The administration of antimicrobial drug therapy involves special considerations to ensure that the therapeutic drug effect is achieved while maintaining patient safety and minimizing complications.
Let’s consider some of the variables that may impact antimicrobial administration:
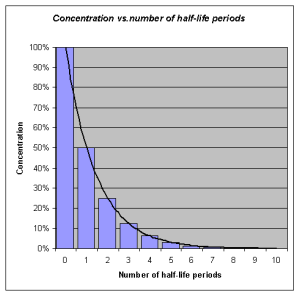
Half-Life
Many antimicrobial medications are administered to ensure a certain therapeutic level of medication remains in the bloodstream, which may require interval or repeated dosing throughout the day. The half-life, or rate at which 50% of a drug is eliminated from the plasma, can vary significantly between drugs. Some drugs have a short half-life of only 1 hour and must be given multiple times a day, but other drugs have half-lives exceeding 12 hours and can be given as a single dose every 24 hours. Although a longer half-life can be considered an advantage for an antibacterial when it comes to convenient dosing intervals, the longer half-life can also be a concern for a drug with serious side effects. Medications that have longer half-life and more concerning side effects will exert these side effects over a longer period of time.
See Figure 3.6[1] for an illustration of half-life and the time it takes for a medication to be eliminated from the bloodstream.
Life Span Considerations
Many medications are calculated based on the patient’s age and weight. Patient age and size are especially vital in pediatric patients. A child’s stage of development and the size of their internal organs impact how the body absorbs, digests, metabolizes, and eliminates medications.
Liver & Renal Function
There are many antimicrobial medications that require tailored dosing based on individual patient response and the impact of the medication on the patient’s liver and renal function. For more information about the effects of liver and renal function on medications, refer to Chapter 1 regarding metabolism and excretion. Often times, pharmacists and providers will evaluate drug peak and trough drug blood levels to determine how an individual patient’s body is responding to an antimicrobial. Follow-up interval dosing is then prescribed based on these blood levels. This is especially important for older adults or those with known liver and/or renal impairment. Individuals with diminished liver and renal function are more prone to drug toxicity because of the reduced ability of the body to metabolize or clear medications from the body. For more information about peak and trough levels, refer to Chapter 1 regarding medication safety.[2]
Dose Dependency/Time Dependency
The goal of antimicrobial therapy is to select an optimal dosage that will result in clinical cure, while reducing the patient complications or significant side effects. Many medications may be dose dependent. This means that there is a more significant killing of the bacteria with increasing levels of the antibiotic. For example, fluroquinolones are dose-dependent medications with the treatment goal to optimize the amount of the drug.
Other medications are time dependent. Time-dependent medications have optimal bacterial-killing effect at lower doses over a longer period of time. Time-dependent antimicrobials exert the greatest effect by binding to the microorganism for an extensive length of time. Penicillin is an example of a time-dependent medication where the goal is to optimize the duration of exposure.[3]
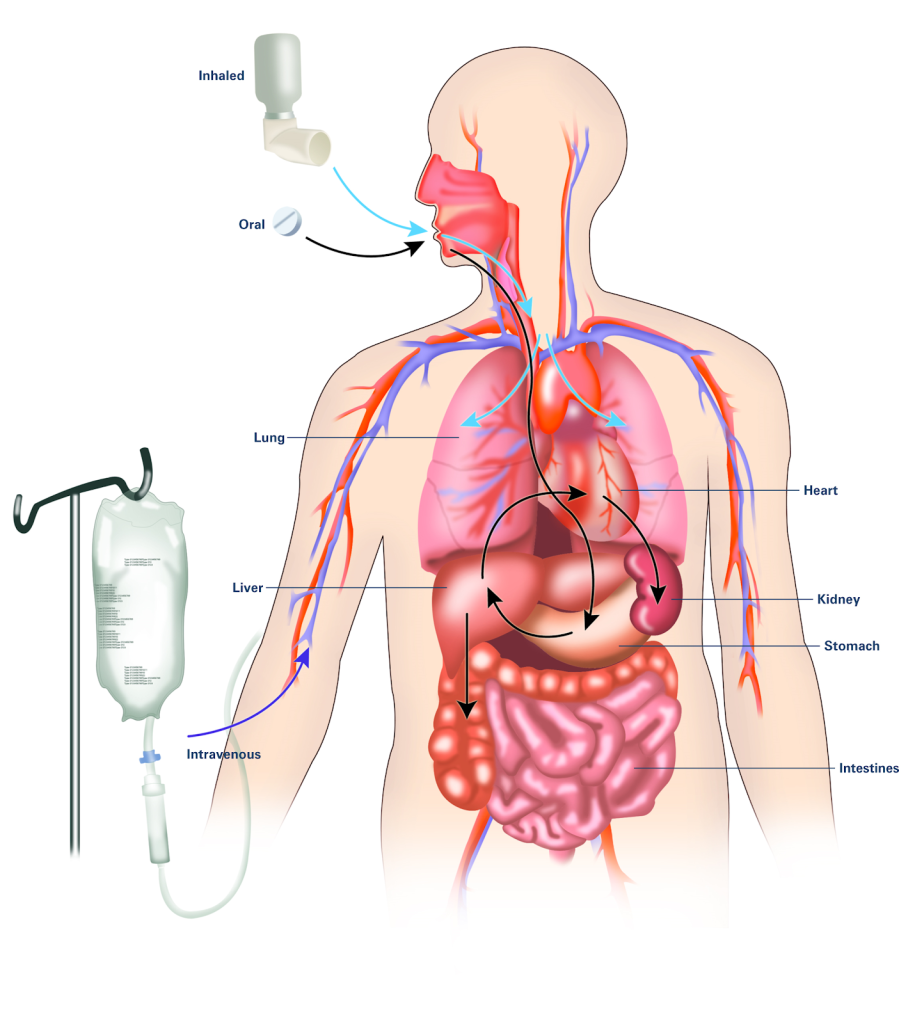
Route
It is also important to consider the route of drug administration within the patient’s body. Many of us may have been prescribed oral antibiotics and have simply filled our prescription and completed the drug regimen within the comfort of our own homes. However, there are many types of infections or disease processes that do not respond well to the use of oral antimicrobial therapy. For these diseases, patients may require intravenous or intramuscular injections. Patients requiring intravenous or intramuscular injections may need to be hospitalized, have home health nursing arranged, or travel to the hospital/clinic for their therapy. Concerns with treatment compliance exists with all routes of administration. For more information about considerations regarding routes of administration, refer to Chapter 1 on absorption. See Figure 3.7[4] for an illustration of three common routes of medication within the body.
Drug Interactions
For the optimum treatment of certain infections, two antibacterial drugs may be administered together. In this manner, concurrent drug administration produces a synergistic interaction that is better than the efficacy of either drug alone. In this case, TWO is truly better than ONE! A classic example of synergistic drug combinations is trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim). Individually, these two drugs provide only bacteriostatic inhibition of bacterial growth, but combined, the drugs are bactericidal.[5]
In contrast to synergistic drug interactions providing a benefit to the patient, antagonistic interactions produce harmful effects. Antagonism can occur between two antimicrobials or between antimicrobials and nonantimicrobials being used to treat other conditions. The effects vary depending on the drugs involved, but antagonistic interactions cause diminished drug activity, decreased therapeutic levels due to elevated metabolism and elimination, or increased potential for toxicity due to decreased metabolism and elimination.
Let’s consider an example of an antagonistic interaction. Many antibacterials are absorbed most effectively from the acidic environment within the stomach. However, if a patient takes antacids, the antacids increase the pH of the stomach and negatively impact the absorption of the antibacterial, thus decreasing their effectiveness in treating an infection.
Interactive Activity
[h5p id=”7″]
- “Concentration_vs_number_of_half-life_periodes.png” by OPPSD is licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 ↵
- This work is a derivative of Microbiology by OpenStax licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/microbiology/pages/1-introduction ↵
- This work is a derivative of Microbiology by OpenStax licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/microbiology/pages/1-introduction ↵
- “A drug's life in the body (with labels)” by National Institute of General Medical Sciences Image and Video Gallery is licensed under CC NC-SA 3.0 ↵
- This work is a derivative of Microbiology by OpenStax licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/microbiology/pages/1-introduction ↵
- “Antimicrobial Knowledge Check” by E. Christman for Open RN is licensed under CC BY 4.0 ↵
The rate at which 50% of a drug is eliminated from the bloodstream.
A more significant response occurs in the body when the medication is administered in large doses to provide a large amount of medication to the site of infection for a short period of time.
Time dependency occurs when greater therapeutic effects are seen with lower blood levels over a longer period of time.
Concurrent drug administration producing a synergistic interaction that is better than the efficacy of either drug alone. An example of synergistic drug combinations is trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim).
Concurrent administration of two drugs causes harmful effects such as a decrease of drug activity, decreased therapeutic levels due to increased metabolism and elimination, or increased potential for toxicity due to decreased metabolism and elimination. An example of an antagonistic interaction is taking antacids with antibiotics, causing decreased absorption of the antibiotic.
