4
Meggie Mapes
Learning Objectives
- Consider implied or implicated audiences
- Explain ethnocentrisms
- Explain ways an individual can improve their listening when in an audience
A well-developed standup routine can leave us engaged and on the edge of our seats; it can leave us feeling like each joke was crafted for us.
Sadly, many of us have sat through less-engaging routines where awkward silence fills the space after an ill-placed punchline.
“Wow. Wrong audience,” the comic often nervously responds.
Similar to standup, audiences are central to public speeches. They are the main focus of our advocacies, and when we know more about our audiences, we can craft messages that effectively inform or move them toward action. We can craft messages to call them in and speak confidently to them.
When you speak out, you’re not speaking into thin air; instead, you’re inviting the audience to listen—you’re calling them in. To call in means creating a message that both relates to and implicates your audience; it is to summon. Paul Watzlawick, Janet Beavin, and Don Jackson (1967) write that communication always involves a content dimension and a relationship dimension. Nowhere does that become more important than working to call our audience in. You are not using the speech to dump a large amount of content on the audience; you are making that content important, meaningful, and applicable to them. Additionally, the way the audience perceives you and your connection to them—such as whether there is mutual trust and respect—will largely determine your success with the audience. The speaker must respect the audience as well as the audience trusting the speaker for “calling in” to be a success.
As you can see, calling an audience in is a process, and a complex one at that. In this chapter, we explore audiences in public speaking. To start, we answer the question: what’s an audience, anyway?
What’s an Audience?
In this chapter, we approach the audience in three ways.
First, by “audience” we mean the explicit audience that’s present when a speaker directs their message. The people sitting in chairs. Because public speeches require an audience, and because public speakers are asking the audience to listen to an argument, it’s important to analyze the group receiving a message – who you are speaking to. This is your explicit audience.
In addition, there are implied or implicated audiences who may or may not be present. Like we discussed in Chapter 1, public speaking is presenting an advocacy that engages for and with your community. When you are representing a group, culture, or an individual, they become an implicit audience. You are responsible for how you communicate about that audience or other groups who may be implicated by the advocacy.
Finally, you will be an audience member. The third dimension of “audience,” then, is you! As an audience member, your primary goal is to listen and reflect on what the speaker is presenting. Listening isn’t as easy as it sounds. So, we’ll also discuss listening, barriers, and best practices.
Who you’re speaking to, who you’re speaking for or about, and when you’re receiving a message are all components of the “audience.” Below, we’ll begin discussing analyzing the first dimension of audience: the explicit, formal group that listens to your message.
Speaking to an Audience
Public speaking requires an audience. After all, when speaking, your goal is to share a relevant message and provide unique insight that will benefit those present. To accomplish that goal, you need to get to know the explicit audience you’re speaking to: you need to analyze them.
You may wonder, “Okay, but how do I do that?” Information gathering is the answer.
The more information you have, the more you’re able to isolate any overlapping beliefs, values, or goals that the audience shares. Audiences are unique, diverse, and sometimes unpredictable; information gathering will allow you to select an argument that’s most relevant to what your audience needs.
By needs, we mean identifying important deficiencies that we are motivated to resolve.
You may already be familiar with the well-known diagram, Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs—a framework to think about human needs. It is commonly discussed in the fields of management, psychology, and health professions. A version of it is shown in Figure 4.1 (More recent versions show it with 8 levels.) In trying to understand human motivation, Maslow theorized that, as our needs represented at the base of the pyramid are fulfilled, we move up the hierarchy to fulfill other types of needs (McLeod, 2014).
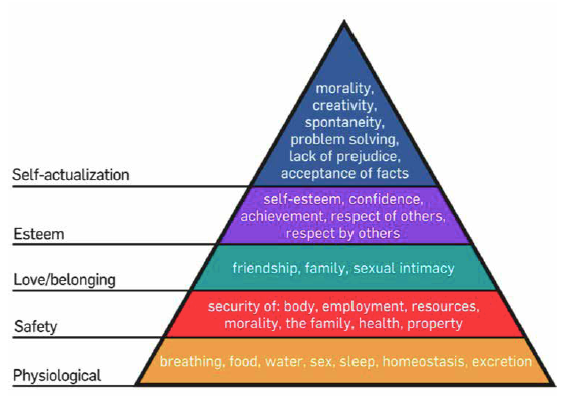
According to Maslow’s theory, our most basic physiological or survival needs must be met before we move to the second level, which is safety and security. When our needs for safety and security are met, we move up to relationship or connection needs, often called “love and belongingness.” The fourth level up is esteem needs, which could be thought of as achievement, accomplishment, or self-confidence. The highest level, self-actualization, is achieved by those who are satisfied and secure enough in the lower four that they can make sacrifices for others. Self-actualized persons are usually thought of as altruistic or charitable.
Unfortunately, humans aren’t always aware of what their needs are, so part of your task is learning about the audience and isolating needs that they may or may not be conscious of. For example, you’re reading out of an open textbook: this book was free of charge. Until you were assigned the book, you may not have been aware that open textbooks (or open educational resources) were an option. It was a need that you weren’t conscious of. A good speaker highlights the presence of a need by relating that issue to their audience.
When addressing an audience, determining what they need and where that need falls on the pyramid can influence how you make content that’s relatable – it can help you call them in. Diving deeper into the speaking context, audience demographics, and audience values all provide necessary information to identify needs and craft relevant arguments.
Researching the Context
Analyzing your audience needs begins by asking top-level questions about the public speaking context: why will your audience be there? What’s bringing them together? What’s motivating them to attend? Determining why your audience will be in attendance can help uncover more about who they are.
If you aren’t familiar with the why—why the audience is attending— conduct preliminary research. Use resources that are at your disposal to learn more and dig deep. If you’re speaking at a formal convention, for example, what’s the convention about? Is there a convention theme? Does the convention provide insight into past convention participants? How many people does the event accept?
Your research can help identify what’s bringing the audience together. You might learn, for example, that conference attendees share a common career, participate in a common organization, or have a similar hobby. When you speak in a class, the course content (or university requirement) brings the audience together. If you’re at a neighborhood meeting, the audience likely lives in that neighborhood, and you can learn about the key issues being discussed at the meeting.
As you research, try to determine what’s motivating your audience to be present. Identifying motivations can help assist in identifying what your audience needs or what needs they’re trying to fulfill.
Speaking for an Audience
Gathering information about your explicit audience—the formal audience you’re speaking in front of – is certainly important. The second audience to consider is the implied or implicated audience. In this section, we discuss how we talk about who we’re talking about: how we’re talking about the groups that are either represented and/or affected by our message.
Let’s use a state congressional hearing as an example. Imagine a group of congresspeople meeting to advocate for a bill’s passage that decreases environmental protections for a city in that state. The bill’s author stands and advocates passionately for the bill’s passage, noting that reducing the environmental protections would allow more business and jobs in the area. The speaker works to craft an argument that’s compelling for the explicit audience – the audience of other congresspeople who are present.
However, there are other implied audiences – the communities that would be most impacted by environmental pollution; residents who live in the area; business owners themselves. These audiences are important because they are both represented in the advocacy and would be impacted by the results of the speech. They may not, though, be part of the explicit audience.
To determine your implied audience, ask: Who are you speaking about/advocating for? Are you sharing information about a culture, group, or individual? If so, who? Are you sharing information that will impact a culture, group, or individual? If so, who?
It may seem odd to consider audiences that are implied or not present. After all, isn’t the explicit audience who you’re trying to inform, persuade, or entertain? Yes, your explicit audience is important, but as we discussed in Chapter 1, communication is constitutive. When you communicate or advocate for an idea, you are participating in world-making. The way that you talk or represent groups, cultures, or individuals has lasting impacts, even outside your explicit speech event. It can impact your implied audience. So, the “talk” about an implied audience matters.
Asking ourselves to be accountable to implied audiences also encourages us to use ethical communication, pay attention to power, and reduce stereotypes.
For example, if a speaker advocated to intervene in a country through military means, they might argue that “The United States needs to intervene because, right now, the other country is exhibiting barbaric tendencies.”
First, ask: Who is the implied audience in this example? What audiences would be implicated (but are likely not present)? A clear implied audience includes the non-U.S. population or cultural group, i.e. “the other country.”
Second, ask, how has this group been represented? What kind of talk is being used to describe these implied audiences? You’ll notice that “barbaric” was used to describe individuals in this culture. In this instance, “barbaric” seems to imply that the United States intervention is justified; barbaric seems bad and, alternatively, the United States does not exhibit those “barbaric tendencies” so, the U.S. may be best suited to intervene.
However, this explanation is using ethnocentrism—or the belief that one’s own culture is superior—as part of their argument. This type of talk should be avoided because it often represents other cultures in unethical, stereotypical, or unjust ways. If the speech’s argument requires an ethnocentric perspective, the argument isn’t based on good reasons (we’ll discuss this more in a later chapter).
So far, we’ve discussed your implied and impacted audience as groups that are discussed, represented, or implicated by your speech. A final implied audience includes any groups, cultures, or an individual’s ideas that you’re using.
Have you ever had a friend who re-tells your joke but doesn’t give you credit? Not cool! The same is true for speech advocacies. Any time you use or adapt an idea from a group or individual, you must give that implied audience credit. Failing to do so is known as plagiarism, or representing someone’s ideas as your own (more on this in Chapter 4). Once you’ve finished writing an advocacy, make sure to double-check that anyone and everyone’s information has been properly cited.
Identifying your implied audience can take time, but don’t worry. We’ll continue building critical thinking skills throughout the book to practice ethical and just public speaking with your explicit and implied audience in mind.
Listening in the Audience
The third component of “audience” includes you! You will be an audience member many, many times, and you should take that job seriously. Your job in the audience is to listen and ethically reflect on what the speaker is saying. In this section, we explore listening as a key audience concept.
Listening is not the same thing as hearing. Hearing is a physical process in which sound waves hit your eardrums and send a message to your brain. You may hear cars honking or dogs barking when you are walking down the street because your brain is processing the sounds, but that doesn’t mean that you are listening to them. Listening implies an active process where you are specifically making an effort to understand, process, and retain information.
In an audience, listening can be a difficult process. Unlike reading, which allows you to re-read a passage, you often have one chance to listen to an argument in a speech. Many studies have been conducted to find out how long we remember oral messages, and often the level of memory from oral communication is not very high (Bostrom & Bryant, 1980). The solution? Try to enact different listening techniques and reduce your barriers to listening.
Types of Listening
In this section, we will focus on types of listening. Ideally, we recommend working toward comprehensive or active listening, which is listening focused on understanding and remembering important information from a public speaking message. There are other “types” of listening, based on the context and purpose.
The first is empathetic listening, or understanding the feelings and motivations of another person, usually with a goal of helping. For example, if a friend says that she is thinking about dropping out of college at the end of the semester, you would want to listen for the reasons and feelings behind her choice, recognizing that you might need to ask sensitive questions and not just start telling her what to do or talk about your own feelings.
The second type of listening is appreciative, which takes place while listening to music, poetry, or literature, or watching a play or movie. For example, knowing that the melodies of classical music have a certain A-B pattern informs us how to listen to Mozart. To be good at this kind of listening, it helps to study the art form to learn the patterns and devices.
The third type is critical listening. In critical listening, the audience member is evaluating the validity of the arguments and information and deciding whether the speaker is persuasive and whether the message should be accepted. This often occurs when listening to persuasive arguments.
What can a speaker do to encourage listening for an audience?
Planned redundancy refers to purposeful ways of repeating and restating parts of the speech to help the audience listen and retain the content. You might not be able to cover or dump a great deal of information in a speech (and you probably shouldn’t), but you can make the information meaningful through planned redundancy and repeating or underscoring key components of your argument.
A speaker can also help the audience’s listening abilities by using presentation aids (discussed in Chapter 15), stories and examples (discussed in Chapter 19), audience interaction or movement at key points in the speech (discussed in Chapter 14), and specific attention-getting techniques (discussed in Chapter 10).
In short, listening is hard work, but you can meet your audience halfway by using certain strategies and material to make listening easier for them. At the same time, an audience member has a responsibility to pay attention and listen well.
In the next section, we will look at how you can improve your listening ability in public speaking situations.
Barriers to Effective Listening
Since hearing is a physiological response to auditory stimuli, you hear things whether you want to or not. Just ask anyone who has tried to go to sleep with the neighbor’s dog barking all night. However, listening–really listening– is intentional and hard work. And there are three common barriers to be conscious of.
Noise – physical and mental – is the first barrier to listening. We have constant mental distractions in our lives, something that you might not even be aware of if you have always lived in the world of the Internet, cell phones, iPods, tablets, and 24/7 news channels. We are dependent on and constantly wired to the Internet. Focus is difficult. Not only do electronic distractions hurt our listening, but life concerns can distract us as well. An ill family member, a huge exam next period, your car in the shop, deciding on next semester’s classes—the list is endless.
Physical noisiness and distractions also contribute to difficulty listening. Perhaps someone next to you is on their cell phone, and you hear the constant click of their keyboard. Perhaps they are whispering to each other and impeding your ability to hear the speaker clearly. The physical environment can also exert noise. Maybe it’s raining outside or someone is vacuuming through the door.
Confirmation bias is a second barrier to listening. This term means “a tendency to search for or interpret information in a way that confirms one’s preconceptions” (Nickerson, 1998). Although the concept has been around a long time, we are more aware of confirmation bias today. It leads us to listen to news outlets and Internet sources that confirm what we believe already rather than being challenged to new ways of thinking by reading or listening to other sources of information. It can cause us to discount, reject, or reinterpret information to fit our preconceptions.
Finally, information processing is the third barrier. Our minds can usually process much faster than a speaker can speak clearly. We may be able to listen, when really trying, at 200 words per minute, but few speakers can articulate that many words clearly; an average rate for normal speech is around 100-120 (Foulke, 1968). That leaves a great deal of time when the mind needs to pull itself back into focus. During those gaps, we might find it more enjoyable to think of lunch, the new person we are dating, or our vacation at the beach.
These are all the possible obstacles to listening, but there might also be reasons that are particular to you, the listener. We often go into listening situations with no purpose; we are just there physically but have no plans for listening. We go in unprepared. We are tired and mentally and physically unready to listen well. We are hungry or fatigued. We do not sit in a comfortable position to listen. We do not bring proper tools to listen, specifically to take notes. So, what do we do?
Intentional Listening
As audience members, barriers prohibit our ability to absorb information that could benefit us.
Your own barrier might be not coming prepared, being quick to prejudge, or allowing gadgets to distract you. Obviously, recognizing the cause of your poor listening is the first step to becoming a better listener. Here are some steps, in summary:
- Practice the skill. Believe that good listening and improving your own listening are important. You would not want to be called upon in a meeting at work when you were daydreaming or being distracted by a cell phone. Consider listening to speeches in a prepared manner and practice listening as a skill.
- Practice reflexive listening. Since it is so easy to react to a speaker’s ideas with confirmation bias, go into listening knowing that you might disagree and that the automatic “turn off” tendency is a possibility. In other words, tell yourself to keep an open mind.
- Be prepared to listen. This means putting away mobile devices, having a pen and paper, and situating yourself physically to listen (not slouching or slumping). Have a purpose in listening. There is actual research to indicate that we listen better and learn/retain more when we take notes with a pen and paper than when we type them on a computer or tablet (Mueller & Oppenheimer, 2014). Situate yourself by making decisions that will aid in your listening.
- When taking notes, keep yourself mentally engaged by writing questions that arise. This behavior will fill in the gaps, create an interactive experience with the speaker, and reduce the likelihood that your mind will wander. However, taking notes does not mean “transcribing” the speech or lecture. Whether in class or a different listening situation, do not (try to) write everything the speaker says down. Instead, start with looking for the overall purpose and structure, then for pertinent examples of each main point. Repetition by a speaker usually indicates you should write something down.
Conclusion
Audiences are central to a speaker’s success. All three audience dimensions are key to consider, whether you’re speaking or listening. Use this chapter throughout the public speaking process to create a relevant argument that’s engaging to your audience. Work to call them in: to summon them to actively listen to your advocacy.
creating a message that both relates to and implicates your audience; it is to summon
the audience that’s present when a speaker directs their message
important deficiencies that we are motivated to resolve
speaker credibility
the groups that are either represented and/or affected by our message.
the belief that one’s own culture is superior to others
physical process in which sound waves hit your ear drums and send a message to your brain
an active process where you are specifically making an effort to understand, process, and retain information
listening focused on understanding and remembering important information from a public speaking message
understanding the feelings and motivations of another person, usually with a goal of helping
takes place while listening to music, poetry, or literature, or watching a play or movie
evaluating the validity of the arguments and information and deciding whether the speaker is persuasive and whether the message should be accepted
purposeful ways of repeating and restating parts of the speech to help the audience listen and retain the content
anything, whether physical or mental, that interrupts the listening process
searching for or interpreting information in a way that confirms one’s preconceptions
The ability to understand the message being communicated. Our minds can usually process much faster than a speaker can speak clearly. Also known as excess mental capacity.
