A political cartoon in Puck magazine on January 25, 1899, captures the mind-set of American imperialists. Library of Congress.
I. Introduction
The word empire might conjure images of ancient Rome, the Persian Empire, or the British Empire—powers that depended variously on military conquest, colonization, occupation, or direct resource exploitation—but empires can take many forms and imperial processes can occur in many contexts. One hundred years after the United States won its independence from the British Empire, had it become an empire of its own?
In the decades after the American Civil War, the United States exerted itself in the service of American interests around the world. In the Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East, and most explicitly in the Spanish-American War and under the foreign policy of Theodore Roosevelt and William Howard Taft, the United States expanded on a long history of exploration, trade, and cultural exchange to practice something that looked remarkably like empire. The question of American imperialism, then, seeks to understand not only direct American interventions in such places as Cuba, the Philippines, Hawaii, Guam, and Puerto Rico, but also the deeper history of American engagement with the wider world and the subsequent ways in which American economic, political, and cultural power has shaped the actions, choices, and possibilities of other groups and nations.
Meanwhile, as the United States asserted itself abroad, it acquired increasingly higher numbers of foreign peoples at home. European and Asian immigrants poured into the United States. In a sense, imperialism and immigration raised similar questions about American identity: Who was an “American,” and who wasn’t? What were the nation’s obligations to foreign powers and foreign peoples? And how accessible—and how fluid—should American identity be for newcomers? All such questions confronted late-nineteenth-century Americans with unprecedented urgency.
II. Patterns of American Interventions
American interventions in Mexico, China, and the Middle East reflected the United States’ new eagerness to intervene in foreign governments to protect American economic interests abroad.
The United States had long been involved in Pacific commerce. American ships had been traveling to China, for instance, since 1784. As a percentage of total American foreign trade, Asian trade remained comparatively small, and yet the idea that Asian markets were vital to American commerce affected American policy and, when those markets were threatened, prompted interventions.1 In 1899, secretary of state John Hay articulated the Open Door Policy, which called for all Western powers to have equal access to Chinese markets. Hay feared that other imperial powers—Japan, Great Britain, Germany, France, Italy, and Russia—planned to carve China into spheres of influence. It was in the economic interest of American business to maintain China for free trade. The following year, in 1900, American troops joined a multinational force that intervened to prevent the closing of trade by putting down the Boxer Rebellion, a movement opposed to foreign businesses and missionaries operating in China. President McKinley sent the U.S. Army without consulting Congress, setting a precedent for U.S. presidents to order American troops to action around the world under their executive powers.2
The United States was not only ready to intervene in foreign affairs to preserve foreign markets, it was willing to take territory. The United States acquired its first Pacific territories with the Guano Islands Act of 1856. Guano—collected bird excrement—was a popular fertilizer integral to industrial farming. The act authorized and encouraged Americans to venture into the seas and claim islands with guano deposits for the United States. These acquisitions were the first insular, unincorporated territories of the United States: they were neither part of a state nor a federal district, and they were not on the path to ever attain such a status. The act, though little known, offered a precedent for future American acquisitions.3
Merchants, of course, weren’t the only American travelers in the Pacific. Christian missionaries soon followed explorers and traders. The first American missionaries arrived in Hawaii in 1820 and China in 1830, for example. Missionaries, though, often worked alongside business interests, and American missionaries in Hawaii, for instance, obtained large tracts of land and started lucrative sugar plantations. During the nineteenth century, Hawaii was ruled by an oligarchy based on the sugar companies, together known as the “Big Five.” This white American (haole) elite was extremely powerful, but they still operated outside the formal expression of American state power.4
As many Americans looked for empire across the Pacific, others looked to Latin America. The United States, long a participant in an increasingly complex network of economic, social, and cultural interactions in Latin America, entered the late nineteenth century with a new aggressive and interventionist attitude toward its southern neighbors.
American capitalists invested enormous sums of money in Mexico during the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, during the long reign of the corrupt yet stable regime of the modernization-hungry president Porfirio Diaz. But in 1910 the Mexican people revolted against Díaz, ending his authoritarian regime but also his friendliness toward the business interests of the United States. In the midst of the terrible destruction wrought by the fighting, Americans with investment interests pleaded for governmental help. But the U.S. government tried to control events and politics that could not be controlled. More and more American businessmen called for military intervention. When the brutal strongman Victoriano Huerta executed the revolutionary, democratically elected president Francisco Madero in 1913, newly inaugurated American president Woodrow Wilson put pressure on Mexico’s new regime. Wilson refused to recognize the new government and demanded that Huerta step aside and allow free elections to take place. Huerta refused.5
When Mexican forces mistakenly arrested American sailors in the port city of Tampico in April 1914, Wilson saw the opportunity to apply additional pressure on Huerta. Huerta refused to make amends, and Wilson therefore asked Congress for authority to use force against Mexico. But even before Congress could respond, Wilson invaded and took the port city of Veracruz to prevent, he said, a German shipment of arms from reaching Huerta’s forces. The Huerta government fell in July 1914, and the American occupation lasted until November, when Venustiano Carranza, a rival of Huerta, took power. When Wilson threw American support behind Carranza, and not his more radical and now-rival Pancho Villa, Villa and several hundred supporters attacked American interests and raided the town of Columbus, New Mexico, in March 1916, and killed over a dozen soldiers and civilians. Wilson ordered a punitive expedition of several thousand soldiers led by General John J. “Blackjack” Pershing to enter northern Mexico and capture Villa. But Villa eluded Pershing for nearly a year and, in 1917, with war in Europe looming and great injury done to U.S.-Mexican relations, Pershing left Mexico.6
The United States’ actions during the Mexican Revolution reflected long-standing American policy that justified interventionist actions in Latin American politics because of their potential bearing on the United States: on citizens, on shared territorial borders, and, perhaps most significantly, on economic investments. This example highlights the role of geography, or perhaps proximity, in the pursuit of imperial outcomes. But American interactions in more distant locations, in the Middle East, for instance, look quite different.
In 1867, Mark Twain traveled to the Middle East as part of a large tour group of Americans. In his satirical travelogue, The Innocents Abroad, he wrote, “The people [of the Middle East] stared at us everywhere, and we [Americans] stared at them. We generally made them feel rather small, too, before we got done with them, because we bore down on them with America’s greatness until we crushed them.”7 When Americans later intervened in the Middle East, they would do so convinced of their own superiority.
The U.S. government had traditionally had little contact with the Middle East. Trade was limited, too limited for an economic relationship to be deemed vital to the national interest, but treaties were nevertheless signed between the U.S. and powers in the Middle East. Still, the majority of American involvement in the Middle East prior to World War I came not in the form of trade but in education, science, and humanitarian aid. American missionaries led the way. The first Protestant missionaries had arrived in 1819. Soon the American Board of Commissioners for Foreign Missions and the boards of missions of the Reformed Church of America became dominant in missionary enterprises. Missions were established in almost every country of the Middle East, and even though their efforts resulted in relatively few converts, missionaries helped establish hospitals and schools, and their work laid the foundation for the establishment of Western-style universities, such as Robert College in Istanbul, Turkey (1863), the American University of Beirut (1866), and the American University of Cairo (1919).8
III. 1898
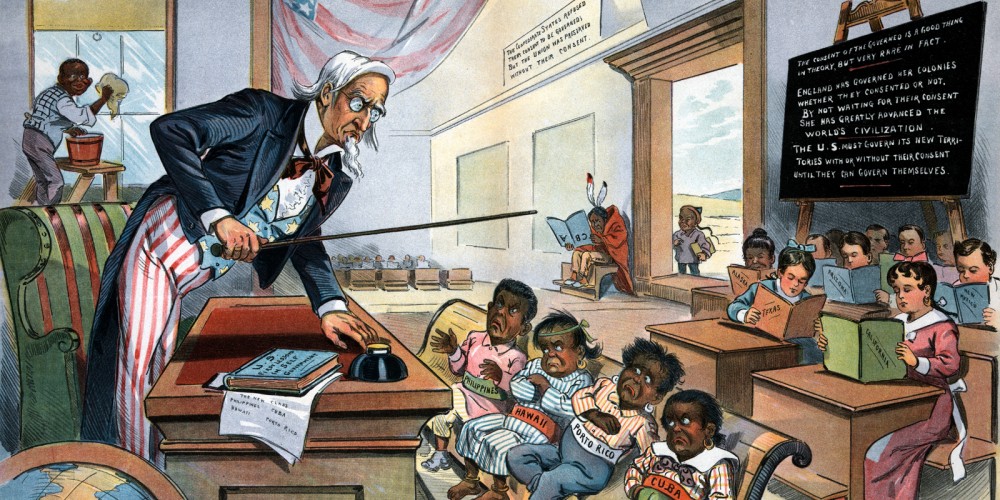
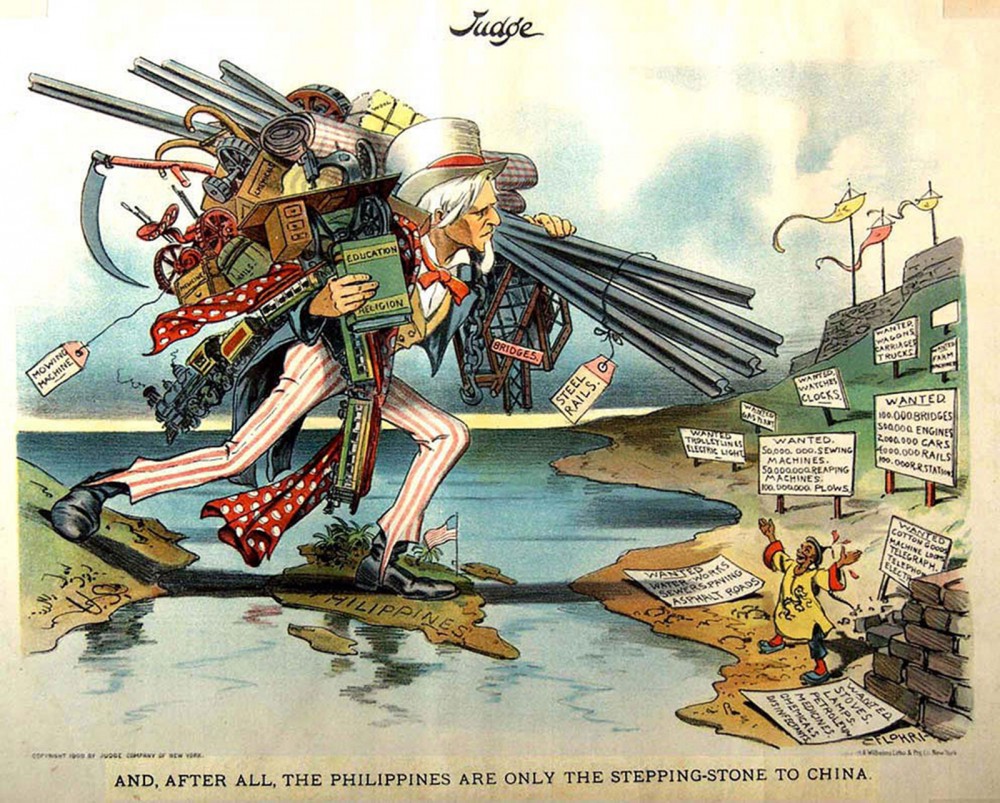
In this political cartoon, Uncle Sam, loaded with the implements of modern civilization, uses the Philippines as a stepping-stone to cross the Pacific to China, which excitedly awaits Sam’s arrival. Such cartoons captured Americans’ growing infatuation with imperialist and expansionist policies. C. 1900–1902. Wikimedia.
Although the United States had a long history of international economic, military, and cultural engagement that stretched back deep into the eighteenth century, the Spanish-American and Philippine-American Wars (1898–1902) marked a crucial turning point in American interventions abroad. In pursuing war with Spain, and then engaging in counterrevolutionary conflict in the Philippines, the United States expanded the scope and strength of its global reach. Over the next two decades, the United States would become increasingly involved in international politics, particularly in Latin America. These new conflicts and ensuing territorial problems forced Americans to confront the ideological elements of imperialism. Should the United States act as an empire? Or were foreign interventions and the taking of territory antithetical to its founding democratic ideals? What exactly would be the relationship between the United States and its territories? And could colonial subjects be successfully and safely incorporated into the body politic as American citizens? The Spanish-American and Philippine-American Wars brought these questions, which had always lurked behind discussions of American expansion, out into the open.
In 1898, Americans began in earnest to turn their attention southward to problems plaguing their neighbor Cuba. Since the middle of the nineteenth century, Cubans had tried unsuccessfully again and again to gain independence from Spain. The latest uprising, and the one that would prove fatal to Spain’s colonial designs, began in 1895 and was still raging in the winter of 1898. By that time, in an attempt to crush the uprising, Spanish general Valeriano Weyler y Nicolau had been conducting a policy of reconcentration—forcing Cubans living in certain cities to relocate en masse to military camps—for about two years. Prominent newspaper publishers sensationalized Spanish atrocities. Cubans in the United States and their allies raised cries of Cuba Libre! And while the U.S. government proclaimed a wish to avoid armed conflict with Spain, President McKinley became increasingly concerned about the safety of American lives and property in Cuba. He ordered the battleship Maine to Havana harbor in January 1898.
The Maine sat undisturbed in the harbor for about two weeks. Then, on the evening of February 15, a titanic explosion tore open the ship and sent it to the bottom of the ocean. Three quarters of the ship’s 354 occupants died. A naval board of inquiry immediately began an investigation to ascertain the cause of the explosion, but the loudest Americans had already decided that Spanish treachery was to blame. Capitalizing on the outrage, “yellow journals”—newspapers that promoted sensational stories, notoriously at the cost of accuracy—such as William Randolph Hearst’s New York Journal called for war with Spain. When urgent negotiations failed to produce a mutually agreeable settlement, Congress officially declared war on April 25.
Although America’s war effort began haphazardly, Spain’s decaying military crumbled. Military victories for the United States came quickly. In the Pacific, on May 1, Commodore George Dewey engaged the Spanish fleet outside Manila, the capital of the Philippines (another Spanish colonial possession), destroyed it, and proceeded to blockade Manila harbor. Two months later, American troops took Cuba’s San Juan Heights in what would become the most well-known battle of the war, winning fame not for regular soldiers but for the irregular, especially Theodore Roosevelt and his Rough Riders. Roosevelt had been the assistant secretary of the navy but had resigned his position in order to see action in the war. His actions in Cuba made him a national celebrity. As disease began to eat away at American troops, the Spanish suffered the loss of Santiago de Cuba on July 17, effectively ending the war. The two nations agreed to a cease-fire on August 12 and formally signed the Treaty of Paris in December. The terms of the treaty stipulated, among other things, that the United States would acquire Spain’s former holdings of Guam, Puerto Rico, and the Philippines.
Secretary of state John Hay memorably referred to the conflict as a “splendid little war,” and at the time it certainly appeared that way. Fewer than four hundred Americans died in battle in a war that lasted about fifteen weeks. Contemporaries celebrated American victories as the providential act of God. The influential Brooklyn minister Lyman Abbott, for instance, declared that Americans were “an elect people of God” and saw divine providence in Dewey’s victory at Manila.9 Some, such as Senator Albert J. Beveridge of Indiana, took matters one step further, seeing in American victory an opportunity for imperialism. In Beveridge’s view, America had a “mission to perform” and a “duty to discharge” around the world.10 What Beveridge envisioned was nothing less than an American empire.
This 1914 political cartoon shows embodiments of colonies and territories before and after American interventions. The differences are obvious and exaggerated, with the top figures described as “oppressed” by the weight of industrial slavery until America “rescued” them, turning them into the respectable and successful businessmen seen on the bottom half. Those who claimed that American imperialism brought civilization and prosperity to destitute peoples used such visuals to support their cause. Wikimedia.
But the question of whether the United States should become an empire was sharply debated across the nation in the aftermath of the Spanish-American War and the acquisition of Hawaii in July 1898. At the behest of American businessmen who had overthrown the Hawaiian monarchy, the United States annexed the Hawaiian Islands and their rich plantations. Between Hawaii and a number of former Spanish possessions, many Americans coveted the economic and political advantages that increased territory would bring. Those opposed to expansion, however, worried that imperial ambitions did not accord with the nation’s founding ideals. American actions in the Philippines brought all of these discussions to a head.
The Philippines were an afterthought of the Spanish-American War, but when the smoke cleared, the United States found itself in possession of a key foothold in the Pacific. After Dewey’s victory over the Spanish fleet in the Battle of Manila Bay, conversations about how to proceed occupied the attention of President McKinley, political leaders from both parties, and the popular press. American and Philippine forces (under the leadership of Emilio Aguinaldo) were in communication: Would the Americans offer their support to the Filipinos and their ongoing efforts against the Spanish? Or would the Americans replace the Spanish as a colonial occupying force? American forces were instructed to secure Manila without allowing Philippine forces to enter the Walled City (the seat of the Spanish colonial government), hinting, perhaps, at things to come. Americans wondered what would happen next. Perhaps a good many ordinary Americans shared the bewildered sentiments of Mr. Dooley, the fictional Irish-American barkeeper whom humorist Finley Peter Dunne used to satirize American life: “I don’t know what to do with th’ Ph’lippeens anny more thin I did las’ summer, befure I heerd tell iv thim. . . . We can’t sell thim, we can’t ate thim, an’ we can’t throw thim into the th’ alley whin no wan is lookin’’.”11
As debates about American imperialism continued against the backdrop of an upcoming presidential election, tensions in the Philippines escalated. Emilio Aguinaldo was inaugurated as president of the First Philippine Republic (or Malolos Republic) in late January 1899; fighting between American and Philippine forces began in early February; and in April 1899, Congress ratified the 1898 Treaty of Paris, which concluded the Spanish-American War and gave Spain $20 million in exchange for the Philippine Islands.12
Like the Cubans, Filipinos had waged a long war against their Spanish colonizers. The United States could have given them the independence they had long fought for, but, instead, at the behest of President William McKinley, the United States occupied the islands and from 1899 to 1902 waged a bloody series of conflicts against Filipino insurrectionists that cost far more lives than the war with Spain. Under the leadership of Emilio Aguinaldo, Filipinos who had fought for freedom against the Spanish now fought for freedom against the very nation that had claimed to have liberated them from Spanish tyranny.13
The Philippine Insurrection, or the Philippine-American War, was a brutal conflict of occupation and insurgency. Contemporaries compared the guerrilla-style warfare in challenging and unfamiliar terrain to the American experiences in the so-called Indian Wars of the late nineteenth century. Many commented on its brutality and the uncertain mission of American troops. An April 1899 dispatch from a Harper’s Weekly correspondent began, “A week has passed—a week of fighting and marching, of jungles and rivers, of incident and adventure so varied and of so rapid transition that to sit down to write about it makes one feel as if he were trying to describe a dream where time, space, and all the logical sequences of ordinary life are upset in the unrelenting brutality of war.”14 John Bass described his experiences in detail, and his reportage, combined with accounts that came directly from soldiers, helped shape public knowledge about the war. Reports of cruelty on both sides and a few high-profile military investigations ensured continued public attention to events across the Pacific.
Amid fighting to secure the Philippine Islands, the federal government sent two Philippine Commissions to assess the situation in the islands and make recommendations for a civilian colonial government. A civilian administration, with William H. Taft as the first governor-general (1901–1903), was established with military support. Although President Theodore Roosevelt declared the war to be over in 1902, resistance and occasional fighting continued into the second decade of the twentieth century.15
Debates about American imperialism dominated headlines and tapped into core ideas about American identity and the proper role of the United States in the larger world. Should a former colony, established on the principles of freedom, liberty, and sovereignty, become a colonizer itself? What was imperialism, anyway? Many framed the Filipino conflict as a Protestant, civilizing mission. Others framed American imperialism in the Philippines as nothing new, as simply the extension of a never-ending westward American expansion. It was simply destiny. Some saw imperialism as a way to re-energize the nation by asserting national authority and power around the globe. Others baldly recognized the opportunities the Philippine Islands presented for access to Asian markets. But critics grew loud. The American Anti-Imperialist League, founded in 1899 and populated by such prominent Americans as Mark Twain, Andrew Carnegie, and Jane Addams, protested American imperial actions and articulated a platform that decried foreign subjugation and upheld the rights of all to self-governance. Still, others embraced anti-imperialist stances because of concerns about immigration and American racial identity, afraid that American purity stood imperiled by contact with strange and foreign peoples. For whatever reason, however, the onset or acceleration of imperialism was a controversial and landmark moment in American history. America had become a preeminent force in the world.
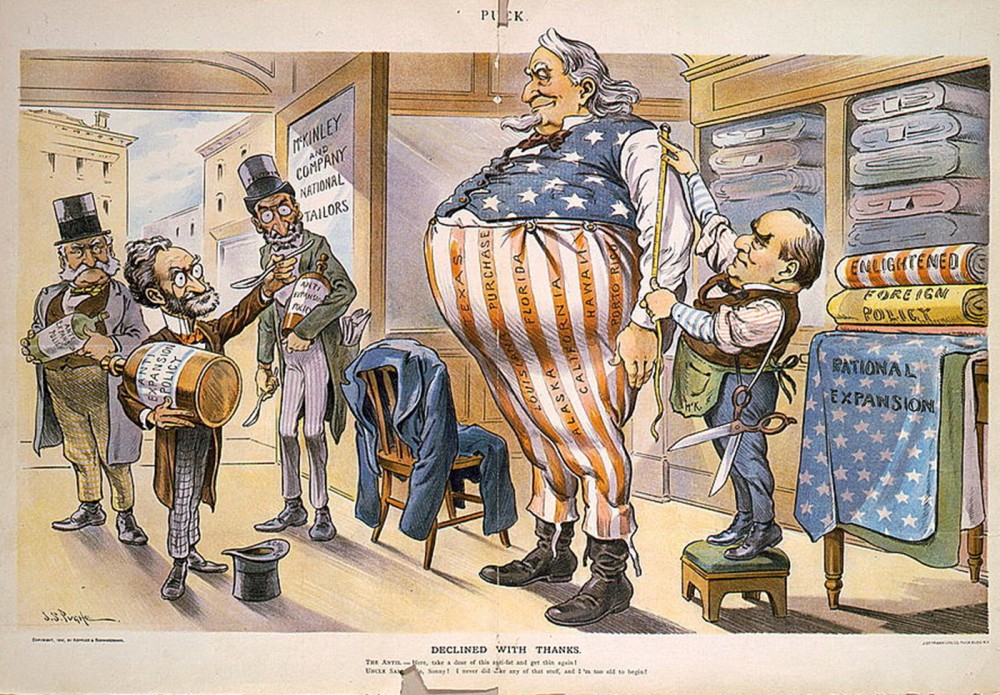
In this 1900 political cartoon, President McKinley measures an obese Uncle Sam for larger clothing, while anti-expansionists like Joseph Pulitzer unsuccessfully offer him a weight-loss elixir. As the nation increased its imperialistic presence and mission, many worried that America would grow too big for its own good. Wikimedia.
IV. Theodore Roosevelt and American Imperialism
Under the leadership of President Theodore Roosevelt, the United States emerged from the nineteenth century with ambitious designs on global power through military might, territorial expansion, and economic influence. Though the Spanish-American War had begun under the administration of William McKinley, Roosevelt—the hero of San Juan Hill, assistant secretary of the navy, vice president, and president—was arguably the most visible and influential proponent of American imperialism at the turn of the century. Roosevelt’s emphasis on developing the American navy, and on Latin America as a key strategic area of U.S. foreign policy, would have long-term consequences.
In return for Roosevelt’s support of the Republican nominee, William McKinley, in the 1896 presidential election, McKinley appointed Roosevelt as assistant secretary of the navy. The head of the department, John Long, had a competent but lackadaisical managerial style that allowed Roosevelt a great deal of freedom which he used to network with such luminaries as military theorists Alfred Thayer Mahan and naval officer George Dewey and politicians such as Henry Cabot Lodge and William Howard Taft. During his tenure he oversaw the construction of new battleships and the implementation of new technology and laid the groundwork for new shipyards, all with the goal of projecting America’s power across the oceans. Roosevelt wanted to expand American influence. For instance, he advocated for the annexation of Hawaii for several reasons: it was within the American sphere of influence, it would deny Japanese expansion and limit potential threats to the West Coast, it had an excellent port for battleships at Pearl Harbor, and it would act as a fueling station on the way to pivotal markets in Asia.16
Teddy Roosevelt, a politician turned soldier, gained fame after he and his Rough Riders took San Juan Hill. Images like this poster praised Roosevelt and the battle as Americans celebrated a “splendid little war.” 1899. Wikimedia.
Roosevelt, after winning headlines in the war, ran as vice president under McKinley and rose to the presidency after McKinley’s assassination by the anarchist Leon Czolgosz in 1901. Among his many interventions in American life, Roosevelt acted with vigor to expand the military, bolstering naval power especially, to protect and promote American interests abroad. This included the construction of eleven battleships between 1904 and 1907. Alfred Thayer Mahan’s naval theories, described in his The Influence of Sea Power upon History, influenced Roosevelt a great deal. In contrast to theories that advocated for commerce raiding, coastal defense, and small “brown water” ships, the imperative to control the sea required battleships and a “blue water” navy that could engage and win decisive battles with rival fleets. As president, Roosevelt continued the policies he established as assistant secretary of the navy and expanded the U.S. fleet. The mission of the Great White Fleet, sixteen all-white battleships that sailed around the world between 1907 and 1909, exemplified America’s new power.17
Roosevelt insisted that the “big stick” and the persuasive power of the U.S. military could ensure U.S. hegemony over strategically important regions in the Western Hemisphere. The United States used military intervention in various circumstances to further its objectives, but it did not have the ability or the inclination to militarily impose its will on the entirety of South and Central America. The United States therefore more often used informal methods of empire, such as so-called dollar diplomacy, to assert dominance over the hemisphere.
The United States actively intervened again and again in Latin America. Throughout his time in office, Roosevelt exerted U.S. control over Cuba (even after it gained formal independence in 1902) and Puerto Rico, and he deployed naval forces to ensure Panama’s independence from Colombia in 1903 in order to acquire a U.S. Canal Zone. Furthermore, Roosevelt pronounced the Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine in 1904, proclaiming U.S. police power in the Caribbean. As articulated by President James Monroe in his annual address to Congress in 1823, the United States would treat any military intervention in Latin America by a European power as a threat to American security. Roosevelt reaffirmed the Monroe Doctrine and expanded it by declaring that the United States had the right to preemptive action through intervention in any Latin American nation in order to correct administrative and fiscal deficiencies.18
Roosevelt’s policy justified numerous and repeated police actions in “dysfunctional” Caribbean and Latin American countries by U.S. Marines and naval forces and enabled the founding of the naval base at Guantanamo Bay, Cuba. This approach is sometimes referred to as gunboat diplomacy, wherein naval forces and Marines land in a national capital to protect American and Western personnel, temporarily seize control of the government, and dictate policies friendly to American business, such as the repayment of foreign loans. For example, in 1905 Roosevelt sent the Marines to occupy the Dominican Republic and established financial supervision over the Dominican government. Imperialists often framed such actions as almost humanitarian. They celebrated white Anglo-Saxon societies such as those found in the United States and the British Empire as advanced practitioners of nation-building and civilization, helping to uplift debtor nations in Latin America that lacked the manly qualities of discipline and self-control. Roosevelt, for instance, preached that it was the “manly duty” of the United States to exercise an international police power in the Caribbean and to spread the benefits of Anglo-Saxon civilization to inferior states populated by inferior peoples. The president’s language, for instance, contrasted debtor nations’ “impotence” with the United States’ civilizing influence, belying new ideas that associated self-restraint and social stability with Anglo-Saxon manliness.19
Dollar diplomacy offered a less costly method of empire and avoided the troubles of military occupation. Washington worked with bankers to provide loans to Latin American nations in exchange for some level of control over their national fiscal affairs. Roosevelt first implemented dollar diplomacy on a vast scale, while Presidents Taft and Wilson continued the practice in various forms during their own administrations. All confronted instability in Latin America. Rising debts to European and American bankers allowed for the inroads of modern life but destabilized much of the region. Bankers, beginning with financial houses in London and New York, saw Latin America as an opportunity for investment. Lenders took advantage of the region’s newly formed governments’ need for cash and exacted punishing interest rates on massive loans, which were then sold off in pieces on the secondary bond market. American economic interests were now closely aligned with the region but also further undermined by the chronic instability of the region’s newly formed governments, which were often plagued by mismanagement, civil wars, and military coups in the decades following their independence. Turnover in regimes interfered with the repayment of loans, as new governments often repudiated the national debt or forced a renegotiation with suddenly powerless lenders.20
Creditors could not force settlements of loans until they successfully lobbied their own governments to get involved and forcibly collect debts. The Roosevelt administration did not want to deny the Europeans’ rightful demands of repayment of debt, but it also did not want to encourage European policies of conquest in the hemisphere as part of that debt collection. U.S. policy makers and military strategists within the Roosevelt administration determined that this European practice of military intervention posed a serious threat to American interests in the region. Roosevelt reasoned that the United States must create and maintain fiscal and political stability within strategically important nations in Latin America, particularly those affecting routes to and from the proposed Panama Canal. As a result, U.S. policy makers considered intervention in places like Cuba and the Dominican Republic a necessity to ensure security around the region.21
The Monroe Doctrine provided the Roosevelt administration with a diplomatic and international legal tradition through which it could assert a U.S. right and obligation to intervene in the hemisphere. The Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine asserted that the United States wished to promote stable, prosperous states in Latin America that could live up to their political and financial obligations. Roosevelt declared that “wrongdoing, or an impotence which results in a general loosening of the ties of civilized society, may finally require intervention by some civilized nation, and in the Western Hemisphere the United States cannot ignore this duty.”22 President Monroe declared what Europeans could not do in the Western Hemisphere; Roosevelt inverted his doctrine to legitimize direct U.S. intervention in the region.23
Though aggressive and bellicose, Roosevelt did not necessarily advocate expansion by military force. In fact, the president insisted that in dealings with the Latin American nations, he did not seek national glory or expansion of territory and believed that war or intervention should be a last resort when resolving conflicts with problematic governments. According to Roosevelt, such actions were necessary to maintain “order and civilization.”24 Then again, Roosevelt certainly believed in using military power to protect national interests and spheres of influence when absolutely necessary. He also believed that the American sphere included not only Hawaii and the Caribbean but also much of the Pacific. When Japanese victories over Russia threatened the regional balance of power, he sponsored peace talks between Russian and Japanese leaders, earning him a Nobel Peace Prize in 1906.
V. Women and Imperialism
With much satisfaction, Columbia puts on her “Easter Bonnet,” a hat shaped like a warship and labeled World Power. By 1901, when this political cartoon was published, Americans felt confident in their country’s position as a world leader. Wikimedia.
Debates over American imperialism revolved around more than just politics and economics and national self-interest. They also included notions of humanitarianism, morality, religion, and ideas of “civilization.” And they included significant participation by American women.
In the fall of 1903, Margaret McLeod, age twenty-one, originally of Boston, found herself in Australia on family business and in need of income. Fortuitously, she made the acquaintance of Alexander MacWillie, the top salesman for the H. J. Heinz Company, who happened to be looking for a young lady to serve as a “demonstrator” of Heinz products to potential consumers. McLeod proved to be such an attractive purveyor of India relish and baked beans that she accompanied MacWillie on the rest of his tour of Australia and continued on to South Africa, India, and Japan. Wherever she went, this “dainty young girl with golden hair in white cap and tucker” drew attention to Heinz’s products, but, in a much larger sense, she was also projecting an image of middle-class American domesticity, of pure womanhood. Heinz saw itself not only as purveying economical and healthful foodstuffs—it was bringing the blessings of civilization to the world.25
When commentators, such as Theodore Roosevelt in his speech on “the strenuous life,” spoke about America’s overseas ventures, they generally gave the impression that this was a strictly masculine enterprise—the work of soldiers, sailors, government officials, explorers, businessmen, and scientists. But in fact, U.S. imperialism, which focused as much on economic and cultural influence as on military or political power, offered a range of opportunities for white, middle-class, Christian women. In addition to working as representatives of American business, women could serve as missionaries, teachers, and medical professionals, and as artists and writers they were inspired by and helped transmit ideas about imperialism.
Moreover, the rhetoric of civilization that underlay imperialism was itself a highly gendered concept. According to the racial theory of the day, humans progressed through hierarchical stages of civilization in an orderly, linear fashion. Only Europeans and Americans had attained the highest level of civilization, which was superficially marked by whiteness but also included an industrial economy and a gender division in which men and women had diverging but complementary roles. Social and technological progress had freed women of the burdens of physical labor and elevated them to a position of moral and spiritual authority. White women thus potentially had important roles to play in U.S. imperialism, both as symbols of the benefits of American civilization and as vehicles for the transmission of American values.26
Civilization, while often cloaked in the language of morality and Christianity, was very much an economic concept. The stages of civilization were primarily marked by their economic character (hunter-gatherer, agricultural, industrial), and the consumption of industrially produced commodities was seen as a key moment in the progress of “savages” toward civilized life. Over the course of the nineteenth century, women in the West, for instance, had become closely associated with consumption, particularly of those commodities used in the domestic sphere. Thus it must have seemed natural for Alexander MacWillie to hire Margaret McLeod to “demonstrate” ketchup and chili sauce at the same time as she “demonstrated” white, middle-class domesticity. By adopting the use of such progressive products in their homes, consumers could potentially absorb even the virtues of American civilization.27
In some ways, women’s work in support of imperialism can be seen as an extension of the kind of activities many of them were already engaged in among working-class, immigrant, and Native American communities in the United States. Many white women felt that they had a duty to spread the benefits of Christian civilization to those less fortunate than themselves. American overseas ventures, then, merely expanded the scope of these activities—literally, in that the geographical range of possibilities encompassed practically the entire globe, and figuratively, in that imperialism significantly raised the stakes of women’s work. No longer only responsible for shaping the next generation of American citizens, white women now had a crucial role to play in the maintenance of civilization itself. They too would help determine whether civilization would continue to progress.
Of course, not all women were active supporters of U.S. imperialism. Many actively opposed it. Although the most prominent public voices against imperialism were male, women made up a large proportion of the membership of organizations like the Anti-Imperialist League. For white women like Jane Addams and Josephine Shaw Lowell, anti-imperialist activism was an outgrowth of their work in opposition to violence and in support of democracy. Black female activists, meanwhile, generally viewed imperialism as a form of racial antagonism and drew parallels between the treatments of African Americans at home and, for example, Filipinos abroad. Indeed, Ida B. Wells viewed her anti-lynching campaign as a kind of anti-imperialist activism.
VI. Immigration
For Americans at the turn of the century, imperialism and immigration were two sides of the same coin. The involvement of American women with imperialist and anti-imperialist activity demonstrates how foreign policy concerns were brought home and became, in a sense, domesticated. It is also no coincidence that many of the women involved in both imperialist and anti-imperialist organizations were also concerned with the plight of new arrivals to the United States. Industrialization, imperialism, and immigration were all linked. Imperialism had at its core a desire for markets for American goods, and those goods were increasingly manufactured by immigrant labor. This sense of growing dependence on “others” as producers and consumers, along with doubts about their capability of assimilation into the mainstream of white, Protestant American society, caused a great deal of anxiety among native-born Americans.
Between 1870 and 1920, over twenty-five million immigrants arrived in the United States. This migration was largely a continuation of a process begun before the Civil War, though by the turn of the twentieth century, new groups such as Italians, Poles, and Eastern European Jews made up a larger percentage of the arrivals while Irish and German numbers began to dwindle.
Although the growing U.S. economy needed large numbers of immigrant workers for its factories and mills, many Americans reacted negatively to the arrival of so many immigrants. Nativists opposed mass immigration for various reasons. Some felt that the new arrivals were unfit for American democracy, and that Irish or Italian immigrants used violence or bribery to corrupt municipal governments. Others (often earlier immigrants themselves) worried that the arrival of even more immigrants would result in fewer jobs and lower wages. Such fears combined and resulted in anti-Chinese protests on the West Coast in the 1870s. Still others worried that immigrants brought with them radical ideas such as socialism and communism. These fears multiplied after the Chicago Haymarket affair in 1886, in which immigrants were accused of killing police officers in a bomb blast.28
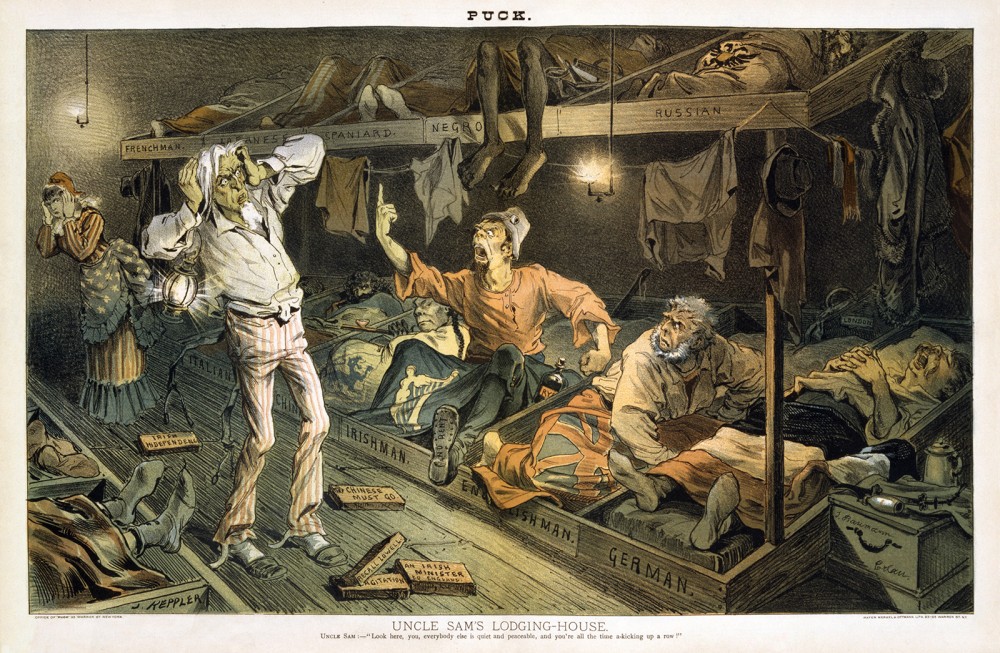
Nativist sentiment intensified in the late nineteenth century as immigrants streamed into American cities. Uncle Sam’s Lodging House, published in 1882, conveys this anti-immigrant attitude, with caricatured representations of Europeans, Asians, and African Americans creating a chaotic scene. Wikimedia.
In September 1876, Franklin Benjamin Sanborn, a member of the Massachusetts Board of State Charities, gave an address in support of the introduction of regulatory federal immigration legislation at an interstate conference of charity officials in Saratoga, New York. Immigration might bring some benefits, but “it also introduces disease, ignorance, crime, pauperism and idleness.” Sanborn thus advocated federal action to stop “indiscriminate and unregulated immigration.”29
Sanborn’s address was aimed at restricting only the immigration of paupers from Europe to the East Coast, but the idea of immigration restrictions was common across the United States in the late nineteenth century, when many variously feared that the influx of foreigners would undermine the racial, economic, and moral integrity of American society. From the 1870s to the 1920s, the federal government passed a series of laws limiting or discontinuing the immigration of particular groups, and the United States remained committed to regulating the kind of immigrants who would join American society. To critics, regulations legitimized racism, class bias, and ethnic prejudice as formal national policy.
The first move for federal immigration control came from California, where racial hostility toward Chinese immigrants had mounted since the mid-nineteenth century. In addition to accusing Chinese immigrants of racial inferiority and unfitness for American citizenship, opponents claimed that they were also economically and morally corrupting American society with cheap labor and immoral practices, such as prostitution. Immigration restriction was necessary for the “Caucasian race of California,” as one anti-Chinese politician declared, and for European Americans to “preserve and maintain their homes, their business, and their high social and moral position.” In 1875, the anti-Chinese crusade in California moved Congress to pass the Page Act, which banned the entry of convicted criminals, Asian laborers brought involuntarily, and women imported “for the purposes of prostitution,” a stricture designed chiefly to exclude Chinese women. Then, in May 1882, Congress suspended the immigration of all Chinese laborers with the Chinese Exclusion Act, making the Chinese the first immigrant group subject to admission restrictions on the basis of race. They became the first illegal immigrants.30
The idea of America as a “melting pot,” a metaphor common in today’s parlance, was a way of arguing for the ethnic assimilation of all immigrants into a nebulous “American” identity at the turn of the 20th century. A play of the same name premiered in 1908 to great acclaim, causing even the former president Theodore Roosevelt to tell the playwright, “That’s a great play, Mr. Zangwill, that’s a great play.” Cover of Theater Programme for Israel Zangwill’s play “The Melting Pot”, 1916. Wikimedia.
On the other side of the country, Atlantic Seaboard states also facilitated the formation of federal immigration policy. Since the colonial period, East Coast states had regulated immigration through their own passenger laws, which prohibited the landing of destitute foreigners unless shipmasters prepaid certain amounts of money in the support of those passengers. State-level control of pauper immigration developed into federal policy in the early 1880s. In August 1882, Congress passed the Immigration Act, denying admission to people who were not able to support themselves and those, such as paupers, people with mental illnesses, or convicted criminals, who might otherwise threaten the security of the nation.
The category of excludable people expanded continuously after 1882. In 1885, in response to American workers’ complaints about cheap immigrant labor, Congress added foreign workers migrating under labor contracts with American employers to the list of excludable people. Six years later, the federal government included people who seemed likely to become wards of the state, people with contagious diseases, and polygamists, and made all groups of excludable people deportable. In 1903, those who would pose ideological threats to American republican democracy, such as anarchists and socialists, also became the subject of new immigration restrictions.
Many immigration critics were responding to the shifting demographics of American immigration. The center of immigrant-sending regions shifted from northern and western Europe to southern and eastern Europe and Asia. These “new immigrants” were poorer, spoke languages other than English, and were likely Catholic or Jewish. White Protestant Americans typically regarded them as inferior, and American immigration policy began to reflect more explicit prejudice than ever before. One restrictionist declared that these immigrants were “races with which the English-speaking people have never hitherto assimilated, and who are most alien to the great body of the people of the United States.” The increased immigration of people from southern and eastern Europe, such as Italians, Jews, Slavs, and Greeks, led directly to calls for tighter restrictive measures. In 1907, the immigration of Japanese laborers was practically suspended when the American and Japanese governments reached the so-called Gentlemen’s Agreement, according to which Japan would stop issuing passports to working-class emigrants. In its forty-two-volume report of 1911, the U.S. Immigration Commission highlighted the impossibility of incorporating these new immigrants into American society. The report highlighted their supposed innate inferiority, asserting that they were the causes of rising social problems in America, such as poverty, crime, prostitution, and political radicalism.31
The assault against immigrants’ Catholicism provides an excellent example of the challenges immigrant groups faced in the United States. By 1900, Catholicism in the United States had grown dramatically in size and diversity, from 1 percent of the population a century earlier to the largest religious denomination in America (though still outnumbered by Protestants as a whole). As a result, Catholics in America faced two intertwined challenges: one external, related to Protestant anti-Catholicism, and the other internal, having to do with the challenges of assimilation.
Externally, the Church and its members remained an “outsider” religion in a nation that continued to see itself as culturally and religiously Protestant. Torrents of anti-Catholic literature and scandalous rumors maligned Catholics. Many Protestants doubted whether Catholics could ever make loyal Americans because they supposedly owed primary allegiance to the pope.
Internally, Catholics in America faced the question every immigrant group has had to answer: to what extent should they become more like native-born Americans? This question was particularly acute, as Catholics encompassed a variety of languages and customs. Beginning in the 1830s, Catholic immigration to the United States had exploded with the increasing arrival of Irish and German immigrants. Subsequent Catholic arrivals from Italy, Poland, and other Eastern European countries chafed at Irish dominance over the Church hierarchy. Mexican and Mexican American Catholics, whether recent immigrants or incorporated into the nation after the Mexican-American War, expressed similar frustrations. Could all these different Catholics remain part of the same Church?
Catholic clergy approached this situation from a variety of perspectives. Some bishops advocated rapid assimilation into the English-speaking mainstream. These “Americanists” advocated an end to “ethnic parishes”—the unofficial practice of permitting separate congregations for Poles, Italians, Germans, and so on—in the belief that such isolation only delayed immigrants’ entry into the American mainstream. They anticipated that the Catholic Church could thrive in a nation that espoused religious freedom, if only they assimilated. Meanwhile, however, more conservative clergy cautioned against assimilation. While they conceded that the United States had no official religion, they felt that Protestant notions of the separation of church and state and of licentious individual liberty posed a threat to the Catholic faith. They further saw ethnic parishes as an effective strategy protecting immigrant communities and worried that Protestants would use public schools to attack the Catholic faith. Eventually, the head of the Catholic Church, Pope Leo XIII, weighed in on the controversy. In 1899, he sent a special letter (an encyclical) to an archbishop in the United States. Leo reminded the Americanists that the Catholic Church was a unified global body and that American liberties did not give Catholics the freedom to alter church teachings. The Americanists denied any such intention, but the conservative clergy claimed that the pope had sided with them. Tension between Catholicism and American life, however, would continue well into the twentieth century.32
The American encounter with Catholicism—and Catholicism’s encounter with America—testified to the tense relationship between native-born and foreign-born Americans, and to the larger ideas Americans used to situate themselves in a larger world, a world of empire and immigrants.
World War I & Its Aftermath

Striking steel mill workers holding bulletins in Chicago, Illinois, September 22, 1919. ExplorePAhistory.com
VII. WWI Introduction
World War I (“The Great War”) toppled empires, created new nations, and sparked tensions that would explode across future years. On the battlefield, gruesome modern weaponry wrecked an entire generation of young men. The United States entered the conflict in 1917 and was never again the same. The war heralded to the world the United States’ potential as a global military power, and, domestically, it advanced but then beat back American progressivism by unleashing vicious waves of repression. The war simultaneously stoked national pride and fueled disenchantments that burst Progressive Era hopes for the modern world. And it laid the groundwork for a global depression, a second world war, and an entire history of national, religious, and cultural conflict around the globe.
VIII. Prelude to War
As the German empire rose in power and influence at the end of the nineteenth century, skilled diplomats maneuvered this disruption of traditional powers and influences into several decades of European peace. In Germany, however, a new ambitious monarch would overshadow years of tactful diplomacy. Wilhelm II rose to the German throne in 1888. He admired the British Empire of his grandmother, Queen Victoria, and envied the Royal Navy of Great Britain so much that he attempted to build a rival German navy and plant colonies around the globe. The British viewed the prospect of a German navy as a strategic threat, but, jealous of what he perceived as a lack of prestige in the world, Wilhelm II pressed Germany’s case for access to colonies and symbols of status suitable for a world power. Wilhelm’s maneuvers and Germany’s rise spawned a new system of alliances as rival nations warily watched Germany’s expansion.
In 1892, German posturing worried the leaders of Russia and France and prompted a defensive alliance to counter the existing triple threat between Germany, Austro-Hungary, and Italy. Britain’s Queen Victoria remained unassociated with the alliances until a series of diplomatic crises and an emerging German naval threat led to British agreements with Tsar Nicholas II and French President Émile Loubet in the early twentieth century. (The alliance between Great Britain, France, and Russia became known as the Triple Entente.)
The other great threat to European peace was the Ottoman Empire, in Turkey. While the leaders of the Austro-Hungarian Empire showed little interest in colonies elsewhere, Turkish lands on its southern border appealed to their strategic goals. However, Austro-Hungarian expansion in Europe worried Tsar Nicholas II, who saw Russia as both the historic guarantor of the Slavic nations in the Balkans and the competitor for territories governed by the Ottoman Empire.
By 1914, the Austro-Hungarian Empire had control of Bosnia and Herzegovina and viewed Slavic Serbia, a nation protected by Russia, as its next challenge. On June 28, 1914, after Serbian Gavrilo Princip assassinated the Austro-Hungarian heirs to the throne, Archduke Franz Ferdinand and his wife, Grand Duchess Sophie, vengeful nationalist leaders believed the time had arrived to eliminate the rebellious ethnic Serbian threat.33
On the other side of the Atlantic, the United States played an insignificant role in global diplomacy—it rarely forayed into internal European politics. The federal government did not participate in international diplomatic alliances but nevertheless championed and assisted with the expansion of the transatlantic economy. American businesses and consumers benefited from the trade generated as the result of the extended period of European peace.
Stated American attitudes toward international affairs followed the advice given by President George Washington in his 1796 Farewell Address, 120 years before America’s entry into World War I. He had recommended that his fellow countrymen avoid “foreign alliances, attachments, and intrigues” and “those overgrown military establishments which, under any form of government, are inauspicious to liberty, and which are to be regarded as particularly hostile to republican liberty.”34
A foreign policy of neutrality reflected America’s inward-looking focus on the construction and management of its new powerful industrial economy (built in large part with foreign capital). The federal government possessed limited diplomatic tools with which to engage in international struggles for world power. America’s small and increasingly antiquated military precluded forceful coercion and left American diplomats to persuade by reason, appeals to justice, or economic coercion. But in the 1880s, as Americans embarked upon empire, Congress authorized the construction of a modern navy. The army nevertheless remained small and underfunded compared to the armies of many industrializing nations.
After the turn of the century, the army and navy faced a great deal of organizational uncertainty. New technologies—airplanes, motor vehicles, submarines, modern artillery—stressed the capability of army and navy personnel to effectively procure and use them. The nation’s army could police Native Americans in the West and garrison recent overseas acquisitions, but it could not sustain a full-blown conflict of any size. The Davis Act of 1908 and the National Defense Act of 1916 inaugurated the rise of the modern versions of the National Guard and military reserves. A system of state-administered units available for local emergencies that received conditional federal funding for training could be activated for use in international wars. The National Guard program encompassed individual units separated by state borders. The program supplied summer training for college students as a reserve officer corps. Federal and state governments now had a long-term strategic reserve of trained soldiers and sailors.35
Border troubles in Mexico served as an important field test for modern American military forces. Revolution and chaos threatened American business interests in Mexico. Mexican reformer Francisco Madero challenged Porfirio Diaz’s corrupt and unpopular conservative regime. He was jailed, fled to San Antonio, and penned the Plan of San Luis Potosí, paving the way for the Mexican Revolution and the rise of armed revolutionaries across the country.
In April 1914, President Woodrow Wilson ordered Marines to accompany a naval escort to Veracruz on the lower eastern coast of Mexico. After a brief battle, the Marines supervised the city government and prevented shipments of German arms to Mexican leader Victoriano Huerta until they departed in November 1914. The raid emphasized the continued reliance on naval forces and the difficulty in modernizing the military during a period of European imperial influence in the Caribbean and elsewhere. The threat of war in Europe enabled passage of the Naval Act of 1916. President Wilson declared that the national goal was to build the Navy as “incomparably, the greatest . . . in the world.” And yet Mexico still beckoned. The Wilson administration had withdrawn its support of Diaz but watched warily as the revolution devolved into assassinations and deceit. In 1916, Pancho Villa, a popular revolutionary in northern Mexico, raided Columbus, New Mexico, after being provoked by American support for his rivals. His raiders killed seventeen Americans and burned down the town center before American soldiers forced their retreat. In response, President Wilson commissioned Army general John “Black Jack” Pershing to capture Villa and disperse his rebels. Motorized vehicles, reconnaissance aircraft, and the wireless telegraph aided in the pursuit of Villa. Motorized vehicles in particular allowed General Pershing to obtain supplies without relying on railroads controlled by the Mexican government. The aircraft assigned to the campaign crashed or were grounded by mechanical malfunctions, but they provided invaluable lessons in their worth and use in war. Wilson used the powers of the new National Defense Act to mobilize over one hundred thousand National Guardsmen across the country as a show of force in northern Mexico.36
The conflict between the United States and Mexico might have escalated into full-scale war if the international crisis in Europe had not overwhelmed the public’s attention. After the outbreak of war in Europe in 1914, President Wilson declared American neutrality. He insisted from the start that the United States be neutral “in fact as well as in name,” a policy the majority of American people enthusiastically endorsed. It was unclear, however, what “neutrality” meant in a world of close economic connections. Ties to the British and French proved strong, and those nations obtained far more loans and supplies than the Germans. In October 1914, President Wilson approved commercial credit loans to the combatants, which made it increasingly difficult for the nation to claim impartiality as war spread through Europe. Trade and financial relations with the Allied nations ultimately drew the United States further into the conflict. In spite of mutually declared blockades between Germany, Great Britain, and France, munitions and other war suppliers in the United States witnessed a brisk and booming increase in business. The British naval blockades that often stopped or seized ships proved annoying and costly, but the unrestricted and surprise torpedo attacks from German submarines were deadly. In May 1915, Germans sank the RMS Lusitania. Over a hundred American lives were lost. The attack, coupled with other German attacks on American and British shipping, raised the ire of the public and stoked the desire for war.37
American diplomatic tradition avoided formal alliances, and the Army seemed inadequate for sustained overseas fighting. However, the United States outdistanced the nations of Europe in one important measure of world power: by 1914, the nation held the top position in the global industrial economy. The United States was producing slightly more than one third of the world’s manufactured goods, roughly equal to the outputs of France, Great Britain, and Germany combined.
IX. War Spreads through Europe
After the assassination of Archduke Ferdinand and Grand Duchess Sophie, Austria secured the promise of aid from its German ally and issued a list of ten ultimatums to Serbia. On July 28, 1914, Austria declared war on Serbia for failure to meet all of the demands. Russia, determined to protect Serbia, began to mobilize its armed forces. On August 1, 1914, Germany declared war on Russia to protect Austria after warnings directed at Tsar Nicholas II failed to stop Russian preparations for war.
In spite of the central European focus of the initial crises, the first blow was struck against neutral Belgium in northwestern Europe. Germany planned to take advantage of sluggish Russian mobilization by focusing the German army on France. German military leaders recycled tactics developed earlier and activated the Schlieffen Plan, which moved German armies rapidly by rail to march through Belgium and into France. However, this violation of Belgian neutrality also ensured that Great Britain entered the war against Germany. On August 4, 1914, Great Britain declared war on Germany for failing to respect Belgium as a neutral nation.
In 1915, the European war had developed into a series of bloody trench stalemates that continued through the following year. Offensives, largely carried out by British and French armies, achieved nothing but huge numbers of casualties. Peripheral campaigns against the Ottoman Empire in Turkey at Gallipoli, throughout the Middle East, and in various parts of Africa either were unsuccessful or had little bearing on the European contest for victory. The third year of the war, however, witnessed a coup for German military prospects: the regime of Tsar Nicholas II collapsed in Russia in March 1917. At about the same time, the Germans again pursued unrestricted submarine warfare to deprive the Allies of replenishment supplies from the United States.38
The Germans, realizing that submarine warfare could spark an American intervention, hoped the European war would be over before American soldiers could arrive in sufficient numbers to alter the balance of power. A German diplomat, Arthur Zimmermann, planned to complicate the potential American intervention. He offered support to the Mexican government via a desperate bid to regain Texas, New Mexico, and Arizona. Mexican national leaders declined the offer, but the revelation of the Zimmermann Telegram helped usher the United States into the war.
X. America Enters the War
By the fall of 1916 and spring of 1917, President Wilson believed an imminent German victory would drastically and dangerously alter the balance of power in Europe. Submarine warfare and the Zimmermann Telegram, meanwhile, inflamed public opinion. Congress declared war on Germany on April 4, 1917. The nation entered a war three thousand miles away with a small and unprepared military. The United States was unprepared in nearly every respect for modern war. Considerable time elapsed before an effective army and navy could be assembled, trained, equipped, and deployed to the Western Front in Europe. The process of building the army and navy for the war proved to be different from previous conflicts. Unlike the largest European military powers of Germany, France, and Austria-Hungary, no tradition existed in the United States to maintain large standing armed forces or trained military reserves during peacetime. Moreover, there was no American counterpart to the European practice of rapidly equipping, training, and mobilizing reservists and conscripts.
The U.S. historically relied solely on traditional volunteerism to fill the ranks of the armed forces. Notions of patriotic duty and adventure appealed to many young men who not only volunteered for wartime service but sought and paid for their own training at army camps before the war. American labor organizations favored voluntary service over conscription. Labor leader Samuel Gompers argued for volunteerism in letters to the congressional committees considering the question. “The organized labor movement,” he wrote, “has always been fundamentally opposed to compulsion.” Referring to American values as a role model for others, he continued, “It is the hope of organized labor to demonstrate that under voluntary conditions and institutions the Republic of the United States can mobilize its greatest strength, resources and efficiency.”39
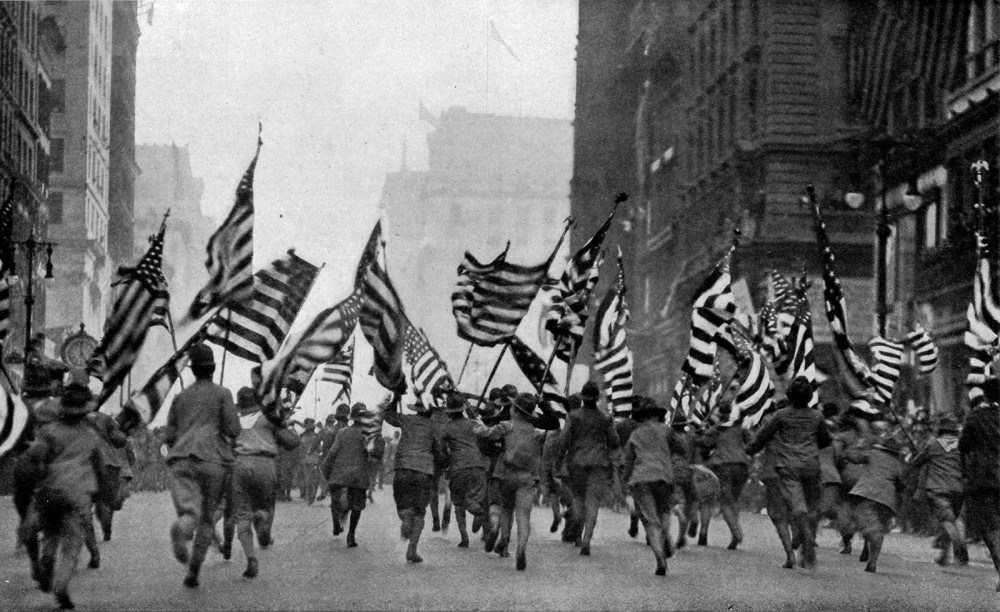

The Boy Scouts of America charge up Fifth Avenue in New York City in a “Wake Up, America” parade to support recruitment efforts. Nearly sixty thousand people attended this single parade. Wikimedia.
Despite fears of popular resistance, Congress quickly instituted a reasonably equitable and locally administered system to draft men for the military. On May 18, 1917, Congress approved the Selective Service Act, and President Wilson signed it a week later. The new legislation avoided the unpopular system of bonuses and substitutes used during the Civil War and was generally received without major objection by the American people.40
The conscription act initially required men from ages twenty-one to thirty to register for compulsory military service. Basic physical fitness was the primary requirement for service. The resulting tests offered the emerging fields of social science a range of data collection tools and new screening methods. The Army Medical Department examined the general condition of young American men selected for service from the population. The Surgeon General compiled his findings from draft records in the 1919 report, “Defects Found in Drafted Men,” a snapshot of the 2.5 million men examined for military service. Of that group, 1,533,937 physical defects were recorded (often more than one per individual). More than 34 percent of those examined were rejected for service or later discharged for neurological, psychiatric, or mental deficiencies.41
To provide a basis for the neurological, psychiatric, and mental evaluations, the army used cognitive skills tests to determine intelligence. About 1.9 million men were tested on intelligence. Soldiers who could read took the Army Alpha test. Illiterates and non-English-speaking immigrants took the nonverbal equivalent, the Army Beta test, which relied on visual testing procedures. Robert M. Yerkes, president of the American Psychological Association and chairman of the Committee on the Psychological Examination of Recruits, developed and analyzed the tests. His data argued that the actual mental age of recruits was only about thirteen years. Among recent immigrants, he said, it was even lower. As a eugenicist, he interpreted the results as roughly equivalent to a mild level of retardation and as an indication of racial deterioration. Years later, experts agreed that the results misrepresented the levels of education for the recruits and revealed defects in the design of the tests.
The experience of service in the army expanded many individual social horizons as native-born and foreign-born soldiers served together. Immigrants had been welcomed into Union ranks during the Civil War, including large numbers of Irish and Germans who had joined and fought alongside native-born men. Some Germans in the Civil War fought in units where German was the main language. Between 1917 and 1918, the army accepted immigrants with some hesitancy because of the widespread public agitation against “hyphenated Americans.” Others were segregated.
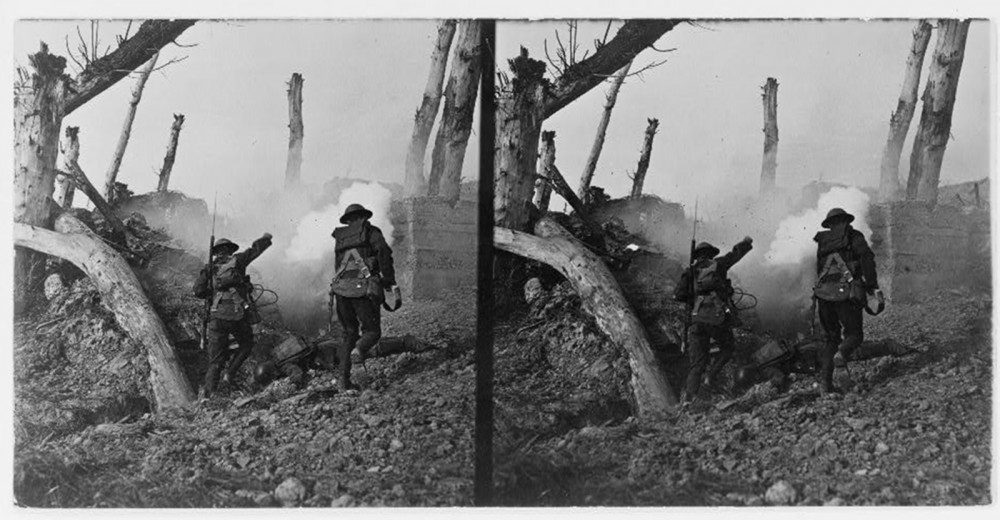

Propagandistic images increased patriotism in a public relatively detached from events taking place overseas. This photograph, showing two United States soldiers sprinting past the bodies of two German soldiers toward a bunker, showed Americans the heroism evinced by their men in uniform. Likely a staged image was taken after the fighting ended, it nonetheless played on the public’s patriotism, telling them to step up and support the troops. “At close grips with the Hun, we bomb the corkshaffer’s, etc.,” c. 1922?. Library of Congress, http://www.loc.gov/pictures/item/91783839/.
Prevailing racial attitudes among white Americans mandated the assignment of white and Black soldiers to different units. Despite racial discrimination, many Black American leaders, such as W. E. B. Du Bois, supported the war effort and sought a place at the front for Black soldiers. Black leaders viewed military service as an opportunity to demonstrate to white society the willingness and ability of Black men to assume all duties and responsibilities of citizens, including wartime sacrifice. If Black soldiers were drafted and fought and died on equal footing with white soldiers, then white Americans would see that they deserved full citizenship. The War Department, however, barred Black troops from combat and relegated Black soldiers to segregated service units where they worked as general laborers. The army also often restricted the privileges of Black soldiers to ensure that the conditions they encountered in Europe did not lead them to question their place in American society. In France, however, the experiences of Black soldiers during training and periods of leave, coupled with their service, proved transformative.
The U.S. government exercised significant social control over its overseas soldiers. To ensure that American “doughboys” did not succumb to European vices, several religious and progressive organizations created an extensive program designed to keep the men pure of heart, mind, and body. With assistance from the Young Men’s Christian Association (YMCA) and other temperance organizations, the War Department put together a program of schools, sightseeing tours, and recreational facilities to provide wholesome and educational outlets. The soldiers welcomed most of the activities from these groups, but many still managed to find and enjoy the traditional recreations of soldiers at war.42
Women reacted to the war preparations by joining several military and civilian organizations. Their enrollment and actions in these organizations proved to be a pioneering effort for American women in war. Military leaders authorized the permanent gender transition of several occupations that gave women opportunities to don uniforms where none had existed before in history. Civilian wartime organizations, although chaired by male members of the business elite, boasted all-female volunteer workforces. Women performed the bulk of volunteer work during the war.43
The admittance of women brought considerable upheaval. The War and Navy Departments authorized the enlistment of women to fill positions in several established administrative occupations. The gendered transition of these jobs freed more men to join combat units. Army women served as telephone operators (Hello Girls) for the Signal Corps, navy women enlisted as yeomen (clerical workers), and the first groups of women joined the Marine Corps in July 1918. Approximately twenty-five thousand nurses served in the Army and Navy Nurse Corps for duty stateside and overseas, and about a hundred female physicians were contracted by the army. Neither the female nurses nor the doctors served as commissioned officers in the military, leaving the status of professional medical women hovering somewhere between the enlisted and officer ranks. As a result, many female nurses and doctors suffered various physical and mental abuses at the hands of their male coworkers with no system of redress in place.44
Millions of women also volunteered in civilian organizations such as the American Red Cross, the Young Men’s and Women’s Christian Associations (YMCA/YWCA), and the Salvation Army. Most women performed their volunteer duties in communal spaces owned by the leaders of the municipal chapters of these organizations. Women met at designated times to roll bandages, prepare and serve meals and snacks, package and ship supplies, and organize community fund-raisers. The variety of volunteer opportunities gave women the ability to appear in public spaces and promote charitable activities for the war effort. Female volunteers encouraged entire communities, including children, to get involved in war work. While most of these efforts focused on support for the home front, a small percentage of female volunteers served with the American Expeditionary Force in France.45
Jim Crow segregation in both the military and the civilian sector stood as a barrier for Black women who wanted to give their time to the war effort. The military prohibited Black women from serving as enlisted or appointed medical personnel. The only avenue for Black women to wear a military uniform existed with the armies of the allied nations. A few Black female doctors and nurses joined the French Foreign Legion to escape the racism in the American army. Black female volunteers faced the same discrimination in civilian wartime organizations. White leaders of the American Red Cross, YMCA/YWCA, and Salvation Army municipal chapters refused to admit Black women as equal participants. Black women were forced to charter auxiliary units as subsidiary divisions and were given little guidance on organizing volunteers. They turned instead to the community for support and recruited millions of women for auxiliaries that supported the nearly two hundred thousand Black soldiers and sailors serving in the military. While most female volunteers labored to care for Black families on the home front, three YMCA secretaries worked with the Black troops in France.46
XI. On the Homefront
In the early years of the war, Americans were generally detached from the events in Europe. Progressive Era reform politics dominated the political landscape, and Americans remained most concerned with the shifting role of government at home. However, the facts of the war could not be ignored by the public. The destruction taking place on European battlefields and the ensuing casualty rates exposed the unprecedented brutality of modern warfare. Increasingly, a sense that the fate of the Western world lay in the victory or defeat of the Allies took hold in the United States.
President Wilson, a committed progressive, articulated a global vision of democracy even as he embraced neutrality. As war engulfed Europe, it seemed apparent that the United States’ economic power would shape the outcome of the conflict regardless of any American military intervention. By 1916, American trade with the Allies tripled, while trade with the Central Powers shrank to less than 1 percent of previous levels.

A membership card for the American Protective League, issued May 28, 1918. German immigrants in the United States aroused popular suspicions during World War I and the American Protective League (APL), a group of private citizens, worked directly with the U.S. government to identify suspected German sympathizers and to eradicate all antiwar and politically radical activities through surveillance, public shaming, and government raids. J. Edgar Hoover, the head of the Bureau of Investigation (later the Federal Bureau of Investigation, or FBI), used the APL to gather intelligence. Wikimedia.
The progression of the war in Europe generated fierce national debates about military preparedness. The Allies and the Central Powers had quickly raised and mobilized vast armies and navies. The United States still had a small military. When America entered the war, the mobilization of military resources and the cultivation of popular support consumed the country, generating enormous publicity and propaganda campaigns. President Wilson created the Committee on Public Information, known as the Creel Committee, headed by Progressive George Creel, to inspire patriotism and generate support for military adventures. Creel enlisted the help of Hollywood studios and other budding media outlets to cultivate a view of the war that pitted democracy against imperialism and framed America as a crusading nation rescuing Western civilization from medievalism and militarism. As war passions flared, challenges to the onrushing patriotic sentiment that America was making the world “safe for democracy” were considered disloyal. Wilson signed the Espionage Act in 1917 and the Sedition Act in 1918, stripping dissenters and protesters of their rights to publicly resist the war. Critics and protesters were imprisoned. Immigrants, labor unions, and political radicals became targets of government investigations and an ever more hostile public culture. Meanwhile, the government insisted that individual financial contributions made a discernible difference for the men on the Western Front. Americans lent their financial support to the war effort by purchasing war bonds or supporting the Liberty Loan Drive. Many Americans, however, sacrificed much more than money.47
XII. Before the Armistice
European powers struggled to adapt to the brutality of modern war. Until the spring of 1917, the Allies possessed few effective defensive measures against submarine attacks. German submarines sank more than a thousand ships by the time the United States entered the war. The rapid addition of American naval escorts to the British surface fleet and the establishment of a convoy system countered much of the effect of German submarines. Shipping and military losses declined rapidly, just as the American army arrived in Europe in large numbers. Although much of the equipment still needed to make the transatlantic passage, the physical presence of the army proved a fatal blow to German war plans.48
In July 1917, after one last disastrous offensive against the Germans, the Russian army disintegrated. The tsarist regime collapsed and in November 1917 Vladimir Lenin’s Bolshevik party came to power. Russia soon surrendered to German demands and exited the war, freeing Germany to finally fight the one-front war it had desired since 1914. The German military quickly shifted hundreds of thousands of soldiers from the eastern theater in preparation for a new series of offensives planned for the following year in France.49
In March 1918, Germany launched the Kaiserschlacht (Spring Offensive), a series of five major attacks. By the middle of July 1918, each and every one had failed to break through the Western Front. On August 8, 1918, two million men of the American Expeditionary Forces joined British and French armies in a series of successful counteroffensives that pushed the disintegrating German lines back across France. German general Erich Ludendorff referred to the launch of the counteroffensive as the “black day of the German army.” The German offensive gamble exhausted Germany’s faltering military effort. Defeat was inevitable. Kaiser Wilhelm II abdicated at the request of the German military leaders and the new democratic government agreed to an armistice (cease-fire) on November 11, 1918. German military forces withdrew from France and Belgium and returned to a Germany teetering on the brink of chaos.50
By the end of the war, more than 4.7 million American men had served in all branches of the military: four million in the army, six hundred thousand in the navy, and about eighty thousand in the Marine Corps. The United States lost over one hundred thousand men (fifty-three thousand died in battle, and even more from disease). Their terrible sacrifice, however, paled before the Europeans’. After four years of brutal stalemate, France had suffered almost a million and a half military dead and Germany even more. Both nations lost about 4 percent of their population to the war. And death was not done.51
XIII. The War and the Influenza Pandemic
Even as war raged on the Western Front, a new deadly threat loomed: influenza. In the spring of 1918, a strain of the flu virus appeared in the farm country of Haskell County, Kansas, and hit nearby Camp Funston, one of the largest army training camps in the nation. The virus spread like wildfire. The camp had brought disparate populations together, shuffled them between bases, sent them back to their homes across the nation, and, in consecutive waves, deployed them around the world. Between March and May 1918, fourteen of the largest American military training camps reported outbreaks of influenza. Some of the infected soldiers carried the virus on troop transports to France. By September 1918, influenza spread to all training camps in the United States. And then it mutated.52
The second wave of the virus, a mutated strain, was even deadlier than the first. It struck down those in the prime of their lives: a disproportionate amount of influenza victims were between ages eighteen and thirty-five. In Europe, influenza hit both sides of the Western Front. The “Spanish Influenza,” or the “Spanish Lady,” misnamed due to accounts of the disease that first appeared in the uncensored newspapers of neutral Spain, resulted in the deaths of an estimated fifty million people worldwide. Reports from the Surgeon General of the Army revealed that while 227,000 American soldiers were hospitalized from wounds received in battle, almost half a million suffered from influenza. The worst part of the epidemic struck during the height of the Meuse-Argonne Offensive in the fall of 1918 and weakened the combat capabilities of the American and German armies. During the war, more soldiers died from influenza than combat. The pandemic continued to spread after the armistice before finally fading in the early 1920s. No cure was ever found.53
XIV. The Fourteen Points and the League of Nations
As the flu virus wracked the world, Europe and America rejoiced at the end of hostilities. On December 4, 1918, President Wilson became the first American president to travel overseas during his term. He intended to shape the peace. The war brought an abrupt end to four great European imperial powers. The German, Russian, Austro-Hungarian, and Ottoman Empires evaporated, and the map of Europe was redrawn to accommodate new independent nations. As part of the armistice, Allied forces followed the retreating Germans and occupied territories in the Rhineland to prevent Germany from reigniting war. As Germany disarmed, Wilson and the other Allied leaders gathered in France at Versailles for the Paris Peace Conference to dictate the terms of a settlement to the war. After months of deliberation, the Treaty of Versailles officially ended the war.
Earlier that year, on January 8, 1918, before a joint session of Congress, President Wilson offered an ambitious statement of war aims and peace terms known as the Fourteen Points. The plan not only dealt with territorial issues but offered principles on which a long-term peace could be built. But in January 1918, Germany still anticipated a favorable verdict on the battlefield and did not seriously consider accepting the terms of the Fourteen Points. The Allies were even more dismissive. French prime minister Georges Clemenceau remarked, “The good Lord only had ten [points].”54
President Wilson labored to realize his vision of the postwar world. The United States had entered the fray, Wilson proclaimed, “to make the world safe for democracy.” At the center of the plan was a novel international organization—the League of Nations—charged with keeping a worldwide peace by preventing the kind of destruction that tore across Europe and “affording mutual guarantees of political independence and territorial integrity to great and small states alike.” This promise of collective security, that an attack on one sovereign member would be viewed as an attack on all, was a key component of the Fourteen Points.55
But the fight for peace was daunting. While President Wilson was celebrated in Europe and welcomed as the “God of Peace,” his fellow statesmen were less enthusiastic about his plans for postwar Europe. America’s closest allies had little interest in the League of Nations. Allied leaders sought to guarantee the future safety of their own nations. Unlike the United States, the Allies endured the horrors of the war firsthand. They refused to sacrifice further. The negotiations made clear that British prime minister David Lloyd-George was more interested in preserving Britain’s imperial domain, while French prime minister Clemenceau sought a peace that recognized the Allies’ victory and the Central Powers’ culpability: he wanted reparations—severe financial penalties—and limits on Germany’s future ability to wage war. The fight for the League of Nations was therefore largely on the shoulders of President Wilson. By June 1919, the final version of the treaty was signed and President Wilson was able to return home. The treaty was a compromise that included demands for German reparations, provisions for the League of Nations, and the promise of collective security. For President Wilson, it was an imperfect peace, but an imperfect peace was better than none at all.
The real fight for the League of Nations was on the American home front. Republican senator Henry Cabot Lodge of Massachusetts stood as the most prominent opponent of the League of Nations. As chair of the Senate Foreign Relations Committee and an influential Republican Party leader, he could block ratification of the treaty. Lodge attacked the treaty for potentially robbing the United States of its sovereignty. Never an isolationist, Lodge demanded instead that the country deal with its own problems in its own way, free from the collective security—and oversight—offered by the League of Nations. Unable to match Lodge’s influence in the Senate, President Wilson took his case to the American people in the hopes that ordinary voters might be convinced that the only guarantee of future world peace was the League of Nations. During his grueling cross-country trip, however, President Wilson suffered an incapacitating stroke. His opponents had the upper hand.56
President Wilson’s dream for the League of Nations died on the floor of the Senate. Lodge’s opposition successfully blocked America’s entry into the League of Nations, an organization conceived and championed by the American president. The League of Nations operated with fifty-eight sovereign members, but the United States refused to join, refused to lend it American power, and refused to provide it with the power needed to fulfill its purpose.57
XV. Aftermath of World War I
The war transformed the world. The Middle East, for instance, was drastically changed. For centuries the Ottoman Empire had shaped life in the region. Before the war, the Middle East had three main centers of power: the Ottoman Empire, Egypt, and Iran. President Wilson’s call for self-determination appealed to many under the Ottoman Empire’s rule. In the aftermath of the war, Wilson sent a commission to investigate the region to determine the conditions and aspirations of the populace. The King-Crane Commission found that most of the inhabitants favored an independent state free of European control. However, these wishes were largely ignored, and the lands of the former Ottoman Empire were divided into mandates through the Treaty of Sèvres at the San Remo Conference in 1920. The Ottoman Empire disintegrated into several nations, many created by European powers with little regard to ethnic realities. These Arab provinces were ruled by Britain and France, and the new nation of Turkey emerged from the former heartland of Anatolia. According to the League of Nations, mandates “were inhabited by peoples not yet able to stand by themselves under the strenuous conditions of the modern world.” Though allegedly for the benefit of the people of the Middle East, the mandate system was essentially a reimagined form of nineteenth-century imperialism. France received Syria; Britain took control of Iraq, Palestine, and Transjordan (Jordan). The United States was asked to become a mandate power but declined. The geographical realignment of the Middle East also included the formation of two new nations: the Kingdom of Hejaz and Yemen. (The Kingdom of Hejaz was ruled by Sharif Hussein and only lasted until the 1920s, when it became part of Saudi Arabia.)58
The 1917 Russian Revolution, meanwhile enflamed American fears of communism. The fates of Nicola Sacco and Bartolomeo Vanzetti, two Italian-born anarchists who were convicted of robbery and murder in 1920 epitomized a sudden American Red Scare. Their arrest, trial, and execution, meanwhile, inspired many leftists and dissenting artists to express their sympathy with the accused, such as in Maxwell Anderson’s Gods of the Lightning or Upton Sinclair’s Boston. The Sacco-Vanzetti case demonstrated an exacerbated nervousness about immigrants and the potential spread of radical ideas, especially those related to international communism.59
When in March 1918 the Bolsheviks signed a separate peace treaty with Germany, the Allies planned to send troops to northern Russia and Siberia to prevent German influence and fight the Bolshevik Revolution. Wilson agreed, and, in a little-known foreign intervention, American troops remained in Russia as late as 1920. Although the Bolshevik rhetoric of self-determination followed many of the ideals of Wilson’s Fourteen Points—Vladimir Lenin supported revolutions against imperial rule across the world—the American commitment to self-rule was hardly strong enough to overcome powerful strains of anticommunism.

With America still at war in World War I, President Wilson sent American troops to Siberia during the Russian civil war to oppose the Bolsheviks. This August 1918 photograph shows American soldiers in Vladivostok parading before the building occupied by the staff of the Czecho-Slovaks. To the left, Japanese marines stand to attention as the American troops march. Wikimedia.
At home, the United States grappled with harsh postwar realities. Racial tensions culminated in the Red Summer of 1919 when violence broke out in at least twenty-five cities, including Chicago and Washington, D.C. The riots originated from wartime racial tensions. Industrial war production and massive wartime service created vast labor shortages, and thousands of Black southerners traveled to the North and Midwest to escape the traps of southern poverty. But the so-called Great Migration sparked significant racial conflict as white northerners and returning veterans fought to reclaim their jobs and their neighborhoods from new Black migrants.60
Many Black Americans, who had fled the Jim Crow South and traveled halfway around the world to fight for the United States, would not so easily accept postwar racism. The overseas experience of Black Americans and their return triggered a dramatic change in Black communities. W. E. B. Du Bois wrote boldly of returning soldiers: “We return. We return from fighting. We return fighting. Make way for Democracy!”61 But white Americans desired a return to the status quo, a world that did not include social, political, or economic equality for Black people.
In 1919, America suffered through the “Red Summer.” Riots erupted across the country from April until October. The massive bloodshed included thousands of injuries, hundreds of deaths, and vast destruction of private and public property across the nation. The Chicago Riot, from July 27 to August 3, 1919, considered the summer’s worst, sparked a week of mob violence, murder, and arson. Race riots had rocked the nation before, but the Red Summer was something new. Recently empowered Black Americans actively defended their families and homes from hostile white rioters, often with militant force. This behavior galvanized many in Black communities, but it also shocked white Americans who alternatively interpreted Black resistance as a desire for total revolution or as a new positive step in the path toward Black civil rights. In the riots’ aftermath, James Weldon Johnson wrote, “Can’t they understand that the more Negroes they outrage, the more determined the whole race becomes to secure the full rights and privileges of freemen?” Those six hot months in 1919 forever altered American society and roused and terrified those that experienced the sudden and devastating outbreaks of violence.62
XVI. Conclusion
While American imperialism flared most brightly for a relatively brief time at the turn of the century, new imperial patterns repeated old practices and lived on into the twentieth century. But suddenly the United States had embraced its cultural, economic, and religious influence in the world, along with a newfound military power, to exercise varying degrees of control over nations and peoples. Whether as formal subjects or unwilling partners on the receiving end of Roosevelt’s “big stick,” those who experienced U.S. expansionist policies confronted new American ambitions. At home, debates over immigration and imperialism drew attention to the interplay of international and domestic policy and the ways in which imperial actions, practices, and ideas affected and were affected by domestic questions. How Americans thought about the conflict in the Philippines, for example, was affected by how they approached immigration in their own cities. And at the turn of the century, those thoughts were very much on the minds of Americans.
World War I decimated millions and profoundly altered the course of world history. Postwar instabilities led directly toward a global depression and a second world war. The war sparked the Bolshevik Revolution, which led to the Soviet Union and later the Cold War. It created Middle Eastern nations and aggravated ethnic tensions that the United States could never overcome. And the United States had fought on the European mainland as a major power. America’s place in the world was never the same. By whipping up nationalist passions, American attitudes toward radicalism, dissent, and immigration were poisoned. Postwar disillusionment shattered Americans’ hopes for the progress of the modern world. The war came and went, leaving in its place the bloody wreckage of an old world through which the United States traveled to a new and uncertain future.
Notes
- Tyler Dennett, Americans in Eastern Asia: A Critical Study of the Policy of the United States with Reference to China, Japan and Korea in the 19th Century (New York: Macmillan, 1922), 580.
- Robert E. Hannigan, The New World Power: American Foreign Policy, 1898–1917 (Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press, 2002).
- Jimmy M. Skaggs, The Great Guano Rush: Entrepreneurs and American Overseas Expansion (New York: Macmillan, 1994); Robert A. Wines, Fertilizer in America: From Waste Recycling to Resource Exploitation (Philadelphia: Temple University Press, 1985).
- Elvi Whittaker, The Mainland Haole: The White Experience in Hawai’i (New York: Columbia University Press, 1986).
- John Mason Hart, Empire and Revolution: The Americans in Mexico Since the Civil War (Berkeley: University of California Press, 2002), 271–307; Mark Benbow, Leading Them to the Promised Land: Woodrow Wilson, Covenant Theology, and the Mexican Revolution, 1913–1915 (Kent, OH: Kent State University Press, 2010), 25–44; Lloyd C. Gardner, Safe for Democracy: The Anglo-American Response to Revolution, 1913–1923 (New York: Oxford University Press, 1984).
- Hart, Empire and Revolution, 326–333.
- Mark Twain, The Innocents Abroad, or The New Pilgrims’ Progress (Hartford, CT: American, 1869), 379.
- Ussama Makdisi, Artillery of Heaven American Missionaries and the Failed Conversion of the Middle East (Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press, 2008).
- Lyman Abbott, Inspiration for Daily Living: Selections from the Writings of Lyman Abbott (Boston: Pilgrim Press, 1919), 175.
- Albert J. Beveridge, The Meaning of the Times: And Other Speeches (Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, 1908), 48.
- Finley Peter Dunne, Mr. Dooley in the Hearts of His Countrymen (Boston: Small, Maynard, 1899), 6.
- Susan K. Harris, God’s Arbiters: Americans and the Philippines, 1898–1902 (New York: Oxford University Press, 2011); Paul A. Kramer, The Blood of Government: Race, Empire, the United States, and the Philippines (Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press, 2006).
- Harris, God’s Arbiters; Kramer, Blood of Government.
- John F. Bass, compiled in Marrion Wilcox, Harper’s History of the War in the Philippines (New York: Harper, 1900), 162.
- Harris, God’s Arbiters; Kramer, Blood of Government.
- William Henry Harbaugh, The Life and Times of Theodore Roosevelt (London: Oxford University Press, 1961); Morton Keller, Theodore Roosevelt; A Profile (New York: Hill and Wang, 1967).
- R. A. Hart, The Great White Fleet: Its Voyage Around the World, 1907–1909 (New York: Little, Brown, 1965).
- Richard Collin, Theodore Roosevelt’s Caribbean: The Panama Canal, The Monroe Doctrine, and the Latin American Context (Baton Rouge: LSU Press, 1990).
- Ibid.
- Emily S. Rosenberg, Financial Missionaries to the World: The Politics and Culture of Dollar Diplomacy, 1900–1930 (Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1999), 3.
- William Everett Kane, Civil Strife in Latin America: A Legal History of U.S. Involvement (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 1972), 73.
- Theodore Roosevelt to Elihu Root, May 20, 1904, in The Letters of Theodore Roosevelt, vol. 4, ed. Elting E. Morrison (Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1951), 801.
- Hannigan, New World Power).
- Theodore Roosevelt to William Bayard Hale, February 26, 1904, in Morrison, Letters of Theodore Roosevelt, vol. 4, 740.
- Mona Domosh, American Commodities in an Age of Empire (New York: Routledge, 2006).
- Kristin L. Hoganson, Fighting for American Manhood: How Gender Politics Provoked the Spanish-American and Philippine-American Wars (New Haven, CT: Yale University Press, 1998).
- Domosh, American Commodities.
- Matthew Frye Jacobson, Barbarian Virtues: The United States Encounters Foreign Peoples at Home and Abroad, 1876–1917 (New York: Hill and Wang, 2000).
- Massachusetts Board of State Charities, Annual Report of the State Board of Charity of Massachusetts (Boston: Wright, 1877), xlvii.
- Jacobson, Barbarian Virtues.
- Roger Daniels, The Politics of Prejudice: The Anti-Japanese Movement in California and the Struggle for Japanese Exclusion (Berkeley: University of California Press, 1999).
- James M. O’Toole, The Faithful: A History of Catholics in America (Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 2009).
- David Stevenson, The First World War and International Politics (London: Oxford University Press, 1988); David Stevenson, Cataclysm: The First World War as Political Tragedy (New York: Basic Books, 2004).
- George Washington, Farewell Address, Annals of Congress, 4th Congress, 2869–2870.
- Paul Koistinen, Mobilizing for Modern War: The Political Economy of American Warfare, 1865–1919 (Lawrence: University Press of Kansas, 1997).
- John S. D. Eisenhower, Intervention! The United States and the Mexican Revolution, 1913–1917 (New York: Norton, 1995); Friedrich Katz, The Secret War in Mexico: Europe, the United States, and the Mexican Revolution (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1981).
- Arthur S. Link, Wilson: The Struggle for Neutrality, 1914–1915 (Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 1960).
- Michael S. Neiberg, Fighting the Great War: A Global History (Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 2005).
- American Federation of Labor, Report of the Proceedings of the Annual Convention (Washington, DC: Law Reporter, 1917), 112.
- Christopher Capozzola, Uncle Sam Wants You: World War I and the Making of the Modern American Citizen (New York: Oxford University Press, 2010).
- Albert Gallitin Love, Defects Found in Drafted Men (Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office, 1920), 73.
- Dawley, Changing the World.
- Susan Zeiger, In Uncle Sam’s Service: Women Workers with the American Expeditionary Force, 1917–1919 (Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press, 2004), 2–4.
- Lettie Gavin, American Women in World War I: They Also Served (Boulder: University Press of Colorado, 1997); Kimberly Jensen, Mobilizing Minerva: American Women in the First World War (Chicago: University of Illinois Press, 2008), 170–172.
- Gavin, American Women, 129–240.
- Nikki Brown, Private Politics and Public Voices: Black Women’s Activism from World War I to the New Deal (Bloomington: Indiana University Press, 2006), 66–107.
- David Kennedy, Over Here: The First World War and American Society (New York: Oxford University Press, 1980).
- Neiberg, Fighting the Great War.
- Ibid.
- Ibid.
- Ibid.
- Nancy K. Bristow, American Pandemic: The Lost Worlds of the 1918 Influenza Epidemic (New York: Oxford University Press, 2012); Alfred W. Crosby, America’s Forgotten Pandemic: The Influenza of 1918 (Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 2003).
- Bristow, American Pandemic; Crosby, America’s Forgotten Pandemic.
- Dawley, Changing the World).
- Thomas J. Knock, To End All Wars: Woodrow Wilson and the Quest for a New World Order (New York: Oxford University Press, 1992).
- John Milton Cooper, Breaking the Heart of the World: Woodrow Wilson and the Fight for the League of Nations (Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 2001).
- Ibid.
- David Fromkin, A Peace to End All Peace: The Fall of the Ottoman Empire and the Creation of the Modern Middle East (New York: Holt, 1989).
- Moshik Temkin, The Sacco-Vanzetti Affair: America on Trial (New Haven, CT: Yale University Press, 2009).
- Isabel Wilkerson, The Warmth of Other Suns: The Epic Story of America’s Great Migration (New York: Vintage Books, 2011).
- W. E. B. Du Bois, “Returning Soldiers,” The Crisis (May 1919): 14.
- William Tuttle, Race Riot: Chicago in the Red Summer of 1919 (Champaign: University of Illinois Press, 1970); Cameron McWhirter, Red Summer: The Summer of 1919 and the Awakening of Black America (New York: Holt, 2011).