Criminal Law and Criminal Procedure

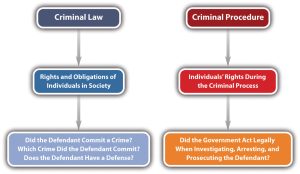
This book focuses on substantive criminal law, but it occasionally touches on issues of criminal procedure, so it is important to differentiate between the two. Whereas criminal law focuses on the community, criminal procedure focuses on the government.
Criminal law generally defines the rights and obligations of individuals in society. Some common issues in criminal law are the elements of specific crimes and the elements of various criminal defenses. Criminal law proscribes a citizen’s conduct within the community – that is, criminal law regulates (limits) our conduct within society. Criminal law tells us what we cannot do; it does not tell us what we should do.
Criminal procedure generally concerns the enforcement of individuals’ rights during the criminal process. Criminal procedure generally addresses the rights of the accused and the process involved in the investigation of crime, detention of individuals suspected of a crime, prosecution of criminal offenses, and the imposition of punishments. Criminal procedure regulates the authority of the government as it seeks to deprive its citizens of liberty. Examples of procedural issues are individuals’ rights during police investigation (Miranda), arrest, filing of charges, trial, and appeal.
Example of Substantive Criminal Law Issues
Clara and Linda go on a shopping spree. Linda insists that they browse an expensive department store. Moments after they enter the lingerie department, Linda surreptitiously places a bra in her purse. Clara watches, horrified, but does not say anything even though a security guard is standing nearby. This example illustrates two issues of criminal law: (1) Which crime did Linda commit when she put the bra in her purse? (2) Did Clara commit a crime when she failed to alert the security guard to Linda’s action? You learn the answers to these issues later in this textbook.
Example of Criminal Procedure Issues
Assume that Linda and Clara attempt to leave the store and an alarm is activated. Linda begins sprinting down the street. Colin, a police officer, just happens to be driving by with the window of his patrol car open. He hears the store alarm, sees Linda running, and begins shooting at Linda from the car. Linda is shot in the leg and collapses. Linda is treated at the hospital for her injury, and when she is released, Colin arrests her and transports her to the police station. He brings her to an isolated room and leaves her there alone. Twelve hours later, he reenters the room and begins questioning Linda. Linda immediately requests an attorney. Colin ignores this request and continues to question Linda about the reason the department store alarm went off. Whether Colin properly arrested and interrogated Linda are criminal procedure issues (the answers to which are beyond the scope of this book). However, this example illustrates one criminal law issue: did Colin commit a crime when he shot Linda in the leg in an effort to effectuate the arrest?
Figure 3.3 – Criminal Law and Criminal Procedure