11
Dr. Sandi Van Lieu

Stages of the Writing Process
- Pre-writing
- Writing (Drafting)
- Revising
- Editing
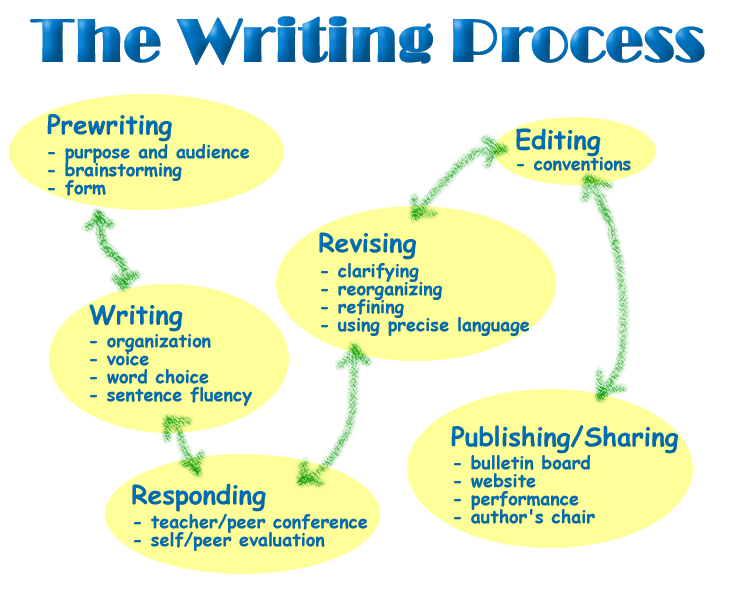
1. Pre-writing
During the pre-writing stage, choose and narrow your topic. You should be able to answer “yes” to these three questions about your topic:
- Does it interest me?
- Do I have something to say about it?
- Is it specific?
- Who are my readers?
- What do my readers know about my topic?
- What do my readers need to know about my topic?
- How do my readers feel about my topic?
- To express
- To inform
- To persuade
- Serious or frivolous/humorous
- Intimate or detached
- Academic/formal
- First person—”I, we”
- Second person—”you”
- Third person—”he, she, they”
- Brainstorming/Listing
- Freewriting
- Clustering/Mapping
- Questioning
- Discussing
- Outlining
2. Writing (Drafting)
During drafting, you should compose a FULL rough draft. A draft is the first whole version of all your ideas put together. The basics of a good draft:
- Has a fully developed introduction and conclusion
- Has fully developed body paragraphs, each containing a topic sentence, and examples and details from the text(s) as support
3. Revising
Revising is finding and correcting problems with content; changing the ideas in your writing to make them clearer, stronger, and more convincing.
- Revising looks at important areas such as essay structure, organization, and sentence structure.
- You should read through your essay numerous times during this stage.
4. Editing
Editing is finding and correcting problems with grammar, style, word choice/usage, and punctuation. In addition:
- Editing focuses on smaller details and involves proofreading.
- Editing also involves making sure citations and the Works Cited are correct.
*You’ll learn more about the writing process in detail over the next several chapters.
Attribution
- “Overview of the Writing Process,” created by Dr. Sandi Van Lieu and licensed under CC BY NC SA 3.0.
