Installs Embedded Steel
Chapter C4 – Installs Embedded Steel
Key Competencies
The NOA for Carpenter (2013) identifies the required competencies (skills) for the task of installing embedded steel. These are:
- Select reinforcing steel material according to specifications
- Select and install chairs to ensure proper coverage of reinforcing steel
- Calculate overlaps required for reinforcing steel or wire mesh according to building code
- Cut and bend reinforcing steel or wire mesh on site using equipment such as benders, quick-cut saws and grinders
- Tie reinforcing steel to ensure spacing continuity according to structural drawings
- Place embeds such as angle irons, anchor bolts and structural steel weld plates
- Install reinforcing components such as stirrups, and vertical and horizontal bars
- Inspect reinforcing steel for defects such as dirt, debris, rust and corrosion before installation
- Place embedded steel according to project drawings and specifications (NOA, p. 40)
https://www.flickr.com/photos/wsdot/48761225012
Concrete has good compressive strength and that it is why it is often chosen as a foundation material. However, concrete has weak tensile strength. Reinforcement is the term given to the adding of rebar or welded wire mesh to concrete to improve its ability to resist tension. Depending on its position and location concrete can have different and multiple stresses exerted upon it. As such reinforcement is added to resist various forces.
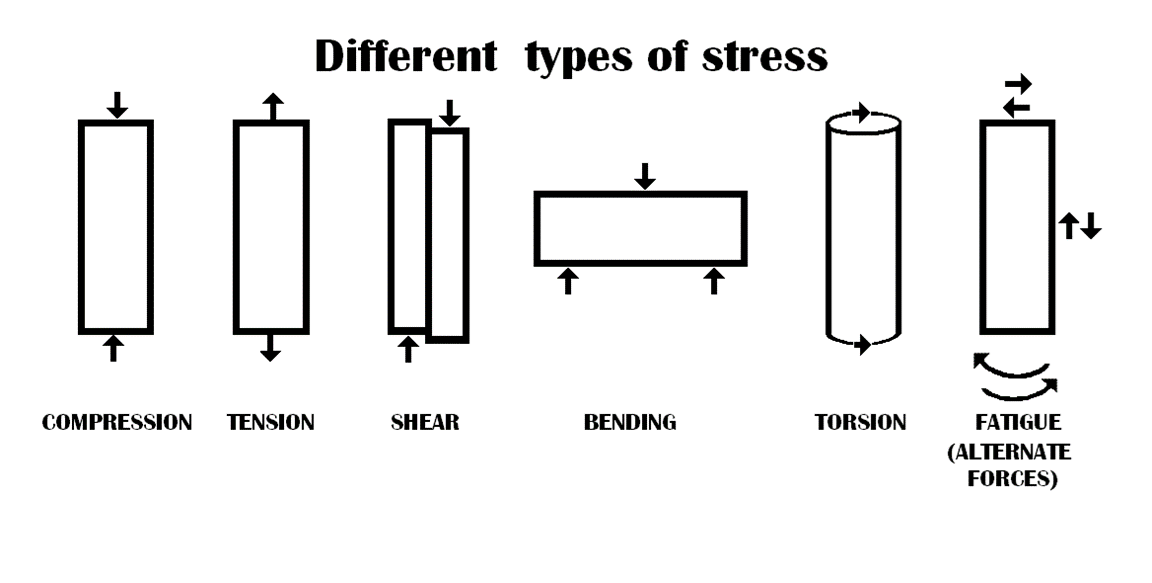
Source: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/e/eb/DIFFERENT_TYPES_OF_STRESS.png
Fibre mesh is reinforcement that can be added to the concrete mix. Proper size and placement of reinforcement in concrete is important if it is to achieve its purpose. Tolerances and requirements for reinforcement are in the National Building Code.
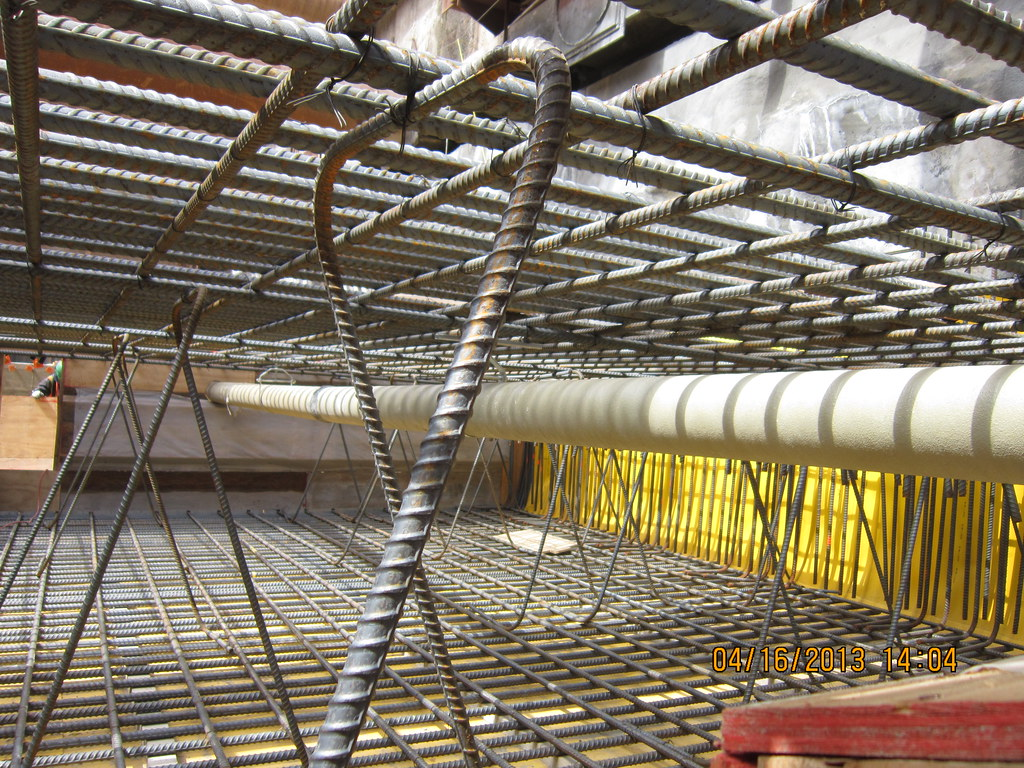

https://www.flickr.com/photos/mtacc-esa/8660301039
For further information review the following:
- Principles and Practices of Commercial Construction, study the chapter on “Reinforced Concrete Frame”
• Canadian Wood-Frame House Construction, study the section on “Slabs-on-Ground”
Review Instruction Sheet (IS) on Brightspace:
FNDT 100 (p. 262 – 279):
- IS 1.2 Concrete Reinforcement
- IS 1.3 Placing Reinforcement for Concrete
Review Questions
- What is the difference between yield strength and ultimate strength in rebar?
- Why does reinforcing require minimum coverage?
- Where should rebar be placed in concrete members such as beams or foundation walls?
- Why are “trussed bars” sometimes used in continuous beams?
- Why should slabs-on-grade have reinforcing placed no more than 50 mm down from the top regardless of slab thickness?
- How much should rebar be lapped at splices?
- When is regular welding of rebar permitted?
- Welded wire fabric is spliced by lapping: _________________________
