What is confirmation bias? Here is a quick definition from the Encyclopaedia Britannica: “The tendency to process information by looking for, or interpreting, information that is consistent with one’s existing beliefs.” Although confirmation bias is typically unintentional, it is strong and widespread, with many significant effects and real-world implications.
Impact on Searching
Some psychologists describe confirmation bias as the selective collection of evidence that supports what one already believes, while ignoring or rejecting evidence that supports a different conclusion. Experiments have found repeatedly that people tend to test hypotheses in a one-sided way, by searching for evidence consistent with their current beliefs. Rather than searching through all the relevant evidence, they phrase questions to receive an answer that supports their theory.
One of the primary types of confirmation bias is the biased search for information. When you type a search or a question into Google, you will want to be careful that your choice of keywords does not unintentionally reflect a bias towards preexisting beliefs, or toward a particular preconceived answer.
Examples
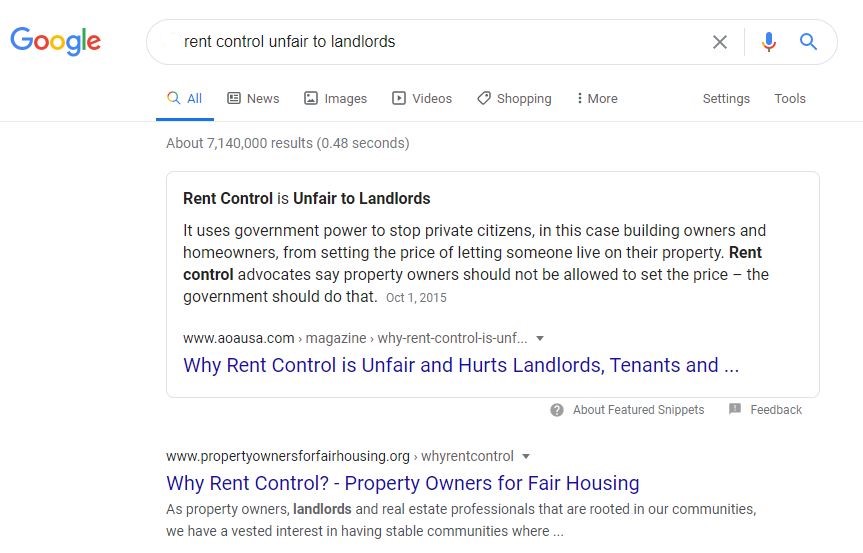
A search for “is rent control unfair to landlords” is likely to get results that describe rent control as unfair to landlords. A better search might be something like “rent control landlords”
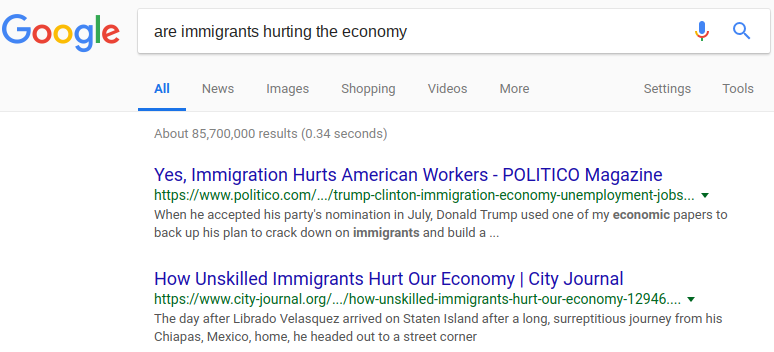
A search for “are immigrants hurting the economy” is likely to get results that argue that immigrants hurt the economy. A better search might be something like “economic effects of immigration”
Sources
Casad, Bettina J. “Confirmation Bias.” Encyclopaedia Britannica, 1 Aug. 2016.
Impact on Searching adapted from “Confirmation bias” by Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0
Page adapted from “Library 10” by Cabrillo College Library, licensed under CC BY 4.0
The collection of evidence that supports what one already believes, while ignoring or rejecting evidence that supports a different conclusion.
