Emily P. Harris
Environmental health is concerned with preventing disease, death, and disability by reducing exposure to adverse environmental conditions and promoting behavioral change. It focuses on the direct and indirect causes of diseases and injuries and taps resources inside and outside the healthcare system to help improve health outcomes.
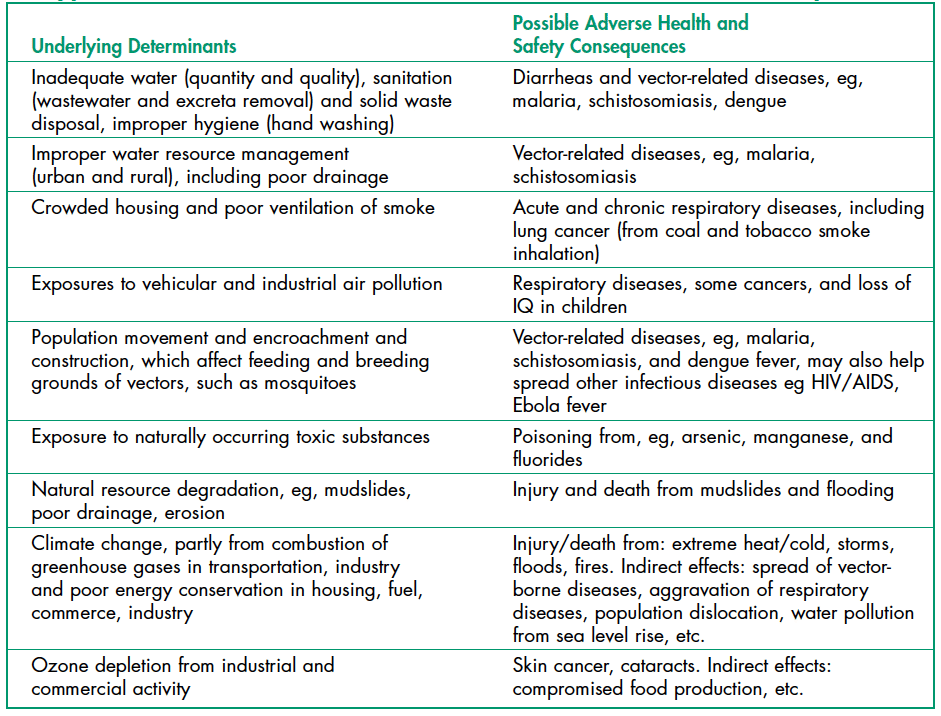
Poverty, Health, and Environment
Environmental health risks can be grouped into two broad categories. Traditional hazards are related to poverty and the lack of development and mostly affect developing countries and poor people. Their impact exceeds modern health hazards by ten times in Africa, five times in Asian countries (except for China), and 2.5 times in Latin America and the Middle East (Figure 1). Water-related diseases caused by inadequate water supply and sanitation impose an especially large health burden in Africa, Asia, and the Pacific region. In India alone, over 700,000 children under five die annually from diarrhea. In Africa, malaria causes about 500,000 deaths annually. More than half of the world’s households use unprocessed solid fuels, particularly biomass (crop residues, wood, and dung) for cooking and heating in inefficient stoves without proper ventilation, exposing people—mainly poor women and children—to high levels of indoor air pollution (IAP). IAP causes about 2 million deaths each year.
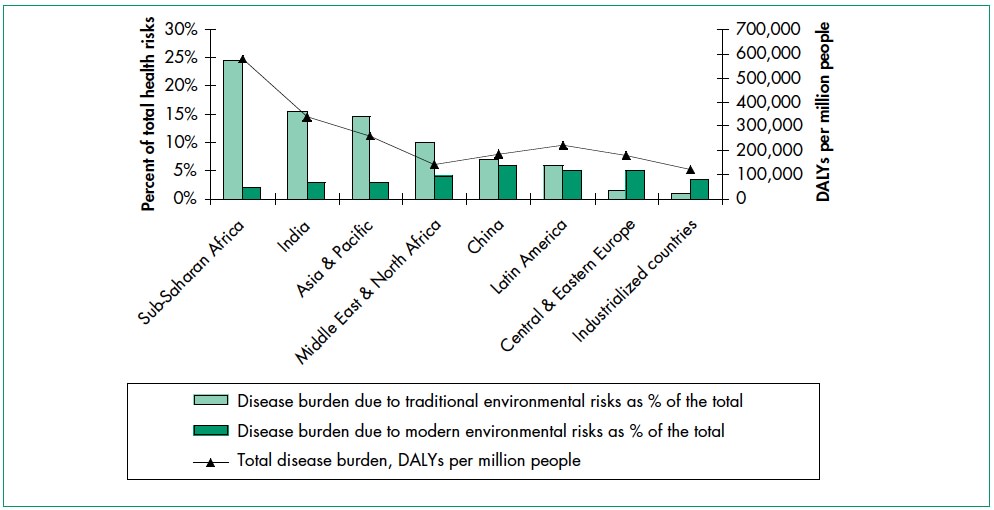
Modern hazards caused by technological development prevail in industrialized countries with low exposure to traditional hazards. The contribution of modern environmental risks to the disease burden in most developing countries is similar to – and in quite a few countries, greater than – that in rich countries. Urban air pollution, for example, is highest in parts of China, India, and some cities in Asia and Latin America. Poor people increasingly experience a “double burden” of traditional and modern environmental health risks. Their total burden of illness and death from all causes per million people is about twice that in rich countries, and the disease burden from environmental risks is 10 times greater.
Environmental Health and Child Survival

Worldwide, the top killers of children under five are acute respiratory infections (indoor air pollution); diarrheal diseases (mostly from poor water, sanitation, and hygiene); and infectious diseases such as malaria. Children are especially susceptible to environmental factors that put them at risk of developing illness early in life. Malnutrition (the condition that occurs when the body does not get enough nutrients) is an important contributor to child mortality—malnutrition and environmental infections are inextricably linked. The World Health Organization (WHO) recently concluded that about 50% of the consequences of malnutrition are caused by inadequate water and sanitation provision and poor hygienic practices.
Poor Water and Sanitation Access
With 1.1 billion people lacking access to safe drinking water and 2.6 billion without adequate sanitation, the magnitude of the water and sanitation problem remains significant. Each year contaminated water and poor sanitation contribute to 5.4 billion cases of diarrhea worldwide and 1.6 million deaths, mostly among children under five years old. Intestinal worms, which thrive in poor sanitary conditions, infect close to 90 percent of children in the developing world and, depending on the severity of the infection, may lead to malnutrition, anemia, or stunted growth. About 6 million people are blind from trachoma, a disease caused by the lack of clean water and poor hygiene practices.
Indoor Air Pollution
Indoor air pollution—a much less publicized source of poor health—is responsible for more than 1.6 million deaths annually and 2.7% of the global disease burden. It is estimated that half of the world’s population, mainly in developing countries, uses solid fuels (biomass and coal) for household cooking and space heating. Cooking and heating with such solid fuels on open fires or stoves without chimneys lead to indoor air pollution and respiratory infections. Exposure to these health-damaging pollutants is particularly high among women and children in developing countries, who spend the most time inside the household. As many as half of the deaths attributable to indoor use of solid fuel are of children under the age of five.
Malaria
Approximately 40% of the world’s people—mostly those living in the world’s poorest countries—are at risk from malaria. Malaria is an infectious disease spread by mosquitoes but caused by a single-celled parasite called Plasmodium. Every year, more than 200 million people become infected with malaria, and about 430,000 die, with most cases and deaths found in Sub-Saharan Africa. However, Asia, Latin America, the Middle East, and parts of Europe are also affected. Pregnant women are especially at high risk of malaria. Non-immune pregnant women risk both acute and severe clinical disease, resulting in fetal loss in up to 60% of such women and maternal deaths in more than 10%, including a 50% mortality rate for those with severe disease. Semi-immune pregnant women with malaria infection risk severe anemia and impaired fetal growth, even if they show no signs of acute clinical disease. An estimated 10,000 women and 200,000 infants die annually from malaria infection during pregnancy.
Emerging Diseases
Emerging and re-emerging diseases have been defined as infectious diseases of humans whose occurrence during the past two decades has substantially increased or threatens to increase in the near future relative to populations affected, geographic distribution, or magnitude of impacts. Examples include the Ebola virus, West Nile virus, Zika virus, sudden acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), H1N1 influenza; swine and avian influenza (swine, bird flu), HIV, and a variety of other viral, bacterial, and protozoal diseases.
Various environmental factors may contribute to the re-emergence of a particular disease, including temperature, moisture, human food or animal feed sources, etc. Disease re-emergence may be caused by the coincidence of several environmental and/or social factors to allow optimal conditions for disease transmission.
Ebola, previously known as Ebola hemorrhagic fever, is a rare and deadly disease caused by infection with one of the Ebola virus strains. Ebola can cause disease in humans and nonhuman primates. The 2014 Ebola epidemic is the largest in history (with over 28,000 cases and 11,302 deaths), affecting multiple countries in West Africa. A few cases were reported in Nigeria and Mali, and a single case was reported in Senegal; however, these cases were contained, with no further spread in these countries.
The HIV/AIDS epidemic has spread with ferocious speed. Virtually unknown 20 years ago, HIV has infected more than 60 million people worldwide. Approximately 14,000 new infections occur daily, more than half of them among young people below the age of 25. Over 95 percent of PLWHA (People Living With HIV/AIDS) are in low- and middle-income countries. Over 20 million have died from AIDS, over 3 million in 2002 alone. AIDS is now the leading cause of death in Sub-Saharan Africa and the fourth-biggest killer globally. The epidemic has cut life expectancy by more than ten years in several nations.
It seems likely that a wide variety of infectious diseases had affected human populations for thousands of years, emerging when the environmental, host, and agent conditions were favorable. Expanding human populations has increased the potential for infectious disease transmission due to close human proximity and increased the likelihood of humans being in “the wrong place at the right time” for disease (e.g., natural disasters or political conflicts). Global travel increases the potential for a disease carrier to transmit infection thousands of miles away in just a few hours, as evidenced by WHO precautions concerning international travel and health.
Antibiotic Resistance
Antibiotics and similar drugs, called antimicrobial agents, have been used for the last 70 years to treat patients with infectious diseases. Since the 1940s, these drugs have greatly reduced illness and death from infectious diseases. However, these drugs have been used so widely and for so long that the infectious organisms the antibiotics are designed to kill have adapted to them, making them less effective. Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria change, reducing the effectiveness of drugs, chemicals, or other agents designed to cure or prevent infections. This is caused by the process of evolution through natural selection (Figure 3). The antibiotic-resistant bacteria survive and continue to multiply, causing more harm.

New forms of antibiotic resistance can easily cross international boundaries and spread between continents. Many forms of resistance spread with remarkable speed. Each year in the United States, at least 2 million people acquire serious infections with bacteria resistant to one or more antibiotics designed to treat those infections. At least 23,000 people die each year in the US due to these antibiotic-resistant infections. Many more die from other conditions that were complicated by an antibiotic-resistant infection. The use of antibiotics is the single most important factor leading to antibiotic resistance around the world.

Antibiotics are among the most commonly prescribed drugs used in human medicine. However, up to 50% of all the antibiotics prescribed for people are not needed or are not optimally effective as prescribed.
In recent years, there has been growing concern over methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), a bacterium resistant to many antibiotics. In the community, most MRSA infections are skin infections. MRSA causes life-threatening bloodstream infections, pneumonia, and surgical site infections in medical facilities.
Suggested Supplementary Reading:
Koch, B.J. et al. 2017. Food-animal production and the spread of antibiotic resistance: the role of ecology. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment (15)6: 309-318.
Notable Excerpts:
“Antibiotic use in food animals is correlated with antibiotic resistance among bacteria affecting human populations.” p. 311
“Microbial genes encoding antibiotic resistance have moved between the food-animal and human health sectors, resulting in illnesses that could not be treated by antibiotics.” p. 312
