AI – Generated Content for Education and Learning
Rafidah Abd Karim
Introduction
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, the connection of artificial intelligence (AI) and education is not just a future possibility; it is forthcoming. The World Economic Forum’s 2020 Education 4.0 Framework outlined eight essential changes that must be made to improve the quality of education in the era of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. We can accelerate the adoption of Education 4.0 by utilising AI, which is emerging as the defining technology of this period, and making sure students are prepared to succeed with it. AI applications, which are designed for cognition and problem-solving based on algorithms and knowledge bases, can effectively support and augment educators’ and learners’ abilities in teaching and learning. This is especially true in the field of education, where learning and teaching are knowledge-intensive cognitive activities (Wang et al.,2024).
AI in education refers to the integration of Artificial Intelligence technologies to increase and enhance the learning and teaching experience. This includes the use of intelligent systems that can analyze data, adapt to students’ needs, automate administrative tasks, and offer personalized learning experiences. AI in education is transforming the way teachers and students interact, learn, and manage the educational process. Here are five ways on how AI applications is transforming AI in education as the following:
- Translation and language learning
- Writing
- Early childhood education
- Teaching
- Tutoring
A new era of innovation and change is being ushered in by artificial intelligence, which is changing the face of education. Traditional educational methods are being transformed by AI technologies, which offer cutting-edge solutions that adjust to the demands of each individual student, expedite administrative duties, and yield insightful data through data analytics. As Figure 1 shows, there are five major AI’s impacts on education and learning which are intelligent tutoring systems, virtual reality and augmented reality, automated content creation, natural language processing and data analytics and predictive analytics.
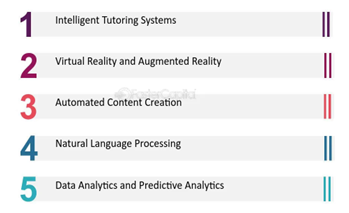
Briefly, AI in education aims to make learning more efficient, accessible, and tailored to the needs of each student, while also reducing administrative burden on teachers. By working together to create a learning environment that is prepared for the future, educators can embrace the revolutionary potential of AI in education.
AI-Generated Content Creation
AI-generated content refers to any educational material or learning resource that has been created using artificial intelligence technology. This can include text, audio, video, or interactive content, such as quizzes, games, and simulations.In short, AI-generated content is text, images, video, or audio content created by an artificial intelligence tool because of human input or prompts. You can produce AI-generated media using tools like OpenAI’s ChatGPT and DALL-E, as well as AI-powered features inside content software like HubSpot and Canva. AI-generated text and images can range in quality from illogical results to excellent content that is almost impossible to tell apart from human creations. Despite being a tool that can change lives, this dichotomy means that it should be handled carefully.
In the context of higher education, the educational effects of Generative AI (GAI), offering guides for both instructors and students on how to effectively integrate AI into their educational practices. Their findings suggest that with proper guidance, GAI can be a powerful tool in enhancing the educational experience, though the technology’s impact varies depending on how it is implemented (Gimpel et al, 2023).
AI’s revolutionary potential, but it should not be used in education without careful consideration. It promotes all-encompassing approaches to maintain human connections, ensure data privacy and security, mitigate biases, enhance system transparency, foster creativity, reduce access disparities, emphasize ethics, prepare teachers, ensure system reliability, and regulate AI-generated content (Al-Zahrani ,2024).
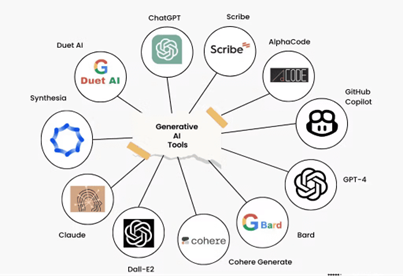
Figure 1 shows the most popular generative AI tools and platforms that people use in 2024. The application tools are ChatGPT, Scribe, AplhaCode, GiHub Copilot, GPT-4, Bard, Cohere Generate, Dall E-2, Calude, Synthesia and Duet AI. For example, ChatGPT may use natural language to produce responses that are human-like, effectively creating an on-demand expert system. ChatGPT can be fine-tuned for specific tasks or domains, increasing its versatility across various industries and applications (Ray, 2023). The public considered the ChatGPT application to be a rather helpful method, and it could increase awareness of smart health (Karim & Kurubacak, 2024).
Advantages of AI-generated Content for Education and Learning
The incorporation of artificial intelligence within the educational sphere holds the promise of elevating academic benchmarks and enhancing the comprehensive quality of learning experiences. AI-generated content for education and learning can be valuable in several ways. Here are some of the advantages:
- Personalized learning: One of the biggest benefits of AI-generated content is that it can be tailored to the individual needs and preferences of each learner.
- Improved engagement: interactive, visually appealing, and designed to be engaging. This can help to capture students’ attention and keep them
- Efficiency and cost-effectiveness: AI-generated content can be created and distributed quickly and at scale, making it a cost-effective solution for educational institutions. Can reduce the workload of teachers and enable them to focus on other aspects of the learning experience.
- Access to high-quality resources: AI-generated content can be based on the latest research and best practices AI in education, ensuring that students have access to high-quality resources that are up-to-date and relevant.
- Enhanced assessment: AI-generated content can also be used for assessment purposes, such as automated grading or formative assessments. This can provide teachers with real-time feedback on students’ progress and help them to identify areas where students may be struggling.
Bobula (2024) emphasised that when applied properly, generative AI in education has a great deal of promise to improve Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion (EDI) and advance inclusive education. As different models become more popular, HEIs must make sure that everyone has equal access to technology. However, traditional plagiarism-detection tools are rendered ineffective in this context, as AI is becoming increasingly proficient at imitating human-like text and AI-generated text is deemed original and thus undetectable (Dwivedi et al., 2023).
Although there is a lot of promise for AI in content creation, there are disadvantages as well. Navigating algorithmic biases, ethical issues, and the requirement for human oversight will remain crucial. However, we think that the future will be characterised by ground-breaking developments and improved user experiences if humans and AI work together with the correct strategy.
The Future of AI in Content Creation and Research
Understanding AI’s role in content creation is crucial before looking to the future. The way we produce, organise, and disseminate content has been completely transformed by artificial intelligence (AI). AI improves the efficacy and efficiency of several phases of the content creation process by utilising state-of-the-art technologies. The future of AI in content creation and research holds immense potential, transforming how we produce, consume, and interact with information. As AI technologies evolve, they will play an increasingly important role in making content creation more efficient, personalized, and accessible while driving innovation in research and knowledge discovery. Here are some key areas where AI will shape the future of content creation and research:
- Smarter AI Models
- Greater personalization
- AI-driven multimedia content
- AI as research assistant
There are countless opportunities for creativity and interaction with AI for instance, in video production in the future. To stay ahead in the rapidly evolving digital market, content creators need to accept and adjust to the latest developments in AI technologies. We can revolutionise the production, distribution, and consumption of content by utilising AI, giving people a more interesting and customised experience.
Conclusion
AI is making waves in the world of content creation, and we are only going to see more of it in the future. By using AI tools to generate high-quality content based on data-driven insights, businesses, and organisations can create more effective and engaging content that really speaks to their audience. The future of AI in education is incredibly promising, with AI technologies set to revolutionize how students learn, how educators teach, and how educational systems function. Parents, stakeholders, legislators, and educators can work together to promote appropriate AI integration. To fully utilise AI’s potential, give educators’ continuous professional development a priority. As AI continues to advance, its applications will become more integrated, personalized, and efficient, leading to significant improvements in educational outcomes. Furthermore, the future of AI-generated content in education is prepared to transform the way learning materials are created, distributed, and consumed. As AI technologies continue to evolve, they will significantly impact both the production of educational content and the way students engage with it. Hence, AI fosters creativity, empowers students, and gets them ready for the challenges of a changing world.
References
Al-Zahrani A. M. (2024). Enhancing postgraduate students’ learning outcomes through Flipped Mobile-Based Microlearning. Research in Learning Technology, 32(2024). https://doi.org/10.25304/rlt.v32.3110
Bobula, M. (2024). Generative artificial intelligence (AI) in higher education: a comprehensive review of challenges, opportunities, and implications. Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education, (30). https://doi.org/10.47408/jldhe.vi30.1137
Dwivedi, Y.K., Kshetri, N., Hughes, L., Slade, E.L., Jeyaraj, A., Kar, A.K., Baabdullah, A.M., Koohang, A. et al. (2023) Opinion Paper: “So what if ChatGPT wrote it?” Multidisciplinary perspectives on opportunities, challenges and implications of generative conversational AI for research, practice and policy, International Journal of Information Management, 71, 102642.
Gimpel, H., Hall, K., Decker, S., Eymann, T., Lämmermann, L., Maedche, A., Röglinger, M., Ruiner, C., et al. (2023) Unlocking the Power of Generative AI Models and Systems such as GPT-4 and ChatGPT for Higher Education A Guide for Students and Lecturers. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.20710.09287/2
Karim & Kurubacak Cakir. (2024) Investigating ChatGPT Usability in Promoting Smart Health Awareness. In Zafar, S., Kumar, S.N., Ahilan, A., & Kurubacak Cakir, G. (Eds.). (2024). Industry 5.0 for Smart Healthcare Technologies: Utilizing Artificial Intelligence, Internet of Medical Things and Blockchain (1st ed., 227-237). CRC Press.
Ray, P. P. (2023). ChatGPT: A comprehensive review on background, applications, key challenges, bias, ethics, limitations and future scope. Internet of Things and Cyber-Physical Systems, 3(2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iotcps.2023.04.003
Wang, S,. Wang, F, Zhen Zhu, Z., Wang, J,. Tran, T & Du, Z. ( 2024). Artificial intelligence in education: A systematic literature review, Expert Systems with Applications, 252, 124167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2024.124167
