22
Learning Objectives
- Define sex, gender, femininity, and masculinity.
- Critically assess the evidence on biology, culture and socialization, and gender.
- Discuss agents of gender socialization.
Although the terms sex and gender are sometimes used interchangeably and do complement each other, they nonetheless refer to different aspects of what it means to be a woman or man in any society.
Sex refers to the anatomical and other biological differences between females and males that are determined at the moment of conception and develop in the womb and throughout childhood and adolescence. Females, of course, have two X chromosomes, while males have one X chromosome and one Y chromosome. From this basic genetic difference spring other biological differences. The first to appear are the genitals that boys and girls develop in the womb and that the doctor (or midwife) and parents look for when a baby is born (assuming the baby’s sex is not already known from ultrasound or other techniques) so that the momentous announcement, “It’s a boy!” or “It’s a girl!” can be made. The genitalia are called primary sex characteristics, while the other differences that develop during puberty are called secondary sex characteristics and stem from hormonal differences between the two sexes. Boys generally acquire deeper voices, more body hair, and more muscles from their flowing testosterone. Girls develop breasts and wider hips and begin menstruating as nature prepares them for possible pregnancy and childbirth. For better or worse, these basic biological differences between the sexes affect many people’s perceptions of what it means to be female or male, as we next discuss.

Babies are born with anatomical and other biological differences that are determined at the moment of conception. These biological differences define the baby’s sex.
Abby Bischoff – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Gender as a Social Construction
If sex is a biological concept, then gender is a social concept. It refers to the social and cultural differences a society assigns to people based on their (biological) sex. A related concept, gender roles, refers to a society’s expectations of people’s behavior and attitudes based on whether they are females or males. Understood in this way, gender, like race as discussed in Chapter 3 “Racial and Ethnic Inequality”, is a social construction. How we think and behave as females and males is not etched in stone by our biology but rather is a result of how society expects us to think and behave based on what sex we are. As we grow up, we learn these expectations as we develop our gender identity, or our beliefs about ourselves as females or males.
These expectations are called femininity and masculinity. Femininity refers to the cultural expectations we have of girls and women, while masculinity refers to the expectations we have of boys and men. A familiar nursery rhyme nicely summarizes these two sets of traits:
| What are little boys made of? |
| Snips and snails, |
| And puppy dog tails, |
| That’s what little boys are made of. |
| What are little girls made of? |
| Sugar and spice, |
| And everything nice, |
| That’s what little girls are made of. |
As this rhyme suggests, our traditional notions of femininity and masculinity indicate that we think females and males are fundamentally different from each other. In effect, we think of them as two sides of the same coin of being human. What we traditionally mean by femininity is captured in the adjectives, both positive and negative, we traditionally ascribe to women: gentle, sensitive, nurturing, delicate, graceful, cooperative, decorative, dependent, emotional, passive, and weak. Thus when we say that a girl or woman is very feminine, we have some combination of these traits in mind: she is soft, dainty, pretty, and even a bit flighty. What we traditionally mean by masculinity is captured in the adjectives, again both positive and negative, our society traditionally ascribes to men: strong, assertive, brave, active, independent, intelligent, competitive, insensitive, unemotional, and aggressive. When we say that a boy or man is very masculine, we have some combination of these traits in mind: he is tough, strong, and assertive.
These traits might sound like stereotypes of females and males in today’s society, and to some extent they are, but differences between women and men in attitudes and behavior do in fact exist (Aulette & Wittner, 2011). For example, women cry more often than men do. Men are more physically violent than women. Women take care of children more than men do. Women smile more often than men. Men curse and spit more often than women. When women talk with each other, they are more likely to talk about their personal lives than men are when they talk with each other. The two sexes even differ when they hold a cigarette (not that anyone should smoke!). When a woman holds a cigarette, she usually has the palm of her cigarette-holding hand facing upward; when a man holds a cigarette, he usually has his palm facing downward.
The Development of Gender Differences
What accounts for differences in female and male behavior and attitudes? Do the biological differences between the sexes account for these other differences? Or do these latter differences stem, as most sociologists think, from cultural expectations and from differences in the ways in which the sexes are socialized? These are critical questions, for they ask whether the differences between boys and girls and women and men stem more from biology or from society. If we think behavioral and other differences between the sexes are due primarily to their respective biological makeups, we imply that these differences are inevitable or nearly so and that any attempt to change them goes against biology and will likely fail.
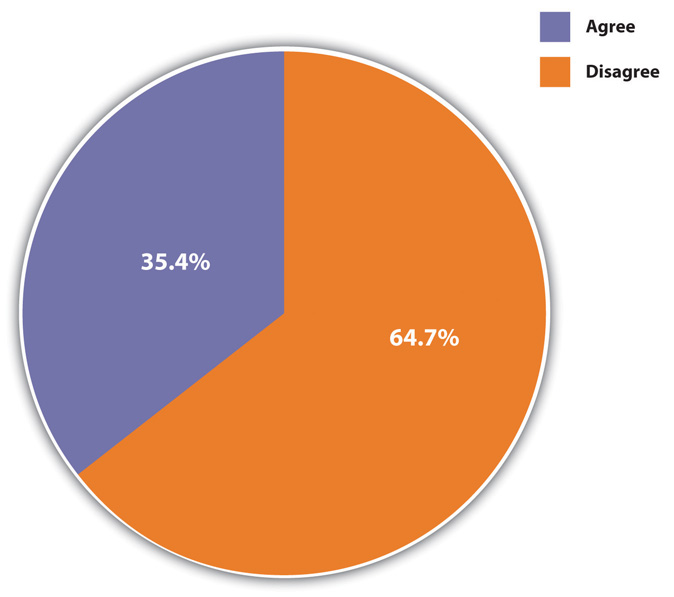
For example, consider the obvious biological fact that women bear and nurse children and men do not. Couple this with the common view that women are also more gentle and nurturing than men, and we end up with a “biological recipe” for women to be the primary caretakers of children. Many people think this means women are therefore much better suited than men to take care of children once they are born, and that the family might be harmed if mothers work outside the home or if fathers are the primary caretakers. Figure 4.1 “Belief That Women Should Stay at Home” shows that more than one-third of the public agrees that “it is much better for everyone involved if the man is the achiever outside the home and the woman takes care of the home and family.” To the extent this belief exists, women may not want to work outside the home or, if they choose to do so, they then face difficulties from employers, family, and friends. Conversely, men may not even think about wanting to stay at home and may themselves face difficulties from employees, family, and friends if they want to do so. A belief in a strong biological basis for differences between women and men implies, then, that there is little we can or should do to change these differences. It implies that “anatomy is destiny,” and destiny is, of course, by definition inevitable.
Figure 4.1 Belief That Women Should Stay at Home
Agreement or disagreement with the statement that “it is much better for everyone involved if the man is the achiever outside the home and the woman takes care of the home and family.”
Source: Data from General Social Survey. (2010). Retrieved from http://sda.berkeley.edu/cgi-bin/hsda?harcsda+gss10.
This implication makes it essential to understand the extent to which gender differences do, in fact, stem from biological differences between the sexes or, instead, stem from cultural and social influences. If biology is paramount, then gender differences are perhaps inevitable and the status quo will remain. If culture and social influences matter much more than biology, then gender differences can change and the status quo may give way. With this backdrop in mind, let’s turn to the biological evidence for behavioral and other differences between the sexes and then examine the evidence for their social and cultural roots.
Biology and Gender
Several biological explanations for gender roles exist, and we discuss two of the most important ones here. One explanation is from the field of evolutionary psychology (Buss, 2012) and argues an evolutionary basis for traditional gender roles.
Scholars advocating this view reason as follows (Thornhill & Gangestad, 2008). In prehistoric societies, two major social roles existed (1) hunting or gathering food to relieve hunger, and (2) bearing and nursing children. Because only women could perform the latter role, they were also the primary caretakers for children for several years after birth. And because women were frequently pregnant, their roles as mothers confined them to the home. Meanwhile, men were better suited than women for hunting because they were stronger and quicker than women. In prehistoric societies, then, biology was indeed destiny: For biological reasons, men in effect worked outside the home (hunted), while women stayed at home with their children.
Evolutionary reasons also explain why men are more violent than women. In prehistoric times, men who were more willing to commit violence against and even kill other men would “win out” in the competition for female mates. They thus were more likely than less violent men to produce offspring, who would then carry these males’ genetic violent tendencies.
If the human race evolved along these lines, evolutionary psychologists continue, natural selection favored those societies where men were stronger, braver, and more aggressive and where women were more fertile and nurturing. Such traits over the millennia became fairly instinctual, meaning that men’s and women’s biological natures evolved differently. Men became, by nature, more assertive, daring, and violent than women, and women became, by nature, more gentle, nurturing, and maternal than men. To the extent this is true, these scholars add, traditional gender roles for women and men make sense from an evolutionary standpoint, and attempts to change them go against the sexes’ biological natures. This in turn implies that existing gender inequality must continue because it is rooted in biology. The title of a book presenting the evolutionary psychology argument summarizes this implication: “Biology at Work: Rethinking Sexual Equality” (Browne, 2002).

According to some evolutionary psychologists, today’s gender differences in strength and physical aggression are ultimately rooted in certain evolutionary processes that spanned millennia.
Vladimir Pustovit – Couple – CC BY 2.0.
Critics challenge the evolutionary explanation on several grounds (Begley, 2009; Fine, 2011). First, much greater gender variation in behavior and attitudes existed in prehistoric times than the evolutionary explanation assumes. Second, even if biological differences did influence gender roles in prehistoric times, these differences are largely irrelevant in modern societies, in which, for example, physical strength is not necessary for survival. Third, human environments throughout the millennia have simply been too diverse to permit the simple, straightforward biological development that the evolutionary explanation assumes. Fourth, evolutionary arguments implicitly justify existing gender inequality by implying the need to confine women and men to their traditional roles.
Recent anthropological evidence also challenges the evolutionary argument that men’s tendency to commit violence was biologically transmitted. This evidence instead finds that violent men have trouble finding female mates who would want them and that the female mates they find and the children they produce are often killed by rivals to the men (Begley, 2009).
A second biological explanation for traditional gender roles attributes males’ higher levels of aggression to their higher levels of testosterone (Mazur, 2009). Several studies find that males with higher levels of testosterone tend to have higher levels of aggression. However, this correlation does not necessarily mean that their testosterone increased their violence; as has been found in various animal species, it is also possible that their violence increased their testosterone. Because studies of human males cannot for ethical and practical reasons manipulate their testosterone levels, the exact meaning of the results from these testosterone-aggression studies must remain unclear, according to a report by the National Academy of Sciences (Miczek, Mirsky, Carey, DeBold, & Raine, 1994).
Another line of research on the biological basis for sex differences in aggression involves children, including some as young as ages 1 or 2, in various situations (Card, Stucky, Sawalani, & Little, 2008). They might be playing with each other, interacting with adults, or writing down solutions to hypothetical scenarios given to them by a researcher. In most of these studies, boys are more physically aggressive in thought or deed than girls, even at a very young age. Other studies are more experimental in nature. In one type of study, a toddler will be playing with a toy, only to have it removed by an adult. Boys typically tend to look angry and try to grab the toy back, while girls tend to just sit there and whimper. Because these gender differences in aggression are found at very young ages, researchers often say they must have some biological basis. However, critics of this line of research counter that even young children have already been socialized along gender lines (Begley, 2009; Fine, 2011), a point to which we return later in the chapter. To the extent this is true, gender differences in children’s aggression may reflect socialization rather than biology.
In sum, biological evidence for gender differences certainly exists, but its interpretation remains very controversial. It must be weighed against the evidence, to which we next turn, of cultural variations in the experience of gender and of socialization differences by gender. One thing is clear: To the extent we accept biological explanations for gender, we imply that existing gender differences and gender inequality must continue to exist. As sociologist Linda L. Lindsey (2011, p. 52) notes, “Biological arguments are consistently drawn upon to justify gender inequality and the continued oppression of women.” In contrast, cultural and social explanations of gender differences and gender inequality promise some hope for change. Let’s examine the evidence for these explanations.
Culture and Gender
Some of the most compelling evidence against a strong biological determination of gender roles comes from anthropologists, whose work on preindustrial societies demonstrates some striking gender variation from one culture to another. This variation underscores the impact of culture on how females and males think and behave.
Extensive evidence of this impact comes from anthropologist George Murdock (1937), who created the Standard Cross-Cultural Sample of almost two hundred preindustrial societies studied by anthropologists. Murdock found that some tasks in these societies, such as hunting and trapping, are almost always done by men, while other tasks, such as cooking and fetching water, are almost always done by women. These patterns provide evidence for the evolutionary argument presented earlier, as they probably stem from the biological differences between the sexes. Even so, there were at least some societies in which women hunted and in which men cooked and fetched water.
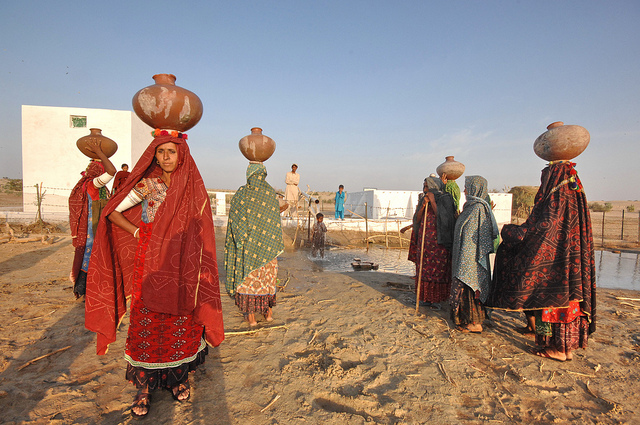

Anthropological research finds a good deal of variation in gender roles for certain tasks, including planting crops, milking, and generating fires. Other tasks, such as hunting and trapping, are typically done by men while tasks such as cooking and fetching water are typically done by women.
World Bank Photo Collection – Somo Samo village well – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
More important, Murdock found much greater gender variation in several of the other tasks he studied, including planting crops, milking, and generating fires. Men primarily performed these tasks in some societies, women primarily performed them in other societies, and in still other societies both sexes performed them equally. Murdock’s findings illustrate how gender roles differ from one culture to another and imply they are not biologically determined.
Anthropologists continue to investigate cultural differences in gender. Some of their most interesting findings concern gender and sexuality (Brettell & Sargent, 2009). Although all societies distinguish “femaleness” and “maleness,” additional gender categories exist in some societies. The Native Americans known as the Mohave, for example, recognize four genders: a woman, a woman who acts like a man, a man, and a man who acts like a woman. In some societies, a third, intermediary gender category is recognized. Anthropologists call this category the berdache, who is usually a man who takes on a woman’s role. This intermediary category combines aspects of both femininity and masculinity of the society in which it is found and is thus considered an androgynous gender. Although some people in this category are born as intersexed individuals (formerly known as hermaphrodites), meaning they have genitalia of both sexes, many are born biologically as one sex or the other but adopt an androgynous identity.
Anthropologists have found another androgynous gender composed of women warriors in thirty-three Native American groups in North America. Walter L. Williams (1997) calls these women “amazons” and notes that they dress like men and sometimes even marry women. In some tribes girls exhibit such “masculine” characteristics from childhood, while in others they may be recruited into “amazonhood.” In the Kaska Indians, for example, a married couple with too many daughters would select one to “be like a man.” When she was about 5 years of age, her parents would begin to dress her like a boy and have her do male tasks. Eventually she would grow up to become a hunter.
The androgynous genders found by anthropologists remind us that gender is a social construction and not just a biological fact. If culture does affect gender roles, socialization is the process through which culture has this effect. What we experience as girls and boys strongly influences how we develop as women and men in terms of behavior and attitudes. To illustrate this important dimension of gender, let’s turn to the evidence on socialization.
Socialization and Gender
Socialization is the process whereby individuals learn the culture of their society. Several agents of socialization exist, including the family, peers, schools, the mass media, and religion, and all these institutions help to socialize people into their gender roles and also help them develop their gender identity (Andersen & Hysock, 2011).
The Family
Socialization into gender roles begins in infancy, as almost from the moment of birth parents begin to socialize their children as boys or girls without even knowing it (Begley, 2009; Eliot, 2011). Parents commonly describe their infant daughters as pretty, soft, and delicate and their infant sons as strong, active, and alert, even though neutral observers find no such gender differences among infants when they do not know the infants’ sex. From infancy on, parents play with and otherwise interact with their daughters and sons differently. They play more roughly with their sons—for example, by throwing them up in the air or by gently wrestling with them—and more quietly with their daughters. When their infant or toddler daughters cry, they warmly comfort them, but they tend to let their sons cry longer and to comfort them less. They give their girls dolls to play with and their boys action figures and toy guns. While these gender differences in socialization are probably smaller now than a generation ago, they certainly continue to exist. Go into a large toy store and you will see pink aisles of dolls and cooking sets and blue aisles of action figures, toy guns, and related items.
Peers
Peer influences also encourage gender socialization. As they reach school age, children begin to play different games based on their gender. Boys tend to play sports and other competitive team games governed by inflexible rules and relatively large numbers of roles, while girls tend to play smaller, cooperative games such as hopscotch and jumping rope with fewer and more flexible rules. Although girls are much more involved in sports now than a generation ago, these gender differences in their play persist and continue to reinforce gender roles. For example, boys’ games encourage them to be competitive, while girls’ games encourage them to become cooperative and trusting. The patterns we see in adult males and females thus have roots in their play as young children (Lindsey, 2011) (see Note 4.13 “Children and Our Future”).
Children and Our Future
Girls and Boys at Play
The text discusses how the types of games that girls and boys play influence their gender-role socialization. Let’s take a closer look at two early sociological studies that provided important evidence for this process.
Janet Lever (1978) studied fifth-grade children in three different communities in Connecticut. She watched them play and otherwise interact in school and also had the children keep diaries of their play and games outside school. Lever found that boys’ games were typically more complex than girls’ games: The boys’ games had a greater number of rules and more specialized roles, and they also involved more individuals playing. She attributed these differences to socialization by parents, teachers, and other adults and argued that the complexity of boys’ play and games helped them to be better able than girls to learn important social skills such as dealing with rules and coordinating actions to achieve goals.
A second sociologist, Barrie Thorne (1993), studied fourth- and fifth-graders in California and Michigan. The boys tended to play team sports and other competitive games, while the girls tended to play cooperative games such as jump rope. These differences led Thorne to conclude that gender-role socialization stems not only from practices by adults but also from the children’s own activities without adult involvement. When boys and girls interacted, it was often “girls against the boys” in classroom spelling contests and in games such as tag. Thorne concluded that these “us against them” contests helped the children learn that boys and girls are two different and antagonistic sexes. Boys also tended to disrupt girls’ games more than the reverse and in this manner both exerted and learned dominance over females. In all these ways, children were not just the passive recipients of gender-role socialization from adults (their teachers), but they also played an active role in ensuring that such socialization occurred.
These two studies were among the first to emphasize the importance of children’s play for the gender-based traits and values that girls and boys learn, which in turn affect the choices they make for careers and other matters later in life. The rise in team sports opportunities for girls in the years since Lever and Thorne did their research is a welcome development, but young children continue to play in the ways that Lever and Thorne found. The body of research on gender differences in children’s play points to the need for teachers, parents, and other adults to encourage girls and boys alike to have a mixture of both competitive and cooperative games so that both sexes may develop a better balance of values that are now commonly considered to be either feminine or masculine.
Schools
School is yet another agent of gender socialization. First of all, school playgrounds provide a location for the gender-linked play activities just described to occur. Second, and perhaps more important, teachers at all levels treat their female and male students differently in subtle ways of which they are probably not aware. They tend to call on boys more often to answer questions in class and to praise them more when they give the right answer. They also give boys more feedback about their assignments and other school work (Sadker & Sadker, 1994). At all grade levels, many textbooks and other books still portray people in gender-stereotyped ways. It is true that the newer books do less of this than older ones, but the newer books still contain some stereotypes, and the older books are still used in many schools, especially those that cannot afford to buy newer volumes.
Mass Media
Gender socialization also occurs through the mass media (Renzetti, Curran, & Maier, 2012). On children’s television shows, the major characters are male. On Nickelodeon, for example, the very popular SpongeBob SquarePants is a male, as are his pet snail, Gary; his best friend, Patrick Star; their neighbor, Squidward Tentacles; and SpongeBob’s employer, Eugene Crabs. Of the major characters in Bikini Bottom, only Sandy Cheeks is a female. For all its virtues, Sesame Street features Bert, Ernie, Cookie Monster, and other male characters. Most of the Muppets are males, and the main female character, Miss Piggy, depicted as vain and jealous, is hardly an admirable female role model. As for adults’ prime-time television, more men than women continue to fill more major roles in weekly shows, despite notable women’s roles in shows such as The Good Wife and Grey’s Anatomy. Women are also often portrayed as unintelligent or frivolous individuals who are there more for their looks than for anything else. Television commercials reinforce this image. Cosmetics ads abound, suggesting not only that a major task for women is to look good but also that their sense of self-worth stems from looking good. Other commercials show women becoming ecstatic over achieving a clean floor or sparkling laundry. Judging from the world of television commercials, then, women’s chief goals in life are to look good and to have a clean house. At the same time, men’s chief goals, judging from many commercials, are to drink beer and drive cars.

Women’s magazines reinforce the view that women need to be slender and wear many cosmetics in order to be considered beautiful.
Photo Editing Services Tucia.com – Glamour /Fashion Retouching by Tucia – CC BY 2.0.
Women’s and men’s magazines reinforce these gender images (Hesse-Biber, 2007; Milillo, 2008). Most of the magazines intended for teenaged girls and adult women are filled with pictures of thin, beautiful models; advice on dieting; cosmetics ads; and articles on how to win and please your man. Conversely, the magazines intended for teenaged boys and men are filled with ads and articles on cars and sports, advice on how to succeed in careers and other endeavors, and pictures of thin, beautiful (and sometimes nude) women. These magazine images again suggest that women’s chief goals are to look good and to please men and that men’s chief goals are to succeed, win over women, and live life in the fast lane.
Religion
Another agent of socialization, religion, also contributes to traditional gender stereotypes. Many traditional interpretations of the Bible yield the message that women are subservient to men (Tanenbaum, 2009). This message begins in Genesis, where the first human is Adam, and Eve was made from one of his ribs. The major figures in the rest of the Bible are men, and women are for the most part depicted as wives, mothers, temptresses, and prostitutes; they are praised for their roles as wives and mothers and condemned for their other roles. More generally, women are constantly depicted as the property of men. The Ten Commandments includes a neighbor’s wife with his house, ox, and other objects as things not to be coveted (Exodus 20:17), and many biblical passages say explicitly that women belong to men, such as this one from the New Testament: “Wives be subject to your husbands, as to the Lord. For the husband is the head of the wife as Christ is the head of the Church. As the Church is subject to Christ, so let wives also be subject in everything to their husbands” (Ephesians 5:22–24).
Several passages in the Old Testament justify the rape and murder of women and girls. The Koran, the sacred book of Islam, also contains passages asserting the subordinate role of women (Mayer, 2009).
A Final Word on the Sources of Gender
Scholars in many fields continue to debate the relative importance of biology and of culture and socialization for how we behave and think as girls and boys and as women and men. The biological differences between females and males lead many scholars and no doubt much of the public to assume that masculinity and femininity are to a large degree biologically determined or at least influenced. In contrast, anthropologists, sociologists, and other social scientists tend to view gender as a social construction. Even if biology does matter for gender, they say, the significance of culture and socialization should not be underestimated. To the extent that gender is indeed shaped by society and culture, it is possible to change gender and to help bring about a society where both men and women have more opportunity to achieve their full potential.
Key Takeaways
- Sex is a biological concept, while gender is a social concept and refers to the social and cultural differences a society assigns to people based on their sex.
- Several biological explanations for gender roles exist, but sociologists think culture and socialization are more important sources of gender roles than biology.
- Families, schools, peers, the mass media, and religion are agents of socialization for the development of gender identity and gender roles.
For Your Review
- Write a short essay about one or two events you recall from your childhood that reflected or reinforced your gender socialization.
- Do you think gender roles are due more to biology or to culture and socialization? Explain your answer.
References
Andersen, M., & Hysock, D. (2011). Thinking about women: Sociological perspectives on sex and gender (9th ed.). Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon.
Aulette, J. R., & Wittner, J. (2011). Gendered worlds (2nd ed.). New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
Begley, S. (2009, June 29). Don’t blame the caveman. Newsweek, 52–62.
Begley, S. (2009, September 14). Pink brain, blue brain: Claims of sex differences fall apart. Newsweek, 28
Brettell, C. B., & Sargent, C. F. (Eds.). (2009). Gender in cross-cultural perspective (5th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Browne, K. (2002). Biology at work: Rethinking sexual equality. New Brunswick, NJ: Rutgers University Press.
Buss, D. (2012). Evolutionary psychology: The new science of the mind (4th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson.
Card, N. A., Stucky, B. D., Sawalani, G. M., & Little, T. D. (2008). Direct and indirect aggression during childhood and adolescence: A meta-analytic review of gender differences, intercorrelations, and relations to maladjustment. Child Development, 79(5), 1185–1229.
Eliot, L. (2011). Pink brain, blue brain: How small differences grow into troublesome gaps—and what we can do about it. London, United Kingdom: Oneworld Publications.
Fine, C. (2011). Delusions of gender: The real science behind sex differences. New York, NY: W. W. Norton.
Hesse-Biber, S. N. (2007). The cult of thinness. New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
Lever, J. (1978). Sex differences in the complexity of children’s play and games. American Sociological Review, 43, 471–483.
Lindsey, L. L. (2011). Gender roles: A sociological perspective (5th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Mayer, A. E. (2009). Review of “Women, the Koran and international human rights law: The experience of Pakistan.” Human Rights Quarterly, 31(4), 1155–1158.
Mazur, A. (2009). Testosterone and violence among young men. In A. Walsh & K. M. Beaver (Eds.), Biosocial criminology: New directions in theory and research (pp. 190–204). New York, NY: Routledge.
Miczek, K. A., Mirsky, A. F., Carey, G., DeBold, J., & Raine, A. (1994). An overview of biological influences on violent behavior. In J. Albert, J. Reiss, K. A. Miczek & J. A. Roth (Eds.), Understanding and preventing violence: Biobehavioral influences (Vol. 2, pp. 1–20). Washington, DC: National Academy Press.
Milillo, D. (2008). Sexuality sells: A content analysis of lesbian and heterosexual women’s bodies in magazine advertisements. Journal of Lesbian Studies, 12(4), 381–392.
Murdock, G. (1937). Comparative data on the division of labor by sex. Social Forces, 15, 551–553.
Renzetti, C. M., Curran, D. J., & Maier, S. (2012). Women, men, and society. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson.
Sadker, M., & Sadker, D. (1994). Failing at fairness: How America’s schools cheat girls. New York, NY: Charles Scribner’s.
Tanenbaum, L. (2009). Taking back God: American women rising up for religious equality. New York, NY: Farrar, Straus and Giroux.
Thorne, B. (1993). Gender play: Girls and boys in school. New Brunswick, NJ: Rutgers University Press.
Thornhill, R., & Gangestad, S. W. (2008). The evolutionary biology of human female sexuality. New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
Williams, W. L. (1997). Amazons of America: Female gender variance. In C. B. Brettell & C. F. Sargent (Eds.), Gender in cross-cultural perspective (2nd ed., pp. 202–213). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.