Are all miles “equally” distant?
Step 1: Go to the ArcGIS Online map, Distance and Scale, above to launch the map.
Distances can feel more substantial or smaller because of cultural similarities, transportation connectivity, telecommunications, and more.
How far can you get?
Step 2: With the Details button underlined, click the button, Show Contents of Map (Content).
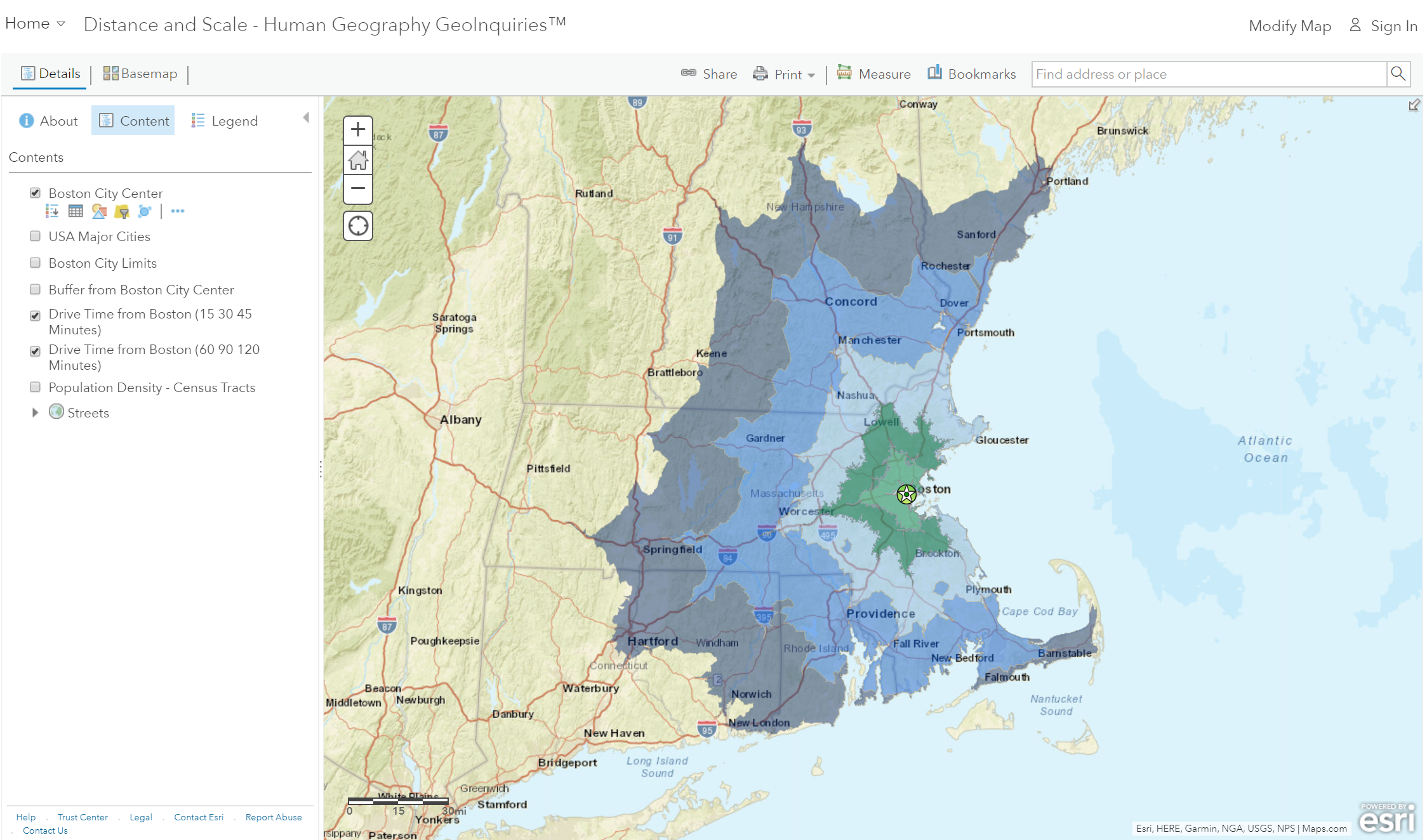
Step 3: Check the box to the left of the layer name, Drive Time From Boston (60, 90, 120 minutes).
- Which major city in New Hampshire can you reach in less than an hour?
- How long would it take to get to Providence, R.I.?
Are we taking the long way around?
Both Manchester and Worchester are at the outer edge of the 60-minute drive time zone. However, as the crow flies, it is 38 miles to Worchester and 48 miles to Manchester.
- What city is located less than 50 miles from Boston (as the crow flies), but cannot be accessed in a 120-minute commute? Hint: water contributes to the time.
- The travel time is so long because you have to drive around Cape Cod Bay. (T/F)
The other forms of transportation, such as water and air travel, might change travel time and accessibility.
How is population density related to travel time?
Step 4: Click the button, Bookmarks. Select BOS-MHT/WOR.
Step 5: Turn on the layer, Population Density – Census Tracts.
Step 6: Compare the Population Density and Drive Time layers by turning them on and off.
- What is the relationship between the drive time and population density?
How do highways affect travel time?
Step 7: Turn off the layers, Drive Time from Boston (xx xx xx Minutes).
Step 8: Change the transparency of the Population Density – Census Tracts layers to 50 percent.
From the Details pane, click the Content button. Click the three small blue dots and hover your pointer over the word “Transparency” to open a drop-down list. You can modify the transparency to see an active layer below the top layer. Set it to 50 percent.
Step 9: Click the button, Bookmarks. Select Traffic.
- How are major roads and population distributions related?
- Travel is faster through more densely populated regions than less densely populated areas because of the high-volume transportation networks that are most commonly found there. Access to major roads, even if they are congested, enables faster commutes.
