Expansion Anchors
Expansion Anchors
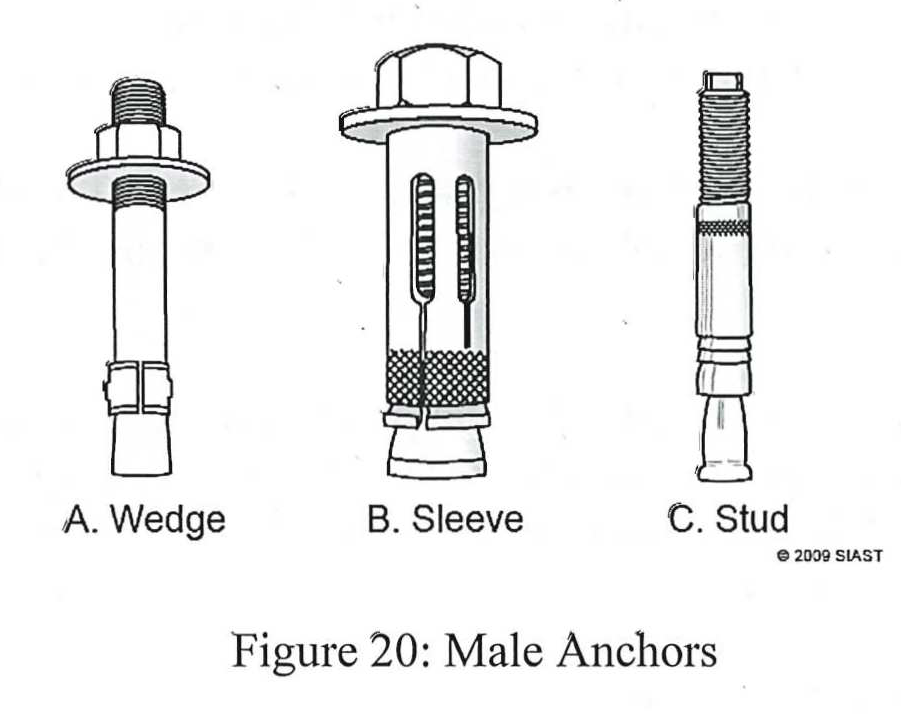 Expansion anchors are placed in concrete that has already set. A hole with the same diameter as the anchor is drilled to receive them. They come in both male and female configurations. The male anchors are driven into a pilot hole that is drilled through both the fastened and base material. It is then tightened which utilizes the expanding mechanism to produce substantial holding power. The three most used varieties are shown in figure 20 (right).
Expansion anchors are placed in concrete that has already set. A hole with the same diameter as the anchor is drilled to receive them. They come in both male and female configurations. The male anchors are driven into a pilot hole that is drilled through both the fastened and base material. It is then tightened which utilizes the expanding mechanism to produce substantial holding power. The three most used varieties are shown in figure 20 (right).
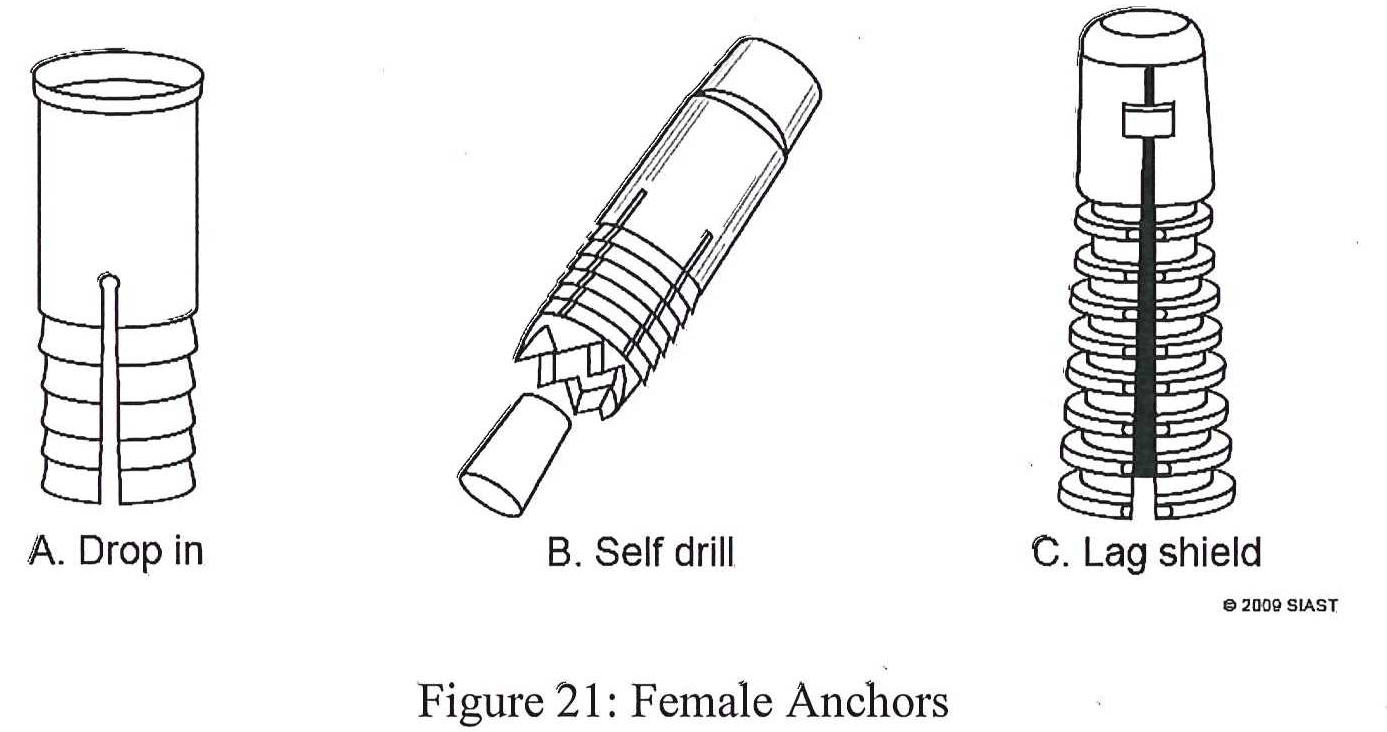
The female anchors are designed to drop into pilot holes and are used in a manner similar to threaded inserts. It comes in three varieties as shown below:
The performance of an expansion anchor depends on a number of factors including:
Hollow Wall Fasteners
The primary consideration that must be made when choosing a hollow wall fastener is the type of wall that is being fastened to. Typically, this will be either drywall or masonry. The weight and type of load is the next factor that will determine which fastener to choose. Shear load is the most common and refers to the force that pulls straight down and perpendicular to the fastener, such as hanging a mirror. A fasteners shear capacity is an indication of its ability to counteract these forces. Combination loads exert an outward force such as with drawers in a cabinet and require a stronger hold. Dead loads, where the pull is constant such as with hanging a plant from a ceiling require more anchorage, however, shock loads will require the most where the load may be subjected to sudden impacts or increased weight.
If the user is unsure of the amount and type of load the fastener will be subjected to, it is always a good idea to go with a heavier duty than required as failure can have serious consequences in some circumstances.
Common Types of Hollow Wall Fasteners
For illustrations, see Hollow Wall Fasteners in Chapter 10 in Carpentry
Plastic Anchors – These can be used in either solid or hollow walls. Used wherever a wood screw would normally be used. These can provide strong holding power in solid wall applications but are only suitable for light duty in hollow walls such as hanging pictures, mirrors, and accessories.
Toggle Bolts – These fasteners are single use as the wings will either spring open or fold over after the fastener is inserted. The provide a great deal of holding power and can be used to hold up cabinets, shelves, and grab bars. As the toggle must fit, it produces large holes in the wall being fastened to. Placement of the anchor needs to be precise.
Hollow Wall Expansion Anchors – Provides a great deal of holding power and can be used for mirrors, cabinets, and shelf brackets. Must be chosen to fit the thickness of drywall or masonry being fastened to. It can be reused, however, the hole drilled must be precisely placed and centered at the desired location.
Self-Drilling Drywall Anchors – A self-drilling anchor that does not require a pilot hole, they can be made of either plastic or metal. They provide moderate holding power and are suitable for attaching anything that is normally screwed into place. The rating must be matched to the load.
Review Questions
- What are five factors that affect the performance of an expansion anchor?
- What prevents a toggle bolt from turning during fastening?
- What type of hollow wall fastener will withstand the largest direct pull?
- Describe shear capacity of an anchor.
- According to the NBC, what is the minimum required diameter and spacing of cast-in-place anchor bolts for a rough sill?
