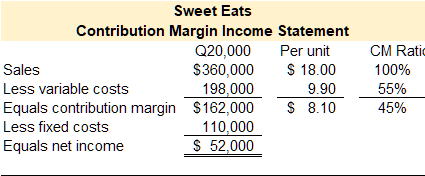3 Cost Volume Profit (CVP) Analysis
Student Learning Objectives:
- Compile a contribution margin income statement
- Explain how changes in activity affect contribution margin and net operating income
- Show the effects on net operating income from changes in variable costs, fixed costs, selling price, and sales volume
- Determine the level of sales needed to achieve the desired target profit
- Compute break-even point
Purpose of cost volume profit (CVP) analysis
Cost volume profit (CVP) analysis helps managers make many important decisions such as what products and services to offer, what prices to charge, what marketing strategy to use, and what cost structure to maintain. Its primary purpose is to estimate how profits are affected by the following five factors:
-
- Selling prices
- Sales volume
- Unit variable costs
- Total fixed costs
- Mix of products sold
Cost volume profit (CVP) analysis using a contribution margin income statement
Cost volume profit analysis is based on cost behavior. Cost behavior is how a cost reacts to changes in production or sales quantity. Cost behavior is classified as variable, fixed, or mixed.
Variable cost—cost is the same per unit: total depends on quantity
Fixed cost—cost is the same total regardless of quantity: per unit cost changes
Mixed cost—cost has both a variable and a fixed component
Cost behavior must be considered to estimate how profits are affected by changes in sales prices, sales volume, unit variable costs, total fixed costs, and the mix of products sold. The contribution margin income statement classifies costs on the basis of cost behavior. For this reason, it is an essential tool for cost volume profit analysis.
Video Illustration 1: Contribution margin income statement
Kinsley Shuck, the founder of Kinsley’s Koncepts, designed a radical new toy that can be programmed to perform various tasks. The programmable toy was an immediate success, and sales grew to the point that Kinsley moved the company’s headquarters out of her garage and into a rented manufacturing space. Kinsley sold 500 toys in the first year of operation. Kinsley’s Koncepts reported the following contribution margin income statement for their first year of operations.
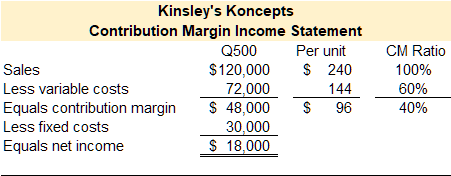

How much would net income change if Kinsley sold one more unit?
The contribution margin represents the gross margin or gross sales revenue you can make or lose as the number of units sold increases or decreases. If Kinsley sells one more unit she will gain $240 in sales revenue and incur $144 of variable expenses. Therefore, net income would increase by $96 or her current contribution margin. The contribution margin ratio represents the percentage of sales dollars of gross margin you can make or lose as the number of units sold increases or decreases.
Video Illustration 2: Using the contribution margin income statement to forecast changes in profit from an increase in sales
The contribution margin income statement can be used to forecast and analyze projected changes in selling prices, sales volume, unit variable costs, total fixed costs, and the mix of products sold.
Kinsley’s Koncepts is currently selling 500 toys per year. Assume sales increase from 500 toys to 550 toys.



Break even and target profit
The contribution margin income statement can be used to compute break even and target profit. Break even is the point at which net operating income equals zero. Or, an organization breaks even when its sales revenue covers total costs–both variable and fixed. Break even is an important calculation, especially in new or start-up organizations. An organization should know how many units it needs to sell in order to cover its costs. In fact, most business plans and start-up business financing requests require the break even calculation to be reported. For example, an organization might discover they need to sell 10,000 units to break even when the demand for the product is only 2,000 units. In this case, the company cannot break even given current expenses and sales demand so they should not produce the product or they need to reduce costs.
Target profit is the point at which net operating income equals a specified amount. The calculation for target profit is closely related to break even. Target profit is calculated when an organization needs to know the quantity of sales required to cover total costs and earn a certain net profit.
The formulas to compute break even and target profit are provided below.
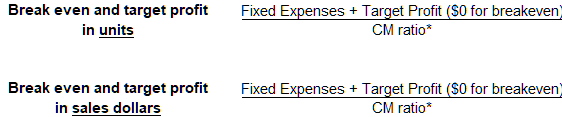
*Contribution margin ratio or CM ratio (contribution margin in dollars/sales revenue in dollars)
Video Illustration 3: Calculating breakeven and target profit
Kinsley’s Koncepts reported the following contribution margin income statement for their first year of operations. Use this data to compute break even in units and sales dollars.

Break even in units sold
Break even in sales dollars
Assume that the company wants to earn a target profit of $10,000 compute the number of sales required in units and sales dollars.
Target profit in units sold
Target profit in sales dollars

Practice Video Problems
Practice Video Problem 1 Part 1: Cost volume profit (CVP) analysis
Kinsley’s Koncepts is currently selling 500 toys per year. Kinsley’s Koncepts reported the following contribution margin income statement for their first year of operations.
Required 1: The sales manager feels that a $6,000 increase in the monthly advertising budget would increase monthly sales by $9,600 to a total of 540 units. Should the advertising budget be increased?



Practice Video Problem 1 Part 2: Cost volume profit (CVP) analysis
Refer to the original data. Kinsley’s Koncepts is currently selling 500 toys per year. Kinsley’s Koncepts reported the following contribution margin income statement for their first year of operations.
Required 2: Kinsley is considering the use of higher-quality components, which would increase variable costs (and thereby reduce the contribution margin) by $6 per toy. However, the sales manager predicts that using higher-quality components would increase sales to 550 toys per year. Should the higher-quality components be used?



Practice Video Problem 1 Part 3: Cost volume profit (CVP) analysis
Refer to the original data. Kinsley’s Koncepts is currently selling 500 toys per year. Kinsley’s Koncepts reported the following contribution margin income statement for their first year of operations.
Required 3: To increase sales, the sales manager would like to cut the selling price by $40 per toy and increase the advertising budget by $15,000 per year. The sales manager believes that if these two steps are taken, unit sales will increase by 200 toys per year. Should the changes be made?



Practice Video Problem 2 Part 1: Calculating break even and target profit
Sweet Eats reported the following contribution margin income statement for their first year of operations.
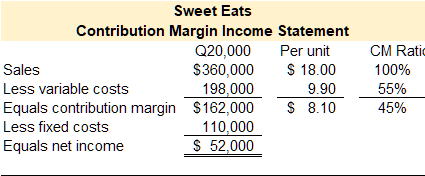
Required 1: Compute the break even in both sales units and sales dollars for Sweet Eats.
Break even in units sold
Break even in sales dollars
Required 2: Compute target profit in both sales units and sales dollars assuming that Sweet Eats is projecting $75,000 in net income.
Target profit in units sold
Target profit in sales dollars

Practice Video Problem 2 Part 2: Cost volume profit (CVP) analysis
Refer to the original data. Sweet Eats is currently selling 20,000 treats per year.
Required 3: Compute net income assuming the selling price decreases by $1.50 per unit, fixed expenses increase by $10,000, and the number of units sold decreases by 5%.
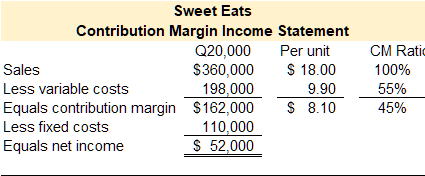


Practice Video Problem 2 Part 3: Cost volume profit (CVP) analysis
Refer to the original data. Sweet Eats is currently selling 20,000 treats per year.
Required 4: Compute net income assuming the selling price increases by 5%, variable expenses decrease by 0.45 cents per unit, and the number of units sold increases by 12%.