II. Counterpoint and Galant Schemas
16th-Century Contrapuntal Style
Mark Gotham
Key Takeaways
- The 16th-century contrapuntal style is related—but not identical—to the principles outlined in species counterpoint.
- This chapter sets out some key principles and practice exercises especially for imitation.
The 16th-century contrapuntal style has historically enjoyed a prominent position in the teaching of music theory. “Pastiche” or “counterfactual” composition of 16th-century imitative choral polyphony (especially in the style of Palestrina) has frequently appeared in curricula and is sometimes conflated with the later, 18th-century notion of species counterpoint which we met in the previous chapters. This chapter sets out some rules of thumb to bear in mind when completing style-composition exercises based on this repertoire where you are given a partial score to complete. At the end, you’ll find a couple of example exercises in this format.
Imitation
Imitation involves two or more parts entering separately with the same melody, or versions of the same melody. This is a common practice in 16th-century contrapuntal music, particularly for beginning whole movements and large sections in those movements (with the introduction of a new line of text, for instance). You might think of it as a precursor to the later fugue (which we’ll return to in the High Baroque Fugal Exposition chapter).
Here is an example from Vicente Lusitano’s “Ave spes nostra” from the
In this opening passage, a “point of imitation” setting the text “Ave spes nostra” appears in all five voices. The imitation is exact, give or take small changes. The first voice to enter starts on F and descends to C, then it repeats the text a second time, now starting on C and descending to F with a similar melody, adding one more note at the end. Other parts imitate either this pattern (F–C then C–F) or this pair the other way round (C–F, then F–C).
The end of this example sees the start of a second imitative point setting the next line “Dei genitrix … ”. This new figure has a “turn”-like shape: original note, note above, note below, original note (C-D-Bb-C). What follows is a sectnmio based on that second point. As is common in this style, the two phrase overlap (i.e., the new phrase begins before the end of the previous one) and the imitation for this second point is treated more freely than the first. You can even see a couple of subtle rhythmic changes to the first point in this last bar shown where this overlap takes place.
When completing an exercise involving imitation, let the existing material be your guide and consider the following guidelines:
- Identify (potential) points of imitation: In any given part, look for changes of text (often preceded by a comma or rest), and particularly any repetition of text with the same music.
- Pitch interval: The interval between imitative parts at the start of a section or movement is usually a perfect consonance. That said, others are eminently possible, especially later in the movement. Note that we are talking about the primary corresponding interval between the parts and not necessarily the very first pitch. We sometimes see examples of the tonal answer typical of the later high Baroque fugue, discussed in the next chapter.
- Meter: Imitate at metrically comparable positions (strong beat → strong beat; weak beat → weak beat).
- When working out what imitative relationships will work, try out all options in both directions. As the section governed by one imitative point often overlaps with the next, imitative entries around that section change may come from other point.
- Make sure there is meaningful overlap between consecutively entering imitative parts. To achieve that, shorter points of imitation may require correspondingly shorter intervals between entering parts.
- Consider how much of the point to imitate. Longer melodies eventually go from being a point to imitate exactly, to free counterpoint. Where does that change occur in this case?
- Consider how closely to imitate the point. Try to preserve at least the rhythm and the distinctive intervals/contour/shape of the point’s opening.
- Remember that phrases and sections can overlap, even at strong cadences.
Melody
- Contrary motion predominates between parts (partly to maintain independence of lines). Avoid too much parallel writing even of permitted intervals (but note the exceptional case of the “fauxbourdon,” which is an extended passage of parallel
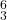 triads).
triads). - Conjunct motion predominates within parts.
- Approach the final by step (in most parts).
- Raise the leading note when approaching the final from below (in most modal contexts, though not Phrygian).
- Melodic intervals:
- Seconds, thirds, fourths, fifths, and octaves are all permitted;
- The status of sixths is more complex. Rising minor sixths are used fairly freely (814 times in the Palestrina masses), rising major sixths are rarer (54 times), and descending sixths are extremely rare (7 descending minor, 1 single case of descending major).
- Sevenths and tritones are avoided. Do not even outline these intervals with successive leaps or by the boundaries (high and low points) of a melodic gesture.
- Successive leaps in the same direction are generally avoided. If you do have such successive leaps, then position the larger leap lower (first when rising, second when descending).
- Large leaps are to be followed (and often preceded) by motion in the opposite direction. This is connected to both the idea of gap-fill and regression to the middle of the tessitura.
- Avoid outlining triads as if you were arpeggiating chords.
- Contour: The arch shape is common for melodies (what goes up must come down!).
- Range per part: A common recommendation is to place each voice within an octave, corresponding to either the authentic or plagal ranges of the piece’s mode. But in practice, parts more often span a slightly wider range of 14 semitones. Extremely few parts exceed the twelfth (octave plus fifth), so take that as a maximum.
- Common melodic devices:
- Suspensions: Suspended notes are to be “prepared” as a consonance on a weak metrical tied to a dissonance (on a strong position) and resolved by moving the suspended dissonant part down a step. For 7–6 and 4–3 suspensions, this involves dissonance in the upper voice; for 2–3 suspension, the dissonance is in the lower voice (as an inversion of 7–6). This is explained further in the chapter on fourth-species counterpoint.
- While not a suspension, the oblique motion from fifth to sixth is also common.
- Decorations at the end of a phrase are more common than at the beginning.
Rhythm and Meter
- The original notation for this repertoire lacks bar lines, but metrical thinking is abundantly clear. While modern editions will usually put bar lines in explicitly, remember that these are editorial interventions, not original. Editors may also change the tactus-level note values to be shorter than what was originally notated (from half to quarter notes, for instance). With those caveats borne in mind, the editorial intervention can be helpful—barlines are helpful for rehearsal and for conducting, and some performers may feel more comfortable reading in shorter note values. Editorial choices may also offer subtler hints, such as the use of “longer” meters (
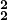 in place of
in place of 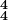 ) to hint at the possibility of thinking in terms of longer beat, and thus the possibility of longer dissonances, for instance.
) to hint at the possibility of thinking in terms of longer beat, and thus the possibility of longer dissonances, for instance. - Melodic lines frequently start (and often end) with slower rhythmic movement.
- Half-tactus (quarter-note) movement should begin on weak metrical positions—on an unaccented beat (2 or 4), or between beats (as part of a dotted rhythm).
- Ties connect long notes to shorter ones (not vice versa).
- In the (relatively rare) cases of triple meter, rhythms generally divide into 2+1 rather than 1+2 (as in many styles).
Text Setting
- Clarity of music and text was held in high regard by many composers of this time.[2]
- Meter: The above caveats notwithstanding, match textual and musical meters by placing strong syllables on “strong beats.” Systematic exceptions follow the conventions outlined above including syncopations, suspensions, and “metrical dissonance” (use of a consistent meter in one part that is contrary to that prevailing in other parts (usually the one notated in modern editions).
- Musical phrases follow the text.
- Typically use at least one beat (half note) for each syllable.
- Exceptions include dotted rhythms, where the shorter (quarter) note frequently receives its own syllable. This may be thought of as a modification of a “straight” rhythm, which meets the “one per beat” guideline.
- Syllable changes immediately after sub-tactus (quarter-note) motion are rare.
Texture
- The appropriate texture is usually clear from the given parts in these exercises.
- To generalize rather crudely, broad conventions for textures in Mass settings are as follows (where I = usually imitative; H = may be [more] homophonic):
- Kyrie (I).
- Gloria (H). The “qui tollis” frequently exists as a separate section.
- Credo (H). Especially often homophonic at important moments. “Crucifixus” separable.
- Sanctus (I). Hosanna (H).
- Benedictus (I). Often for fewer voices. (Second Hosanna usually a repeat of the first.)
- Agnus Dei (I). There may be a second or third Agnus, often with more parts and canons.
- The Magnificat tends to be a freer genre that is more flexible with the points of imitations.
Harmony
Composers of this era did not think in terms of chords, Roman numerals, inversions, and so on the way that we typically do today. Instead, they were principally concerned with intervallic relationships among parts. With this in mind, following are some guidelines for the vertical combination of parts in this style.
- Parallel fifths and parallel octaves: Avoid, as in later idioms. However, unlike in later idioms, those involving diminished fifths must also be avoided.
- Direct fifths or octaves:
- Avoid in principle (some rationalize this on the basis that they imply parallels that would present if the intervening passing notes were added).
- More common at cadences and/or when mitigated by strong contrary motion in one or more other parts.
- Diminished triad:
- Used not infrequently in Palestrina’s music, mostly in first inversion.
- Useful especially as a solution for cadences in multi-part music with
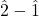 motion in the bass, for instance.
motion in the bass, for instance. - Resolve according to standard voice-leading: re–do, ti–do, fa–mi
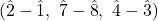 .
.
- Dissonance: types and treatment:
- Suspensions: preparation (weak beat) – suspension (strong) – resolution (weak).
- “Inessential” dissonances: passing tones, neighbor tones at the sub-tactus (quarter-note) level.
- Nota cambiata, “changed note”: generally do–ti–sol–la
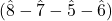 . The only case of a dissonance left by leap.
. The only case of a dissonance left by leap.
- Final chord: Bare fifth or major triad (picardy third).
- The raised (“Picardy”) third “originated c. 1500 when for the first time, the third was admitted in the final chord of a piece … in the second half of the sixteenth century this practice became fairly common” (Apel 1969, 677).
- By Palestrina, major triads are the most common kind of final chord (accounting for around 85% of cases in the Palestrina masses).
- Apel, Willi. “Picardy Third.” 1969. Harvard Dictionary of Music. 2nd ed. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
In addition to well-known libraries like IMSLP, there are some interesting projects dedicated specifically to Renaissance music.
- Perhaps most notable and relevant is Citations: The Renaissance Imitation Mass Project (CRIM), where you can explore a wide range of relevant repertoire in attractive, modern editions, along with related information.
- For a similar curatorial approach to a slightly earlier repertoire, you may wish to explore the Josquin Research Project (JRP)
- Imitative writing in the 16th-century contrapuntal style. These exercises provide at least one complete part for reference, and one part with missing passages to complete in a suitable style. Original note values are used, with modern time signatures for those values (
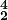 ), some editorial accidentals (ficta), and only G and F clefs.
), some editorial accidentals (ficta), and only G and F clefs.
- IMSLP has this numbered simply as No. “10”, but if consulting the source, note that the parts are numbered as follows in book order: Supranus 24 (“XXIIII”, name and numbering sic), Altus 26 (“XXVI”), Tenor 25 (XXV”), Bassus 23 (XXIII, sic even though the source index page says 22), and Quinta Pars 25 (XXV), remaining parts not applicable. The transcription is in modern notation, but preserves original pitch and note values. ↵
- This is said to be especially true of Palestrina, and further said to have appeased the Council of Trent in its review of recent developments in music. ↵
A traditional approach to composition pedagogy focused on counterpoint as a way of learning to think of music horizontally (melodically) and vertically (harmonically) simultaneously. Consists of five “species,” each of which focuses on a single compositional element.
Imitation sees two or more parts enter separately with (versions of) the same melody.
An imitative repetition of a subject that is not an exact transposition of the subject (that is, a real answer) but modifies the intervals to fit within the same key as the original subject. A common modification is to change a perfect fifth do–sol (1̂–5̂) in the subject to a perfect fourth sol–do (5̂–1̂) in the answer. The term "tonal answer" refers to the fact that this preserves the tonal relationships (e.g., between do and sol) instead of preserving intervallic relationships.
When two voices move melodically in opposite directions—that is, one voice moves up and the other moves down.
An augmented fourth or diminished fifth. The name reflects that the two notes of a tritone are three (tri-) whole steps (tones) apart.
A principle of melody writing suggesting that any large leaps that open up a new register ought to be filled in afterward with stepwise motion.
In church modes, authentic modes are those that range from final to final.
A mode with a range of a fifth above and fourth below its tonic.
An embellishing tone that is approached via static note and left by step down. The suspension is on a strong part of the beat.
When one voice moves melodically while another voice remains on the same pitch.
Connects two or more notes of the same pitch; notes after the initial one are not rearticulated.
When two voices move melodically in the same direction and by the same interval—for example, both voices move upward by a melodic second. (Note: the quality of the interval may vary, and it still counts as parallel motion.) By definition, two voices moving in parallel motion will also maintain the same harmonic interval between them.
Similar motion into a fifth or octave. Also called hidden fifths or octaves.
A type of motion where a chord tone moves by step to another tone, then resolves by step in the same direction. For example, C–D–E above a C major chord would be an example of neighboring motion, in which D can be described as a passing tone. Entire harmonies may be said to be passing when embellishing another harmony, when the voice-leading between the two chords involves mainly passing tones (as in the passing 6/4 chord).
A triad whose third is minor and fifth is diminished.
A type of motion where a chord tone moves by step to another tone, then moves back to the original chord tone. For example, C–D–C above a C major chord would be an example of neighboring motion, in which D can be described as a neighbor tone. Entire harmonies may be said to be neighboring when embellishing another harmony, when the voice-leading between the two chords involves only neighboring and common-tone motion (as in the common-tone diminished seventh chord).
A five-note species counterpoint embellishment that may occur in one of two different forms:
1) Down by step, down by third, up by step, up by step
2) Up by step, up by third, down by step, down by step
Substituting a major I chord for a minor I chord (for example, using C major instead of C minor in a piece that is in C minor overall).
Musica ficta are un-notated accidentals added to Renaissance music. Competent performers know to add ficta in appropriate places. In modern editions of Renaissance music, ficta are often provided by the editor.
