Chapter E4 – Installs Exterior Windows
Instruction Sheet 14.04.1– Installs Exterior Windows
Key Competencies
The NOA for Carpenter (2013) identifies the required competencies (skills) for the task of installing exterior windows. These are:
- Select and use tools and equipment such as levels, tape measures, hammers and cordless drills
- Assess and adjust rough openings for existing conditions such as out-of-square, out-of-level and wrong size or location
- Ensure adjacent jambs or frames are aligned with each other and other units
- Place and secure window in rough opening using shims and fasteners to level and plumb
- Verify proper operation such as latching, spacing and alignment
- Install membrane and flashing at top and membrane around casing (NOA, p. 57).
Window frames are constructed from wood, vinyl, prefinished aluminum, fiberglass, or composite materials. Windows are classified by their method of operation into three main types and have variations within each one.
Window Types
- Fixed – picture, fixed, horizontal
- Sliding – horizontal or vertical
- Swinging – awning, casement, hopper, Jalousie
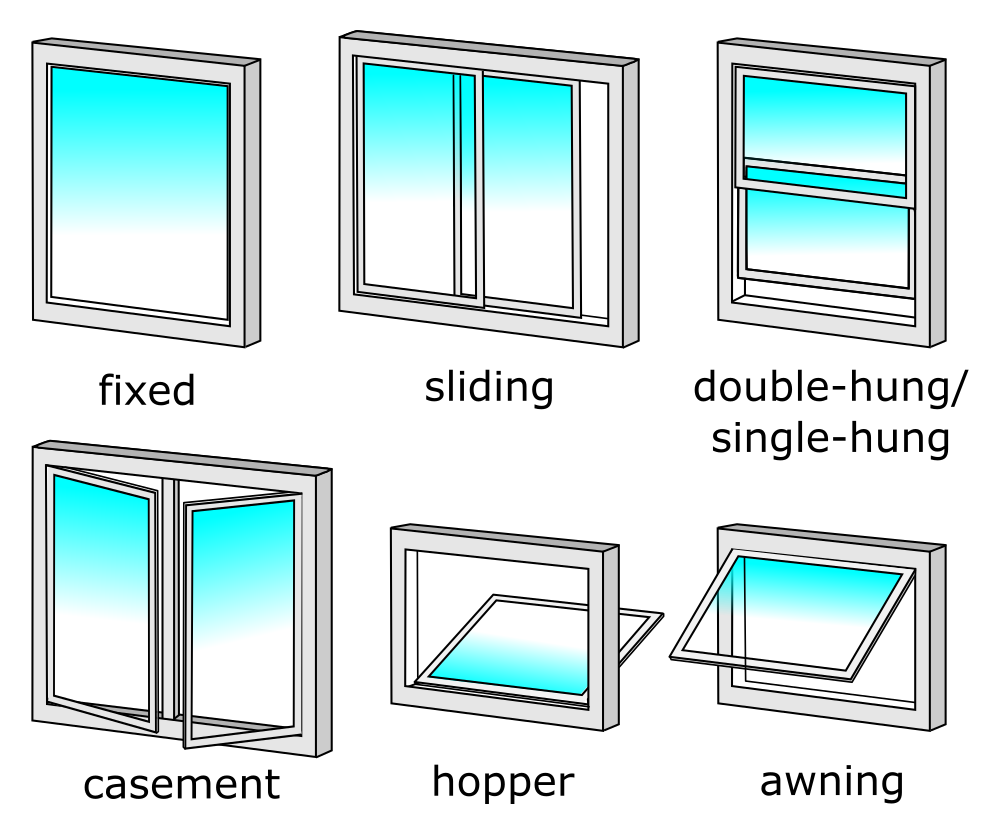
Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Window_Types_United_States.png
Window types may be grouped into different configurations and shapes. On a blueprint, windows are identified by type on the window schedule for easy reference.
- Bay Windows
- Bow Windows
- Garden Windows
- Quarter- Round Windows
- Half-Round Windows
- Full Round Windows
- Octagon Windows
- Arch Windows
- Extended Chord Windows
- Rake Head Windows
- Transom Windows
Passive solar window design can improve the solar heat gain coefficient and improve the comfort and operational costs of a building. Heat can be gained or lost through conduction, radiation or air leakage. Windows may be glazed or filled with inert gases for added energy efficiency.
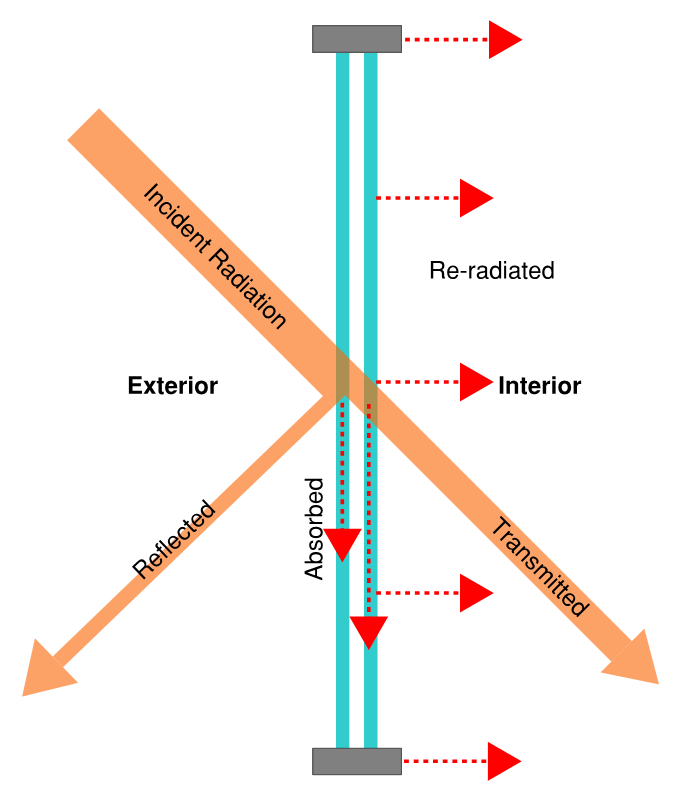
Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Solar_Heat_Gain_V2.png
Proper window installation will protect the home from mold and rot due to moisture. Installation will vary by type of window and manufacturer’s recommendations. However, the sequence of installation should prevent water infiltration and shed water away from the opening using the “shingling” effect.
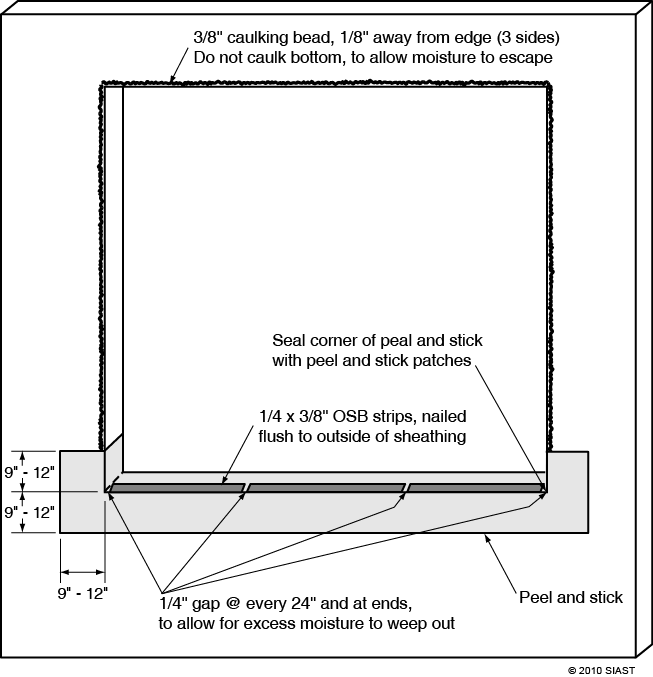
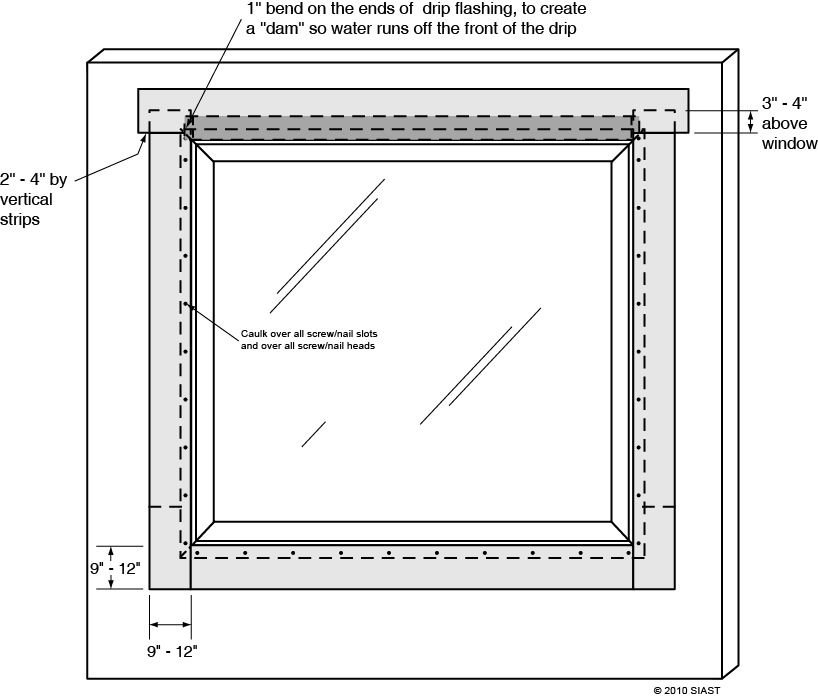
For additional information and terminology please review:
- Carpentry, Chapter 58 “Window Terms and Types” and Chapter 59 “Window Installation”
- Principles and Practices of Commercial Construction, study the section called “Windows”
- Canadian Wood Frame House Construction, study the section titled, “Windows and Doors”
- National Building Code of Canada, study section 9.7 sub-section 3.7.2, “Windows,” and section 9.32, “Ventilation”
For more details on this, review Brightspace Instruction Sheets:
EXFN 201/221 Exterior Windows and Doors (2017):
Review Questions
- The three main types of windows are:
- What is the difference between a fixed window and a picture window?
- What are two types of sliding windows?
- Name three types of “swinging” windows
- On an elevation view of a window, the dashed lines that meet in V point to what?
- What is the difference between a bay and a bow window?
- Where are half-round and half-ellipse style windows used?
- What is a rake-head window?
- What are muntins?
- Name four types of glazing available for windows.
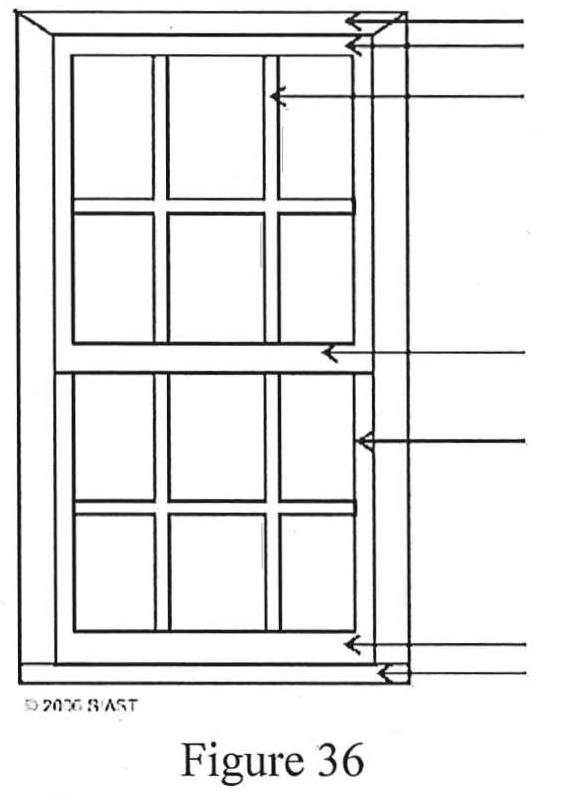 Identify the parts of the double hung window shown below by inserting the appropriate letter from the list
Identify the parts of the double hung window shown below by inserting the appropriate letter from the list
- Identify the parts of the fixed window shown below:
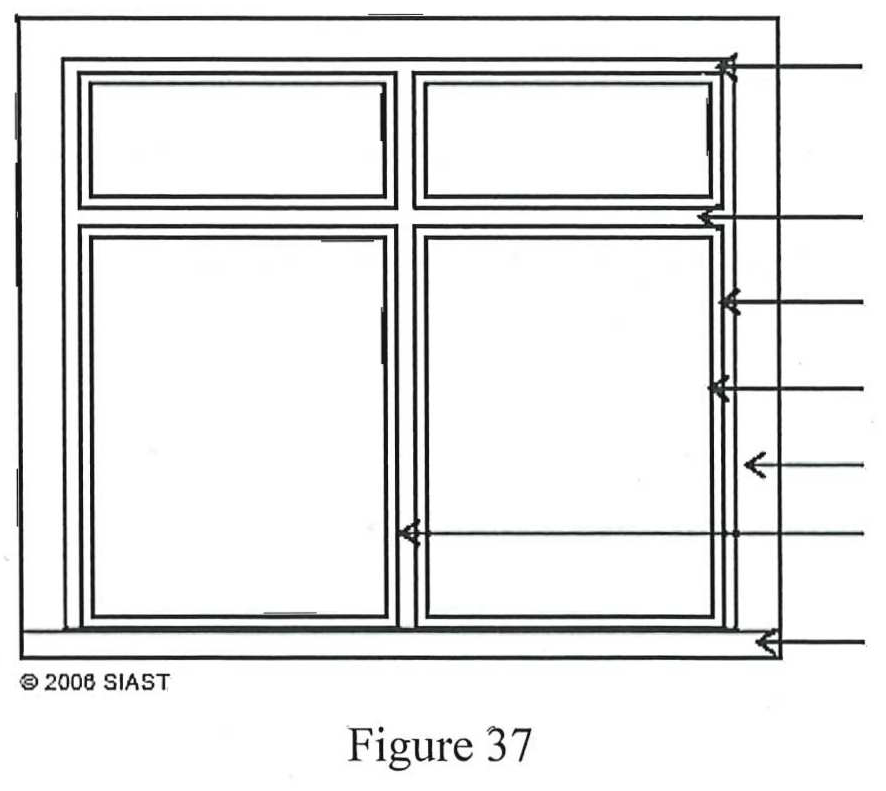
- What are two methods that can be used to hold the glass unit in place?
- Explain the use of setting blocks under the glazing.
- Select the letter beside the window type and place it beside the corresponding definition.
- ___ Consists of an upper and lower sash that slides A) Hopper
- ___ Used mainly for light and aesthetics B) Double-hung
- ___ Open with the use of a side mechanism C) Awning
to allow the window to open outwards D) Casement
- ___ Window that is hinged on the top and opens outward E) Jalousie
- ___ One sash slides past another sash sideways F) Stationary
- ___ A series of glass or metal slats that can be G) Horizontal sliding
opened or closed as desired
- ___ A window that is hinged on the bottom and opens most often to the interior
- If there is no bedroom door directly to the outside, at least one window must be openable from the inside without the use of _____, _____, or _____.
- What is the minimum obstructed opening required for a bedroom window?
- If the rough opening size for a window isn’t given on the construction documents, where can you find the size of the R.O.?
- The minimum area of a window in a bedroom which opens for ventilation is _____.
- Where a bedroom window opens into a window well, a clearance of not less than _____ mm shall be provided in front of the window in the window well.
- Bathrooms within a dwelling unit require a minimum unobstructed window area of _____ m2 for natural ventilation.
- A bathroom in a dwelling unit that does not have a window for natural ventilation shall require mechanical ventilation with an air exchange rate of _____.
- A bedroom that is 380 mm wide must be at least _____ mm high to provide a minimum opening width of _____ m2.
- Fixed, sliding, swinging
- A fixed window has a sash whereas a picture window does not.
- Horizontal sliders and vertical sliders (double hung).
- Casement, hopper, and awning
- The hinges in a swinging window.
- A bay window consists of 3 units, two at 45° to the wall; a bow window consists of 4 or 5 units arranged in a curved shape and project outward from the wall
- Usually sit on top of other windows or door units.
- Has a sloping top, usually to match the slope of a roof.
- Vertical and horizontal bars that divide up a large pane into smaller panes.
- Plain glass, low E glass, heat absorbing glass, and reflective glass.
- Answers from top to bottom: G, C, F, A, D, E, B
- Answers from top to bottom: E, C, G, F, A, B, D
- Rabbet on one side, window stop on the other; or plain window jamb with window stops on both sides.
- Setting blocks are 2 small wooden or hard rubber blocks placed under the sealed glazing unit at its quarter points. This allows some movement in the wall without cracking the glass.
-
- B
- F
- D
- C
- G
- E
- A
- Keys, tools, or special working knowledge. (9.9.10.1)
- Area no less than 0.35m2 with no dimensions less than 380 mm (9.9.10.1-2)
- In a manufacturer’s catalogue from the supplier who supplied the windows.
- 0.28 m2 (Table 9.32.2.2)
- 760 mm (9.9.10.1-3)
- 0.09 m2 (Table 9.32.2.2)
- 5 L/s
- 920 mm, 0.38 m2
