Section 3D – Constructs Wall Systems
Chapter D4 – Constructs Dimensional Lumber and Steel Stud Wall Framing
Topic 1 – Frame Exterior Walls
Types of Wall Framing
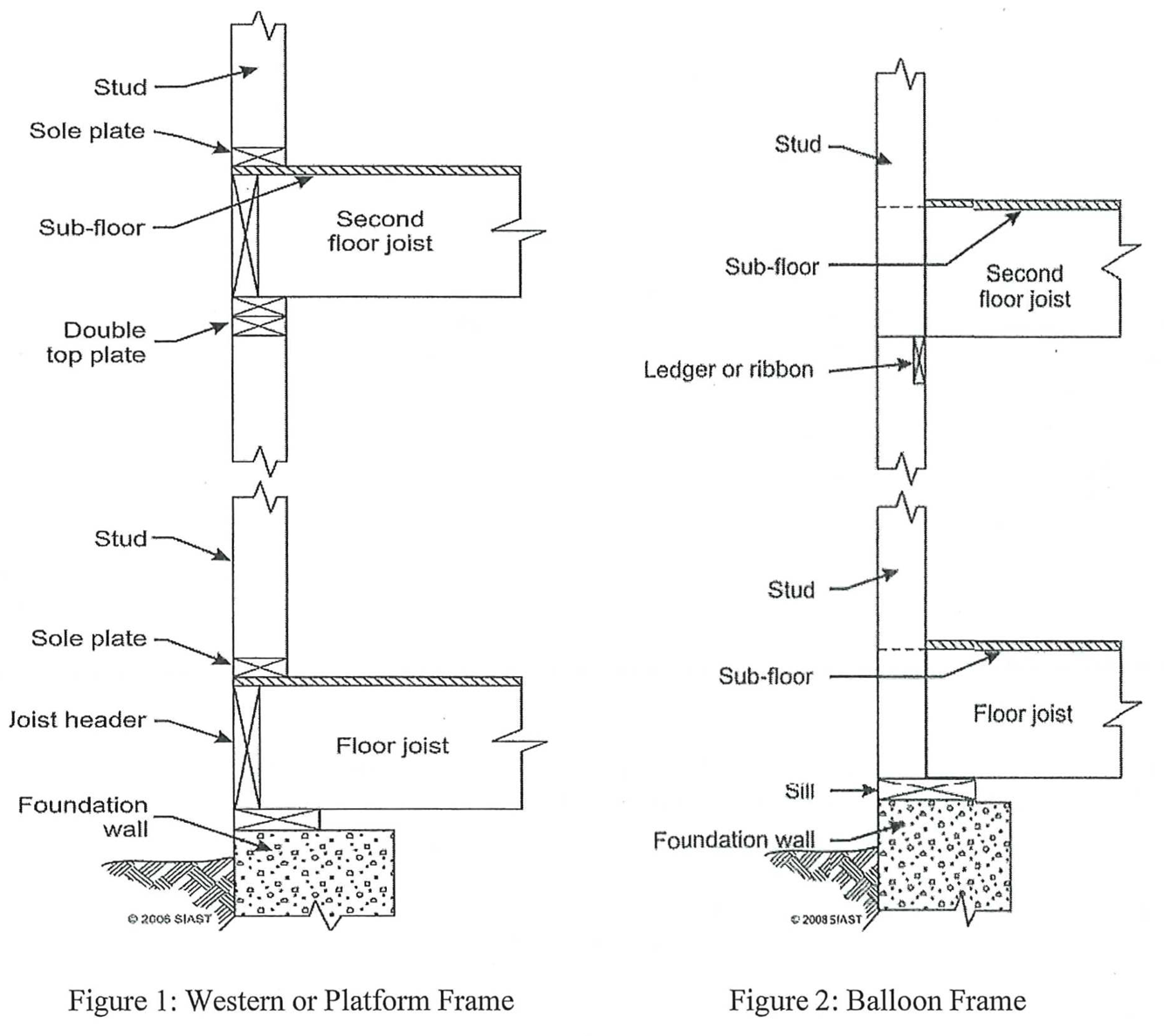
There are two systems used for wall framing: western (platform) framing, and balloon framing (see figure 1 and 2 below). While there are many parallels between each, they differ by their method of starting the frame at the foundation, the length of the studs, and method of floor framing at each level.
In platform framing, each wall is one storey high. The floor is framed as a separate system and the first storey walls are built on top. If a second storey is built, a second floor system is installed on top of the first storey walls. This system is used almost exclusively.
Balloon framing the wall studs are situated on top of the foundation sill plate. The studs run the entire height of the building. The second storey floor system is supported by the studs with a combination of a ribbon (or ledger) and face nails into the studs. The ribbon is inserted into notches which are cut into the studs.
Framing Openings in Exterior Walls
Openings in exterior walls all contain specific parts that are shown in the image below:

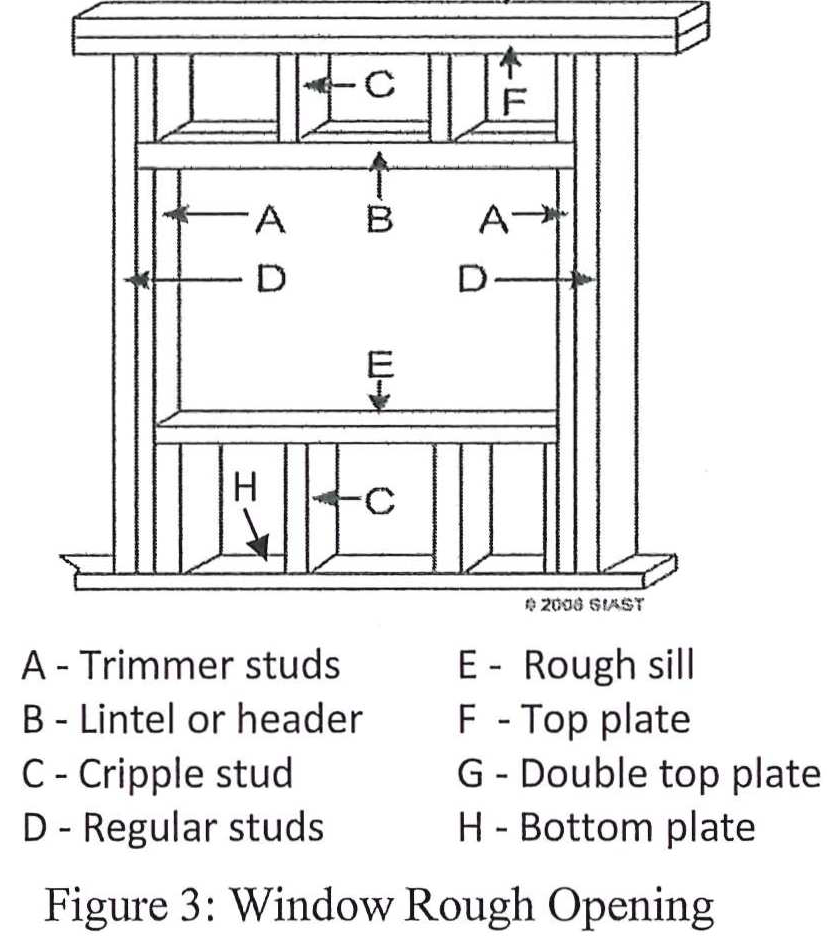
Door Opening are framed in much the same way, but do not have a rough sill or cripples underneath. The bottom plate is also removed inside the door opening after the wall is stood.
Finding Required Header
The size of header required can be found in Tables 9.23.12.3-A, B, and C. There are a number of factors which influence what size is required:
- The load supported refers to the structure above. If a lintel is placed on the second storey of a two storey house, it is only supporting the roof and ceiling. A lintel placed on the first storey of a two story house is supporting is supporting the roof, ceiling, and 1 storey
- Only end walls with overhangs of 12” and a rafter spacing of 24” (or overhangs of 16” and 16” rafter spacing) use tributary width of 0.6 m
- All lintels within side walls, and any end wall with an overhang of 24” has a tributary width greater than 0.6 m
- Example: a 2 ply 2×10 Douglas Fir lintel supporting a roof and ceiling in a side wall with non-structural sheathing under a 2.0 kPa snow load is able to span up to 2.03 m. If structural sheathing were to be applied, that same lintel is now able to span 2.33 m (2.03 + 15%).
* Tributary width is essentially the “supported length” for lintels. In side walls, this is equal to half of the span of the rafters. Only applying to gable end walls, it is the length of overhang plus half of the rafter spacing. In most cases, the tributary width of 0.6 m is exceeded, and we would use the maximum tributary width of 4.9 m instead. In hip roofs, the tributary width of 0.6 m is disregarded.
- Example 1: Find the lintel required
- Bungalow House, lintel in side wall
- Douglas Fir #2 material
- 1.5 kPa snow load
- R.O. – 1.8 m wide
- Non-structural sheathing, 24” O.H.
- Example 2: Find the lintel required
- Two storey house, lintel on first storey in end wall
- Spruce # 1 material
- 2.5 kPa snow load
- R.O. – 2.2 m x 1.6 m
- ½” OSB sheathing, 12” O.H.
Review Questions
Use the NBC and Carpentry to answer the following:
- Why is the supporting ribbon “let in” to the studs?
- When is it permissible to use studs on the flat?
- In load bearing exterior wall the minimum size of studs that may be used is _____.
- When must studs be tripled at openings? How many of these are trimmers and full length studs?
- Is the upper rough sill permitted to sit between the lintel and trimmers?
- How do you calculate the length of lintels?
- Double studs at openings shall be nailed with _____ mm nails spaced not more than _____ mm O.C.
- Determine the minimum size of the lintel:
- Determine the lintel sizes for the following openings:
- Determine the following:
- What is the length of the trimmers and cripples?
- 36” x 42” window
- 92 5/8” studs
- 2×12 header, tight to top plate
- Double top plate
Answers:
- Provides better support for the second floor joists and provides a flush surface for finishes where the ceiling meets the exterior walls.
- On non load-bearing walls where studs are spaced no more than 16” (400 mm) O.C. (9.23.10.3-2)
- A
- When the opening exceeds 3.0 m in width, 2 trimmers and 2 full length stud (9.23.10.6-1)
- No
- R.O. width + trimmers (76 if single trimmers, 152 if double trimmers)
- 76 mm, 750 mm O.C. (9.23.3.4)
-
-
- 2 – 38 x 286 (table 9.23.12.3-C)
- 2 – 38 x 235
-
-
- 2 -38 x 184
- 2 – 38 x 140
-
- 2 – 38 x 286
- 2029
- Trimmers – 81 3/8”; Cripples – 36 3/8”
