Chapter B7 Performs Site Layout
Topic 4 – Perform Basic Transit Functions
A transit can perform the same layout functions as a builder’s level as the telescope also rotates 360 degrees horizontally. The transit can tilt vertically to shoot vertical angles up to 45 degrees. Like an inch can be broken down into smaller units (fractions), degrees can be subdivided into smaller portions. The units that make up a degree are called minutes. Each degree has 60 minutes. Each minute can be further divided into seconds. Each minute has 60 seconds. Transits use a vernier scale. Readings are taken either clockwise or counter clockwise. Theodolites are digital transits which eliminate having to read a vernier scale.
For example, 26 degrees 30 minutes 20 seconds is expressed as 26° 30’ 20”.
Set up and leveling of a transit is the is the same as a builder’s level.
For further information on types and parts of transits as well as diagrams refer to Instruction Sheets on Brightspace.
CNST 204 (Page 3-40):
- Instruction Sheet 1.2 Types and Parts of a Transit
- Instruction Sheet 3.2 Preparing to Use the Transit
Also, more information in text:
- Principles and Practices of Commercial Construction “Survey Equipment and Transits”
Review Questions
- Name four types of transits used in the construction industry.
- What can be used to increase accuracy when reading the vernier and horizontal scale?
- List the natural sources which may create errors in your readings.
- True or False:
- To test for level, the bubble will not move when the transit is turned horizontally
- Clean the lens of a telescope with an ammonia-based commercial glass cleaner
- An error of one degree will distort your measurement enough to affect accuracy
- What is the purpose of the upper motion screw?
- What is the purpose of the lower motion screw on the transit?
- Describe the circles on a transit.
- Degrees are divided into _____ and _____.
- Record the clockwise and counter-clockwise readings on the following vernier scales (to the nearest minute):
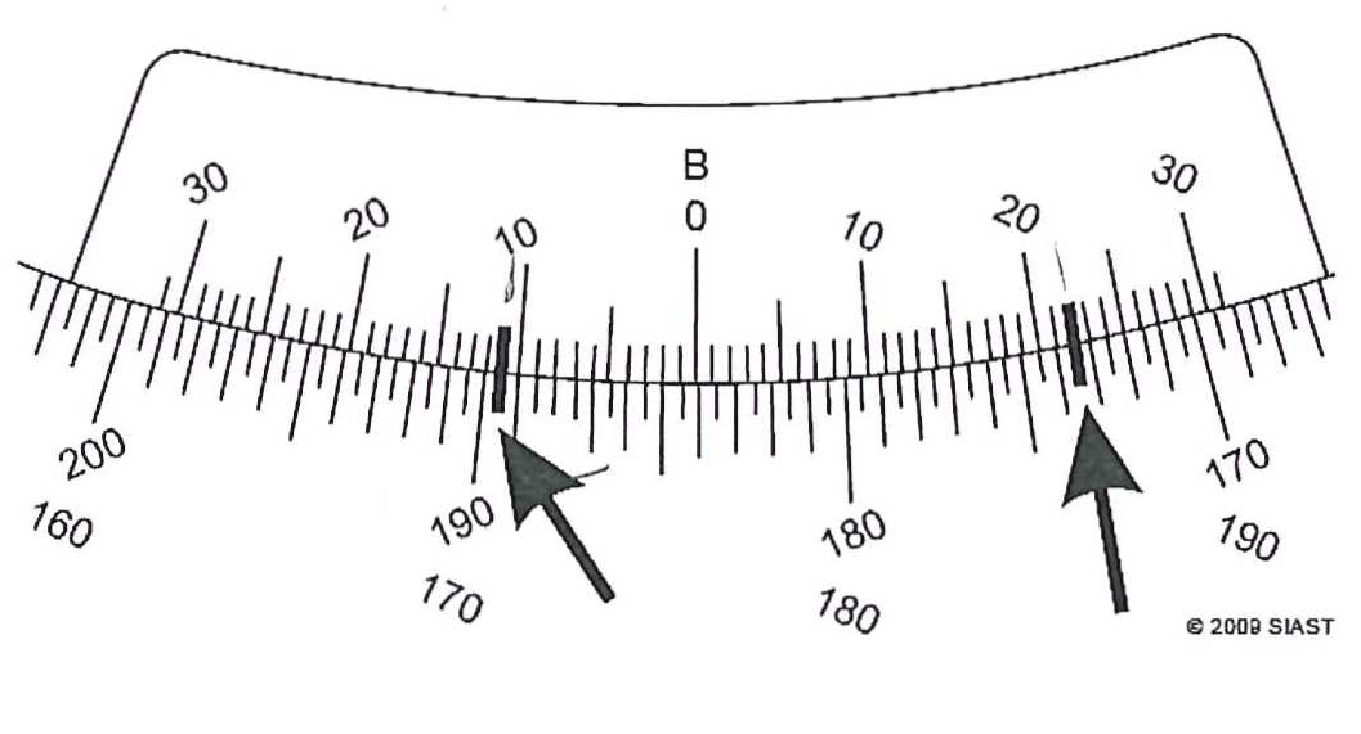
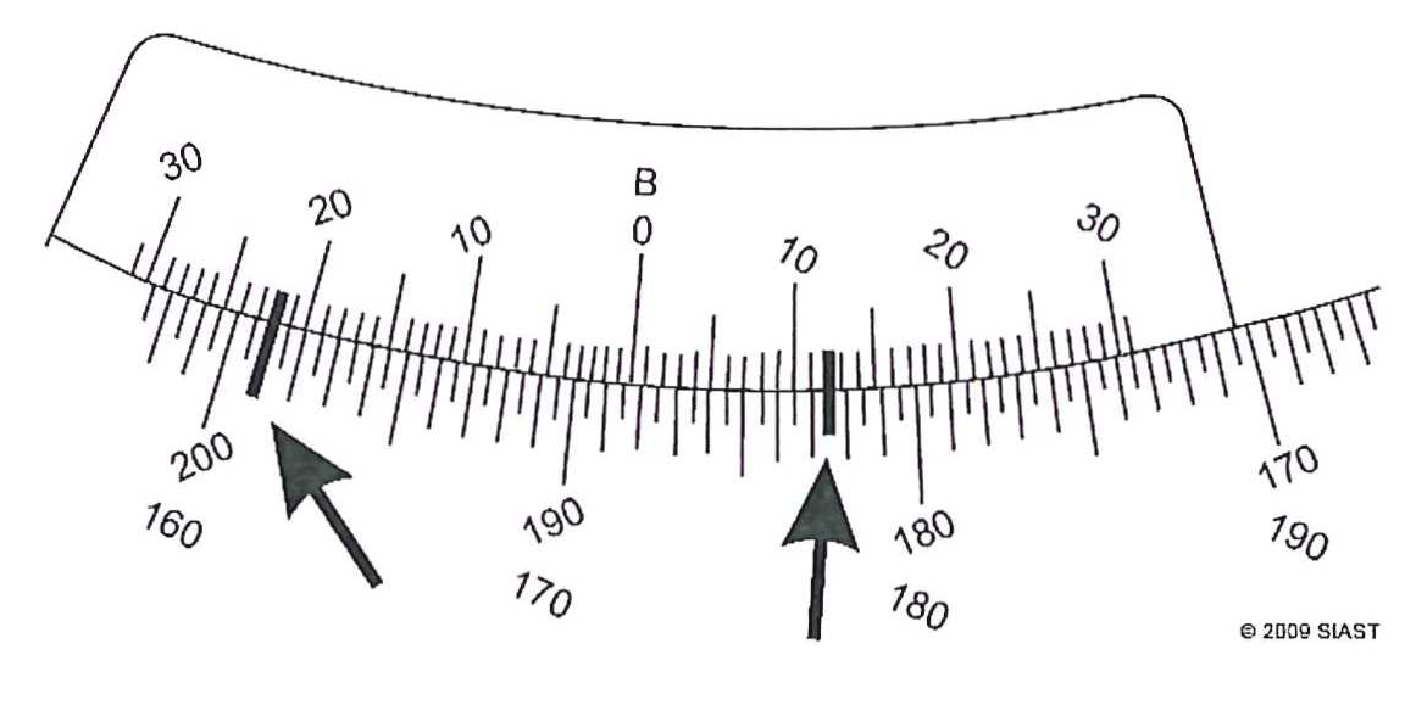
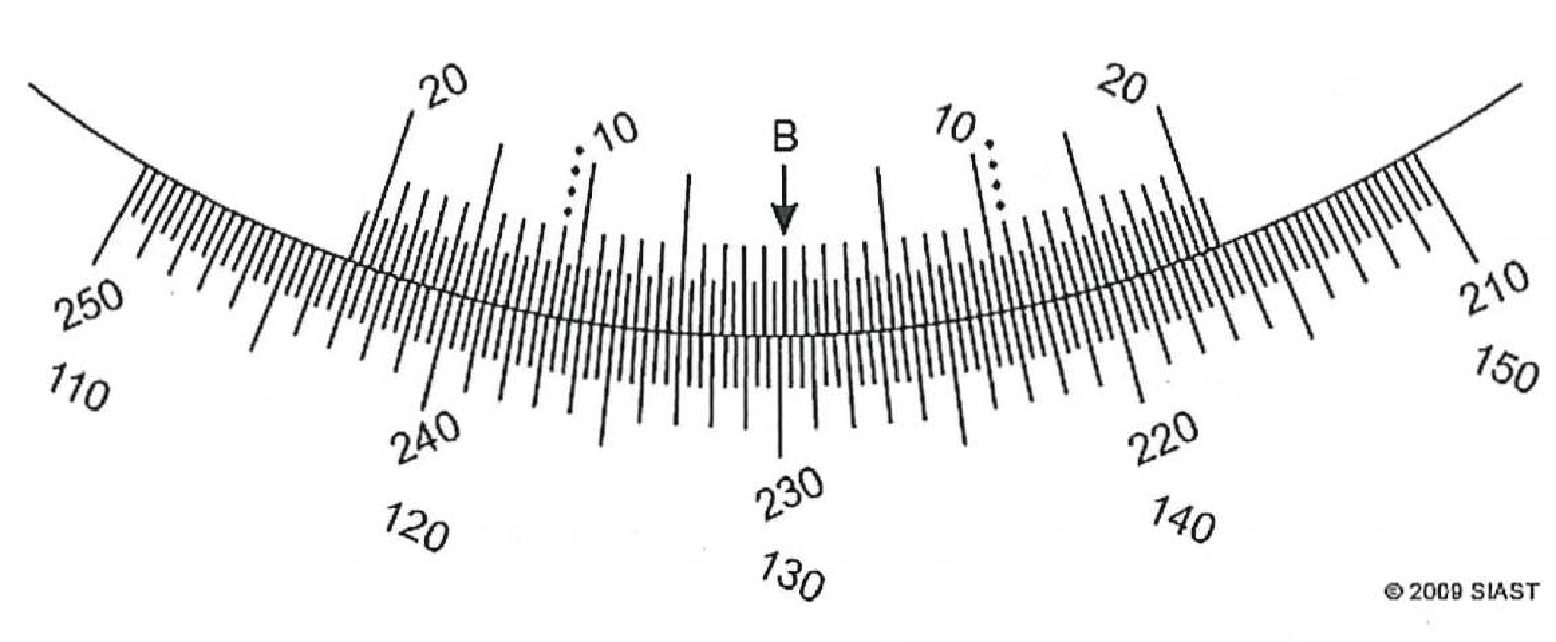
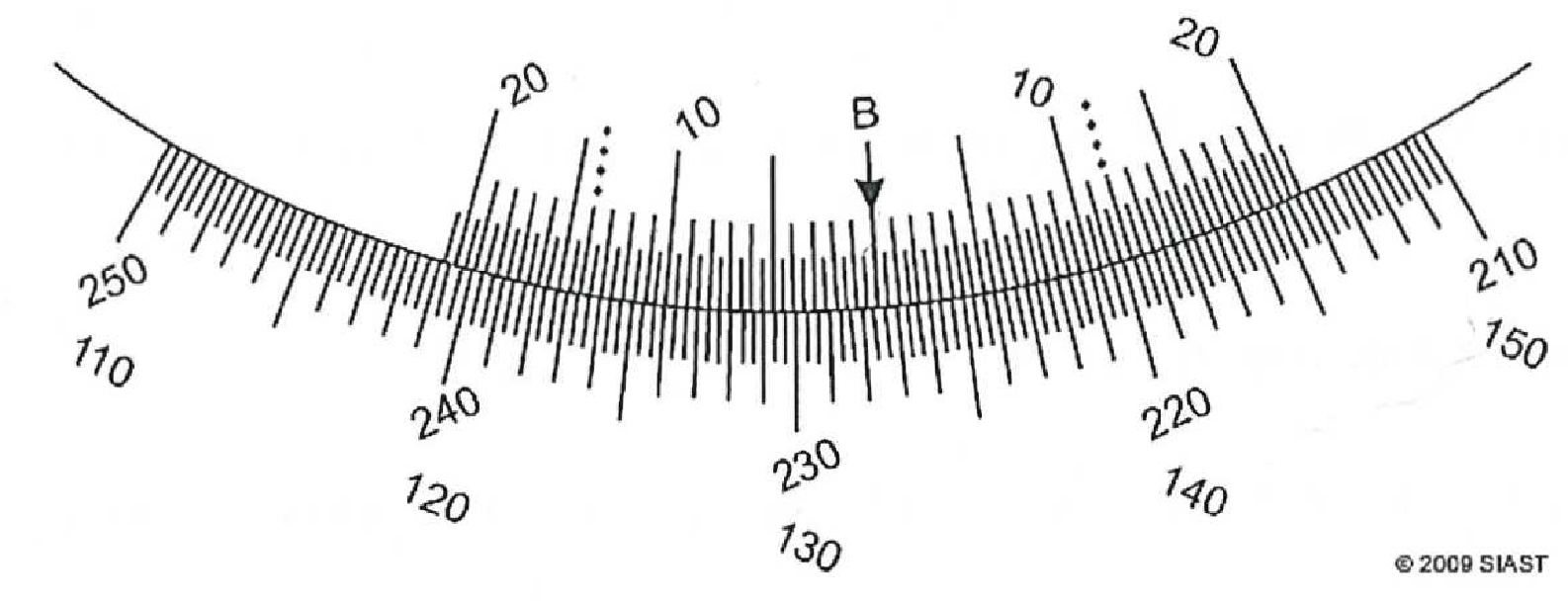
- True or False:
- Each degree contains 30 minutes.
- Each minute contains 60 seconds.
- When storing a transit, all locking screws should be left loose.
- When levelling the transit base levels, both base levels should be used to bring the instrument perfectly level.
- The telescope on a transit may turn 360° vertically.
- An error of 1 degree in layout work will result in an error of 1.745 ft over a distance of 100 feet.
- When doing layout work using a steel tape, a 50 N pull should be maintained on the tape for accurate measurements.
Answers:
-
- Three point
- Four point
- Transit level
- Electronic theodolite
- Magnifying glass
- Wind, temperature change, heat waves, soft ground, vibration in the ground, dust, fog, and poor lighting
-
- True
- False
- True
- To make fine adjustments to the horizontal vernier scale.
- Moves the telescope horizontally to line up with a target or a point.
- Moves the telescope horizontally to line up with a target or a point.
- 60 minutes per degree, 60 seconds per minute
-
- Clockwise: 184°11’; CCW: 175°52’
- Clockwise: 188°22’; CCW: 171°42’
- Clockwise: 229°51’; CCW: 130°11’
- Clockwise: 227°34’; CCW: 132°32’
-
- False
- True
- True
- False
- False
- True
- True
