15
Kennedy Madden
Introduction
“COVID-19 Physical Distancing” by Alexandra Koch is in the Public Domain
Keywords
- Restrictions
- Regulations
- Social life
- Coronavirus
- Safety
- Precautions
- Mandatory protocols
- COVID-19
Learning Objectives
- Identify the social restrictions and new rules that have been put in place due to COVID-19
- Learn about the social support systems in place to aid during the times of uncertainty
- Understand the reasoning behind the COVID-19 regulations and their impact on society
- Distinguish the effects of social restrictions between children/teens and adults
- Recognize how the Coronavirus pandemic has altered the overall quality of life
- Emphasize societal changes due to COVID-19 protocols and their effects on physical activity and health
Life is extremely different because of COVID-19. The daily routines of almost everyone living during the Coronavirus pandemic have been changed due to new social restrictions and regulations put in place. The restrictions are in place with good intentions of maintaining health and safety in a time of uncertainty, but the mandatory rules and protocols are very new and have been very hard to adjust to as COVID-19 is unlike anything ever experienced before.
This chapter will highlight the social restrictions, new rules, safety precautions, and mandatory protocols that have been implemented in response to COVID-19. A variety of social support systems will be evaluated as well as their effectiveness in supporting the public during times of social restrictions. The chapter will identify the types of social impacts that isolation has on children, teens, and adults, as well as the effect of the virus on the quality of life of people around the world.
“Coronavirus ” by CDC is in the Public Domain
New Rules
Key Takeaways
New government issued rules have greatly contributed to the significant alterations of normality and the lives of people. Stay at home orders have been passed, requiring people to stay at home and avoid going out, unless absolutely necessary. Stay at home orders have made life different, as typical day-to-day activities are limited, and remaining home has been enforced. The stay-at-home orders have led to physical isolation from people which has caused social life and social events to be limited. Such changes to the social aspect of life have caused a difficult adjustment, as it is different from anything that anyone has ever experienced before, and has contributed to the large amounts of the loneliness felt amidst the Coronavirus pandemic.
The daily routines of people have been greatly changed as they are encouraged to stay at home and to not go out, and when they do go places for necessary means, they must physically distance themselves from each other and wear masks. People must avoid contact with each other and cannot be within 6 feet of each other in fear of contracting the highly contagious virus. These measures are ones that have never been implemented before in the past and are different from anything that has ever had to be done in response to a virus. New rules include mandatory mask rules which require masks to be worn at all times. They must be worn inside buildings, in stores, and while shopping. The mask protocols require workers to wear masks at all times while working and require them to be worn by customers inside of restaurants unless eating and drinking (Studdert, 2020).
Stores have had to make substantial changes as well and have implemented new rules to combat the virus. Checkout lines in grocery stores and shopping areas have placed markers on the floors which are spaced 6 feet apart for customers to stand on while waiting in line to ensure that the proper distancing measures and distancing are being enforced. Additionally, arrows have been put up in areas of high concentrations of people to direct the traffic flow of shoppers and to ensure that everyone is walking in the correct direction to avoid large congestion of crowds in public places. In implementing these new rules, physical distancing measures are able to be better enforced and followed (Briscese, 2020).
The New England Journal of Medicine discusses how stricter cleaning and sanitation has become a reality in public places as well, as areas of high touch must be cleaned and sanitized regularly as the germs of Covid-19 are so easily spread. The number of people in public places must be monitored, and stores, grocery stores, and shopping centers much control the number of people in buildings, and only certain percentages of people are allowed in areas based on the building capacity in an attempt to further enforce social distancing and limit amounts of people congregating in locations, and restaurants will only seat small numbers of people, rather than large parties. Furthermore, rules have been put in place which only allows people to be in small groups, and places, where people are in groups with more than the maximum number of people, are at risk of being fined (Studdert, 2020).
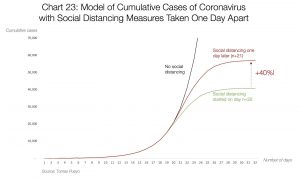
“Covid-19 Importance of Social Distancing” by Johannes Kalliauer is in the Public Domain
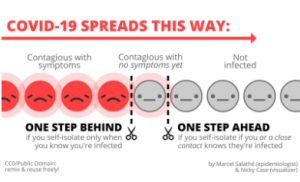
“How COVID-19 Spreads” by Marcel Salathe is in the Public Domain.
Social Support
Great amounts of social support efforts have been made to decrease the feelings of loneliness within people during times of isolation and social distancing. Online resources have been dependent on much more during these times, and resources like facetime, phone calls, text messaging, and social media have been widely used to increase online interaction during times in which face to face interactions cannot occur. Social outlets like zoom have been widely used for social events, and online events have been transitioned to online as social restrictions have prevented the gathering of people. Online social events are different than in person but are still something that people can look forward to while social distancing measures must be maintained (Masters, 2020).

“Social Media Communication” by Geralt is in the Public Domain.
Social Impacts of Isolation on Children & Teens
Key Takeaways
Young people have been forced to make extreme adjustments to their everyday lives while living in the midst of a pandemic. Children have especially been impacted, as their daily schedules have been changed completely. Kids in schools have had to make the drastic switch to online learning which is very different from anything they have ever done or had to deal with. Learning outside of the classroom brings challenges of its own as online learning has proven to be more difficult than typical face to face instruction. Additionally, young people have been cut off from interaction with teachers and their friends with in-person-learning, and a large benefit of face-to-face instruction is the social aspect of the school where kids/teens get to interact with their teachers and friends, benefiting them in the learning environment. However, due to Covid-19, such social interactions are no longer a reality and young people have been forced to adjust accordingly (Singh, 2020).
Due to the social impacts of Covid-19 and mandatory isolation has put teens at a higher risk to develop anxiety, depression, and mental disorders due to their typical social interactions and social support systems being cut off because of the virus. Teens who have more connections and relationships socially are proven to be less likely to develop such mental disorders, depression, and anxiety which is why teens have been placed at much higher risks of their development during the pandemic, as they cannot interact socially due to the restrictions like they usually would, or like they need to. In addition, depression, loneliness, and sadness in young people has been very prominent as events and social life has been put on hold and canceled completely due to the protocols with the virus, leaving kids and teens without much to look forward to as social distancing and life itself cannot operate as usual due to Covid-19 combating measures (Singh, 2020).

“Online learning” by Ajay Khadka is in the Public Domain
Social Impacts of Isolation on Adults
Not only young people impacted by the social restrictions and adjustments of Covid-19, but adults have been greatly impacted as well. Higher levels of loneliness, declines in wellbeing, and decreases in physical activity have been observed in adults amidst the pandemic, and the social restrictions put in place because of the virus are direct contributors. Social distancing has created feelings of great loneliness as adults cannot interact in a society like they used to, and the adjustments have been difficult to get used to.
According to an article published by Cornell University, with adults, they have been unable to attend the workplace and their daily schedules have been disrupted. Many have had to work from home and make adjustments work-wise which has resulted in the same effects as children doing school work from home, a decrease in social interactions, increased feelings of loneliness, and an overall decline in wellbeing as humans need human interaction, and isolation, distancing measures, and social restrictions do not allow for people to satisfy that need (Singh, 2020).
Parents have also had increased stress due to the pandemic as normal childcare means, such as daycare and schools, have closed down, meaning parents who normally work while kids are in school, must balance childcare and work from home, which is a difficult task. The additional stress to keep up with adds another challenge to adults, teens, and children alike in living during a global pandemic (Adamo, 2020).
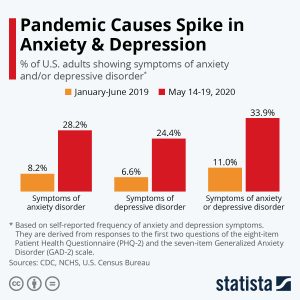
“Pandemic Causes Spike in Anxiety & Depression” by Statista is licensed under CC BY-NC-ND
Effect of Social Restrictions on the Quality of Life
Key Takeaways
The current article by Science Direct states that, as a result of the pandemic, the overall quality of life has declined as precautions and social restrictions have constantly been made to remain safe. Rules and regulations can seem repetitive at times, as the new rules, such as social distancing 6 feet, closures, masks protocols, and stay at home orders have been requirements to be followed. Mandatory testing has been required in areas in attempts to lower the number of cases and to prevent the spread of the disease, which can be burdensome to manage a busy schedule with weekly required tests and other government issues protocols. While burdensome and repetitive, all of the social restrictions are in place for the good of the population, and with everyone’s health and safety in mind at all times as much is still unknown with the pandemic (Azizi, 2020).
The Medicine Anthropology Theory discusses in an article that people must remain cautious at all times, and often have to avoid seeing friends and family in order to prevent the spread or prevent catching the virus which has caused a decrease in quality of life as usual gatherings with family and friends cannot happen. Studies have shown that long-term isolation and home confinement leads to negative effects on mental health including increased stress, negative emotions and thoughts, and lower cognition (Long, 2020).
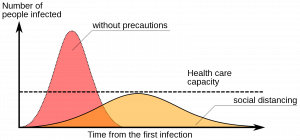
“Covid-19 Health Care Limit” by Johannes Kalliauer is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0
Effect of Social Restrictions on Physical Activity
Immune systems can be suppressed as a result of long term isolation as physical activity is limited when social restrictions are in place. Many gyms closed for periods of time, and even upon reopening, places have to be reserved ahead of time, and limited amounts of people can go, which in turn has resulted in a decrease in physical activity overall. In efforts to maintain social distancing only a select amount of gym equipment is allowed to be used as well, which contributes to a decline in physical activity because of Covid-19’s effects (Azizi).
Chapter Summary
- Many new rules have been implemented as a result to keep citizens safe during the Coronavirus pandemic. New rules and social restrictions include mandatory mask laws, stay at home orders, social distancing, the cancellation of social events, limited amounts of people in public areas and stores, increased sanitation of heavily touched areas, and more.
- Social support outlets like online events, zoom, facetime, and social media have been heavily relied on for social interactions while social distancing is a reality.
- The social restrictions of covid-19 have led to negative impacts on children, teens, and adults both mentally and physically as life is very different than it was before the virus was a reality.
- During the Covid-19 pandemic, the overall quality of life has diminished due to the strict social restrictions and protocols in place, and physical and mental health has diminished as well due to all the impacts of combating the virus.
- While difficult to follow, all of the rules and regulations are in place for the good of the world, to keep people safe from a very dangerous and deadly virus.
Exercises
- Why have teens been placed at higher risks for developing depression and anxiety during the pandemic?
- a.) Genetic predispositions
- b.) Lack of social interaction
- c.) Decreased connections with support systems
- d.) Both B & C
- Which of the following have aided in the pandemic’s effect on children?
- a.) Online school
- b.) Event cancellations
- c.) Lack of face to face interaction
- d.) All of the above
- Studies have shown that long-term isolation and home confinement has led to negative effects on mental health including which 3 things?
- a.) Happiness, thoughtfulness, organization
- b.) Cleanliness, honesty, carefulness
- c.) Stress, negative thoughts, lower cognition
- d.) Thinking, playing, learning
- True or false: While the rules and regulations for social restrictions are difficult to adjust to, the best interest of the country and population’s safety is in mind at all times.
- Name 2 new rules which have been effective in combating the Coronavirus.
- In your opinion, which Covid-19 social restriction or protocol has been the most effective?
Answers
- D
- D
- C
- True
- Answers may include mask-wearing, increased sanitation, directed traffic flow in public areas of high population, increased sanitation stations, social distancing measures, isolation, and stay at home orders, etc.
- Answers will vary – possible answers may include: mandatory masks, the limited group gathers, stay at home orders, increased sanitation of public areas, limited capacity in stores/restaurants, etc.
References
Adamo, M. (2020, July 30). June 2020 at a Glance: Focus on Covid-19, Quality of Life, and Comorbidities. Https://Onlinelibrary-Wiley-Com.Libproxy.Clemson.Edu/Doi/Full/10.1002/Ejhf.1515.
Azizi, A. (2020, October). Health Related Quality of Life and Behavior-Related Lifestyle Changes Due to Covid-19. Science Direct. https://www-sciencedirect-com.libproxy.clemson.edu/science/article/pii/S2352340920311331?via%3Dihub.
Briscese, G. (2020, December 8). Compliance with COVID-19 Social Distancing Methods in Italy: The Role of Expectations and Duration. Https://Www-Nber-Org.Libproxy.Clemson.Edu/Papers/W26916.
Long, N. J. (2020, July 27). View of From social distancing to social containment. Medicine Anthropology Theory. http://www.medanthrotheory.org/index.php/mat/article/view/5029/7126.
Luchetti, M. (2020, October 7). The Trajectory of Loneliness in Response to COVID-19. Martina Luchetti. https://psycnet.apa.org.
Masters, N. B. (2020, September 11). Social Distancing in Response to the Novel Coronavirus in the United States. Https://Journals.Plos.Org/Plosone/Article?Id=10.1371/Journal.Pone.0239025.
Singh, R. (2020, March 26). Age-structured impact of social distancing on the COVID-19 epidemic in India. ArXiv.Org. https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.12055
Slimani, M. (2020, August 7). The Relationship Between Physical Activity and Quality of Life During the Confinement Induced by COVID-19 Outbreak: A Pilot Study in Tunisia. PubMed Central (PMC). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7427614/
Studdert, D. M. (2020, July 7). Disease Control, Civil Liberties, and Mass Testing – Calibrating Restrictions During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Https://Www.Nejm.Org/Doi/Full/10.1056/NEJMp200763.
