Research Methodology
9 Measuring Perception: Commonly Used Techniques
To evaluate foods, sensory science uses an array of techniques. The choice of method depends on the research question and the population. Are you interested in an analytical evaluation or a hedonic evaluation? And maybe you want panellists to say which product they prefer?
An important distinction is made between direct and indirect scaling techniques, as they provide distinct types of information. Indirect tests always give you an indirect evaluation, a comparison with another product. Ranking and triangle tests are typical indirect techniques. Direct tests give you direct information about a specific product, for example how sweet a specific product is. As this product is probably tasted in a session with other comparable products, they set the reference. Quantitative Description Analysis (QDA) is an example of a direct technique.
There are also many variations and combinations of direct and indirects methods developed. These go, however, beyond the introductory nature of this textbook. Video 5 explains the conceptual difference between direct and indirect scaling in more detail.
Video 5. Explanatory video explaining the difference between direct and indirect techniques.
Direct scales
Direct scales are used to rate products directly on a specific attribute. There are distinct types of scales, they differ in their layout and the number of answer options that you have.
Visual analogue scale
A visual analogue scale (VAS) is usually a 10 cm or 15 cm line which participants or panellists use to rate sensory attributes. As a frame of reference, it has a label at the left and right anchor.
An example of a VAS can be seen in Figure 6. To write down the evaluation, the participant is instructed to draw a vertical line across the horizontal line. The outcome is the distance between the left anchor and the crossing of the two lines. This is expressed in an absolute distance in mm or a proportional distance (%).

9-point labeled hedonic scale
An example of a hedonic scale is a 9-point hedonic scale, see Figure 7. This scale is used for hedonic questions in sensory research and has nine anchors on which participants or panellists rate to what extent they like the product or sample.
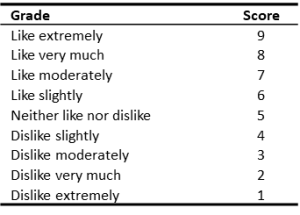
Figure 7. Example of a 9-point hedonic scale with labels. “WUR, SSEB -9-point hedonic scale”. License: Creative Commons Attribution
Other DIRECT scales
Other scales used in sensory research can be the 5- or 7-point hedonic scale, which is like the 9-point hedonic scale but with fewer anchors points, making it easier to fill out, but less sensitive to detect differences between products.
Another scale is the generalised Labelled Magnitude Scale (gLMS). It measures the perceived intensity of sensory properties using a vertical scale with labels from “barely detectable” to “strongest imaginable.” It can be used in sensory science to quantify and compare sensory perceptions.
In the Dutch context, the Dutch grading system is often used. This scale is anchored from 1 to 10. For people that are familiar with the Dutch grading system, all grades stand for a certain feeling. For people that are not aware of this grading system this scale is not valid.
For sensory research with children or non-verbal participants, scales with smiley faces standing for the sensation are often used (see Figure 8, for an example).

Figure 8. The smiley face scale is a visual tool used to measure how much a person likes or dislikes a product by choosing a face that shows their feeling, from incredibly happy to incredibly sad. “WUR, SSEB – smiley face hedonic scale”. License: Creative Commons Attribution
Which direct scale is used depends on the research population and the research question. Generally, a visual analogue scale is more sensitive as the panellist can give a more precise answer, i.e. there are more answer options. On the other hand, it is more difficult to interpret as a VAS usually has a limited frame of reference and everyone will interpret it differently.
Analytical testing refers to the objective measurement of the intensity of a sensation
In direct scaling techniques, questions are asked that directly affect the sample. For example: how sweet is the sample.
In indirect scaling, samples are compared to eachother. For example a ranking test (one solution is more sweet than another).
Visual Analogue Scale: a rating scale measuring the response from 0 to 100.
Scale with 9 anchors used for hedonic questions.
hedonic testing refers to the subjective evaluation of a sensation, for example, liking or palatability.