This section will review key anatomy concepts in the autonomic nervous system (ANS) related to the mechanism of action of medications.
To review detailed information regarding the autonomic nervous system, use these hyperlinks to view related content in Open Stax Anatomy and Physiology[1]:
Review the basic structure and function of the nervous system.
Review the anatomy of sensory perception.
Review the anatomy of motor responses.
Review the divisions of the autonomic nervous system.
Review autonomic reflexes and homeostasis.
Review information on a few drugs that affect the autonomic nervous system.
Review of the Anatomy and Functions of the Nervous System
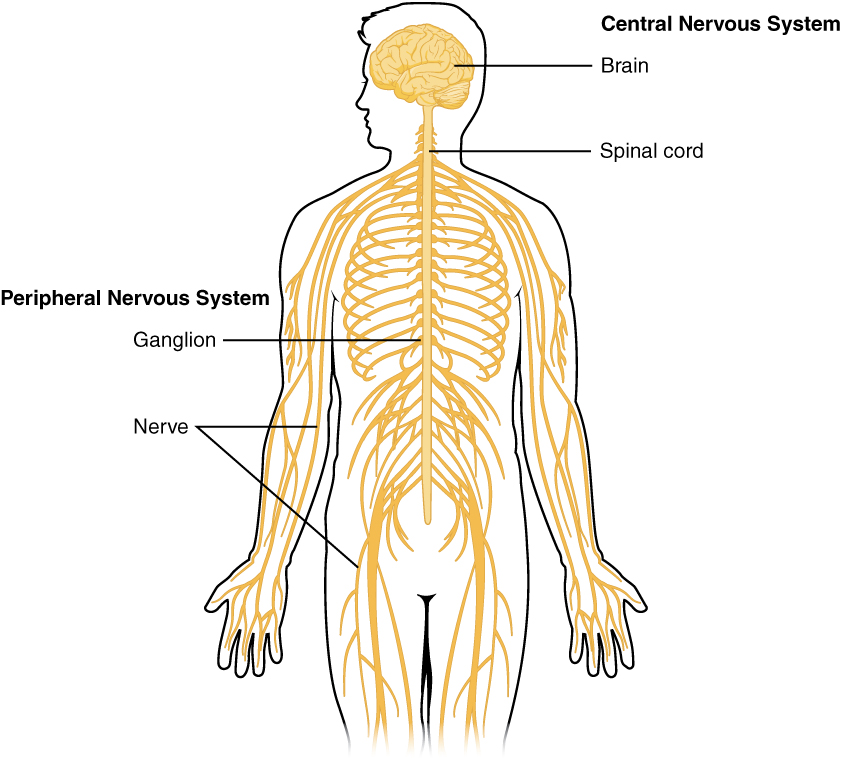
The nervous system has two major components: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system. See Figure 4.1.[2] The central nervous system (CNS) is composed of the brain and the spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes nerves outside the brain and spinal cord and consists of sensory neurons and motor neurons. Sensory neurons sense the environment and conduct signals to the brain that become a conscious perception of that stimulus. This conscious perception may lead to a motor response that is conducted from the brain to the peripheral nervous system via motor neurons to cause a movement. Motor neurons consist of the somatic nervous system that stimulates voluntary movement of muscles and the autonomic nervous system[3] that controls involuntary responses. This chapter will focus on the autonomic nervous system.
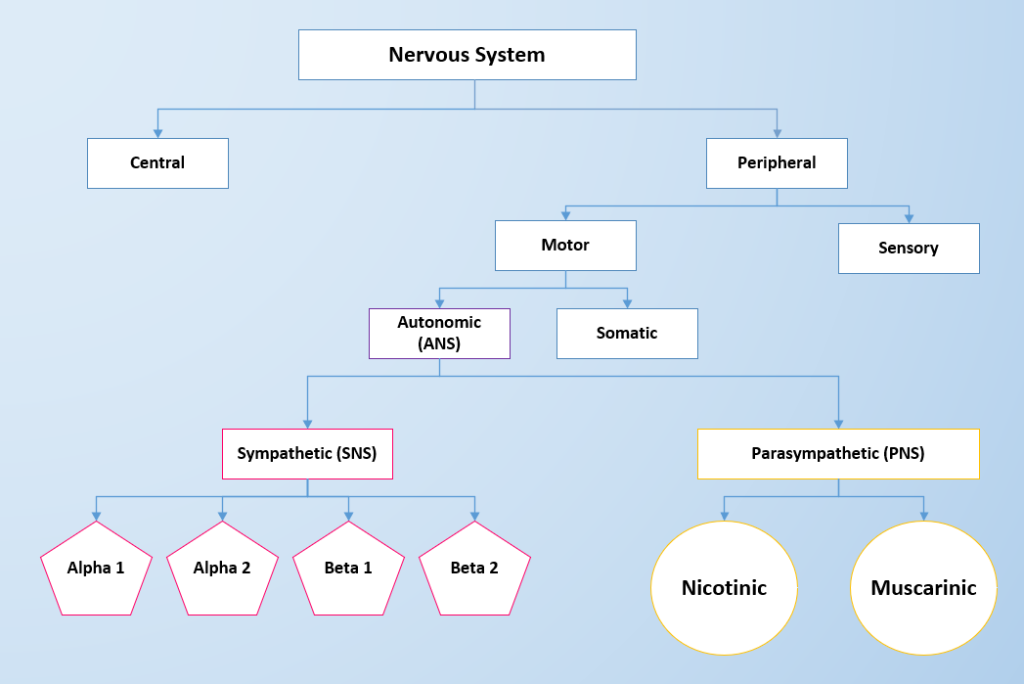
The two divisions of the autonomic nervous system are the sympathetic division (SNS) and the parasympathetic division (PNS). The SNS contains alpha- and beta-receptors, and the PNS contains nicotinic and muscarinic receptors. Each type of receptor has a specific action when stimulated. See Figure 4.2 for an image of the divisions of the nervous system and the receptors in the ANS.[4]
SNS and PNS Functions and Homeostasis
The sympathetic system is associated with the “fight-or-flight” response, and parasympathetic activity is often referred to as “rest and digest.” See Figure 4.3[5] to compare the effects on PNS and SNS stimulation on target organs. The autonomic nervous system regulates many of the internal organs through a balance of these two divisions and is instrumental in homeostatic mechanisms in the body.[6]
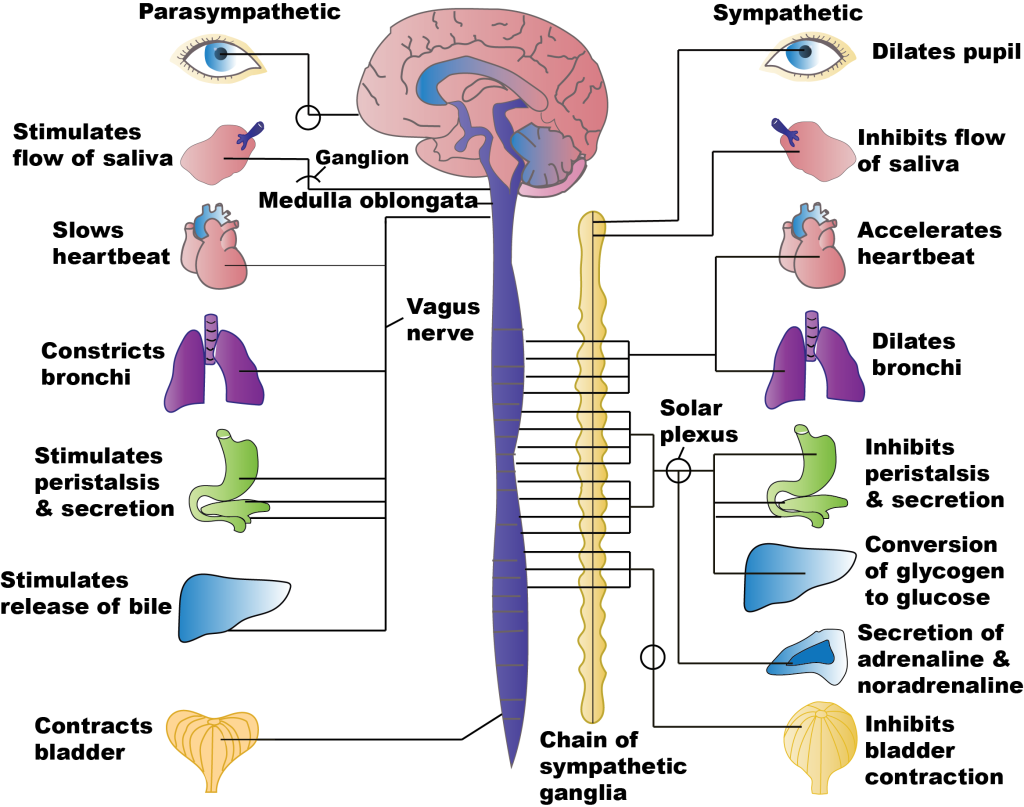
Stimulation of the SNS primarily produces increased heart rate, increased blood pressure via the constriction of blood vessels, and bronchial dilation. In comparison, stimulation of the PNS causes slowing of the heart, lowering of blood pressure due to vasodilation, bronchial constriction, and focuses on stimulating intestinal motility, salivation, and relaxation of the bladder.
Homeostasis is the balance between the two systems. At each target organ, dual innervation determines activity. For example, the heart receives connections from both the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions. SNS stimulation causes the heart rate to increase, whereas PNS stimulation causes the heart rate to decrease.
To respond to a threat – to “fight or flight” – the sympathetic system stimulates many different target organs to achieve this purpose. For example, if a person sees a grizzly bear in the wilderness, the individual has the choice to stand and fight the bear or to run away. For either choice, several things must occur for additional oxygen and glucose to be delivered to skeletal muscle to fight or run. The respiratory, cardiovascular, and musculoskeletal systems are all activated to breathe rapidly, cause bronchodilation in the lungs to inhale more oxygen, stimulate the heart to pump more blood, and increase blood pressure to deliver it to the muscles.[7] The liver creates more glucose for energy for the muscles to use. The pupils dilate to see the threat (or the escape route) more clearly. Sweating prevents the body from overheating from excess muscle contraction. Because the digestive system is not needed during this time of threat, the body shunts oxygen-rich blood to the skeletal muscles. To coordinate all these targeted responses, catecholamines such as epinephrine and norepinephrine are released in the sympathetic system and disperse to the many neuroreceptors on the target organs simultaneously.[8]
Chemical Signaling in the Autonomic Nervous System
Neurons conduct impulses to the synapse of a target organ. The synapse is a connection between the neuron and its target cell. See Figures 4.4[9] and 4.5[10] for images of synapse connections.
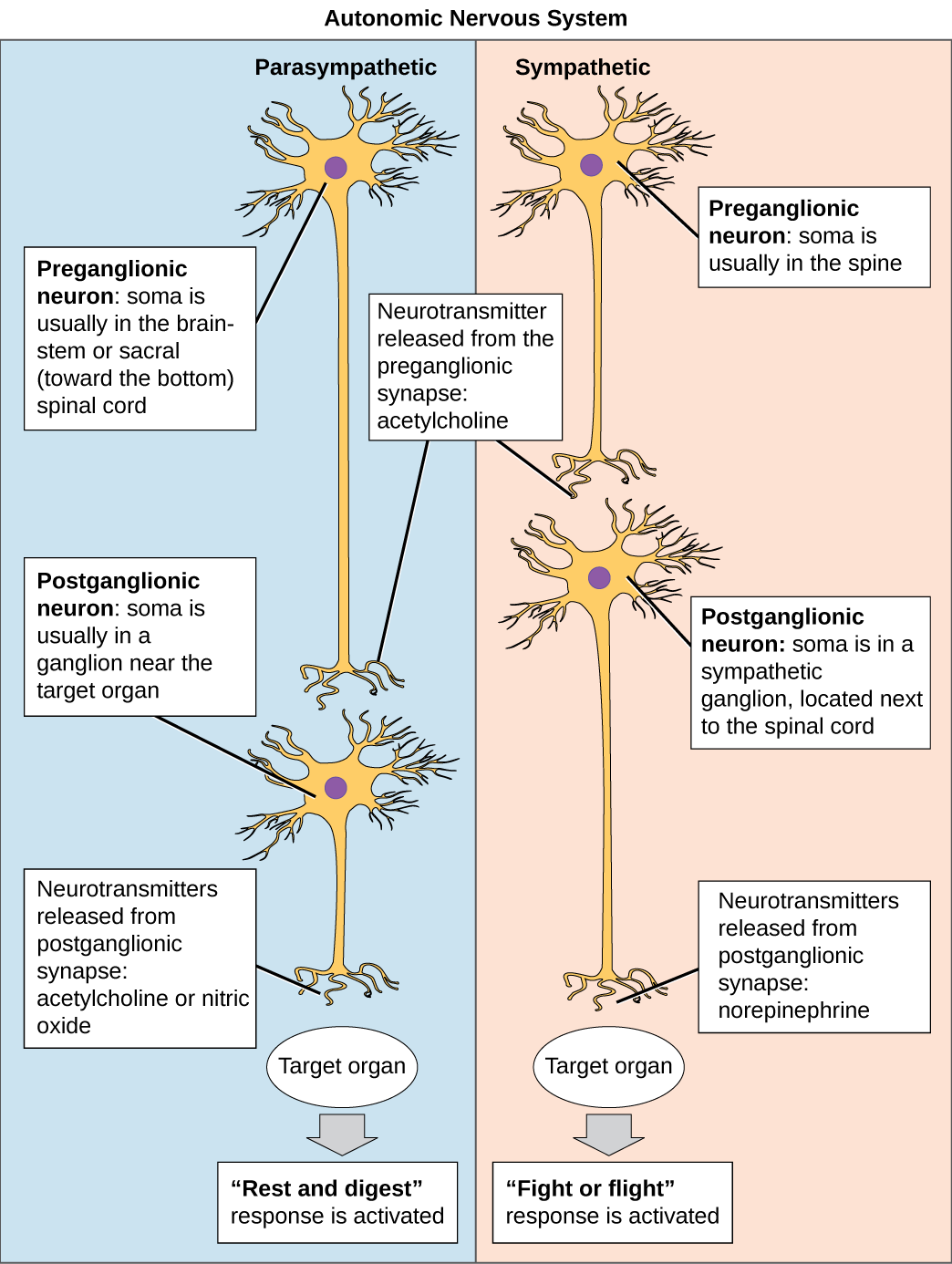
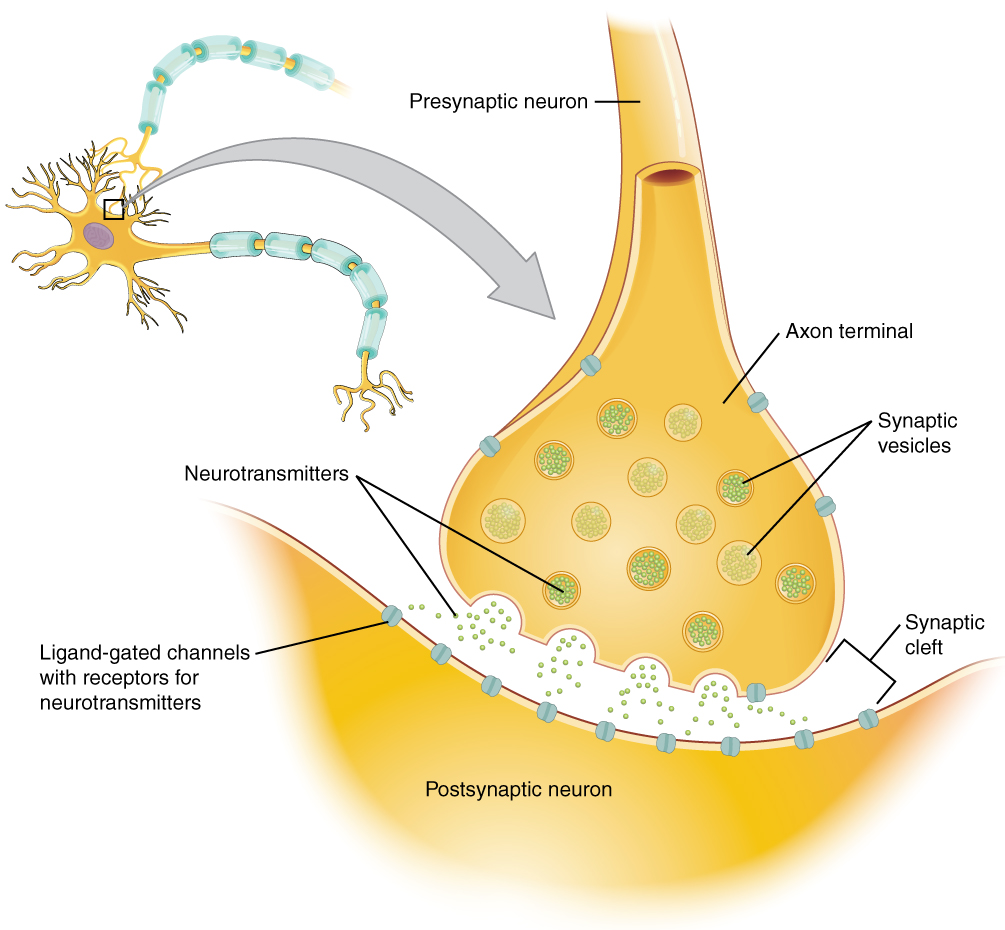
Preganglionic Neurons
The synapse is composed of a preganglionic (presynaptic) neuron and a postganglionic (postsynaptic) neuron. Preganglionic neurons release acetylcholine (ACh) onto nicotinic receptors on the postganglionic neuron. Nicotine, found in tobacco products, also binds to and activates nicotinic receptors, mimicking the effects of ACh. This is worth noting, because if medications were developed to impact the nicotinic receptors, then it would impact both the SNS and PNS systems at the preganglionic level. Instead, most medications target the postganglionic neurons because each type of postganglionic neuron has different neurotransmitters and different target receptors.
Postganglionic Neurons
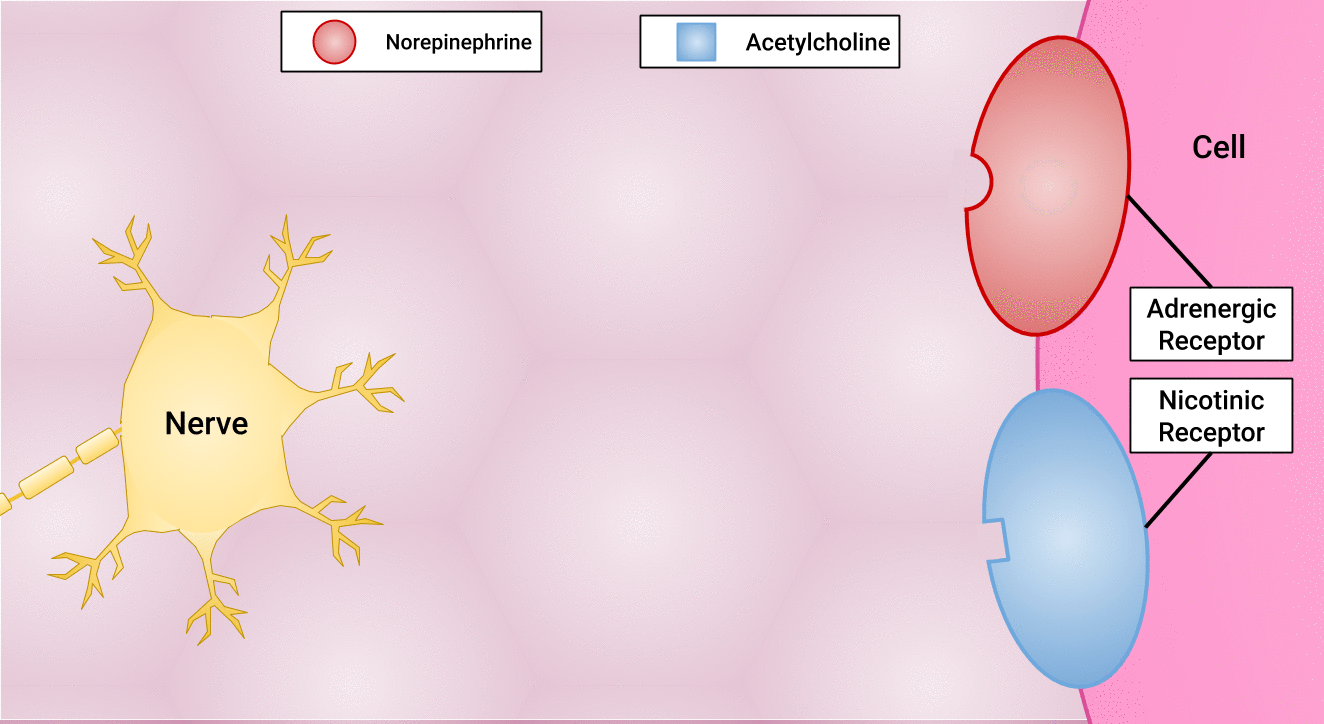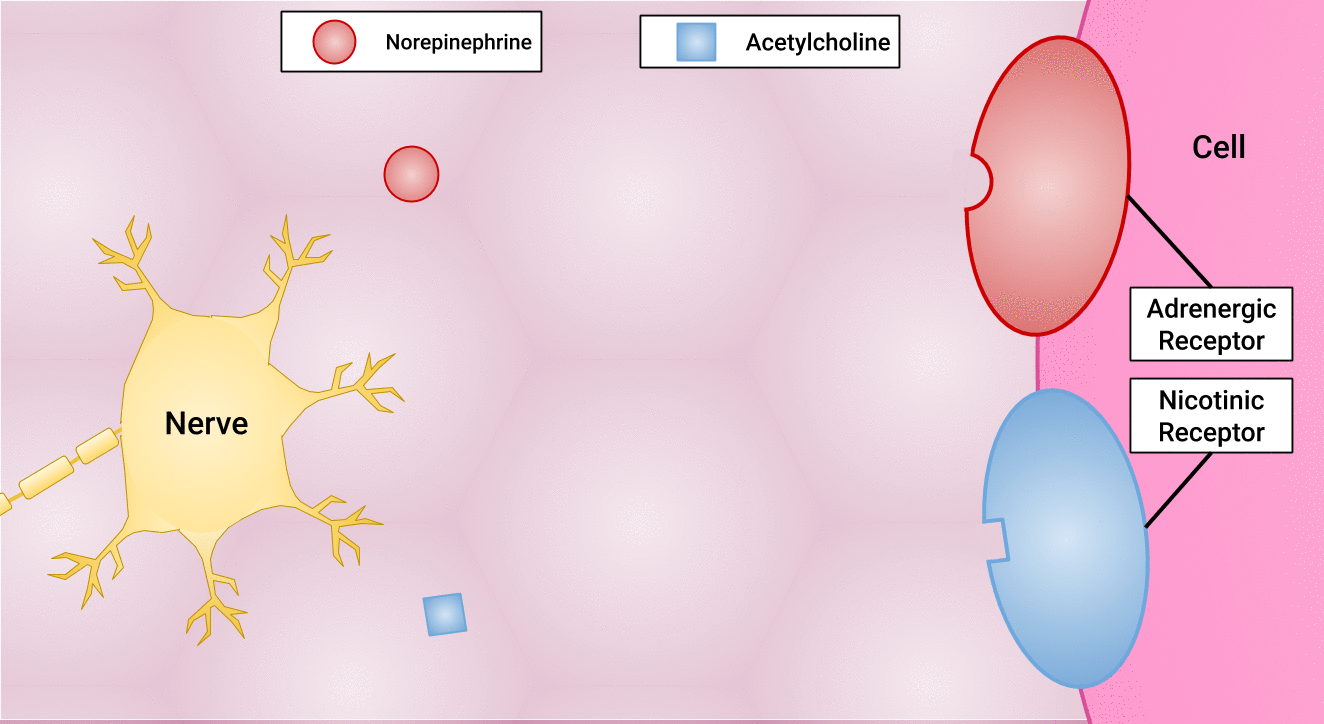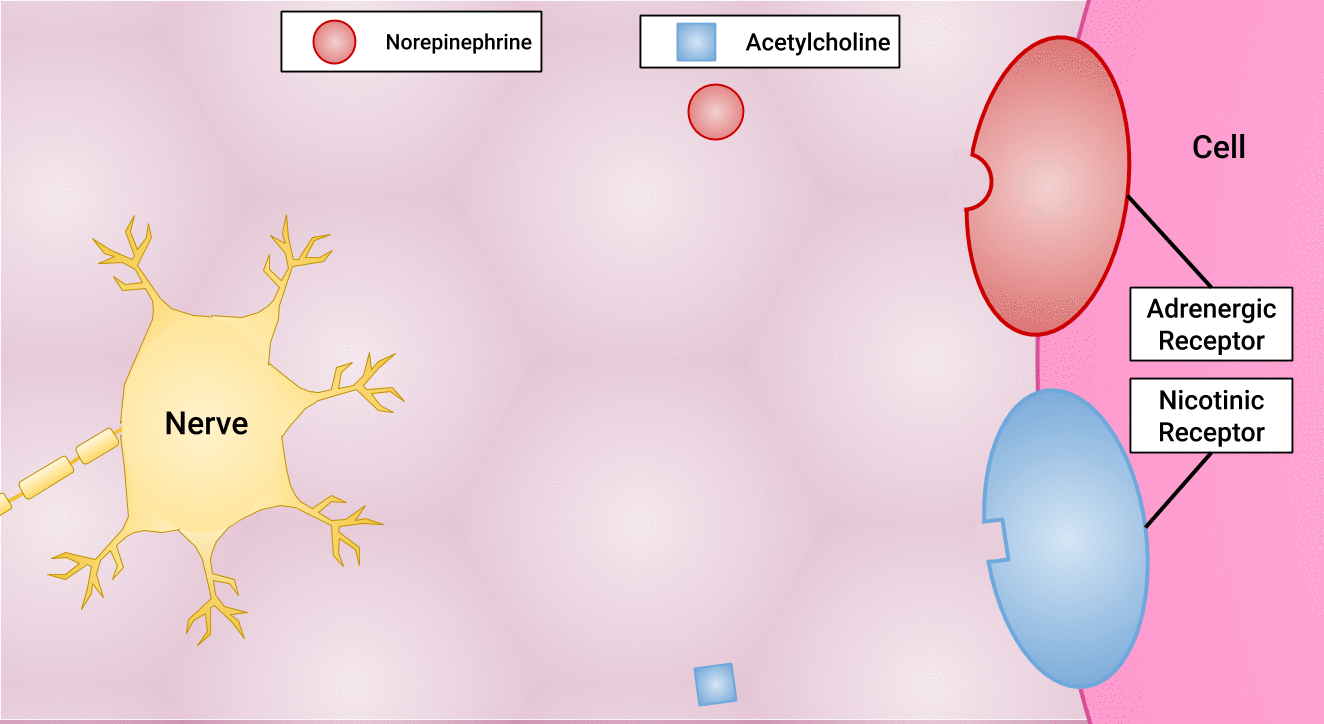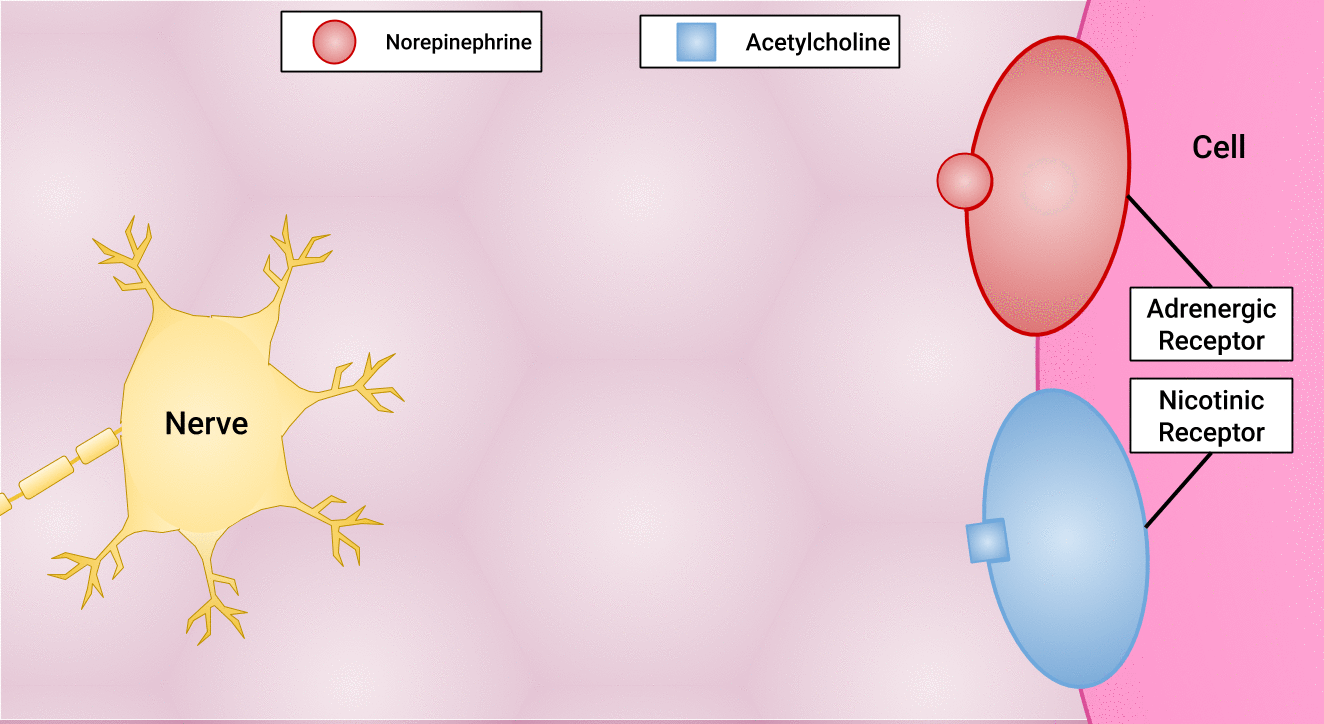
There are different types of postganglionic neurons in the SNS and PNS branches of the autonomic nervous system. Postganglionic neurons of the PNS branch are classified as cholinergic, meaning that acetylcholine (ACh) is released, whereas postganglionic neurons of the SNS are classifed as adrenergic, meaning that norepinephrine (NE) is released. The terms cholinergic and adrenergic refer not only to the signal that is released, but also to the class of neuroreceptors that each binds. (See Figure 4.6 for an image of the release of ACh and NE and their attachment to the corresponding adrenergic or nicotinic receptors.)
The cholinergic system of the PNS includes two classes of postganglionic neuroreceptors: the nicotinic receptor and the muscarinic receptor. Both receptor types bind to ACh and cause changes in the target cell. The situation is similar to locks and keys. Imagine two locks—one for a classroom and the other for an office—opened by two separate keys. The classroom key will not open the office door, and the office key will not open the classroom door. This is similar to the specificity of nicotine and muscarine for their receptors. However, a master key can open multiple locks, such as a master key for the biology department that opens both the classroom and the office doors. This is similar to ACh that binds to both types of receptors.
The adrenergic system of the SNS has two major types of neuroreceptors: the alpha (α)-adrenergic receptor and beta (β)-adrenergic receptor. There are two types of α-adrenergic receptors, termed α1 and α2, and there are two types of β-adrenergic receptors, termed β1 and β2. An additional aspect of the adrenergic system is that there is a second neurotransmitter in addition to norepinephrine. The second neurotransmitter is called epinephrine. The chemical difference between norepinephrine and epinephrine is the addition of a methyl group (CH3) in epinephrine. The prefix “nor-” actually refers to this chemical difference in which a methyl group is missing.[11]
The term adrenergic should remind you of the word adrenaline, which is associated with the fight-or-flight response described earlier. Adrenaline and epinephrine are two names for the same molecule. The adrenal gland (in Latin, ad- = “on top of”; renal = “kidney”) secretes adrenaline. The ending “-ine” refers to the chemical being derived, or extracted, from the adrenal gland.[12]
Interactive Activity
[h5p id=”10″]
ANS Neuroreceptors and Effects
The effects of stimulating each type of neuroreceptor are outlined in this section and sample uses of medications are provided.
Sympathetic Nervous System
SNS receptors include Alpha-1, Alpha-2, Beta-1, and Beta-2 receptors. Epinephrine and norepinephrine stimulate these receptors, causing the overall fight-or-flight response in various target organs. Medications causing similar effects are called adrenergic agonists, or sympathomimetics, because they mimic the effects of the body’s natural SNS stimulation. On the other hand, adrenergic antagonists block the effects of the SNS receptors. Dopamine also stimulates these receptors, but it is dosage-based. Dopamine causes vasodilation of arteries in the kidney, heart, and brain, depending on the dosage. See Table 4.2a for a comparison of stimulation and inhibition of these SNS receptors.
Table 4.2a Comparison of Medication Effects of Adrenergic Receptor Stimulation and Inhibition
Receptor |
Effects of Stimulation |
Effects of Inhibition |
|---|---|---|
Alpha-1 |
|
|
Alpha-2 |
|
|
Beta-1 |
|
|
Beta-2 |
|
|
Interactive Activity
[h5p id=”11″]
Adrenergic Agonists
Adrenergic agonists stimulate Alpha-1, Alpha-2, Beta-1, or Beta-2 receptors. Stimulation of each type of receptor has different effects and further explained below.
Alpha-1 receptor agonists: Stimulation of Alpha-1 receptors causes vasoconstriction in the periphery, which increases blood pressure. Vasoconstriction also occurs in mucus membranes, which decreases swelling and secretions for patients experiencing upper respiratory infections. Examples of Alpha-1 agonist medications are pseudoephedrine or phenylephrine and are used to treat nasal congestion.
Alpha-2 receptor agonists: Stimulation of Alpha-2 receptors reduces CNS stimulation and is primarily used as an antihypertensive or a sedative. An example of an Alpha-2 agonist medication is clonidine, which is used to treat hypertension and also used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.
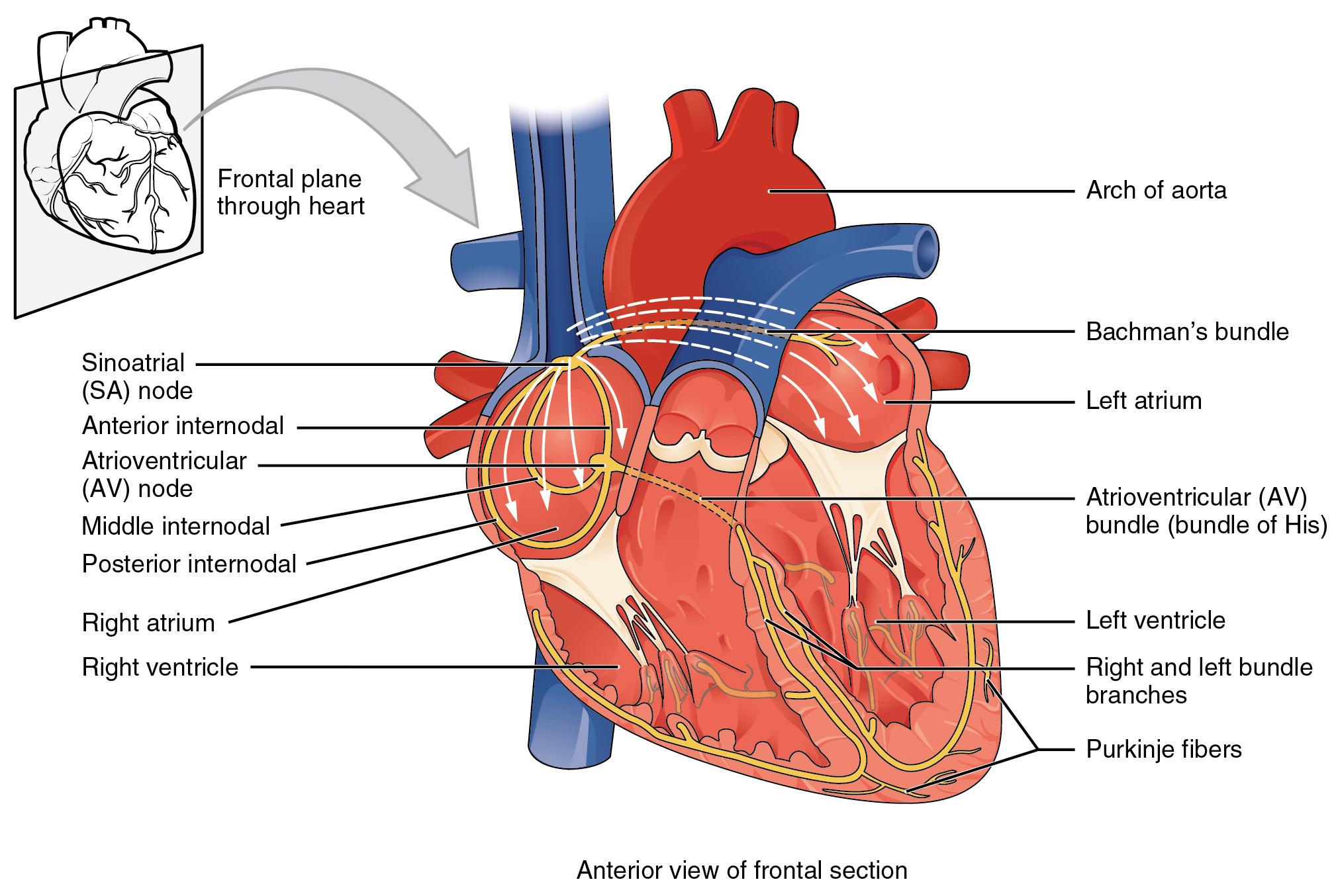
Beta-1 receptor agonists: Stimulation of Beta-1 receptors primarily affects the heart by increasing heart rate and contractility. It also causes the kidneys to release renin. Effects on the heart are described as having a positive chronotropic (increases heart rate), positive inotropic (increases force of contraction), and positive dromotropic (increases speed of conduction between SA and AV node) properties. Medications that stimulate Beta-1 receptors are primarily used during cardiac arrest, acute heart failure, or shock. An example of a Beta-1 receptor agonist medication is dobutamine, which is used to increase cardiac output in someone experiencing acute heart failure or shock. See Figure 4.7[15] illustrating dromotropic properties of stimulating Beta-1 receptors.
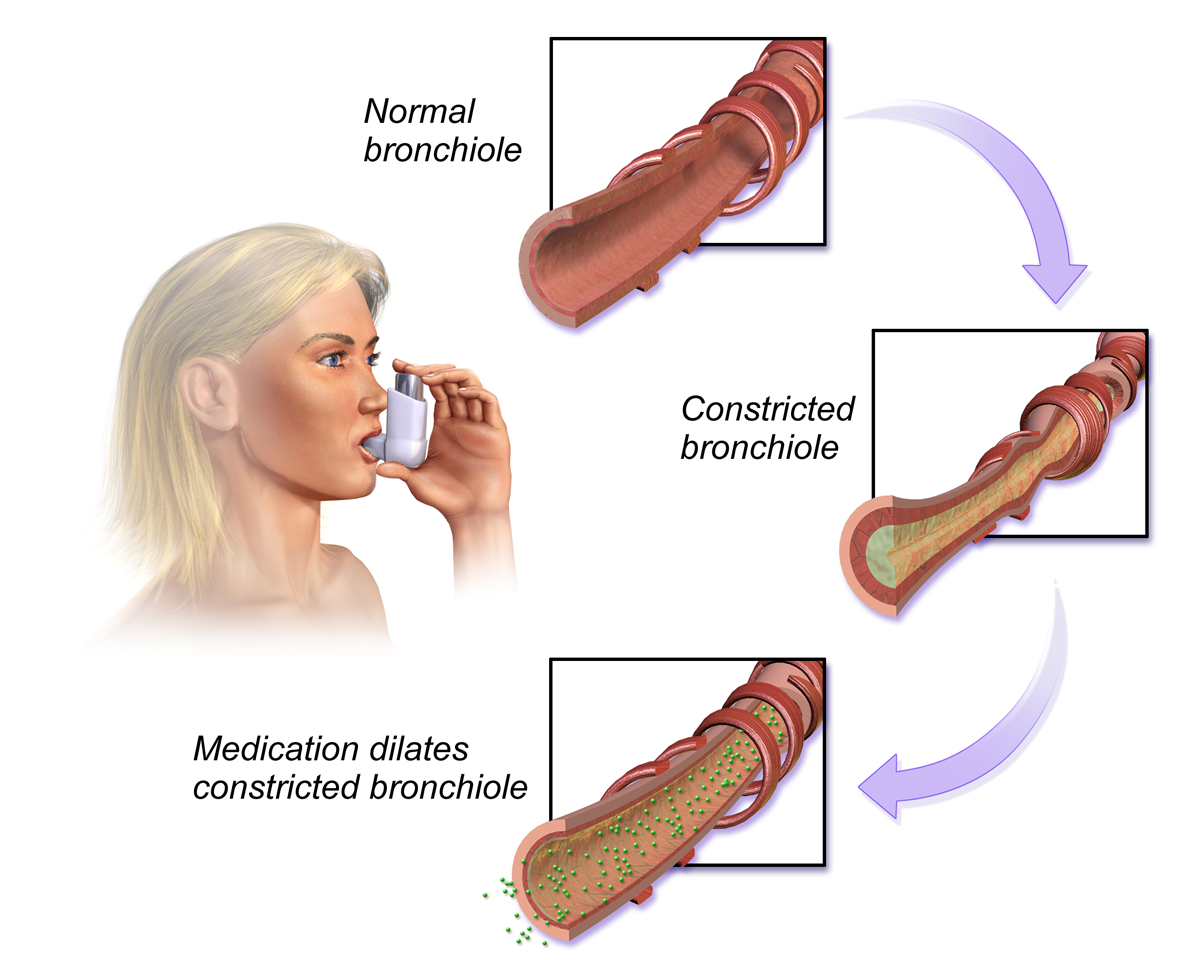
Beta-2 receptor agonists: Stimulation of Beta-2 receptors causes relaxation in smooth muscle in the lungs, GI, uterus, and liver. Medications that stimulate Beta-2 receptors are primarily used to promote bronchodilation, which opens the airway, and are often used to treat patients with asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). An example of a Beta-2 receptor agonist medication used in asthma is albuterol. See Figure 4.8[16] for an illustration of the effects of stimulating Beta-2 receptors in the lungs.
Side effects of Beta-2 receptor agonists are related to stimulation of Beta-2 receptors in other locations in the body. For example, albuterol can cause tachycardia by stimulating Beta-2 receptors in the heart. Stimulation of Beta-2 receptors can also inadvertently cause hyperglycemia in patients with diabetes because of activation of Beta-2 receptors in the liver, causing glycogenolysis.
Adrenergic Antagonists
Adrenergic antagonist medications inhibit the Alpha-1, Alpha-2, Beta-1, and Beta-2 receptors. The effects of inhibition of each receptor are explained further below.
Alpha-1 antagonists: Alpha-1 antagonists are primarily used to relax smooth muscle in the bladder and cause vasodilation.
Examples include the following:
- Tamsulosin is used to decrease resistance of an enlarged prostate gland and improve urine flow.
- Prazosin is used to cause vasodilation and decrease blood pressure in patients with hypertension.
Alpha-2 antagonists: This classification is used in research but has limited clinical application.
There are two types of beta antagonists: selective beta-blockers, which inhibit Beta-1 receptors and affect the heart only, and nonselective beta-blockers, that block both Beta-1 and Beta-2 receptors, thus affecting both the heart and lungs. Beta-blockers are also referred to as having negative chronotropic (decreased heart rate), negative inotropic (decreased force of contraction), and negative dromotropic (decreased speed of conduction between SA and AV nodes) properties. It is also important for a nurse to remember that beta-blockers can mask the usual hypoglycemic symptoms of tremor, tachycardia, and nervousness in patients with diabetes.
Beta-1 antagonists: Beta-1 antagonists primarily block receptors in the heart, causing decreased heart rate and decreased blood pressure. An example is metoprolol, a selective beta-blocker used to treat high blood pressure, chest pain due to poor blood flow to the heart, and several conditions involving an abnormally fast heart rate.
Beta-2 antagonists: Nonselective beta-blockers block Beta-1 receptors and Beta-2 receptors in the lungs. An example is propranolol, which is used to lower blood pressure by decreasing the heart rate and cardiac output. However, it can also cause bronchoconstriction by inadvertently blocking Beta-2 receptors, so it must be used cautiously in patients with asthma or COPD.
Interactive Activity
[h5p id=”12″]
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Acetylcholine (ACh) stimulates nicotinic and muscarinic receptors. Drugs that stimulate nicotinic and muscarinic receptors are called cholinergics. Medications are primarily designed to stimulate muscarinic receptors. Nicotine stimulates pre- and post-ganglionic nicotinic receptors, causing muscle relaxation and other CNS effects. An example of a medication designed to stimulate nicotinic receptors is the nicotine patch, which is used to assist with smoking cessation.
Muscarinic agonists are also called parasympathomimetics and primarily cause smooth muscle contraction, resulting in decreased heart rate, bronchoconstriction, increased gastrointestinal/genitourinary tone, and pupillary constriction. There are two types of muscarinic agonists: direct-acting and indirect-acting. Direct-acting agonists bind to the muscarinic receptor. Indirect-acting muscarinic agonists work by preventing the breakdown of ACh, thus increasing the amount of acetylcholine available to bind receptors.
Examples of direct-acting muscarinic agonist medications are as follows:
- Pilocarpine: Used to treat glaucoma by causing the ciliary muscle to contract and allow for the drainage of aqueous humor
- Bethanechol: Used for urinary retention by stimulating the bladder causing urine output
Examples of indirect-acting muscarinic agonist medications include the following:
- Pyridostigmine: Used to reverse muscle weakness in patients with myasthenia gravis
- Physostigmine: Used to treat organophosphate insecticide poisoning
- Donepezil: Enhances memory in some patients with early Alzheimer’s disease
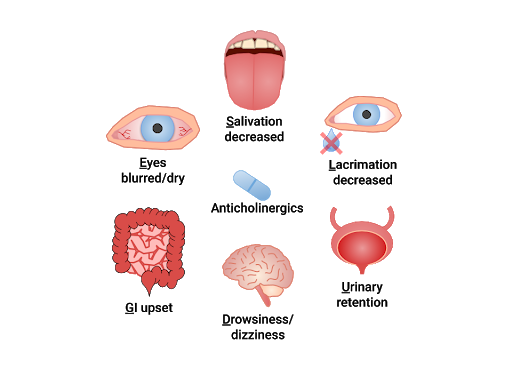
Muscarinic antagonists are referred to as anticholinergics or “parasympatholytics.” Anticholinergics inhibit ACh and allow the SNS to dominate, creating similar effects as adrenergics. Their overall use is to relax smooth muscle. “SLUDGE” is a mnemonic commonly used to recall the effects of anticholinergics: Salivation decreased, Lacrimation decreased, Urinary retention, Drowsiness/dizziness, GI upset, Eyes (blurred vision/dry eyes). Anticholinergics may also cause confusion and constipation and must be used cautiously in the elderly. See Figure 4.9[18] for an illustration of the "SLUDGE" effects of anticholinergics.
These are examples of anticholinergic medications:
- Atropine: Specific anticholinergic responses are dose-related. Small doses of atropine inhibit salivary and bronchial secretions and sweating; moderate doses dilate the pupil, inhibit accommodation, and increase the heart rate (vagolytic effect); larger doses will decrease motility of the gastrointestinal (GI) and urinary tracts; very large doses will inhibit gastric acid secretion
- Oxybutynin: Relaxes overactive bladder
- Benztropine: Reduces tremor and muscle rigidity in Parkinson’s disease or in treatment of extrapyramidal reactions from antipsychotic medications
- Scopolamine: Decreases GI motility and GI secretions; used for motion sickness and post-operative nausea and vomiting[19],[20],[21],[22]
Please review Table 4.2b for additional examples of anticholinergic medications.
Table 4.2b Common Anticholinergic Medications
| Drug Class | Examples |
|---|---|
| Antihistamines | Diphenhydramine (Benadryl), Loratadine |
| Antipsychotics | Chlorpromazine, Haloperidol, Quetiapine |
| Antidepressants | Amitriptyline, Doxepin, Imipramine |
| Antiemetics | Scopolamine, Ondansetron, Prochlorperazine |
| Antispasmodics | Dicyclomine, Hyoscyamine |
| Bladder antimuscarinics | Oxybutynin, Tolterodine |
| Bronchodilators | Ipratropium, Tiotropium |
| Gastrointestinal agents | Atropine, Hyoscyamine, Glycopyrrolate |
| Muscle relaxants | Cyclobenzaprine, Orphenadrine |
- This work is a derivative of Anatomy and Physiology by OpenStax licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/1-introduction ↵
- “1201 Overview of Nervous System.jpg” by CNX OpenStax. is licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/12-1-basic-structure-and-function-of-the-nervous-system ↵
- “Component of the Nervous System” by Blaire Babbit at Chippewa Valley Technical College is licensed under CC BY 4.0 ↵
- “Component of the Nervous System” by Blaire Babbitt at Chippewa Valley Technical College is licensed under CC BY 4.0 ↵
- “Updated SNS-PNS image.png” by Meredith Pomietlo for Open RN is licensed under CC BY 4.0 ↵
- This work is a derivative of Anatomy and Physiology by OpenStax licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/1-introduction ↵
- This work is a derivative of Anatomy and Physiology by OpenStax licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/1-introduction ↵
- This work is a derivative of Anatomy and Physiology by OpenStax licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/1-introduction ↵
- “Autonomic Nervous System” by CNX OpenStax is licensed under CC BY 4.0 ↵
- “The Synapse” by CNX OpenStax is licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/12-5-communication-between-neurons ↵
- “Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Pre-and Postganglionic fibers and neuroreceptors” by Dominic Slausen at Chippewa Valley Technical College is licensed under CC BY 4.0 ↵
- This work is a derivative of Anatomy and Physiology by OpenStax licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/1-introduction ↵
- “PNS vs SNS Quiz” by E. Christman for Open RN is licensed under CC BY 4.0 ↵
- “ANS Knowledge Check Basics” by E. Christman for Open RN is licensed under CC BY 4.0 ↵
- “2018 Conduction System of Heart.jpg” by OpenStax College is licensed under CC BY 3.0 ↵
- “Bronchodilators” by BruceBlaus is licensed under CC BY 4.0 ↵
- “SNS Receptor Match” by E. Christman for Open RN is licensed under CC BY 4.0 ↵
- “'SLUDGE' effects of Anticholinergics” by Dominic Slausen at Chippewa Valley Technical College is licensed under CC BY 4.0 ↵
- McCuistion, L., Vuljoin-DiMaggio, K., Winton, M., & Yeager, J. (2018). Pharmacology: A patient-centered nursing process approach. Elsevier. ↵
- Gersch, C., Heimgartner, N., Rebar, C., & Willis, L. (Eds.). (2017). Pharmacology made incredibly easy. Wolters Kluwer. ↵
- Lilley, L., Collins, S., & Snyder, J. (2014). Pharmacology and the nursing process. Elsevier. ↵
- This work is a derivative of Principles of Pharmacology by LibreTexts licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 ↵
Anatomical division of the nervous system located within the cranial and vertebral cavities, namely the brain and spinal cord.
An anatomical division of the nervous system that is largely outside the cranial and vertebral cavities, namely all parts except the brain and spinal cord.
Sense the environment and conduct signals to the brain that become a conscious perception of that stimulus.
Consist of the somatic nervous system that stimulates voluntary movement of muscles and the autonomic nervous system that controls involuntary responses.
Causes contraction of skeletal muscles; associated with voluntary responses.
Controls cardiac and smooth muscle, as well as glandular tissue; associated with involuntary responses.
Associated with the “fight or flight response.” Stimulation causes the main effects of increased heart rate, increased blood pressure via the constriction of blood vessels, and bronchodilation.
Includes nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. Associated with the “rest and digest” response. Stimulation of PNS causes decreased heart rate, decreased blood pressure via vasodilation, bronchial constriction, and stimulates intestinal motility, salivation, and relaxation of the bladder.
The response when the SNS is stimulated causing the main effects of increased heart rate; increased blood pressure; and bronchodilation.
Balance between the SNS and PNS. At each target organ, dual innervation determines activity. For example, SNS stimulation causes the heart rate to increase, whereas PNS stimulation causes the heart rate to decrease.
Cells that carry electrical impulses to the synapse of a target organ.
The connection between the neuron and its target cell.
All preganglionic neurons (in the SNS and PNS) release acetylcholine (ACh).
Binds to both nicotinic receptors and muscarinic receptors in the PNS.
Postganglionic neurons of the autonomic system are classified as either cholinergic, meaning that acetylcholine (ACh) is released, or adrenergic, meaning that norepinephrine is released.
Postganglionic neuron where acetylcholine (ACh) is released that stimulates nicotinic receptors and muscarinic receptors. Also relating to drugs that inhibit, enhance, or mimic the action of ACh.
Postganglionic neuron where neurotransmitters norepinephrine and epinephrine are released. Includes alpha (α) receptors and beta (β) receptors.
Mimic the effects of the body’s natural SNS stimulation on alpha (α) and beta (β) receptors. Also called sympathomimetics.
Mimic the effects of the body’s natural SNS stimulation of adrenergic receptors. Also called adrenergic agonists.
Block the effects of the SNS receptors.
Drugs may change the heart rate and rhythm by affecting the electrical conduction system of the heart and the nerves that influence it, such as by changing the rhythm (increasing) produced by the sinoatrial node. Positive chronotropes increase heart rate; negative chronotropes decrease heart rate.
Stimulation causes increased force of contraction.
Stimulation causes increases speed of conduction between SA and AV node.
Elevated blood sugar.
The breakdown of glycogen into glucose, causing elevated blood sugar.
Medications that mostly inhibit B1 receptors.
Medications that block both Beta 1 and Beta 2 receptors, thus affecting both the heart and lungs.
Also called parasympathomimetics. Primarily cause smooth muscle contraction, resulting in decreased HR, bronchoconstriction, increased GI/GU tone, and pupil constriction.
Also called muscarinic agonists. Primarily cause smooth muscle contraction, resulting in decreased HR, bronchoconstriction, increased GI/GU tone, and pupil constriction.
Inhibit acetylcholine (ACh) which allows the SNS to dominate. Also called parasympatholytics or muscarinic antagonists. Overall use is to relax smooth muscle.
Mnemonic for the effects of anticholinergics: Salivation decreased; Lacrimation decreased; Urinary retention; Drowsiness/dizziness; GI upset; Eyes (blurred vision/dry eyes).
