- If you find that you are having trouble taking notes effectively, set up an appointment with your school’s academic resource center.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding your individual learning style and preferences can help you identify the study and time-management strategies that will work best for you.
- To manage your time effectively, it is important to look at the short term (daily and weekly schedules) and the long term (major semester deadlines).
- To manage your time effectively, be consistent about maintaining your schedule. If your schedule is not working for you, make adjustments.
- A good note-taking system must differentiate among major points, related subtopics, and supporting details, and it must allow you to record and organize information fairly quickly. Choose the format that is most effective for you.
PDF Creation
Interested in converting this document to PDF for display in Blackboard or printing? Copy and paste the link from the address bar into the link provided here. This site allows the user to delete unwanted page elements before final creation: https://www.printfriendly.com/