17 5.4 Cancer and the cell cycle
Lisa Bartee; Walter Shriner; and Catherine Creech
Cancer comprises many different diseases caused by a common mechanism: uncontrolled cell growth. Despite the redundancy and overlapping levels of cell cycle control, errors do occur. One of the critical processes monitored by the cell cycle checkpoint surveillance mechanism is the proper replication of DNA during the S phase. Even when all of the cell cycle controls are fully functional, a small percentage of replication errors (mutations) will be passed on to the daughter cells. If changes to the DNA nucleotide sequence of a gene are not corrected, a gene mutation results. All cancers start when a gene mutation causes a change in the order of the amino acids that make up a protein that plays a key role in cell reproduction. Changes in the amino acid sequence can change the shape of the protein. Since the shape of the protein is changed, its function may be changed as well. The change in the cell that results from the misshaped protein may be minor: perhaps a slight delay in the binding of Cdk to cyclin or an Rb protein that detaches from its target DNA while still phosphorylated. Even minor mistakes, however, may allow subsequent mistakes to occur more readily. Over and over, small uncorrected errors are passed from the parent cell to the daughter cells and amplified as each generation produces more non-functional proteins from uncorrected DNA damage. Eventually, the pace of the cell cycle speeds up as the effectiveness of the control and repair mechanisms decreases. Uncontrolled growth of the mutated cells outpaces the growth of normal cells in the area, and a tumor (“-oma”) can result.
Proto-oncogenes
The genes that code for the positive cell cycle regulators are called proto-oncogenes. Proto-oncogenes are normal genes that, when mutated in certain ways, become oncogenes, genes that cause a cell to become cancerous. Consider what might happen to the cell cycle in a cell with a recently acquired oncogene. In most instances, a mutation in the DNA sequence of a gene will result in a less functional or non-functional protein. This result is detrimental to the cell and will likely prevent the cell from completing the cell cycle, which means that this cell cannot create daughter cells. In this case, the organism is not harmed because the mutation will not be carried forward and the damage is minimal.
Occasionally, however, a gene mutation causes a change that increases the activity of a positive regulator. For example, a mutation that allows Cdk to be activated without being partnered with cyclin could push the cell cycle past a checkpoint before all of the required conditions are met. If the resulting daughter cells are too damaged to undergo further cell divisions, the mutation would not be propagated and no harm would come to the organism. However, if the atypical daughter cells are able to undergo further cell divisions, subsequent generations of cells will probably accumulate even more mutations, some possibly in additional genes that regulate the cell cycle.
The Cdk gene in the above example is only one of many genes that are considered proto-oncogenes. In addition to the cell cycle regulatory proteins, any protein that influences the cycle can be altered in such a way as to override cell cycle checkpoints. An oncogene is any gene that, when altered, leads to an increase in the rate of cell cycle progression.
Tumor Suppressor Genes
Like proto-oncogenes, many of the negative cell cycle regulatory proteins were discovered in cells that had become cancerous. Tumor suppressor genes are segments of DNA that code for negative regulator proteins. Activated negative regulator proteins prevent the cell from undergoing uncontrolled division. The collective function of the best-understood tumor suppressor gene proteins, Rb, p53, and p21, is to put up a roadblock to cell cycle progression until certain events are completed. A cell that carries a mutated form of a negative regulator might not be able to halt the cell cycle if there is a problem. Tumor suppressors are similar to brakes in a vehicle: Malfunctioning brakes can contribute to a car crash.
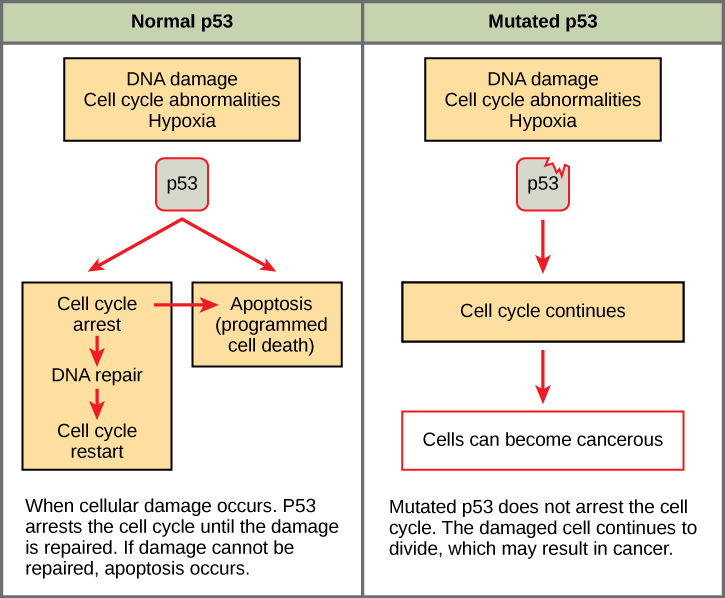
Mutated p53 genes have been identified in more than one-half of all human tumor cells. This discovery is not surprising in light of the multiple roles that the p53 protein plays at the G1 checkpoint. A cell with a faulty p53 may fail to detect errors present in the genomic DNA (Figure 2). Even if a partially functional p53 does identify the mutations, it may no longer be able to signal the necessary DNA repair enzymes. Either way, damaged DNA will remain uncorrected. At this point, a functional p53 will deem the cell unsalvageable and trigger programmed cell death (apoptosis). The damaged version of p53 found in cancer cells, however, cannot trigger apoptosis.
References
Unless otherwise noted, images on this page are licensed under CC-BY 4.0 by OpenStax.
OpenStax, Biology. OpenStax CNX. November 11, 2017 https://cnx.org/contents/GFy_h8cu@10.118:CYZpmedR@7/Cancer-and-the-Cell-Cycle
