Basic Concepts Related to Antimicrobial Therapy
Before we learn about medications that are used to treat infections in our patients, we must first understand the basics of microbiology. Let’s begin with a review of bacteria. Bacteria are found in nearly every habitat on earth, including within and on humans. Most bacteria are harmless or considered helpful, but some are pathogens. A pathogen is defined as an organism causing disease to its host. Pathogens, when overgrown, can cause significant health problems or even death for your patients.
Bacteria may be identified when a patient has an infection by using a culture and sensitivity test or a gram stain test. Antimicrobials may be classified as broad-spectrum or narrow-spectrum, based on the variety of bacteria they effectively treat. Additionally, antibiotics may be bacteriostatic or bactericidal in terms of how they target the bacteria. Finally, the mechanism of action is also considered in the selection of an antibiotic.
In addition to antibiotics, antimicrobials also include medications used to treat viruses and fungi. Each of these topics will be discussed in more detail below, along with the issue of drug resistance.
Culture and Sensitivity
When a patient presents signs or symptoms of an infection, health care providers will begin the detective work needed to identify the source of the infection. A culture is a test performed to examine different body substances for the presence of bacteria or fungus.[1] These culture samples are commonly collected from a patient’s blood, urine, sputum, or wound bed.
Nurses are commonly responsible for the collection of culture samples and must be conscientious to collect the sample prior to the administration of antibiotics. Antibiotic administration prior to a culture can result in a delayed identification of the organism and complicate the patient’s recovery. After culture samples are collected, they are incubated in a solution that promotes bacterial or fungal growth and spread onto a special culture plate.[2] Clinical microbiologists subsequently monitor the culture for signs of organism growth to aid in the diagnosis of the infectious pathogen. A sensitivity analysis is often performed to select an effective antibiotic to treat the microorganism. If the organism shows resistance to the antibiotics used in the test, those antibiotics will not provide effective treatment for the patient’s infection. Sometimes a patient may begin antibiotic treatment for an infection, but will be switched to a different, more effective antibiotic based on the culture and sensitivity results.[3]
Gram-Positive vs. Gram-Negative
A gram stain is another type of test that is used to assist in classification of pathogens. Gram stains are useful for quickly identifying if bacteria are “gram-positive” or “gram-negative,” based on the staining patterns of their cellular walls. Utilizing gram stain allows microbiologists to look for characteristic violet (Gram +) or red/pink (Gram -) staining patterns when they examine the organisms under a microscope.[4] Identification of bacteria as gram-positive or gram-negative assists the health care provider in quickly selecting an appropriate antibiotic to treat the infection.
Sample Gram-Positive Infections
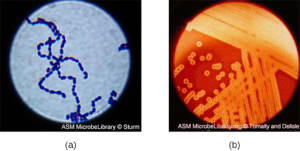
Streptococcus, the name which comes from the Greek word for twisted chain, is responsible for many types of infectious diseases in humans. Streptococcus is an example of a Gram + infection and is identified by its ability to lyse, or breakdown, red blood cells when grown on blood agar.
S. pyogenes is a type of β-hemolytic Streptococcus. This species is considered a pyogenic pathogen because of the associated pus production observed with infections it causes (see Figure 3.1[5] for an image of Streptococcus undergoing gram staining). S. pyogenes is the most common cause of bacterial pharyngitis (strep throat); it is also a common cause of various skin infections that can be relatively mild (e.g., impetigo) or life-threatening (e.g., necrotizing fasciitis, also known as flesh-eating disease).[6]
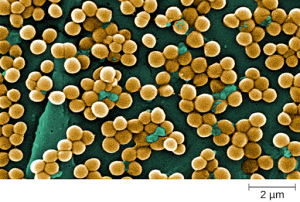
Staphylococcus is a second example of a Gram + bacteria. The bacteria Staphylococcus comes from a Greek word for bunches of grapes, which describes their microscopic appearance in culture. Strains of S. aureus cause a wide variety of infections in humans, including skin infections that produce boils, carbuncles, cellulitis, or impetigo. Many strains of S. aureus have developed resistance to antibiotics. Some antibiotic-resistant strains are designated as methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant S. aureus (VRSA) . These strains, but not just methicillin and vancomycin, are some of the most difficult to treat because they exhibit resistance to nearly all available antibiotics. Because they are difficult to treat with antibiotics, infections can be lethal. MRSA and VRSA are also contagious, posing a serious threat in hospitals, nursing homes, dialysis facilities, and other places where there are large populations of elderly, bedridden, and/or immunocompromised patients.[7] See Figure 3.2[8] for an image of Staphylococcus bacteria microscopically.
Sample Gram-Negative Infections
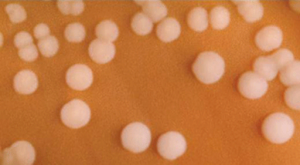
Gram-negative bacteria often grow between aerobic and anaerobic areas (such as in the intestines). Some gram-negative bacteria cause severe, sometimes life-threatening, disease. The genus Neisseria, for example, includes the bacteria N. gonorrhoeae, the causative agent of the sexually transmitted infection gonorrhea, and N. meningitides, the causative agent of bacterial meningitis. See Figure 3.3[9] for an image of Neisseria meningitides. Another common gram-negative infection that is seen in hospitalized patients is Escherichia coli (E. coli). This is a frequent culprit for urinary tract infections due to its presence in the GI tract.
Broad-Spectrum vs. Narrow-Spectrum Antimicrobials
Spectrum of activity is one of the factors that providers use when selecting antibiotics to treat a patient’s infection. A narrow-spectrum antimicrobial targets only specific subsets of bacterial pathogens.[10] For example, some narrow-spectrum drugs only target gram-positive bacteria, but others target only gram-negative bacteria. If the pathogen causing infection has been identified in a culture and sensitivity test, it is best to use a narrow-spectrum antimicrobial and minimize collateral damage to the normal microbacteria.
A broad-spectrum antimicrobial targets a wide variety of bacterial pathogens, including both gram-positive and gram-negative species, and is frequently used to cover a wide range of potential pathogens while waiting on the laboratory identification of the infecting pathogen. Broad-spectrum antimicrobials are also used for polymicrobial infections (a mixed infection with multiple bacterial species) or as prophylactic prevention of infections with surgery/invasive procedures. Finally, broad-spectrum antimicrobials may be selected to treat an infection when a narrow-spectrum drug fails because of development of drug resistance by the target pathogen.[11]
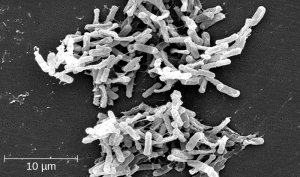
One risk associated with using broad-spectrum antimicrobials is that they will also target a broad spectrum of the normal microbacteria that can cause diarrhea. They also increase the risk of a superinfection , a secondary infection in a patient having a preexisting infection. A superinfection develops when the antibacterial intended for the preexisting infection kills the protective microbiota, allowing another pathogen resistant to the antibacterial to proliferate and cause a secondary infection. Common examples of superinfections that develop as a result of antimicrobial use include yeast infections (candidiasis) and pseudomembranous colitis caused by Clostridium difficile (C-diff), which can be fatal.[12] Probiotics, such as lactobacillus, are commonly used for individuals with C-diff to introduce normal bacteria into the gastrointestinal system and improve bowel function. See Figure 3.4[13] for an image of C-diff microscopically.
Recap
- A broad-spectrum antibiotic will treat gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
- A narrow-spectrum antibiotic will treat either gram-positive or gram-negative bacteria.
If a patient is started on an antibiotic that is gram + and the culture identifies a gram – organism, the medication will not improve the patient’s status. The selection of an incorrect antibiotic can lead to adverse reactions and increase bacterial resistance.
At times, a broad-spectrum antibiotic may be administered prior to receiving the culture report due to the severity of the illness of the patient. Once the culture is reported, the antibiotic therapy is tailored to the patient. It is the nurse’s responsibility to review culture results and ensure that the results have been communicated to the prescribing provider.
Antibacterial Actions: Bacteriostatic vs. Bactericidal
When a provider selects an antibacterial drug, it is important to consider how and where the drug will ultimately target the bacteria. Antibacterial drugs can be either bacteriostatic or bactericidal in their interactions with the offending bacteria. Bacteriostatic drugs cause bacteria to stop reproducing; however, they may not ultimately kill the bacteria. In contrast, bactericidal drugs kill their target bacteria.
The decision about whether to use a bacteriostatic or bactericidal drug often depends on the type of infection and the overall immune status of the patient. In a healthy patient with strong immune defenses, both bacteriostatic and bactericidal drugs can be effective in achieving clinical cure. However, when a patient is immunocompromised, a bactericidal drug is essential for the successful treatment of infections. Regardless of the immune status of the patient, life-threatening infections such as acute endocarditis require the use of a bactericidal drug to eliminate all offending bacteria.[14]
Mechanism of Action
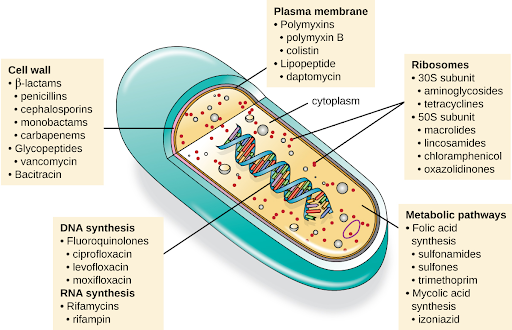
Another consideration in the selection of an antibacterial drug is the drug’s mechanism of action. Each class of antibacterial drugs has a unique mechanism of action , the way in which a drug affects microbes at the cellular level. For example, cephalosporins act on the integrity of the cell wall. In contrast, aminoglycosides impact ribosome function and inhibit protein synthesis, which stops the proliferation of cells.[15] See Figure 3.5[16] for a summary of how various antibiotics affect the cell wall, the plasma membrane, the ribosomes, the metabolic pathways, or DNA synthesis of bacteria.
Antiviral
Similar to antibacterial medications, antiviral drugs directly impact interaction and reproduction of the offending microorganism. Antibacterial medications are required for treating bacterial infections; antivirals treat specific viral infections. For example, oseltamivir (Tamiflu) is commonly prescribed to treat influenza. Unlike antimicrobials, antiviral medications do not kill the offending virus, but they work to reduce replication and development of the virus.[17]
Antifungal
Antifungal, or antimycotic agents, are medications that are used to treat fungal infections. These medications work by killing the cells of the fungus or inhibiting the reproduction of the cells. Unlike antibacterial and antiviral medications, many antifungals are applied topically to the affected area. Fungal infections commonly affect surface areas of the body, including the toes, nails, mouth, groin, etc. For example, Candida albicans is a type of fungi that when overgrown in the mouth produces oral thrush. Patients experiencing thrush may be prescribed oral antifungal swish and spit medication such as nystatin.
Drug Resistance
Although there is a wide availability of medications that are useful for treating infection, greater limitations in effectiveness are being seen. According to the Centers for Disease Control, each year in the United States, at least 2 million people are infected with an antibiotic-resistant infection, and more than 23,000 die.[18]
Prevention Strategies
In the United States and many other countries, most antimicrobial drugs are self-administered by patients at home. Unfortunately, many patients stop taking antimicrobials once their symptoms dissipate and they feel better. If a ten-day course of treatment is prescribed, many patients only take the drug for five or six days, unaware of the negative consequences of not completing the full course of treatment.
The problem with failing to complete a full course of treatment is this not only fails to kill the target organisms to the expected levels but also facilitates the development of drug-resistant variants within the body. A patient’s nonadherence amplifies drug resistance when the recommended course of treatment is long.
For example, treatment for tuberculosis (TB) has a recommended treatment regimen lasting from six months to a year. The CDC estimates that about one third of the world’s population is infected with TB, most living in underdeveloped or underserved regions where antimicrobial drugs are available over the counter. In such countries, there may be even lower rates of adherence than in developed areas. Nonadherence leads to antibiotic resistance and more difficulty in controlling pathogens. As a direct result, the emergence of multidrug-resistant strains of TB is becoming a significant problem.
The overprescription of antimicrobials also contributes to antibiotic resistance. Patients often demand antibiotics for diseases that do not require them, like viral colds and ear infections. Pharmaceutical companies aggressively market drugs to physicians and clinics, making it easy for them to give free samples to patients, and some pharmacies even offer certain antibiotics free to low-income patients with a prescription.
In recent years, various initiatives have been aimed to educate parents and clinicians about the judicious use of antibiotics. However, previous studies have shown the parental expectations for antimicrobial prescriptions for children actually increased.
One possible solution is a regimen called directly observed therapy (DOT), which involves the supervised administration of medications to patients. Patients are either required to visit a health care facility to receive their medications, or health care professionals administer medication in patients’ homes or another designated location. DOT has been implemented in many cases for the treatment of TB and has been shown to be effective. DOT is an integral part of WHO’s global strategy for eradicating TB.
But is DOT a practical strategy for all antibiotics? Would patients taking penicillin, for example, be more or less likely to adhere to the full course of treatment if they had to travel to a health care facility to receive each dose? Who would pay for the increased cost associated with DOT?
When it comes to overprescription , should providers or drug companies be policed when it comes to overprescribing antibiotics to enforce best practices? What group should assume this responsibility, and what penalties would be effective in discouraging overprescription?
This is a complex issue with no clear, easy solution. However, what is clear is that all patients need extensive education regarding the judicious and complete use of medications to increase adherence and decrease the opportunity for antimicrobial resistance.[19]
Critical Thinking Activity 3.2
Reflecting on current health care challenges regarding the ongoing emergence of antimicrobial-resistant organisms, what actions could you take within your nursing practice to help prevent drug resistance?
Note: Answers to the Critical Thinking activities can be found in the “Answer Key” sections at the end of the book.
Interactive Activity
[h5p id=”6″]
- This work is a derivative of Microbiology by OpenStax licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/microbiology/pages/1-introduction ↵
- Kristof, K., & Pongracz, J. (2016). Interpretation of blood microbiology results - function of the clinical microbiologist. The Journal of the International Federation of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine, 27(2), 147-155. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4975230/ ↵
- Vorvick, L. (Ed.). (2019, February 7). Sensitivity analysis. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003741.htm ↵
- This work is a derivative of Microbiology by OpenStax licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/microbiology/pages/1-introduction ↵
- “OSC Microbio 04 04 Strep.jpg” by CNX OpenStax is licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/microbiology/pages/4-4-gram-positive-bacteria ↵
- This work is a derivative of Microbiology by OpenStax licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/microbiology/pages/1-introduction ↵
- This work is a derivative of Microbiology by OpenStax licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/microbiology/pages/1-introduction ↵
- This work is a derivative of “CDC-10046-MRSA.jpg” by Janice Haney Carr, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and is licensed under CC0 ↵
- “OSC Microbio 04 02 Neisseria.jpg” by CNX OpenStax is licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/microbiology/pages/4-2-proteobacteria ↵
- This work is a derivative of Microbiology by OpenStax licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/microbiology/pages/1-introduction ↵
- This work is a derivative of Microbiology by OpenStax licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/microbiology/pages/1-introduction ↵
- This work is a derivative of Microbiology by OpenStax licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/microbiology/pages/1-introduction ↵
- This work is a derivative of “Clostridium difficile 01.jpg” by Lois D. Wiggs at Centers of Disease Control and Prevention and is licensed under CC0 ↵
- This work is a derivative of Microbiology by OpenStax licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/microbiology/pages/1-introduction ↵
- This work is a derivative of Microbiology by OpenStax licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/microbiology/pages/1-introduction ↵
- “OSC Microbio 14 02 Modes.jpg” by CNX Openstax is licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/microbiology/pages/14-3-mechanisms-of-antibacterial-drugs ↵
- This work is a derivative of Microbiology by OpenStax licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/microbiology/pages/1-introduction ↵
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2022). About antimicrobial resistance. https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/about.html ↵
- This work is a derivative of Microbiology by OpenStax licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/microbiology/pages/1-introduction ↵
- “Antimicrobial Definitions” by E. Christman for Open RN is licensed under CC BY 4.0 ↵
An organism causing disease to its host.
A test performed to examine different body substances for the presence of bacteria or fungus.
A test performed in addition to a culture in order to select an effective antibiotic to treat the microorganism.
A characteristic of bacteria demonstrated lack of effective treatment by an antibiotic when a sensitivity analysis is performed.
A test used to quickly diagnose bacterial infection. Identification of bacteria as gram + or gram - assists the health care provider in selecting an appropriate antibiotic to treat the infection.
Infections caused by Streptococcus and Staphylococcus bacteria are examples of Gram + infection.
An infection caused by Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus that is difficult to treat because it exhibits resistance to nearly all available antibiotics.
An infection caused by Vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus that is difficult to treat because it exhibits resistance to nearly all available antibiotics.
Infections that often grow between aerobic and anaerobic areas.
An antibiotic that targets only specific subsets of bacterial pathogens.
An antibiotic that targets a wide variety of bacterial pathogens, including both gram-positive and gram-negative species.
A secondary infection in a patient having a preexisting infection. C-diff and yeast infections as a result of antibiotic therapy are examples of superinfections.
Clostridium difficile causes pseudomembranous colitis, a superinfection that can be caused by broad spectrum antibiotic therapy.
Antimicrobial drugs that cause bacteria to stop reproducing but may not ultimately kill the bacteria.
Antimicrobial drugs that kill their target bacteria.
How a medication works within the body.
Medications used to treat viral infections. For example, Tamiflu is used to treat influenza.
Medications that are used to treat fungal infections. For example, nystatin is used to treat Candida Albicans, a fungal infection.
