17
Key Concept
Copyright – automatic rights given to the original creator of a work that gives them the exclusive rights on how it is used and reused
Copyright issues in the digital world can get complicated and confusing. Digital tools make it easy for anyone to take other’s work and claim it as their own, usually with no repercussions. Being a good digital citizen means understanding why this is ethically wrong, and what you can do to avoid such circumstances. When composing multi-modal works or publishing on the web, it’s important to understand terms such as copyright, Creative Commons, public domain, and fair use. Many believe that any image on the internet is free to share and reuse, but that’s not the case. In this chapter, we’ll look at terms related to copyright and how they might affect us in our writing.
What is Copyright?
Copyright is an intellectual property law, and a protection automatically applied to any original work of authorship. It says you are the exclusive owner and have the exclusive rights to your work. Overall, it limits the ways that people can use your work, and requires them to get permission when using your work outside of the scope of fair use. Copyright lasts for the duration of the author’s life plus 70 years. If you wrote something today, in 2019, passed away in 2090, then your work would have copyright protecting it until 2160!
What is Fair Use?
While all work automatically has copyright applied to it, only allowing people to use your work if you give them permission, fair use actually grants them that permission if they use it under certain circumstances. There are typically four factors associated with this:
- Intention of the work
- Nature of the work
- Portion of the original work used
- Market impact of such use
In other words, if you are using someone’s copyrighted work, you must use a minimal amount and for a new purpose. This, typically, is called remixing: where you are using someone’s work, reworking it, and using it in a different way. This is why memes can exist. They are creating new meaning with old work, typically photographs.
What is the Public Domain?
Work that is in the Public Domain is not protected by copyright law. This work, then, is free to use and doesn’t require permission from the copyright owner. Typically, works go into the public domain after the original copyright on a work expires: 70 years after the death of its author. However, work can also go into the public domain if it is:
- Produced by the U.S. federal government
- Not in a fixed tangible form (speech, lecture, improv)
- Doesn’t have sufficient originality
When you come across historical plays, such as Shakespeare’s “Romeo and Juliet”, posted online for free, this is because they are part of the public domain. In fact, there are large web-based projects out there dedicated to curating old works in the public domain, such as Project Gutenberg.
What is Creative Commons?
Many creators find copyright laws constrictive, as the “all rights reserved” nature of copyright law can prohibit creativity. In a world where remixing is now our culture and we come across so many artistic works on a daily basis, it’s hard to create anything completely original. Because copyright laws can be constrictive, many people are putting Creative Commons licenses on their work.
When an artist creates something, it is automatically given an “all rights reserved” copyright. However, a Creative Commons license gives the author control over what rights are reserved, changing their copyright to “some rights reserved.” A Creative Commons license allows the creator of the work to give blanket permission to anyone who comes across their work, telling them how, exactly, their work can be used. They have control over these four areas:
- Whether it can be shared
- Whether it can be remixed
- Whether it can be used commercially/for profit
- And if any new work created with it must be shared with the same creative commons license
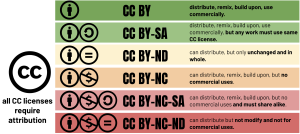
See the charts below for the different Creative Commons icons, different licenses, and what each means.
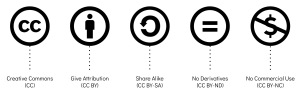
Note: every Creative Commons license still requires attribution — which is always an important factor in writing ethically!
Why Does This Matter?
In today’s digital world, it’s so much easier to copy, paste, transform, and share. You can download almost anything instantly from the Internet, and put it back up there claiming it as your own. While many times people get away with this, despite it infringing on copyright law, it’s not ethical. As a writer, you want to engage in ethical writing.
As a student, this means with any work you’d like to reuse, you should:
- Check who owns it
- Get permission from the owner to use it, unless it has a creative commons license
- Give credit
- Use it responsibility
- Pay for it if necessary
So, Can I Use That Image?
If you’ve found it randomly using Google search, with no perimeters, probably not. Luckily, there are many ways to search the web for images in the public domain or that have Creative Commons licenses. For example, Google allows for you to search images that have Creative Commons licenses, by going to “Tools” and “Usage rights.” Otherwise, there are many websites that only host reusable images:
- https://www.pexels.com
- https://www.flickr.com/creativecommons/
- https://ccsearch.creativecommons.org/
- https://free-images.com/
Please note, again, you should always still give proper attribution back to the original creator!
Recapping the main ideas behind Copyright in the Digital Age
- Copyright is the exclusive rights automatically given to the original creator of a work.
- Fair use allows people to use copyrighted work under certain circumstances, usually restricted by amount used and purpose.
- Creative Commons allows the original creators to modify the copyright placed on their work, changing it from “All Rights Reserved” to “Some Rights Reserved’.
- After a work’s copyright expires (life of the author + 70 years), it enters the public domain, which removes the copyright restrictions and makes it free to use.
- When using someone else’s work, check the copyright, and always give attribution back to the original creator.