6
Paula Hansen
Energy communities come in many shapes and sizes, and a multitude of potential benefits for society, the planet and energy systems. At the same time as energy communities, low-carbon energy is also growing, providing the basis for a clean energy transition. This transition is crucial to achieving the decarbonization goals agreed by governments nationally and internationally. Energy communities promote renewable energy production and can foster greater acceptance of new forms of energy production, storage, distribution, and consumption.
The challenge of decarbonizing energy systems is compounded by the electrification of transport, residential and commercial buildings (including space and water heating), cooking, as well as industrial processes. This is leading to a growing demand for electricity overall, in addition to the need for more clean energy. Countries thus face the challenge of replacing existing fossil fuels while simultaneously meeting growing demand, and ensuring energy security, reliability, and affordability. Energy communities can be part of the solution.
Energy communities have several benefits, on various levels. They have benefits for individuals and members of communities, local communities, and economies. These benefits may be environmental, economic, social or relate to the power system itself.
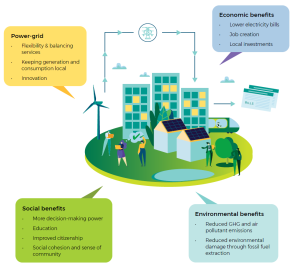
Environmental benefits
One of the most prominent benefits of energy communities is that they focus on sustainable ways of producing and consuming energy. To achieve the climate change goals set by the EU, countries need to transform their energy systems completely, replace their fossil fuels and adapt their systems to the inevitable growth of renewable energy production. It is predicted that energy communities could account for over 17 % of all wind power production and 21 % of solar power production by 2030, which makes them an important player in the energy transition.
Economic benefits
Economic benefits are one of the key factors that motivate people to join energy communities. By joining an energy community, members often save money on their electricity bills. In some communities, revenue streams may be created by selling off excess energy produced within the community. This can lead to positive outcomes for local communities if money earned is invested back into the local community. The development of renewable energy generation plants may also create jobs, attract new investment, or support local economic development in other ways.
Social benefits
While economic and environmental benefits of energy communities are often prioritized in decision-making, they can also have a range of social benefits. Energy communities empower local communities, giving them more autonomy and control over their environment. Energy communities may also improve energy literacy, for example by involving people in energy-related decision-making, introducing new technologies, or even organizing field visits for schools. Participation in energy communities also encourages people to actively participate in other aspects of energy citizenship, helping them have more influence on local decision-making processes or sharing their experience and knowledge with peers.
Energy system benefits
Energy communities also affect the energy system directly. One potential benefit is that they may improve local coordination of resources by better matching production and consumption. Energy communities can help the energy system become more flexible; and they offer the possibility to test and develop innovative new solutions. They also promote more local energy production which helps improve the security, reliability and resilience of energy networks.