5
Stand up, Speak out
Learning Objectives
- Explain how the three levels of the ethics pyramid might be used in evaluating the ethical choices of a public speaker or listener.
- Understand how to apply the National Communication Association (NCA) Credo for Ethical Communication within the context of public speaking.
- Understand how you can apply ethics to your public speaking preparation process.
- Define the concept of free speech and discuss its origins.
- Discuss the First Amendment to the US Constitution in terms of free speech.
- Describe how free speech relates to other freedoms guaranteed by the First Amendment to the US Constitution.
-
(Credit: Pixabay/Angel-Chess-Devil/CC0 public domain)
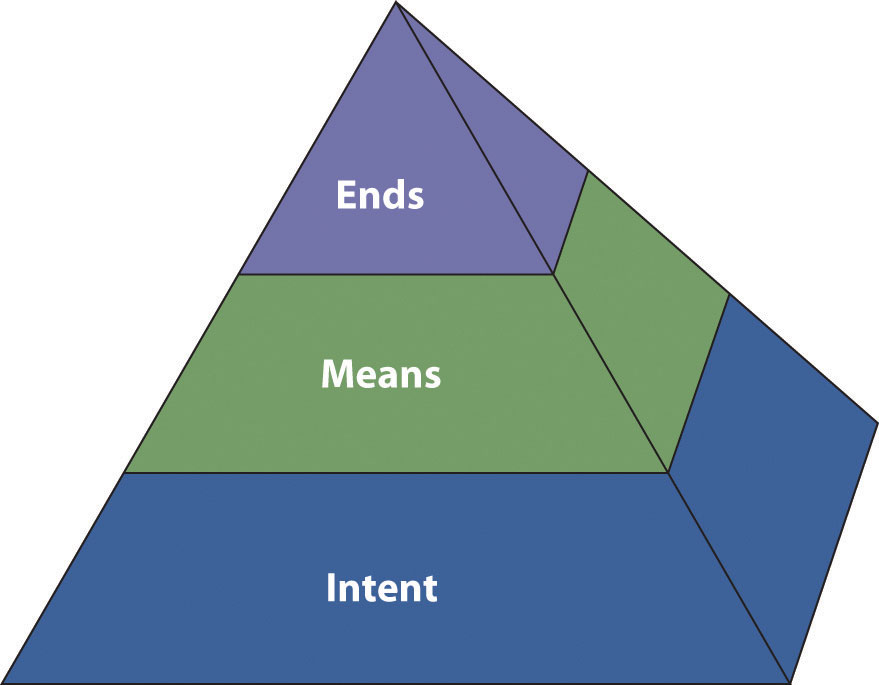
The Ethics Pyramid
The word “ethics” can mean different things to different people. Whether it is an ethical lapse in business or politics or a disagreement about medical treatments and end-of-life choices, people come into contact with ethical dilemmas regularly. Speakers and listeners of public speech face numerous ethical dilemmas as well. What kinds of support material and sources are ethical to use? How much should a speaker adapt to an audience without sacrificing his or her own views? What makes a speech ethical?
Elspeth Tilley, a public communication ethics expert from Massey University, proposes a structured approach to thinking about ethics (Tilley, 2005). Her ethics pyramid involves three basic concepts: intent, means, and ends. Figure 5.1 “Ethical Pyramid” illustrates the Tilley pyramid.
Intent
According to Tilley, the first major consideration to be aware of when examining the ethicality of something is the issue of intent. To be an ethical speaker or listener, it is important to begin with ethical intentions. For example, if we agree that honesty is ethical, it follows that ethical speakers will prepare their remarks with the intention of telling the truth to their audiences. Similarly, if we agree that it is ethical to listen with an open mind, it follows that ethical listeners will be intentional about letting a speaker make his or her case before forming judgments.
One option for assessing intent is to talk with others about how ethical they think a behavior is; if you get a variety of answers, it might be a sign that the behavior is not ethical and should be avoided. A second option is to check out existing codes of ethics. Many professional organizations, including the Independent Computer Consultants Association, American Counseling Association, and American Society of Home Inspectors, have codes of conduct or ethical guidelines for their members. Individual corporations such as Monsanto, Coca-Cola, Intel, and ConocoPhillips also have ethical guidelines for how their employees should interact with suppliers or clients. Even when specific ethical codes are not present, you can apply general ethical principles, such as whether a behavior is beneficial for the majority or whether you would approve of the same behavior if you were listening to a speech instead of giving it.
In addition, it is important to be aware that people can engage in unethical behavior unintentionally. For example, suppose we agree that it is unethical to take someone else’s words and pass them off as your own—a behavior known as plagiarism. What happens if a speaker makes a statement that he believes he thought of on his own, but the statement is actually quoted from a radio commentator whom he heard without clearly remembering doing so? The plagiarism was unintentional, but does that make it ethical?
Means
Tilley describes the means you use to communicate with others as the second level of the ethics pyramid. According to McCroskey, Wrench, and Richmond (McCroskey, Wrench, & Richmond, 2003), “means” are the tools or behaviors we employ to achieve a desired outcome. We must realize that there is a range of possible behavioral choices for any situation and that some choices are good, some are bad, and some fall in between.
For example, suppose you want your friend Marty to spend an hour reviewing a draft of your speech according to criteria, such as audience appropriateness, adequate research, strong support of assertions, and dynamic introduction and conclusion. What means might you use to persuade Marty to do you this favor? You might explain that you value Marty’s opinion and will gladly return the favor the next time Marty is preparing a speech (good means), or you might threaten to tell a professor that Marty cheated on a test (bad means). While both of these means may lead to the same end—having Marty agree to review your speech—one is clearly more ethical than the other.
Ends
The final part of the ethics pyramid is the ends. According to McCroskey, Wrench, and Richmond (McCroskey, Wrench, & Richmond, 2003), ends are those outcomes that you desire to achieve. Examples of ends might include persuading your audience to make a financial contribution for your participation in Relay for Life, persuading a group of homeowners that your real estate agency would best meet their needs, or informing your fellow students about newly required university fees. Whereas the means are the behavioral choices we make, the ends are the results of those choices.
Like intentions and means, ends can be good or bad, or they can fall into a gray area where it is unclear just how ethical or unethical they are. For example, suppose a city council wants to balance the city’s annual budget. Balancing the budget may be a good end, assuming that the city has adequate tax revenues and areas of discretionary spending for nonessential services for the year in question. However, voters might argue that balancing the budget is a bad end if the city lacks these things for the year in question, because in that case balancing the budget would require raising taxes, curtailing essential city services, or both.
When examining ends, we need to think about both the source and the receiver of the message or behavior. Some end results could be good for the source but bad for the receiver, or vice versa. Suppose, for example, that Anita belongs to a club that is raffling off a course of dancing lessons. Anita sells Ben a ten-dollar raffle ticket. However, Ben later thinks it over and realizes that he has no desire to take dancing lessons and that if he should win the raffle, he will never take the lessons. Anita’s club has gained ten dollars—a good end—but Ben has lost ten dollars—a bad end. Again, the ethical standards you and your audience expect to be met will help in deciding whether a particular combination of speaker and audience ends is ethical.
Thinking through the Pyramid
Ultimately, understanding ethics is a matter of balancing all three parts of the ethical pyramid: intent, means, and ends. When thinking about the ethics of a given behavior, Tilley recommends asking yourself three basic questions:
- “Have I discussed the ethicality of the behavior with others and come to a general consensus that the behavior is ethical?”
- “Does the behavior adhere to known codes of ethics?”
- “Would I be happy if the outcomes of the behavior were reversed and applied to me?” (Tilley, 2005)
While you do not need to ask yourself these three questions before enacting every behavior as you go through a day, they do provide a useful framework for thinking through a behavior when you are not sure whether a given action, or statement, may be unethical. Ultimately, understanding ethics is a matter of balancing all three parts of the ethical pyramid: intent, means, and ends.
Ethics in Public Speaking
The study of ethics in human communication is hardly a recent endeavor. One of the earliest discussions of ethics in communication (and particularly in public speaking) was conducted by the ancient Greek philosopher Plato in his dialogue Phaedrus. In the centuries since Plato’s time, an entire subfield within the discipline of human communication has developed to explain and understand communication ethics.
Communication Code of Ethics
In 1999, the National Communication Association officially adopted the Credo for Ethical Communication (see the following sidebar). Ultimately, the NCA Credo for Ethical Communication is a set of beliefs communication scholars have about the ethics of human communication.
National Communication Association Credo for Ethical Communication
Questions of right and wrong arise whenever people communicate. Ethical communication is fundamental to responsible thinking, decision making, and the development of relationships and communities within and across contexts, cultures, channels, and media. Moreover, ethical communication enhances human worth and dignity by fostering truthfulness, fairness, responsibility, personal integrity, and respect for self and others. We believe that unethical communication threatens the quality of all communication and consequently the well-being of individuals and the society in which we live. Therefore we, the members of the National Communication Association, endorse and are committed to practicing the following principles of ethical communication:
- We advocate truthfulness, accuracy, honesty, and reason as essential to the integrity of communication.
- We endorse freedom of expression, diversity of perspective, and tolerance of dissent to achieve the informed and responsible decision-making fundamental to a civil society.
- We strive to understand and respect other communicators before evaluating and responding to their messages.
- We promote access to communication resources and opportunities as necessary to fulfill human potential and contribute to the well-being of families, communities, and society.
- We promote communication climates of caring and mutual understanding that respect the unique needs and characteristics of individual communicators.
- We condemn communication that degrades individuals and humanity through distortion, intimidation, coercion, and violence, and through the expression of intolerance and hatred.
- We are committed to the courageous expression of personal convictions in pursuit of fairness and justice.
- We advocate sharing information, opinions, and feelings when facing significant choices while also respecting privacy and confidentiality.
- We accept responsibility for the short- and long-term consequences of our own communication and expect the same of others.
Applying the NCA Credo to Public Speaking
The NCA Credo for Ethical Communication is designed to inspire discussions of ethics related to all aspects of human communication. For our purposes, we want to think about each of these principles in terms of how they affect public speaking.
We Advocate Truthfulness, Accuracy, Honesty, and Reason as Essential to the Integrity of Communication
As public speakers, one of the first ethical areas we should be concerned with is information honesty. While there are cases where speakers have blatantly lied to an audience, it is more common for speakers to prove a point by exaggerating, omitting facts that weigh against their message, or distorting information. We believe that speakers build a relationship with their audiences, and that lying, exaggerating, or distorting information violates this relationship. Ultimately, a speaker will be more persuasive by using reason and logical arguments supported by facts rather than relying on emotional appeals designed to manipulate the audience.
It is also important to be honest about where all your information comes from in a speech. As speakers, examine your information sources and determine whether they are biased or have hidden agendas. For example, you are not likely to get accurate information about nonwhite individuals from a neo-Nazi website. While you may not know all your sources of information firsthand, you should attempt to find objective sources that do not have an overt or covert agenda that skews the argument you are making. We will discuss more about ethical sources of information later in this book.
The second part of information honesty is to fully disclose where we obtain the information in our speeches. As ethical speakers, it is important to always cite your sources of information within the body of a speech. Whether you conducted an interview or read a newspaper article, you must tell your listeners where the information came from. We mentioned earlier in this chapter that using someone else’s words or ideas without giving credit is called plagiarism. The word “plagiarism” stems from the Latin word plagiaries, or kidnapper. The American Psychological Association states in its publication manual that ethical speakers do not claim “words and ideas of another as their own; they give credit where credit is due” (American Psychological Association, 2001).
In the previous sentence, we placed quotation marks around the sentence to indicate that the words came from the American Psychological Association and not from us. When speaking informally, people sometimes use “air quotes” to signal direct quotations—but this is not a recommended technique in public speaking. Instead, speakers need to verbally tell an audience when they are using someone else’s information. The consequences for failing to cite sources during public speeches can be substantial. For example, the student newspaper at Malone University in Ohio alleged that the university president, Gary W. Streit, had plagiarized material in a public speech. Streit retired abruptly as a result.
Even if you are not running for president of the United States or serving as a college president, citing sources is important to you as a student. Many universities have policies that include dismissal from the institution for student plagiarism of academic work, including public speeches. Failing to cite your sources might result, at best, in lower credibility with your audience and, at worst, in a failing grade on your assignment or expulsion from your school. While we will talk in more detail about plagiarism later in this book, we cannot emphasize enough the importance of giving credit to the speakers and authors whose ideas we pass on within our own speeches and writing.
Speakers tend to fall into one of three major traps with plagiarism. The first trap is failing to tell the audience the source of a direct quotation. In the previous paragraph, we used a direct quotation from the American Psychological Association; if we had not used the quotation marks and clearly listed where the cited material came from, you, as a reader, wouldn’t have known the source of that information. To avoid plagiarism, you always need to tell your audience when you are directly quoting information within a speech.
The second plagiarism trap public speakers fall into is paraphrasing what someone else said or wrote without giving credit to the speaker or author. For example, you may have read a book and learned that there are three types of schoolyard bullying. In the middle of your speech, you talk about those three types of schoolyard bullying. If you do not tell your audience where you found that information, you are plagiarizing. Typically, the only information you do not need to cite is information that is general knowledge. General knowledge is information that is publicly available and widely known by a large segment of society. For example, you would not need to provide a citation within a speech for the name of Delaware’s capital. Although many people do not know the capital of Delaware without looking it up, this information is publicly available and easily accessible, so assigning credit to one specific source is not useful or necessary.
The third plagiarism trap that speakers fall into is re-citing someone else’s sources within a speech. To explain this problem, let’s look at a brief segment from a research paper written by Wrench, DiMartino, Ramirez, Oviedio, and Tesfamariam:
The main character on the hit Fox television show House, Dr. Gregory House, has one basic mantra, “It’s a basic truth of the human condition that everybody lies. The only variable is about what” (Shore & Barclay, 2005). This notion that “everybody lies” is so persistent in the series that t-shirts have been printed with the slogan. Surprisingly, research has shown that most people do lie during interpersonal interactions to some degree. In a study conducted by Turner, Edgley, and Olmstead (1975), the researchers had 130 participants record their own conversations with others. After recording these conversations, the participants then examined the truthfulness of the statements within the interactions. Only 38.5% of the statements made during these interactions were labeled as “completely honest.”
In this example, we see that the authors of this paragraph cited information from two external sources: Shore and Barclay and Turner, Edgley, and Olmstead. These two groups of authors are given credit for their ideas. The authors make it clear that they did not produce the television show House or conduct the study that found that only 38.5 percent of statements were completely honest. Instead, these authors cited information found in two other locations. This type of citation is appropriate.
However, if a speaker read the paragraph and said the following during a speech, it would be plagiarism: “According to Wrench DiMartino, Ramirez, Oviedio, and Tesfamariam, in a study of 130 participants, only 38.5 percent of the responses were completely honest.” In this case, the speaker is attributing the information cited to the authors of the paragraph, which is not accurate. If you want to cite the information within your speech, you need to read the original article by Turner, Edgley, and Olmstead and cite that information yourself.
There are two main reasons we do this. First, Wrench, DiMartino, Ramirez, Oviedio, and Tesfamariam may have mistyped the information. Suppose the study by Turner, Edgley, and Olstead really actually found that 58.5 percent of the responses were completely honest. If you cited the revised number (38.5 percent) from the paragraph, you would be further spreading incorrect information.
The second reason we do not re-cite someone else’s sources within our speeches is that it’s intellectually dishonest. You owe your listeners an honest description of where the facts you are relating came from, not just the name of an author who cited those facts. It is more work to trace the original source of a fact or statistic, but by doing that extra work you can avoid this plagiarism trap.
We Endorse Freedom of Expression, Diversity of Perspective, and Tolerance of Dissent to Achieve the Informed and Responsible Decision Making Fundamental to a Civil Society
This ethical principle affirms that a civil society depends on freedom of expression, diversity of perspective, and tolerance of dissent and that informed and responsible decisions can only be made if all members of society are free to express their thoughts and opinions. Further, it holds that diverse viewpoints, including those that disagree with accepted authority, are important for the functioning of a democratic society.
If everyone only listened to one source of information, then we would be easily manipulated and controlled. For this reason, we believe that individuals should be willing to listen to a range of speakers on a given subject. As listeners or consumers of communication, we should realize that this diversity of perspectives enables us to be more fully informed on a subject. Imagine voting in an election after listening only to the campaign speeches of one candidate. The perspective of that candidate would be so narrow that you would have no way to accurately understand and assess the issues at hand or the strengths and weaknesses of the opposing candidates. Unfortunately, some voters do limit themselves to listening only to their candidate of choice and, as a result, base their voting decisions on incomplete—and, not infrequently, inaccurate—information.
Listening to diverse perspectives includes being willing to hear dissenting voices. Dissent is by nature uncomfortable, as it entails expressing opposition to authority, often in very unflattering terms. Legal scholar Steven H. Shiffrin has argued in favor of some symbolic speech (e.g., flag burning) because we as a society value the ability of anyone to express their dissent against the will and ideas of the majority (Shiffrin, 1999). Ethical communicators will be receptive to dissent, no matter how strongly they may disagree with the speaker’s message because they realize that a society that forbids dissent cannot function democratically.
Ultimately, honoring free speech and seeking out a variety of perspectives is very important for all listeners. We will discuss this idea further in the chapter on listening.
We Strive to Understand and Respect Other Communicators before Evaluating and Responding to Their Messages
This is another ethical characteristic that is specifically directed at receivers of a message. As listeners, we often let our perceptions of a speaker’s nonverbal behavior—his or her appearance, posture, mannerisms, eye contact, and so on—determine our opinions about a message before the speaker has said a word. We may also find ourselves judging a speaker based on information we have heard about him or her from other people. Perhaps you have heard from other students that a particular teacher is a really boring lecturer or is really entertaining in class. Even though you do not have personal knowledge, you may prejudge the teacher and his or her message based on information you have been given from others. The NCA credo reminds us that to be ethical listeners, we need to avoid such judgments and instead make an effort to listen respectfully; only when we have understood a speaker’s viewpoint are we ready to begin forming our opinions of the message.
Listeners should try to objectively analyze the content and arguments within a speech before deciding how to respond. Especially when we disagree with a speaker, we might find it difficult to listen to the content of the speech and, instead, work on creating a rebuttal the entire time the speaker is talking. When this happens, we do not strive to understand the speaker and do not respect the speaker.
Of course, this does not just affect the listener in the public speaking situation. As speakers, we are often called upon to evaluate and refute potential arguments against our positions. While we always want our speeches to be as persuasive as possible, we do ourselves and our audiences a disservice when we downplay, distort, or refuse to mention important arguments from the opposing side. Fairly researching and evaluating counterarguments is an important ethical obligation for the public speaker.
We Promote Access to Communication Resources and Opportunities as Necessary to Fulfill Human Potential and Contribute to the Well-Being of Families, Communities, and Society
Human communication is a skill that can and should be taught. We strongly believe that you can become a better, more ethical speaker. One of the reasons the authors of this book teach courses in public speaking and wrote this college textbook on public speaking is that we, as communication professionals, have an ethical obligation to provide others, including students like you, with resources and opportunities to become better speakers.
We Promote Communication Climates of Caring and Mutual Understanding That Respect the Unique Needs and Characteristics of Individual Communicators
Speakers need to take a two-pronged approach when addressing any audience: caring about the audience and understanding the audience. When you as a speaker truly care about your audience’s needs and desires, you avoid setting up a manipulative climate. This is not to say that your audience will always perceive their own needs and desires in the same way you do, but if you make an honest effort to speak to your audience in a way that has their best interests at heart, you are more likely to create persuasive arguments that are not just manipulative appeals.
Second, it is important for a speaker to create an atmosphere of mutual understanding. To do this, you should first learn as much as possible about your audience, a process called audience analysis. We will discuss this topic in more detail in the audience analysis chapter.
To create a climate of caring and mutual respect, it is important for us as speakers to be open with our audiences so that our intentions and perceptions are clear. Nothing alienates an audience faster than a speaker with a hidden agenda unrelated to the stated purpose of the speech. One of our coauthors once listened to a speaker give a two-hour talk, allegedly about workplace wellness, which actually turned out to be an infomercial for the speaker’s weight-loss program. In this case, the speaker clearly had a hidden (or not-so-hidden) agenda, which made the audience feel disrespected.
We Condemn Communication That Degrades Individuals and Humanity through Distortion, Intimidation, Coercion, and Violence and through the Expression of Intolerance and Hatred
This ethical principle is very important for all speakers. Hopefully, intimidation, coercion, and violence will not be part of your public speaking experiences, but some public speakers have been known to call for violence and incite mobs of people to commit atrocities. Thus distortion and expressions of intolerance and hatred are of special concern when it comes to public speaking.
Distortion occurs when someone purposefully twists information in a way that detracts from its original meaning. Unfortunately, some speakers take information and use it in a manner that is not in the spirit of the original information. One place we see distortion frequently is in the political context, where politicians cite a statistic or the results of a study and either completely alter the information or use it deceptively. FactCheck.org, a project of the Annenberg Public Policy Center (http://www.factcheck.org), and the St. Petersburg Times’s Politifact (http://www.politifact.com) are nonpartisan organizations devoted to analyzing political messages and demonstrating how information has been distorted.
Expressions of intolerance and hatred that are to be avoided include using ageist, heterosexist, racist, sexist, and any other form of speech that demeans or belittles a group of people. Hate speech from all sides of the political spectrum in our society is detrimental to ethical communication. As such, we as speakers should be acutely aware of how an audience may perceive words that could be considered bigoted. For example, suppose a school board official involved in budget negotiations used the word “shekels” to refer to money, which he believes the teachers’ union should be willing to give up (Associated Press, 2011). The remark would be likely to prompt accusations of anti-Semitism and distract listeners from any constructive suggestions the official might have for resolving budget issues. Although the official might insist that he meant no offense, he damaged the ethical climate of the budget debate by using a word associated with bigotry.
At the same time, listeners need to pay attention to expressions of intolerance or hatred. Extremist speakers sometimes attempt to disguise their true agendas by avoiding bigoted “buzzwords” and using mild-sounding terms instead. For example, a speaker advocating the overthrow of a government might use the term “regime change” instead of “revolution”; similarly, proponents of genocide in various parts of the world have used the term “ethnic cleansing” instead of “extermination.” By listening critically to the gist of a speaker’s message as well as the specific language he or she uses, we can see how that speaker views the world.
We Are Committed to the Courageous Expression of Personal Convictions in Pursuit of Fairness and Justice
We believe that finding and bringing to light situations of inequality and injustice within our society is important. Public speaking has been used throughout history to point out inequality and injustice, from Patrick Henry arguing against the way the English government treated the American colonists and Sojourner Truth describing the evils of slavery to Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech and Army Lt. Dan Choi’s speeches arguing that the military’s “don’t ask, don’t tell policy” is unjust. Many social justice movements have started because young public speakers have decided to stand up for what they believe is fair and just.
We Advocate Sharing Information, Opinions, and Feelings When Facing Significant Choices While Also Respecting Privacy and Confidentiality
This ethical principle involves balancing personal disclosure with discretion. It is perfectly normal for speakers to want to share their own personal opinions and feelings about a topic; however, it is also important to highlight information within a speech that represents your own thoughts and feelings. Your listeners have a right to know the difference between facts and personal opinions.
Similarly, we have an obligation to respect others’ privacy and confidentiality when speaking. If information is obtained from printed or publicly distributed material, it’s perfectly appropriate to use that information without getting permission, as long as you cite it. However, when you have a great anecdote one of your friends told you in confidence or access to information that is not available to the general public, it is best to seek permission before using the information in a speech.
This ethical obligation even has legal implications in many government and corporate contexts. For example, individuals who work for the Central Intelligence Agency are legally precluded from discussing their work in public without prior review by the agency. And companies such as Google also have policies requiring employees to seek permission before engaging in public speaking in which sensitive information might be leaked.
We Accept Responsibility for the Short- and Long-Term Consequences of Our Own Communication and Expect the Same of Others
The last statement of NCA’s ethical credo may be the most important one. We live in a society where a speaker’s message can literally be heard around the world in a matter of minutes, thanks to our global communication networks. Extreme remarks made by politicians, media commentators, and celebrities, as well as ordinary people, can unexpectedly “go viral” with regrettable consequences. It is not unusual to see situations where a speaker talks hatefully about a specific group, but when one of the speaker’s listeners violently attacks a member of the group, the speaker insists that he or she had no way of knowing that this could have happened. Washing one’s hands of responsibility is unacceptable: all speakers should accept responsibility for the short-term and long-term consequences of their speeches. Although it is certainly not always the speaker’s fault if someone commits an act of violence, the speaker should take responsibility for her or his role in the situation. This process involves being truly reflective and willing to examine how one’s speech could have tragic consequences.
Furthermore, attempting to persuade a group of people to take any action means you should make sure that you understand the consequences of that action. Whether you are persuading people to vote for a political candidate or just encouraging them to lose weight, you should know what the short-term and long-term consequences of that decision could be. While our predictions of short-term and long-term consequences may not always be right, we have an ethical duty to at least think through the possible consequences of our speeches and the actions we encourage.
Free Speech
-

(Credit: Wikimedia Commons/Supreme Court front dusk/ Public Domain)
Free speech has been a constitutional right since the founding of the United States, and according to Merriam Webster’s Dictionary of Law, free speech entails “the right to express information, ideas, and opinions free of government restrictions based on content and subject only to reasonable limitations (as the power of the government to avoid a clear and present danger) esp. as guaranteed by the First and Fourteenth Amendments to the U.S. Constitution” (Freedom of speech). Free speech is especially important to us as public speakers because expressing information and ideas is the purpose of public speaking. It is also important to audiences of public speeches because free speech allows us to hear and consider multiple points of view so that we can make more informed decisions.
The First Amendment to the Constitution
Free speech was so important to the founders of the United States that it is included in the first of the ten amendments to the US Constitution that are known as the Bill of Rights. This is not surprising, considering that many American colonists had crossed the Atlantic to escape religious persecution and that England had imposed many restrictions on personal freedoms during the colonial era. The text of the First Amendment reads, “Congress shall make no law respecting an establishment of religion, or prohibiting the free exercise thereof; or abridging the freedom of speech, or of the press; or the right of the people peaceably to assemble, and to petition the Government for a redress of grievances” (National Archives and Records Administration, 2011).
The freedoms protected by the First Amendment may seem perfectly natural today, but they were controversial in 1791 when the Bill of Rights was enacted. Proponents argued that individuals needed protection from overreaching powers of government, while opponents believed these protections were unnecessary and that amending them to the Constitution could weaken the union.
Freedom of speech, of the press, of religion, of association, of assembly, and petition are all guaranteed in amendments to the US Constitution. Free speech allows us to exercise our other First Amendment rights. Freedom of assembly means that people can gather to discuss and protest issues of importance to them. If free speech were not protected, citizens would not be able to exercise their right to protest about activities such as war or policies such as health care reform.
Free speech does not mean, however, that every US citizen has the legal right to say anything at any time. If your speech is likely to lead to violence or other illegal acts, it is not protected. A recent example is a 2007 Supreme Court decision in the Morse et al. v. Frederick case. In this case, a high school student held up a sign reading “Bong Hits 4 Jesus” across from the school during the 2002 Olympic Torch Relay. The principal suspended the teenager, and the teen sued the principal for violating his First Amendment rights. Ultimately, the court decided that the principal had the right to suspend the student because he was advocating illegal behavior (Supreme Court of the United States, 2007; U.S. Courts 2021).
The meaning of “free speech” is constantly being debated by politicians, judges, and the public, even within the United States, where this right has been discussed for over two hundred years. If you live in the United States, it is important to be aware of both the protections afforded by free speech and its limits so that we can be both articulate speakers and critical listeners when issues such as antiwar protests at military funerals or speech advocating violence against members of specific groups come up within our communities.
the tools or behaviors we employ to achieve a desired outcome
outcomes that you desire to achieve
using someone else’s words or ideas without giving credit
when someone purposefully twists information in a way that detracts from its original meaning
the right to express information, ideas, and opinions free of government restrictions based on content and subject only to reasonable limitations