Evaluating Sources
Sometimes, the first source that shows up on our search results is great. It’s relevant and recent, and it’s written by someone who really knows what they are talking about. Much more often, however, the first source is not actually reliable. And sometimes it can be hard to tell.
Part of being a critical thinker is learning to evaluate your sources. Arguments built on lousy sources won’t hold up, so you need to know if you are using sources that are reliable. It’s not enough to find a source that addresses your topic. It has to be a good source.
So how can you tell the difference between a good source and a not-so-good source?
You may have heard of the CRAAP test for evaluating sources: Currency, Reliability, Authority, Accuracy, and Purpose. This system, developed by Molly Beestrum, asks you to look at how recent your source is (and how much that matters), whether the source is too one-sided or lacking sources of its own, who the author is and what their credentials are, and what the source is trying to accomplish. These are all excellent areas for investigation.
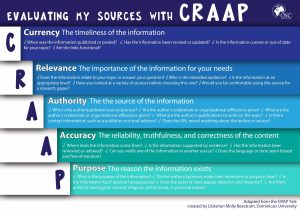
Graphic Representation of CRAAP
This system is really useful, but I recommend rearranging the order. I treat “authority” as the most important criterion for determining the credibility of a source. If the source doesn’t have authority, move on to another source. If the information is sound, another source with more authority will also discuss those ideas. And if you only find the ideas in one source, consider that a red flag.
Here are some of the red flags to look for:
- Authority
- You cannot find an author and the organization is questionable.
- The author has experience or credentials, but their credentials aren’t relevant to the material they are writing about.
- The site is a .com or .net, and seems to be more focused on selling you something than on providing accurate information.
- Currency
- The site was published before recent events relevant to your topic.
- The sources used by the site are too old for your topic.
- Relevance/Intended Audience
- The information isn’t really related to your topic, even if the information itself seems good.
- The information is presented in a simplistic way or ignores complexities that you know exist.
- The site is written for children or adolescents and may be oversimplifying the information in ways that aren’t appropriate for college-level work.
- Accuracy
- You can only find the information in this one source.
- When you check the sources, they don’t seem to be saying what the site says they do.
- Purpose/Objectivity
- The site has an identifiable conflict of interest. In particular, examine any advertising on the site. Would the revenue stream interfere with objectivity and balance in the presentation of information?
- The site is trying to make people angry or arouse other strong emotions.
- The site provides arguments on only one side of an issue or presents opposing arguments unfairly or in too simplistic a fashion.
Use the questions below to help you evaluate one of the sources you are considering using. Try writing out the answers, even if your instructor doesn’t require it.
Step 1
If your instructor is collecting this, be sure to start your evaluation with the title you are evaluating and publication location. Even if the evaluation is only for yourself, it will help to note which source you are evaluating.
Step 2
Answer the following questions about the site:
Authority
- Who is the author and what are his/her/their credentials?
- Are those credentials verifiable?
- Can you contact the author?
- What organization is sponsoring the site?
- What kind of domain is it (.com, .org, .edu, .gov)?
Currency
- Is there a date on the source?
- How up-to-date is the information?
Relevance/Intended Audience
- How is the source relevant for your project?
- Who is the target audience?
- Is the information presented at an appropriate level of complexity for your purposes?
Accuracy
- Does the author provide complete citations for sources or links to reliable information on other sites?
- If so, look at one of those sources. Where is it? Does it say what the author says it says?
- Can you find another source that presents some of the same information?
Purpose/Objectivity
- What is the purpose of the source?
- How objective or biased is the author’s position?
- If there is bias, does the bias get in the way of a clear and fair position?
- What alternative viewpoints does the author present, and are they treated fairly?
- Is there any identifiable conflict of interest?
- What’s the relationship between the content and the advertising (if any)?
You may not be able to answer all the questions, but you should be able to answer enough to come to a conclusion for each section about how credible that aspect of the site is.
Step 3
After you have answered these questions, write a general statement about how credible you think the source is and why.
This may seem like a long and tedious process, but after you practice this for a while, you will get much better at quickly determining whether a site is trustworthy or not. I can evaluate about 95% of all sites I see as reputable or not in less than a minute. You can get this quick, too.
Key Points: Evaluating Sources
- Evaluate sources using five criteria: authority, currency, relevance/intended audience, accuracy, and purpose/objectivity.
- If a source’s authority is in question, pass it by. If the information is good, you’ll find it elsewhere.
- If you practice this kind of evaluation, you will be able to do it quickly.
Media Attribution
“CRAAP Test Graphic” created by Molly Beestrum is used under a CC BY-NC 4.0 license.
