16. FYI: How to use CORE to learn about online acronyms
Bruna Andrade; Julia Ribeiro; Raquel Silva; and Johanna Tumux
Bruna Andrade
Undergraduate student at Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul
Julia Ribeiro
Undergraduate student at Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul
Raquel Silva da Silva
Undergraduate student at Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul
Johanna Tumux
Undergraduate student at Montclair State University
Goals: To teach students how to use CORE to understand acronyms used online.
Audience: Young adults in advanced or intermediate classes
Duration: 40 to 50 minutes
INTRODUCTION
It is safe to say that social media websites are everywhere. We use Twitter, Facebook, Instagram and many others to exchange messages with our friends and family all the time. Even though the world wide web has only been widely accessible for the past 2 or 3 decades, a lot has changed in this time, especially when it comes to the language we use online. As a consequence of social media use, we’ve been using more and more abbreviations like “IRL”, “TBH”, “w/”, and “BRB”. These abbreviations can be a challenge to learners of English as a second language.
In our own experience using English in social media, we noticed a number of celebrities using acronyms, such as “LMAO”, “LOL” and “IDK” on their Instagram posts, but as language learners we could not tell the meaning of these words. Therefore, we decided to focus on this chapter on the meaning of some of the most common acronyms we find online.
We propose two steps for the development of this lesson:
- We’ll demonstrate how to use CORE to analyze the meaning of acronyms and show how they are used in context.
- A brief exercise to test learners’ knowledge of acronyms.
STEP 1: CORPUS ANALYSIS
To analyze and explain the meaning of online acronyms, we are going to use the Corpus of Online Registers of English (CORE), which is part of the English Corpora suite of corpus (https://www.english-corpora.org/). This corpus contains more than 50 million words of text from the web. In this section, we will illustrate the use of CORE with five selected acronyms, but the teacher could select a number of other acronyms that occur in the corpus.
After creating an account in the English Corpora website, the teacher can select the CORE corpus and search one of the acronyms. In our example, we searched for “FYI” using the list search. Then, click on “Find Matching Strings”.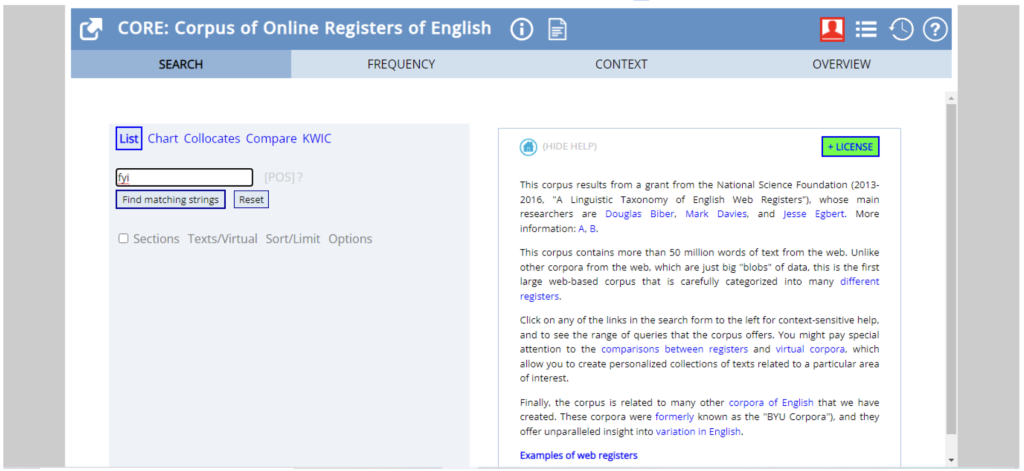
Figure 1 – CORE List Search for “FYI”
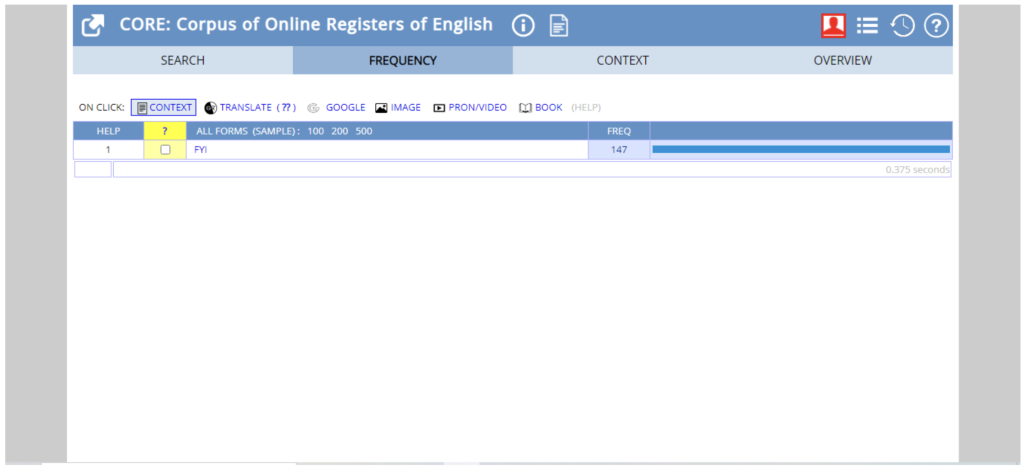
Figure 2 – CORE List Search results for “FYI”
Repeat the same steps with: FYI, XO, WTH, OMG and ASAP. The following paragraphs outline some of the points that should be highlighted when showing the concordance lines to students in the classroom. As an alternative, the teacher might print the concordance lines before class.
FYI:
As we can see from the concordance lines below, this expression is used in order to introduce additional information to the text that the writer/speaker considers relevant to the reader/listener. The concordance lines show that ‘FYI’ is usually used in parentheses, or after “just as an,” in both cases it works to indicate that it introduces additional information.
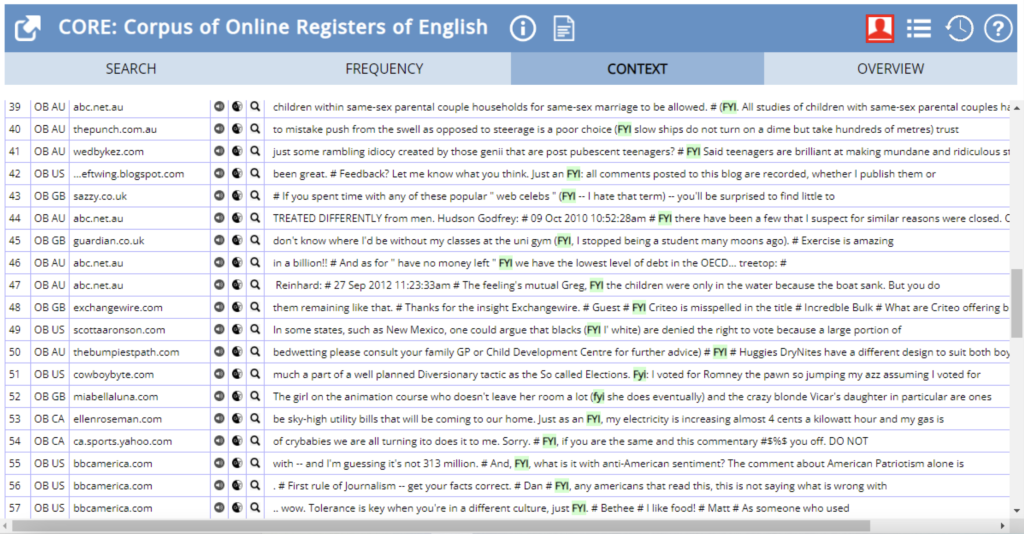
Figure 3 – CORE Context Search results for “FYI”
XO:
As we can see in the concordance lines below, it is an informal term used to express sincerity, love and friendship. The concordance lines also reveal that it is usually used at the end of a written letter, email or text message.
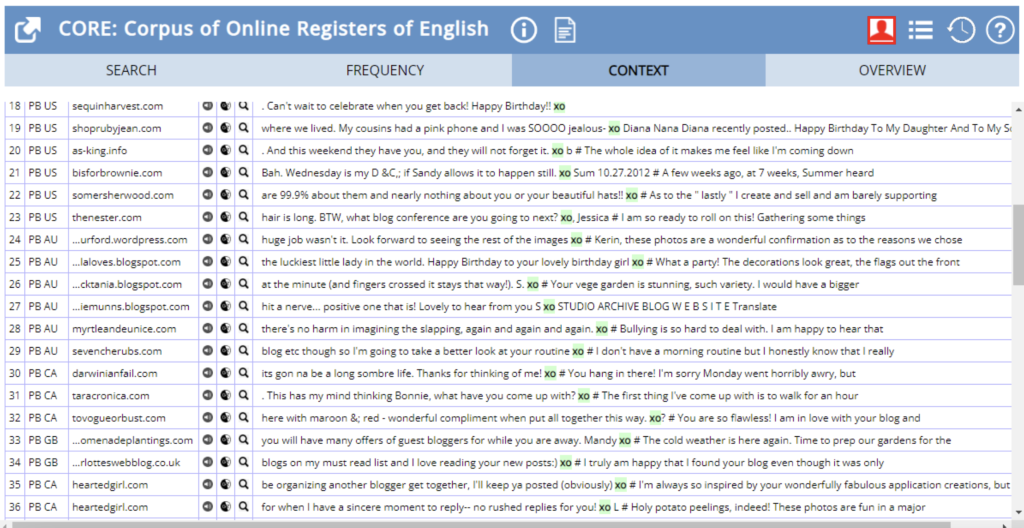
Figure 4 – CORE Context Search results for “XO”
WTH:
As we can see in the concordance lines below, many different emotions are shown depending on the context in which it is inserted. From the image, we can conclude that instances often express confusion.
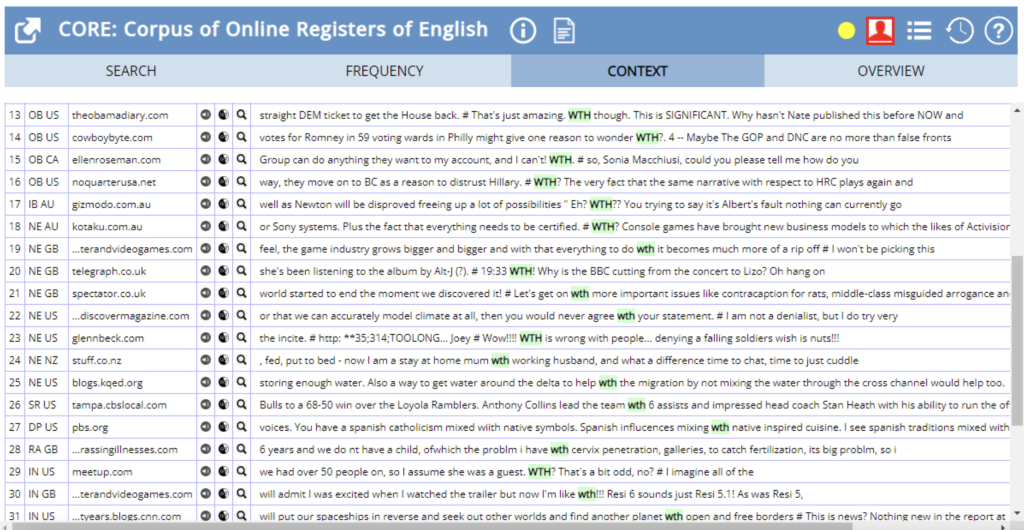
Figure 5 – CORE Context Search results for “WTH”
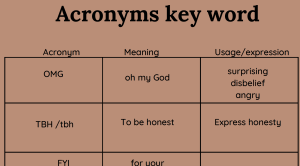
OMG:
As we can see in the concordance lines below, this acronym is used to indicate that something is considered surprising, or to express anger or disbelief. This expression is often used in text messages and informal written emails.
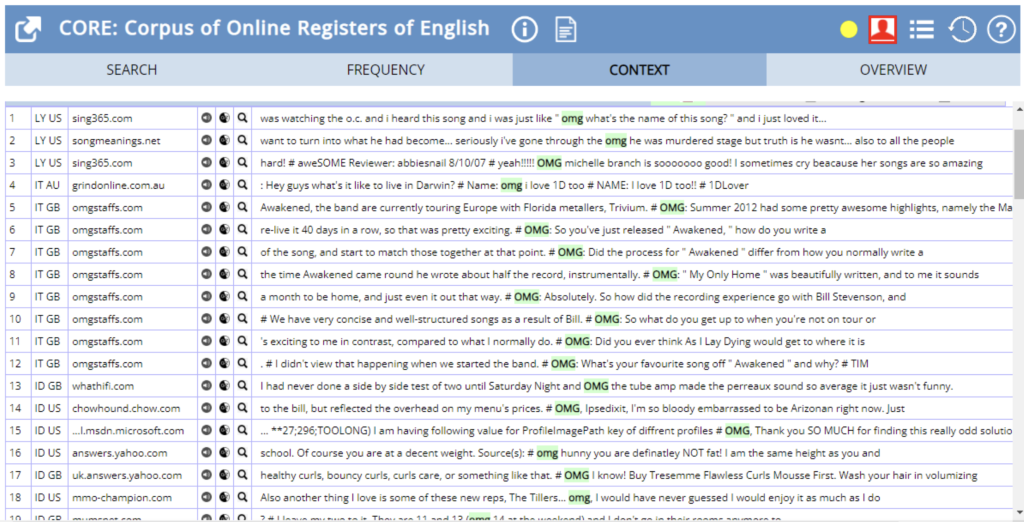
Figure 6 – CORE Context Search results for “OMG”
ASAP:
The concordance lines show that this expression means “immediately” or “right away”. We can also see that it usually occurs at the end of the sentence.
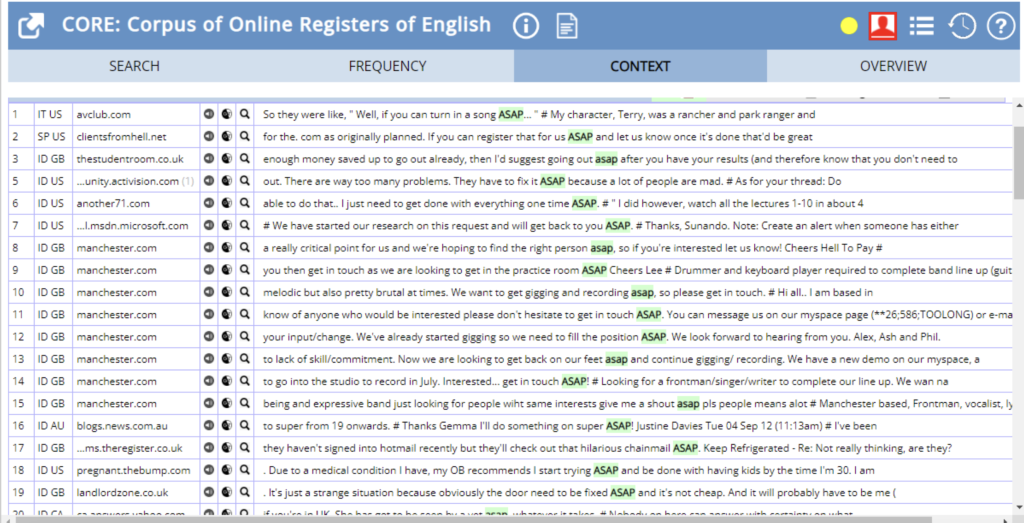
Figure 7 – CORE Context Search results for “ASAP”
STEP 2: PRACTICE ACTIVITY
Activity 1: Crossword
To give students a chance to check their understanding of acronyms, we developed a crossword puzzle using puzzel.org. Teachers can either use the puzzle we developed, or create a new crossword using the Puzzel tool. For low-tech classrooms, teachers can print the crossword.
https://puzzel.org/pt/crossword/play?p=-MosQrBOLltU7fvaks8t
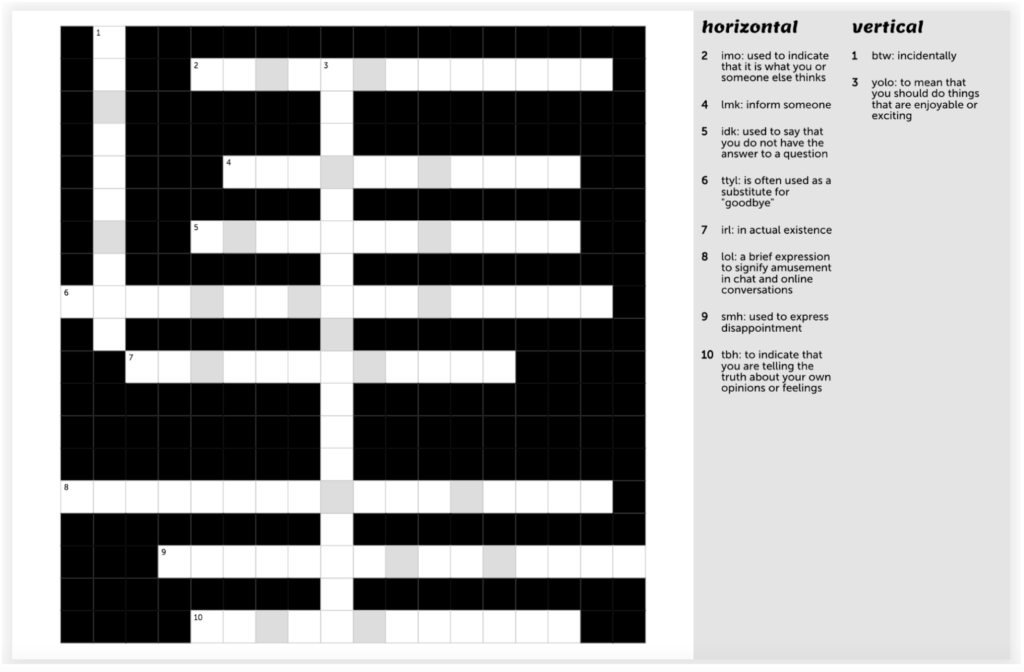
Figure 8 – Puzzel Crossword
You can also access a printable version of this puzzle via the following Google Docs link:
https://docs.google.com/document/d/1TWsxeVCZuMQpa3v6CY__GbWM3RSCiJQq8FMU9TcDDoU/edit?usp=sharing
Alternative activity: The teacher can complete the searches described above as a class. Then, divide the class in groups and raffle other acronyms from this list:
https://abbreviations.yourdictionary.com/articles/common-accronyms.html. Students can then explain the use of different acronyms to other members of their group.
Activity 2: Mad Libs
In this activity, students get a summary of the different acronyms and then they have to complete a series of text messages with the correct acronyms. Download the handout with the MadLibs here.
Andrade, B., Ribeiro, J., Silva, R., & Tumux, J. (2023). FYI: How to use CORE to learn about online acronyms. In L. Goulart & I. Veloso (Eds). Corpora in English Language Teaching: Classroom Activities for Teachers New to Corpus Linguistics. Open Educational Resource. Montclair State University.
