Chapter 9.2 Verb Tense
Verb Tense

Actions happen in three tenses: past, present, and future.
The tense of a verb usually gives readers a sense of time. In other words, verb tense explains if the action in the sentence 1) took place previously (past tense), 2) is taking place right now (present tense), 3) or will take place at some time in the future (future tense).
You want to be sure that you are always consistent with your verb tense. When you shift verb tenses for no reason, and this is an easy mistake to make, you can really confuse your readers.
If you’re writing in the present tense, be sure you stay in the present tense. If you’re writing in the past tense, be sure you stay in the past tense. The exception would be if you need to shift tenses to tell a story, but that would be purposeful shifting. It’s the random, accidental shifting that causes the problems, as illustrated in the following example:
Example
She grabbed my hand then flips me like I weighed nothing. This shows what a good self-defense course has done.
These sentences begin in the past tense, then switch to the present tense. Here is what a corrected version of the sentence looks like:
Example
She grabbed my hand then flipped me like I weighed nothing. This showed what a good self-defense course has done.
Regular Verbs and the Past Tense
Regular verbs follow regular patterns when shifting from the present to past tense. For example, to form a past-tense verb form, add -ed or -d to the end of a verb. You can avoid mistakes by understanding this basic pattern.
Examples: ask (present) → asked (past) play (present) → played (past)
Irregular Verbs and the Past Tense
Most verbs in English are regular verbs. However, some verbs are irregular, which means the past tense of irregular verbs is not formed using the patterns that regular verbs follow.
Examples: teach (present) → taught (past) go (present) → went (past)
see (present) → saw (past)
Irregular verbs are one of many reasons why English is a challenging language to learn; be patient with people who are learning the language and correct with kindness. Even people who have spoken and written English their entire lives get confused by irregular verbs.
Study the below table of “Irregular Verbs,” which lists the most common irregular verbs.
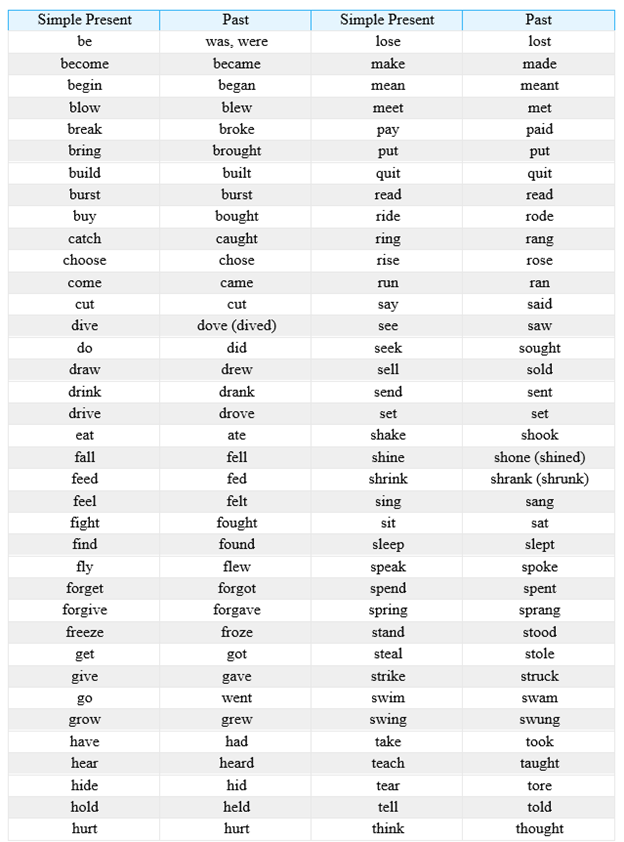

Exercise 9.2.1
On a separate sheet of paper, select the correct form of the irregular verb in simple present, simple past, or simple future tense.
- Marina finally (forgived, forgave, will forgive) her sister for snooping around her room.
- The house (shook, shaked, shakes) as the airplane rumbled overhead.
- I (buyed, bought, buy) several items of clothing at the thrift store on Wednesday.
- She (put, putted, puts) the lotion in her shopping basket and proceeded to the checkout line.
- The prized goose (layed, laid, lay) several golden eggs last night.
- Mr. Batista (teached, taught, taughted) the class how to use correct punctuation.
- I (drink, drank, will drink) several glasses of sparkling cider instead of champagne on New Year’s Eve next year.
- Although Hector (growed, grew, grows) three inches in one year, we still called him “Little Hector.”
- Yesterday, our tour guide (lead, led, will lead) us through the maze of people in Times Square.
- The rock band (burst, bursted, bursts) onto the music scene with their catchy songs.
Attributions
Verb Tense Shift is from Excelsior Online Writing Lab (OWL). This site is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-4.0 International License.
2.3: Verb Tense is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Anonymous via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform.
SB2: Choosing Appropriate Verb Tense is adapted from “Sentence Building” in Writer’s Handbook, 2012, used according to Creative Commons CC BY-NC-SA 3.0
Media Attributions
- Photo of Woman Punching © Excelsior Online Writing Lab (OWL) is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Irregular Verbs List 1
- Irregular Verbs List 2
