Identify Fasteners and Their Use
Topic 4 – Identify Fasteners and Their Use
Nails
The most commonly used fastener in the construction industry, nails are a quick and effective way to fasten material together. They are available in countless varieties of heads, lengths, diameters, points, and shank styles. Choosing the correct nail for the task is vitally important in ensuring long-term structural integrity.
Most nails have a smooth shank and yet are able to retain their hold by severing the wood fibres which grasp the nail with a compressive force and prevent pulling out. While nails can be used for many purposes, they are primarily used in structural applications as they possess a very high shear strength which is capable of withstanding the forces that a wood frame is subjected to.
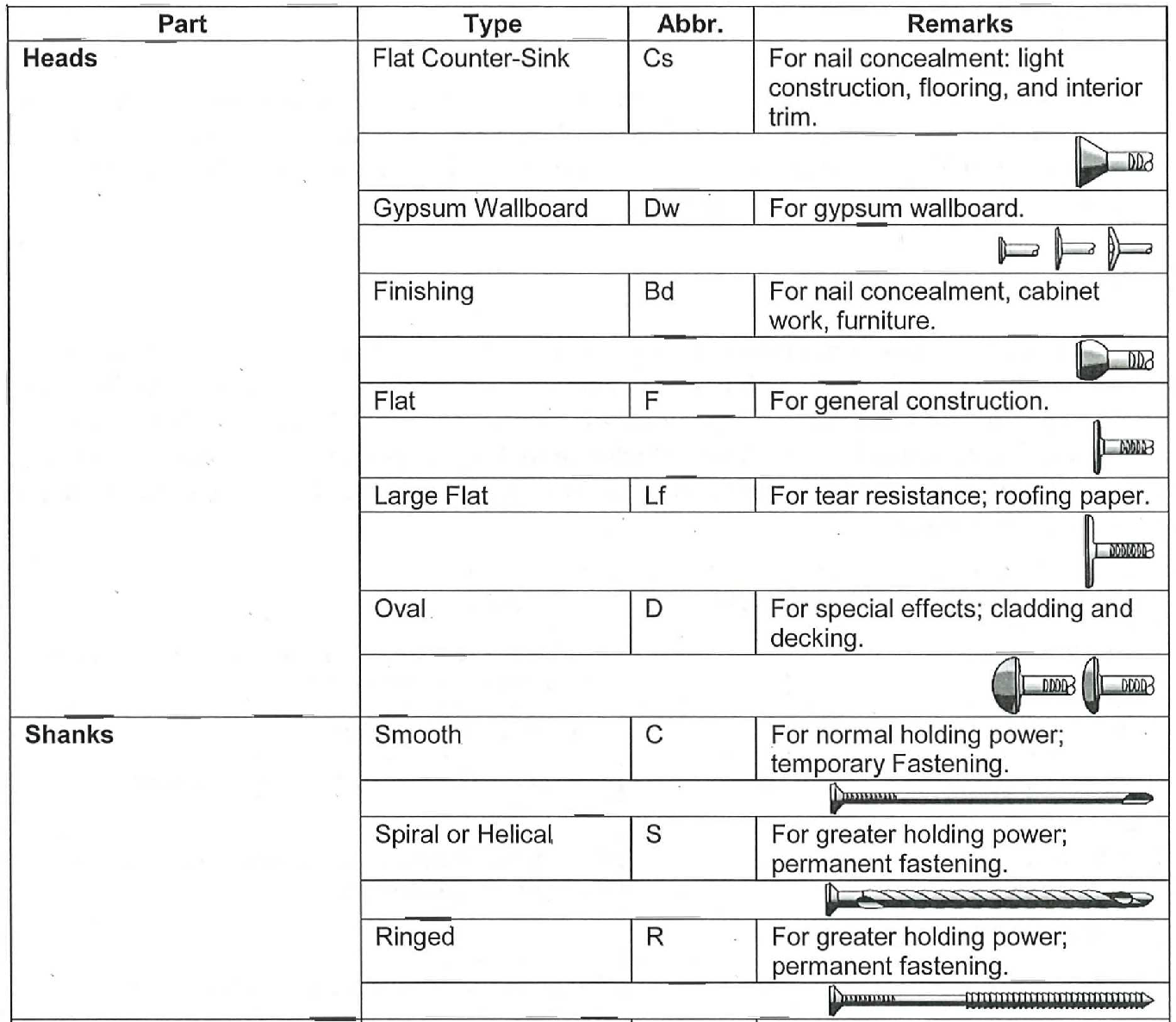 Nails are specified by their type and length (see the table on the next page for common examples). Some are also produced with a variety of heads, shanks, and points. The heads can be designed to maximize holding power, create a specific finish, or allow a high level of concealment, among other things. The shanks have the greatest effect on holding power. They can be designed with rings or spirals to help prevent the nail from pulling out over time. The table on the right shows some common heads and shanks.
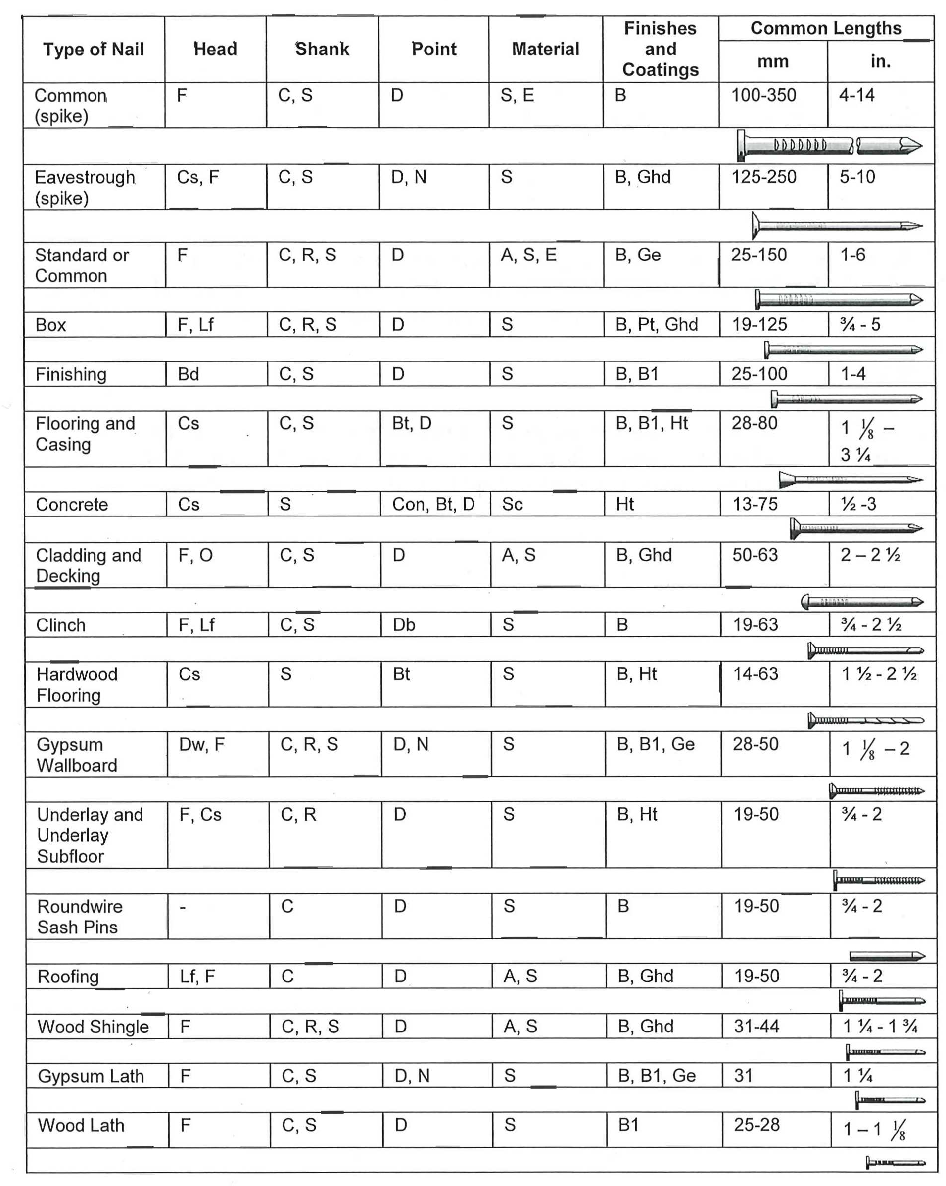
Nails are specified by their type and length (see the table on the next page for common examples). Some are also produced with a variety of heads, shanks, and points. The heads can be designed to maximize holding power, create a specific finish, or allow a high level of concealment, among other things. The shanks have the greatest effect on holding power. They can be designed with rings or spirals to help prevent the nail from pulling out over time. The table on the right shows some common heads and shanks.
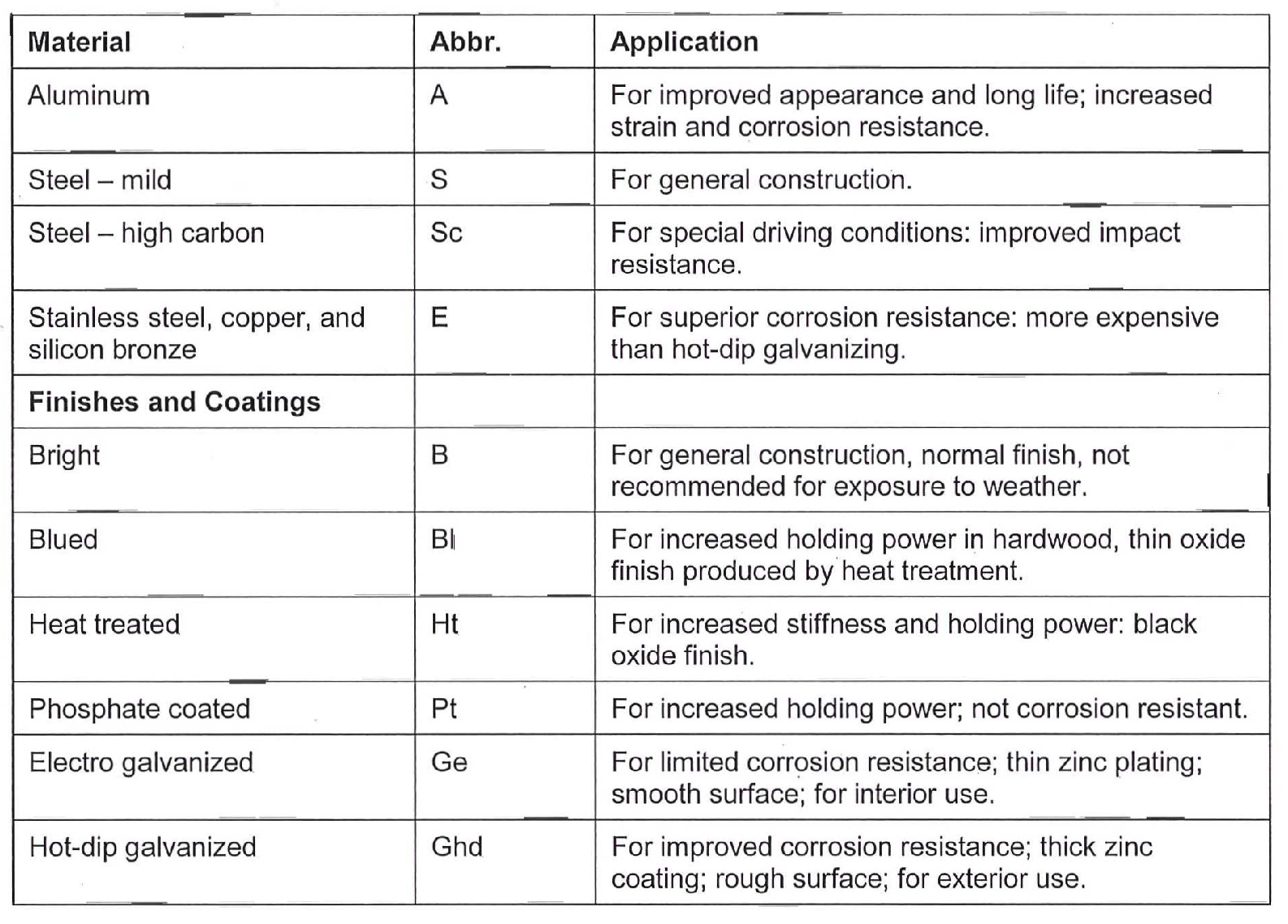
Nails are also available in a variety of materials and coatings which can have a substantial effect on holding power, corrosion resistance, and stiffness. See the table below for examples of materials and coatings.
Screws
Screws come in many variations and are designed based on their application. Screws come in four basic parts as shown in figure 12 below:
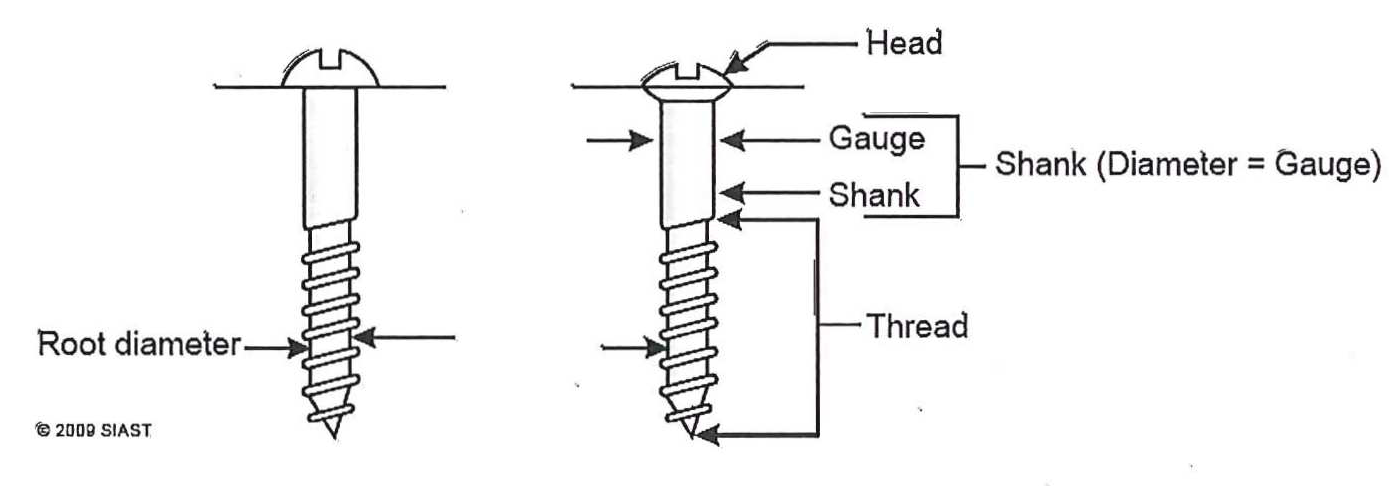
Figure 12: Parts of a screw
There are many different types of screws that are common in the construction industry as listed below:
When fastening with screws, approximately 2/3 of the screw should penetrate into the base material to maximize holding power. Generally, when choosing screws, one needs to consider the material being fastened, and whether or not a pilot hole is required. Additionally, a countersunk hole may be required when drilling a pilot hole to allow the screw head to sit flush or below the material face without causing extensive damage. Pilot holes should be of the same diameter as the root of the screw.
Bolts
Bolts are available in a variety of sizes, types, and materials. For illustrations, see chapter 10 in Carpentry under Bolts. The typical types are outlined below:
Review Questions
- What coating offers optimal protection against corrosion?
- Which nail shank offers the highest amount of holding power?
- What effects does nail coatings have on a nail?
- Which has a thicker shank, a #8 screw or #6 screw?
- What determines the size of a pilot hole?
- What is the difference between machine bolts and stove bolts?
