50 Personal Protective Equipment
Learning Objectives
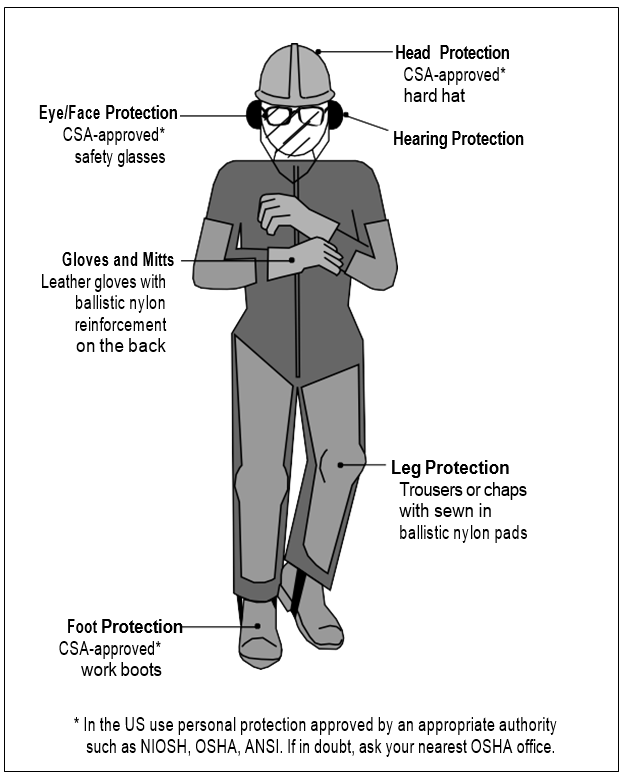
Demonstrate the use of appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) for the job.
General Guidelines
The use of personal protective equipment (PPE) is only one strategy for protecting workers.
Other options should be used first, when ever possible. These include:
- engineering controls
- material substitution
- process change
- revised work practices
- equipment change
- administrative controls and finally,
- the use of personal protective equipment.
Hard Hats
In all situations, if any type of PPE is required, the wearer should be given appropriate training and eduction about:
- when to wear the equipment,
- what hazards the equipment provides protection against.
- the limitations of the equipment,
- how to properly wear the equipment,
- how to inspect the equipment before wearing, and
- how to clean and store the equipment, if necessary.
Safety Glasses and Goggles
Wear CSA or ANSI approved safety glasses/goggles that are appropriate for protecting the eyes from:
- extremely bright light and ultraviolet radiation (UV rays),
- flying objects, and
- very hot, poisonous, and irritating liquids.
Ear Plugs or Muffs
Wear appropriate ear protection to protect ears from excessive noise exposure.
Respirators
Wear respirators as required by your employer while working in an environment where there is danger of breathing air contaminated with toxic gases, vapours, fumes and dusts.
Safety Footwear
Wear safety footwear with metal box toe and puncture resistant sole.
Gloves
Wear appropriate type of gloves when working with chemicals, sol- vents, or toxic substances as well, to protect hands from flying objects and from contact with vibrating machines.
1. Safety Glasses
Selection of Safety Glasses
 Lenses
Lenses
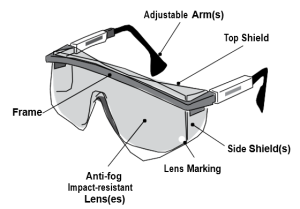
CSA Z94.3/ANSI Z87.1-certified safety glasses have glass, plastic or polycarbonate lenses. They are stronger than regular lenses, are impact-resistant, and come in prescription and non-prescription (plano) forms.
Lens Markings
The manufacturer’s logo is marked (or etched) on all approved safety lenses.
Frames
Safety frames are stronger than street-wear frames and often heat resistant. They are designed to prevent lenses from being pushed into the eyes.
Frame Imprint
All CSA-certified safety frames will be marked with the manufacturer’s trademark, or the logo of the certifying agency.
Correct Fit of Safety Glasses
ENSURE your safety glasses fit properly. Eye size, bridge size and temple length all vary, so safety glasses need to be individually assigned and fitted.
WEAR safety glasses so that the temples fit comfortably over the ears. The frame should be as close to the face as possible and adequately supported by the bridge of the nose.
Proper Care of Safety Glasses
Safety glasses need maintenance.
- CLEAN your safety glasses daily with recommended lens cleaning material. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions. Avoid rough handling which can scratch lenses. Scratches impair vision and can weaken glass lenses.
- STORE your safety glasses in a clean, dry place where they cannot fall or be stepped on. Keep them in a case when they are not being worn.
- REPLACE scratched, pitted, broken, bent or ill-fitting glasses. Damaged glasses interfere with vision and do not provide adequate protection.
2. Safety Footwear
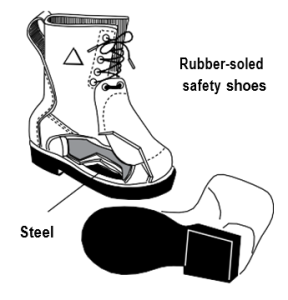
- Safety footwear is designed to protect feet against a wide variety of injuries.
- Impact, compression and puncture are the most common types of foot injury.
- CHOOSE footwear according to the hazard. Refer to CSA Standard Z195 “Protective Footwear” or ANSI Z41 in the US.
- SELECT CSA-certified footwear. Ensure that it has the proper rating for the hazard and the proper sole for the working conditions.
- WALK in new footwear to ensure it is comfortable.
- LACE up boots fully. High-cut boots provide support against ankle injury.
- USE a protective coating to make footwear water-resistant.
- USE metatarsal protection (top of the foot between the toes and ankle) where there is a potential for injury.
- INSPECT footwear regularly for damage. REPAIR or replace worn or defective footwear.
3. Safety Headwear
Headwear consists of a shell and the suspension. These work together as a system and both need regular inspection and maintenance.
CHOOSE the correct headwear for the job. Refer to CSA Standard Z94.1 or ANSI Standard Z89.1, Industrial Protective Headwear – Performance, selection,
Care and Use
Classes of headwear include:
- Type I – protection from impact and penetration at the crown (top) and
- Type II – protection from impact, penetration at the crown (top) and laterally (sides)
Each type is also available in the following classes:
- Class E (20 000 V electrical rating) – non- conducting material (electrical trades)
- Class G (2200 V electrical rating) – non-conducting material (general trades)
- Class C (no electrical rating)
INSPECT headwear before each use. CLEAN the suspension and shell regularly.
DO NOT TRANSPORT headwear in rear windows of vehicles. Heat and UV light can damage the material, making it brittle and less protective.
Shell
- The shell is rigid and light, and is shaped to deflect falling objects. Correct maintenance is important.
- INSPECT and replace a shell that shows signs of wear, cracks, chalky appearance, scratches or gouges.
- A shell exposed to heat, sunlight and chemicals can become stiff or brittle.
- REPLACE headwear when any of the above signs of wear start to appear.
- REPLACE headwear that has been struck, even if no damage is visible.
- REMOVE and destroy any headwear if its protective abilities are in doubt.
- DO NOT DRILL holes, alter or modify the shell.
- Alterations may reduce the protection provided by the headwear.
- DO NOT paint the plastic shell. Paint solvents can make plastic headwear brittle and more susceptible to cracks. Instead, use non-metalic reflective marking tape to make number or symbols for identification purposes. Some headwear may be painted, but check with the manufacturer for approval.
- DO NOT USE winter liners that contain metal or electrically conductive material.
- DO NOT USE metal labels on Class G or E headwear. DO NOT DRAW chin strap over brim or peak.
Suspension
- The suspension system holds the shell away from the head and acts as a shock absorber. It also holds the shell in place on the head and allows air to flow freely.
- ADJUST headband size so that headwear will stay on when wearer is bending over, but not so tight that it leaves a mark on the forehead.
- ENSURE that the suspension is in good condition.
- The main purpose of the suspension is to absorb energy.
- LOOK closely for cracked or torn adjustment slots, frayed material or other signs of wear.
- CHECK suspension lugs carefully. Perspiration and hair oils can cause wear. Long periods of normal use can damage the suspension.
- REPLACE suspension that has torn or broken treads.
- ONLY wear the hard hat with the peak at the back if the suspension has been adjusted do the nape strap remains at the back of the head. Check with the manufacturer to ensure the headwear has been designed to be worn this way.
- DO NOT PUT anything inside headwear. There must be a clearance inside the headwear while it is being worn. In the event of a blow to the head, that space helps absorb the shock.
4. Hearing Protection
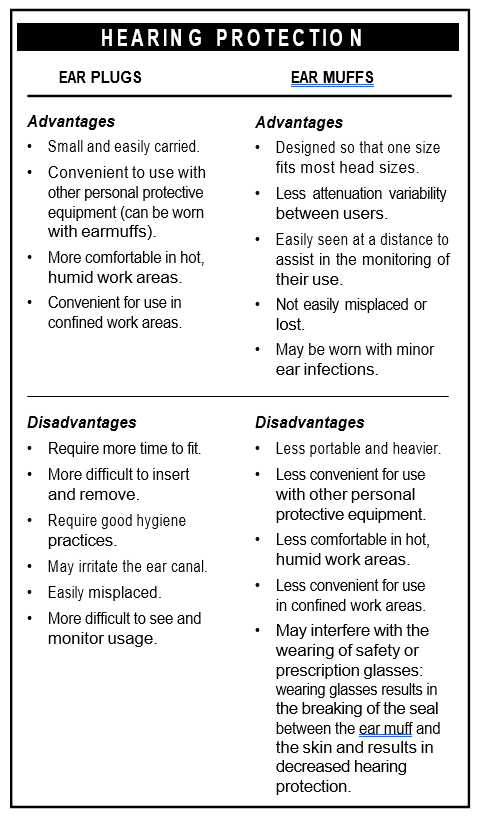
- Hearing protectors reduce the amount of sound energy reaching the ears and hence, reduce the risk of hearing loss.
- SELECT hearing protection that is correct for the job. Refer to CSA Standard Z94.2 Hearing Protection Devices – Performance, Sselection, Care and Use or ANSI Standard S12.6.
- Earplugs are inserted to block the ear canal. They may be premoulded (preformed) or mouldable.
- Canal Caps are comprised of two ear plugs held over the ends of the ear canal by a rigid headband.
- Ear muffs are comprised of hard outer cups, sound-at- tenuating material and soft ear cushions which fit around the ear and hard outer cups. They are held together by a head band.
- DO NOT USE radio headsets as a substitute for hearing protection.
- DO NOT MODIFY hearing protectors.
Proper Care of Hearing Protection
- REFER to manufacturer’s instructions.
- CHECK hearing protection regularly for wear and tear.
- REPLACE ear cushions or plugs that are no longer pliable.
- REPLACE unit when head bands are so stretched that they do not keep ear cushions snugly against the head.
- DISASSEMBLE ear muffs to clean.
- WASH hearing protectors with a mild liquid detergent in warm water, and then rinse in clear warm water.
- ENSURE that sound-attenuating material inside cushions does not get wet.
Proper Fit of Hearing Protection
FOLLOW manufacturer’s instruction. ENSURE hearing protector is tightly sealed within the ear canal or against the side of the head.
5. Hand Protection
Hands are the most vulnerable to injury from accidental contact with tools, machines, chemicals, and hot and cold objects. In some circumstances gloves may provide adequate hand protection. Barrier creams are used in situations where use of gloves is not practicable for protection against chemical exposure.
Gloves
Selection of gloves depends on the type of exposure. Different types of gloves are available to provide protection against different types of exposure. Consider all potential exposures when selecting gloves. Check MSDS/SDS of chemicals to determine suitable gloves. Consult local safety supplier to select from available types of gloves.
Important:
No glove material will remain impervious to a specific chemical forever. Know the limitations of the glove you are using.
No one glove material is resistant to all chemicals.
Use appropriate gloves as hand protection:
- CHOOSE hand protection that adequately protects from the specific hazard.
- WEAR the right type of glove made of the right material for the job. No one glove will protect from all hazards or hazardous products.
- FOLLOW manufacturer’s instructions for care and maintenance of gloves.
- ENSURE all exposed skin is covered by gloves. Gloves should be long enough so that there is no gap between the glove and sleeve.
- FOLLOW manufacturer’s instructions for wearing, removing, and cleaning gloves.
- INSPECT and test gloves for defects before using.
- TEST all rubber or synthetic gloves for leaks by inflating them.
Tips for Inspection of Gloves
- Hold cuff with thumbs inside. Stretch cuff slightly.
- Swing glove outward and over towards the face, two or three times, trapping air inside.
- Squeeze inflated portion of glove with right hand causing rubber to distend and magnify any defect.
- DO NOT USE worn or torn gloves.
- DO NOT WEAR gloves while working on moving equipment; they could get caught.
6. Respirators
A respiratory could save your life or prevent serious illness or disease.
Always assess the potential hazards and choose the respirator that is right for the task.
General
- FOLLOW the respirator protection program developed by your employer/supervisor, including training and fit testing.
- USE the type of respirator as prescribed by your employer/ supervisor.
- INSPECT before and after each use and during cleaning.
- INSPECT equipment designated for “emergency use” at least monthly, in addition to after each use.
- REPLACE all parts that are cracked, torn, broken, missing or worn.
- FOLLOW manufacturer’s instruction and CSA Standard Z94.4 or ANSI Z88.2 for care and maintenance.
The following sections apply to respirators other than dust masks.
Facepiece
- ENSURE that there are no holes or tears.
- INSPECT for cracked, scratched or loose-fitting lenses. For full facepiece, check for missing mounting clips.
- ENSURE that metal nose clip forms easily over the bridge of the nose on disposable respirators.
Headstrap/Harness
- CHECK webbing for breaks.
- LOOK for deterioration of elasticity. TEST excessively worn head harness.
Inhalation and Exhalation Valves
- ENSURE valve and valve seat are free of detergent residue, dust particles, or dirt which may cause a poor seal or reduce efficiency.
- REPLACE missing or defective valve cover.
Filter Element
- ENSURE that filter and mask are certified for use together.
- CHECK filters to see that they are approved for the hazard.
- INSPECT both filter threads and facepiece threads for wear. CHECK filter heads for cracks or dents.
- CHECK end of service life indicator on gas masks.
- CHECK expiration date.
Repair, Cleaning and Storage
- FOLLOW manufacturer’s instructions.
- WASH with a mild dish detergent or a combination of detergent and disinfectant. Use a brush and warm water (49–60° C).
- RINSE with clean water, or rinse once with a disinfectant and once with clean water. The clean water rinse removes excess detergent or disinfectant that can cause skin irritation or dermatitis.
- DRY on a rack, clean surface or hang from a clothes line. Position the respirator so that the facepiece rubber will not “set” crookedly as it dries.
- STORE respirator at the end of each shift to protect it from dust, sunlight, heat, extreme cold, excessive moisture, and chemicals.
- CLEAN and disinfect shared respirators after each use.
PERMIT only trained and qualified personnel to repair respirators. - RECORD repairs and/or inspections.
- CHECK for distortion caused by improper storage.
- DO NOT clean with solvents.
- DO NOT MIX parts from different manufacturers.
7. Clothing
- WEAR snug fitting clothing with all buttons fastened.
- ROLL sleeves up if they are not close fitting – billowing sleeves could get caught in machinery or catch fire.
- WEAR hair nets or other approved hair restraints that health regulations require for all food handlers.
8. Aprons
- WEAR aprons that are made from non-combustible and flame resistant materials which do not melt under heat.
- WEAR aprons for washing jobs that are made from waterproof material and that extend below the top of waterproof boots to prevent water from entering the boots.
