Chapter F13 – Constructs Stairs
Topic 1 – Identify Stair Components and Requirements
Types of Stairs
Stairs come in many different shapes and can be chosen based on layout, appearance, or code requirements. Below are pictured some common types.
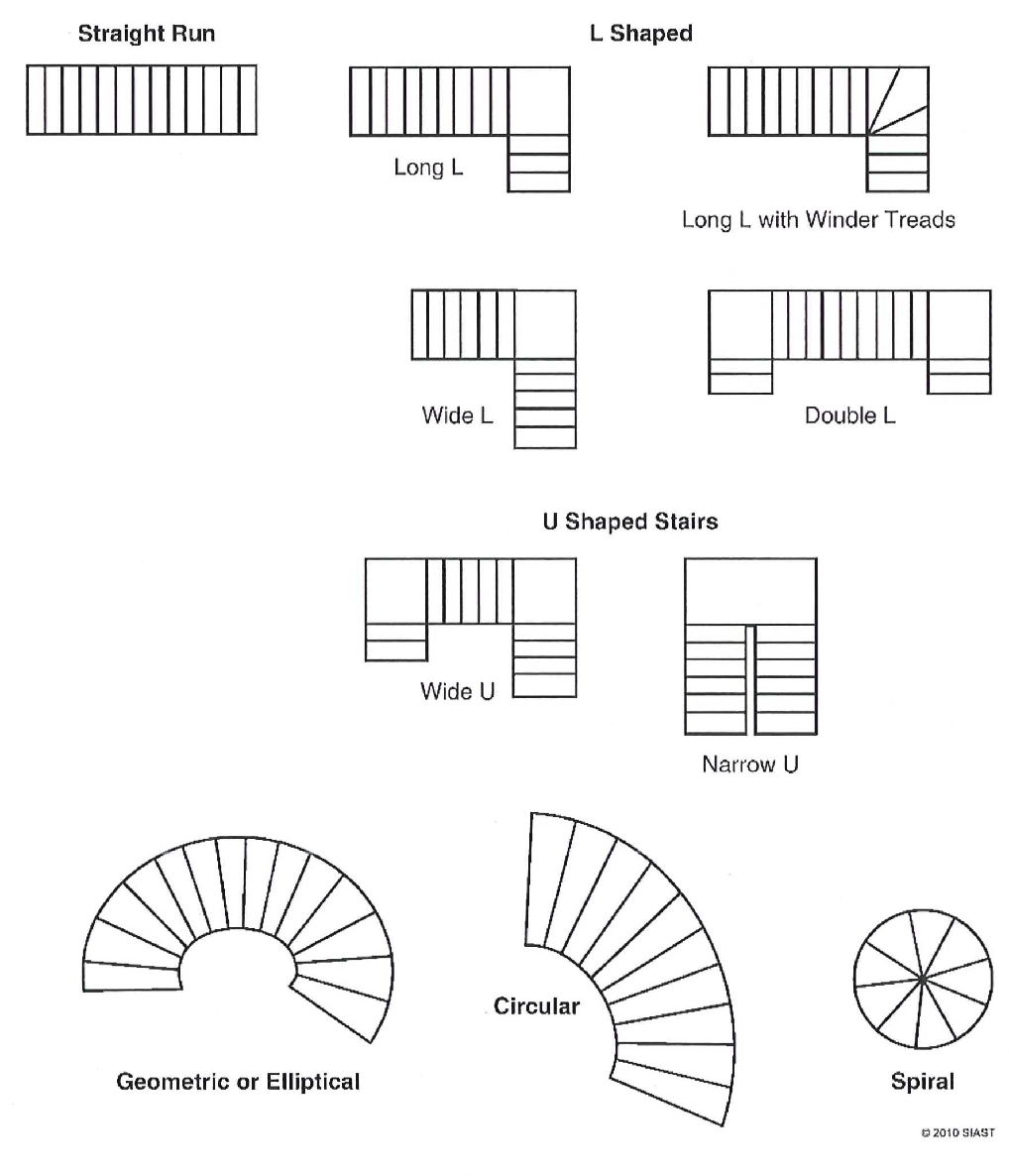
Terminology
When performing calculations on stairs, it is important to understand the basic terminology and components of stairs. Below is an image outlining terms that are common for all stairs.
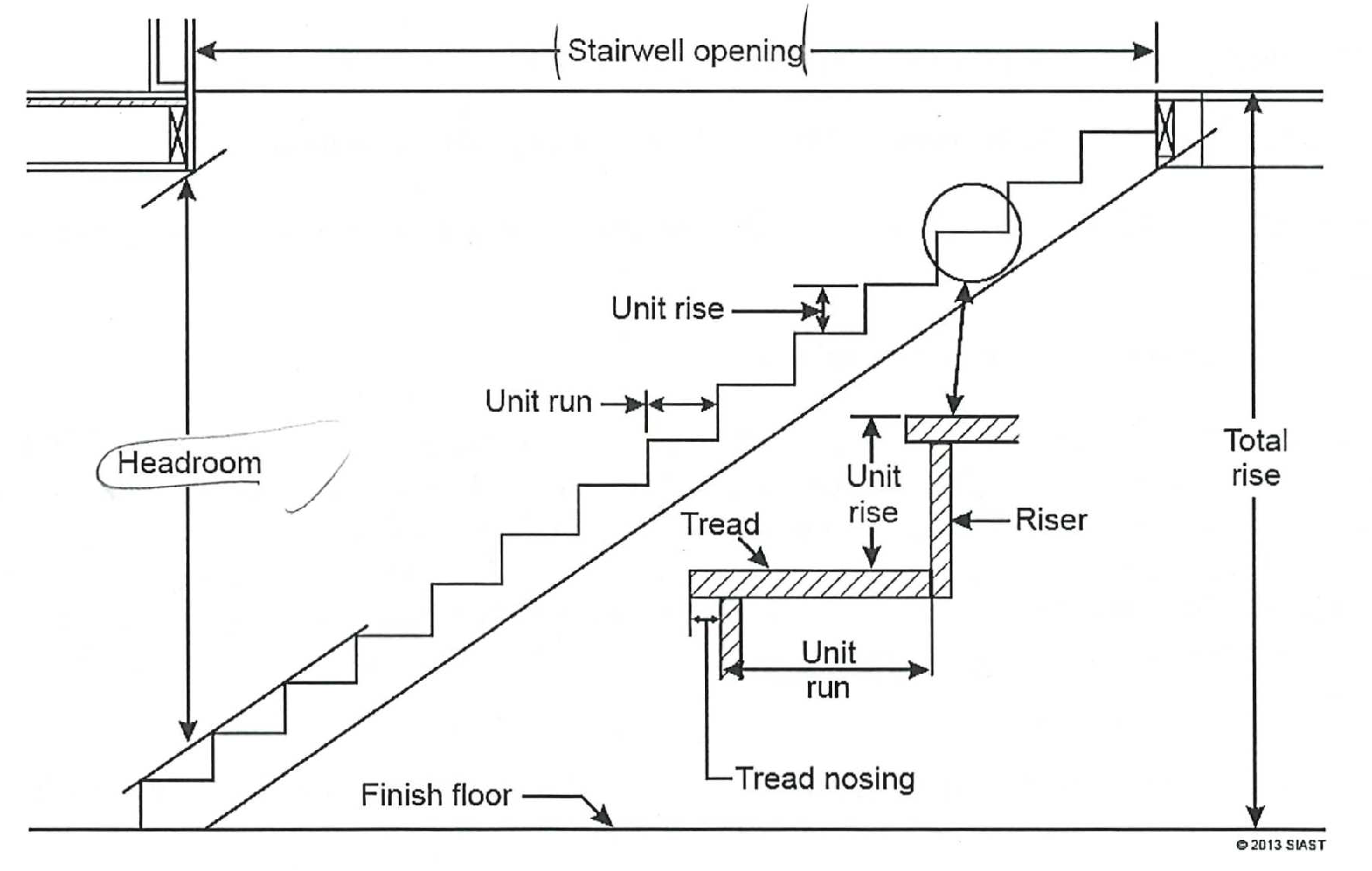
In reference to the above image, it important to understand a few key points:
There are also a number of other key terms that should be known. Find the definitions for the following:
Use the Carpentry textbook and Building Trades Dictionary to define these terms.
Review Questions
- Identify each item in the figure below:
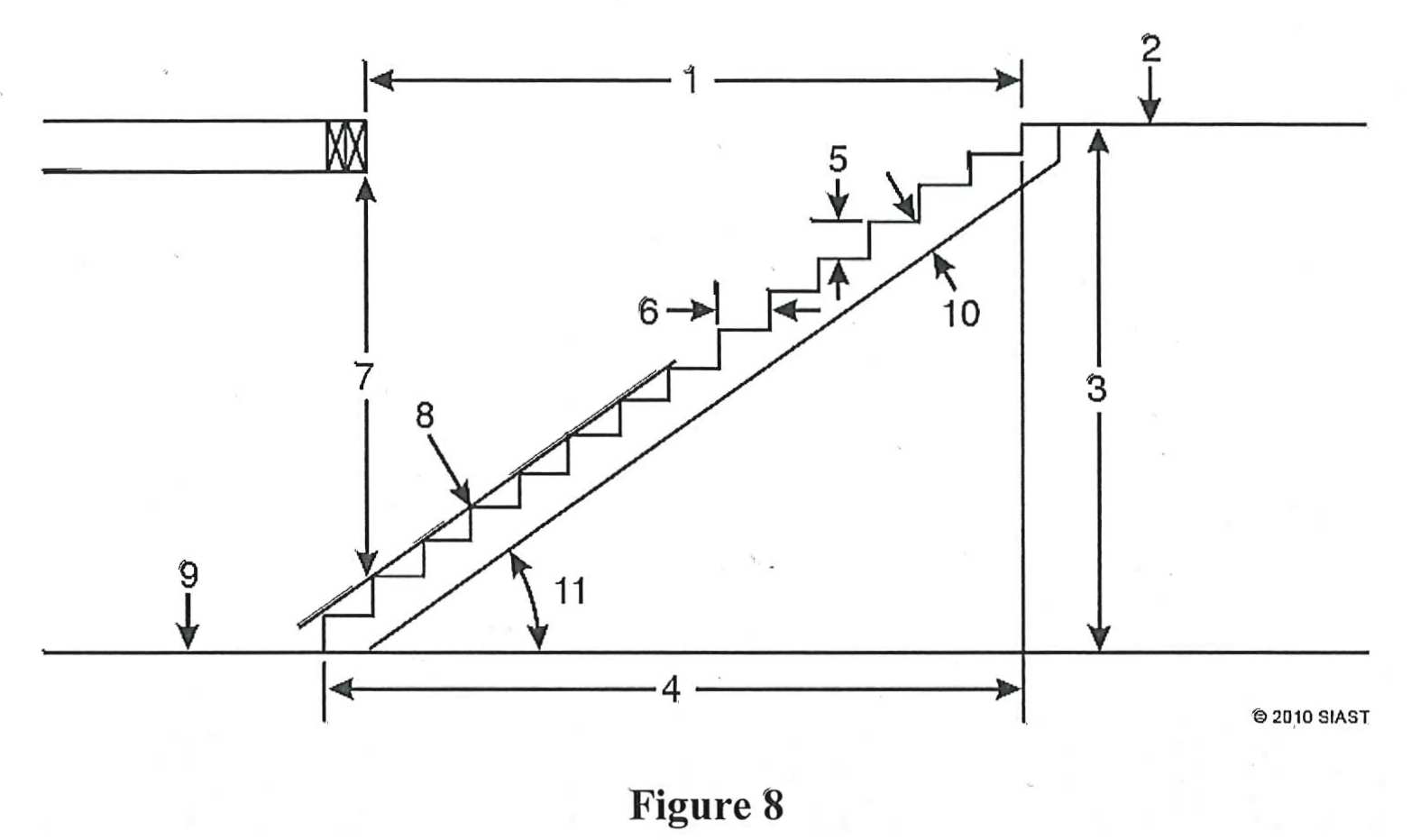
- What two functions does a riser serve in a closed set of stairs?
- Refer to figure 9 below to identify the following stair types:
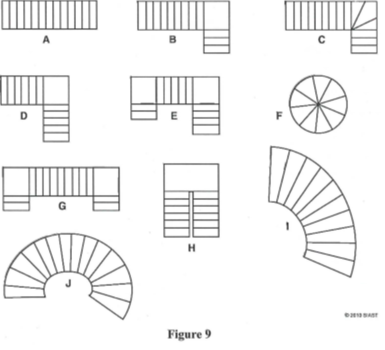
- The NBC in tables 9.8.4.1 and 9.8.4.2 refer to two different types of stairs. Name and describe the two types.
- Interior stairs in a building (except for a dwelling unit) shall have at least _____ risers in any one flight.
- Section 9.8.4.4 states “all treads and risers shall have uniform rise and run in any one flight. Why is this important?
- State the requirements for interior stairs in a single family residence.
- Maximum rise _____ mm
- Minimum rise _____ mm
- Maximum run _____ mm
- Minimum run _____ mm
- Minimum width of stairs (between faces of wall finishes) for the following are
- What is the minimum sized landing required for an L shaped stair, 900 mm wide, withing a dwelling unit?
- When a door swings toward a stair, what is required?
- If a door swings away from the stairs at the top, is a landing required?
- Do the exterior steps leading up to the front door of a building require a landing?
- What is the maximum vertical height of any flight of stairs?
- If public stairs are 1200 mm wide, how many handrails are required?
- Do exterior steps for a single family house having 3 risers require a handrail?
- Heights of handrails on stairs shall be not less than _____ mm and not more than _____ mm.
- Protective barriers on sides of stairs, landings, porches, and balconies are called _____.
- Wood stair stringers must have a minimum effective depth of _____ mm and an overall depth of not less than _____ mm.
- In a single family house, if there are no closed risers in the stairs, the maximum distance between stringers is _____ mm.
- If the stairs have open risers and the stringers are 800 mm apart, the treads must be at least _____ mm thick.
- Maximum spacing of stringers in a house is _____ mm
- Minimum thickness of wood stringers are, when:
-
- Item 1 – stairwell
- Item 2 – upper finished floor
- Item 3 – total rise
- Item 4 – total run
- Item 5 – unit rise
- Item 6 – unit run
- Item 7 – headroom
- Item 8 – line of flight
- Item 9 – lower finish floor
- Item 10 – effective depth
- Item 11 – pitch angle
- Closes the stair between the treads and supports the treads
-
- Straight
- Long L
- Winders
- Wide L
- Wide U
- Spiral
- Double L
- Narrow U
- Circular
- Elliptical
- Private stairs – interior or exterior stairs that serve single dwelling units, houses with a secondary suite including their common spaces or garages that serve either.
Public stairs – all stairs not described as private stairs
- Three (9.8.3.2-1)
- To prevent tripping and stumbling on stairs.
-
- 200 mm
- 125 mm
- 355 mm
- 255 mm
-
- 860 mm
- 900 mm (9.8.2.1)
- 900 x 900 (Table 9.8.6.3)
- A landing is required at the top of the stairs; the full arc of the door must be over the landing. (9.8.6.3-5)
- No (9.8.6.2-2)
- A landing is required at the top of the stairs, except at secondary entrances to a single family house with 3 risers or less. (9.8.6.2-3)
- 3.7 m (9.8.3.3)
- Two handrails (Table 9.8.7.1)
- No (9.8.7.1-3)
- 865 mm; 1070 mm (9.8.7.4-2)
- Guards (9.8.8.1-1)
- 90 mm; 235 mm (9.8.9.4-1a)
- 900 mm (9.8.9.4-1d)
- 38 mm (9.8.9.5-1)
- 1200 mm (9.8.9.4-2)
-
- 25 mm
- 38 mm (9.8.9.4-1c)
