6
Food is a basic human need and considered a human right by the United Nations and many countries and individuals. People who have steady, affordable, and safe access to sufficient food, which means they experience food security, tend to think about food in substantially different ways than people who experience food insecurity, which refers to people whose food access and intake is limited by external factors.
Not only is there an unevenness regarding food consumption and nutritional experiences, choices, and conditions for people across the world, but so too is there an unevenness regarding how food is produced. Food systems and agricultural systems vary greatly across space and through time and globalization has altered the need for urban centers to always be located near an agricultural hearth. As geographers, we continue to ask “What is where, why there, and why care” a la geographer Charles Gritzner (2002), and in this chapter, these questions are oriented around foodstuffs. This chapter will orient you with types and impacts of agriculture and food production and the geography of food consumption.
Domestication & the Birth of Agriculture
The word domestication comes from the Latin words Domesticus and Domus, referring to “belonging to the household” and “house.” In terms of agriculture, as defined by National Geographic, “Domestication is the process of adapting wild plants and animals for human use. Domestic species are raised for food, work, clothing, medicine, and many other uses. Domesticated plants and animals must be raised and cared for by humans. Domesticated species are not wild.”
To domesticate a plant, seeds are gathered and planted in the ground instead of natural forms of distribution to potentially root and grow. Enough sun and water are provided to facilitate growth and then the plants are harvested. To domesticate an animal, wild animals are enclosed and provided a food source; some animals are more easily domesticated than others. Cross-breeding between particularly desirable plant and animal strains and species is common and new species may emerge over time entirely distinct from their wild predecessors.
What did domestication help to directly bring about and set the conditions for?
- Agriculture (i.e. the process of cultivating domesticated species)
- Tool development
- More permanently settled population
- Food surplus
- Specialization of tasks/labor/jobs away from exclusively agriculture
- Hearth areas
- Urbanization (eventually)
- Trade
- Currency
The basic logic goes like this: By growing domesticated plants, you do not have to obtain nourishment by wandering around to follow your food source, which is the norm within hunting-gathering lifestyles. Instead, you stay in one area and produce enough food for yourself (you exceed sustenance) and a surplus. The (first) agricultural revolution refers to when the shift from hunting and gathering to agriculture occurred, about 10,000 years ago.
Now that you are familiar with the “what” and “how” of agriculture, you should be wondering about the “where” of agriculture– where did domestication and agriculture emerge? Take a look below for the locations of where major plants and animals were first domesticated. Pull up a reference map on the internet if you don’t know the locations of the green hearths.
You should notice that domestication is not distributed entirely evenly across place. It is clustered in what are called agricultural hearths, referring to regions of the world where many species were domesticated. Check out the video below for a recap of information about domestication, agriculture, and hearth areas.
Types & Transformations of Agriculture
The most basic way to characterize types of agriculture is into the following:
- Subsistence agriculture: food is produced for family consumption
- Commercial agriculture: food is produced for sale
There are additional types of agriculture within these two categories, including slash-and-burn, shifting cultivation, intensive subsistence, pastoral nomadism, transhumance, plantations, and agribusiness. All of these types of agriculture feature different methods and procedures. Another spectrum of difference in agricultural methods is based on intensification: the amount of agricultural extract per unit land. Agricultural methods can range from extensive to intensive, or from having low human inputs and productive outputs, to having high human inputs and productive outputs. In general, societies tend to become more intensive over time, as it means that more can be produced per unit land. However, intensification does have real drawbacks:
- Agriculture is more work; hunters and gatherers may only need 2-3 days a week to gather necessary sustenance but agriculturalists must work 6-7 days to maintain large plots of crops
- Agriculture is more fragile; one major disaster or pestilence can remove a societies major food source
- Agriculture can be less healthy; if agriculturalists farm and depend upon a single crop, malnourishment may occur
A few other interesting and creative ways to produce food include the following:
-

Aquaculture in Greece. Source: Flickr.com Aquaculture, or cultivating food or animals in water (examples: fish, cranberries, hydroponic lettuce)
- Urban gardening, or cultivating food or animals in an urban as opposed to rural setting (examples: growing a tomato plant on your front stoop or balcony, renting a community garden plot, rooftop gardens)
Agricultural Adaptations
In some ways, the type of agriculture someone can or chooses to do is influenced by the geography of where s/he is, including the topography, land cover, and climate. Humans have adapted how they produce the basic need of food in creative ways. Examples include:
- Terraces in the Incan Empire and Asia, which allow agriculture to take place on steep slopes
- Drip irrigation in arid regions, which releases tiny bits of water so it is absorbed into dry soil
- Fossil acquifers in Arabian Peninsula, which are ancient underground water reserves used to support agriculture on otherwise non-arable land
Aside from the first agricultural revolution, which refers to the birth of agriculture about 10,000 years ago, the second agricultural revolution refers to major transformations in technology used for agriculture, specifically regarding irrigation, harvesting, and transportation, around the time of the Industrial Revolution, ~mid-1700s-mid -1800s.
second agricultural revolutionAn additional agricultural revolution that has taken place is the Green Revolution, referring to the influx of high-yield seeds and fertilizers, and often GMOs (genetically modified organisms).
Consumptive Behaviors & Food (In)security
The amount and type of food we consume varies across space as does our safe and secure access to food. This chapter opened by defining food security as having steady, affordable, and safe access to sufficient food and food insecurity as just the opposite.
DEEPEN YOUR UNDERSTANDING: Read more about food insecurity as explained by Feeding America here and be sure to view the chart that appears on the linked page.
To get an idea of food security and insecurity at a global scale, compare and contrast the maps below and consider the following questions:
- What spatial patterns are present?
- What socio-cultural, economic, political, and physical geographical factors contextualize the spatial distribution of daily per capital caloric supply, obesity, and undernourishment?
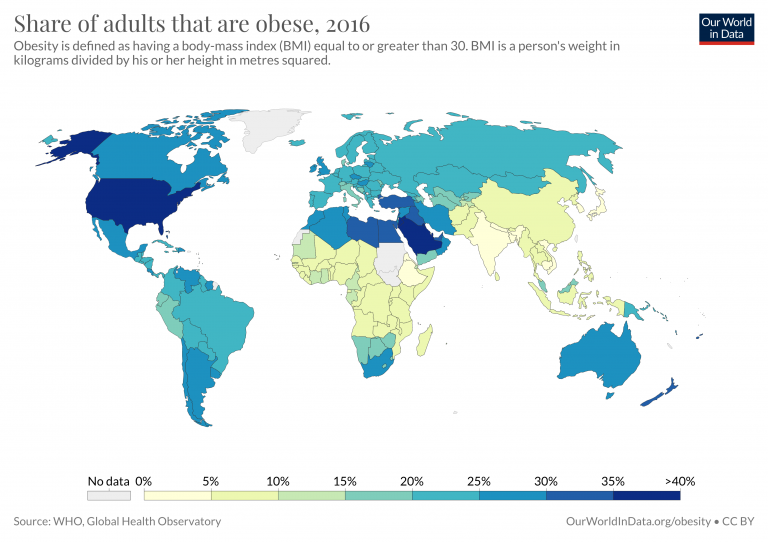
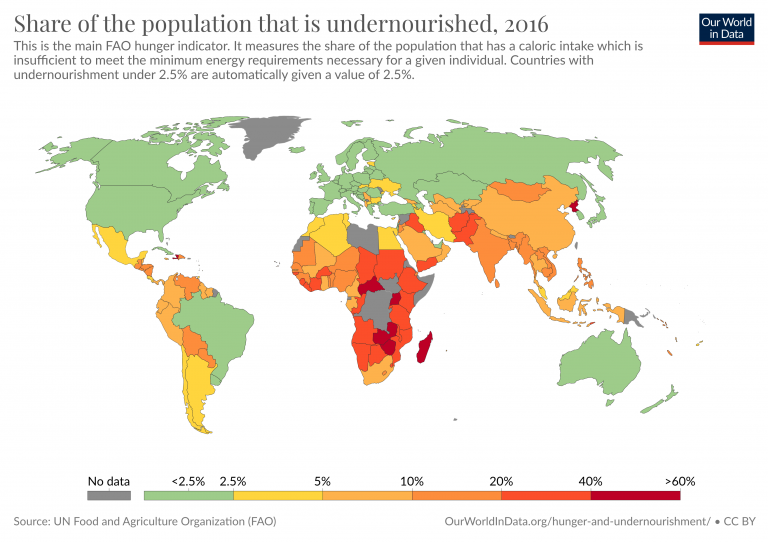
Some people may experience food insecurity due to living in what’s called a food desert. Food deserts refer to “regions of the country often feature large proportions of households with low incomes, inadequate access to transportation, and a limited number of food retailers providing fresh produce and healthy groceries for affordable prices” according to the USDA. Often food deserts are identified by the following parameters:
- Urban food desert: distance to nearest grocery store is 1+ miles in area with primarily low-income residents (profiled in the embedded video below)
- Rural food desert: distance to nearest grocery store is 10+ miles in area with primarily low-income residents
Check out the USDA’s Food Desert Research Atlas to explore patterns in the US and see if you live in or near a food desert. Remember, you may experience food security or food insecurity if you technically live in a food desert; level of food security has to do with your overall access and capability–physical, social, and financial–to food, not just if you live in a designated food desert or not.
Beyond food insecurity and food deserts can be large-scale bouts of hunger called famines. Famines affect large populations and can be regional to national in geographic scale. The common perception is that famine occurs when there is not enough food in a region to support the population. Scholar Amartya Sen argued instead that famines are often failures of the system that links food supply to food demand. Sen showed that the 1943 Bengal famine occurred due to the inability for millions to afford the rapid inflation of food prices, along with with poor distribution, government response and hoarding. The 1959-1962 famine in China coincided with the Great Leap Forward, a program of rapid industrialization. The program may have caused some 35 million people to die in a famine due to processes of collectivization of farms that produced food sent to industrial cities, leading to massive rural starvation.
End of Chapter Activity: Compare & Contrast
This chapter has provided language to describe the differences in agricultural practices and unevenness regarding agricultural lifestyles and individual consumptive behavior. To end, watch the videos below, each of which profiles fish cultivation and answer the following questions pertaining to each video:
- What are the processes for securing fish?
- Who is the typical consumer of the fish?
- What types of economic activity (primary, secondary, etc) are present for each process?
- How would you describe each of these fishing landscapes in terms of culture and economy?
- How are the processes in each video related to globalization?
- How could the different ways of fishing relate to food security and insecurity?
Media Attributions
- 3633424686_7d33467bd8_q
something all people are entitled to
steady, affordable, and safe access to sufficient food
food access and intake is limited by external factors
varied across space
increasingly intensified interconnectedness among people and places across economic and socio-cultural dimension
regions where agriculture originated
process of adapting wild plants and animals for human use
producing new species
the process of cultivating plants and/or livestock
food produced beyond sustenance
complex division of labor
areas of earliest urbanization
process of creating urban areas
wander to obtain nourishment
food needed to sustain self
regions of the world where many species were domesticated
food is produced for family consumption
food is produced for sale
method of shifting agriculture where a plot is burned in increase soil fertility
moving growing areas to maintain soil fertility
producing food for primarily yourself and immediate family or community; relies on animal power
follow food source (animals), which are following a water source; utilize all parts of animal to support lifestyle
pastoral nomadism that alternatives between mountains and lower lying areas
large-scale farm oriented around producing a single item
global marketplace for commercial agriculture
the amount of agricultural extract per unit land
from having low human inputs and productive outputs
high human inputs and productive outputs
cultivating food or animals in water
cultivating food or animals in an urban as opposed to rural setting
alteration of natural slopes to support crop growing
releases tiny bits of water so it is absorbed into dry soil
ancient underground water reserves
major transformations in technology used for agriculture, specifically regarding irrigation, harvesting, and transportation, around the time of the Industrial Revolution, ~mid-1700s-mid -1800s.
period of increased industrial output around mid-1700s to mid-1800s
influx of high-yield seeds and fertilizers, and often GMOs (genetically modified organisms)
genetically modified organisms
regions of the country often feature large proportions of households with low incomes, inadequate access to transportation, and a limited number of food retailers providing fresh produce and healthy groceries for affordable prices
distance to nearest grocery store is 1+ miles in area with primarily low-income residents
distance to nearest grocery store is 10+ miles in area with primarily low-income residents
large scale bouts of hunger affecting majority of population in an area
