7 Standard Costs and Variance Analysis
Student Learning Objectives:
- Describe the purpose of standard costs used for manufacturing costs
- Compute the direct materials price and quantity variances and explain their significance
- Compute the direct labor rate and efficiency variances and explain their significance
- Compute the variable manufacturing overhead rate and efficiency variances and explain their significance
Standard costs
Standards are cost targets that can be used to make financial projections or to measure performance. The cost formulas used for budgeting are considered standards. These standards set forth the expected revenue or cost for a particular item. For example, if the cost formula for supplies is $10 per unit ($10Q), this is also the standard cost for supplies. The standard can be used to make projections about supplies expense or evaluate the actual amount spent on supplies.
Manufacturing costs and the costs associated with providing services also have established standard cost targets. In this module, the focus will be on standard costs for manufacturing costs. Manufacturing costs, or the cost incurred to manufacture a product for resell, are also known as product costs. There are three categories that comprise total product cost—direct material, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. Standard costs are normally established for all product costs.
Standards for manufacturing costs include both a quantity and a price standard. The quantity standard establishes how much of an input is needed to make a product or provide a service. The price standard establishes how much each quantity of input should cost. As mentioned prior, these standards can be used to make financial projections as seen in the module on budgeting. These standards can also be used to evaluate performance by comparing the standards to actual performance at the end of the period as demonstrated in the flexible budgeting module. Any discrepancy is known as a variance between the standard and actual costs. Any standard variance should be considered a red flag for management to investigate and determine its cause.
Video Illustration 1: Standard costs for manufacturing costs
Patty invented a virtually indestructible bicycle lock called Lastlock. The lock is lightweight, retractable, and fits easily in a jacket pocket. Sales of Lastlock skyrocketed when a local celebrity posted about Lastlock on social media. While the sudden increase in sales demand was exciting, Patty was not expecting the sudden increase in production so she experienced a number of production issues. In particular, she ran out of the alloy used to make Lastlock and was forced to purchase a lower quality batch from a different supplier. The lower quality batch; however, was significantly cheaper than her normal alloy. Also, to meet demand she had to hire an additional fabricator. Although the new fabricator was less experienced, her pay rate per hour was lower. Since she paid less for the material and labor, Patty assumed that at the end of the period overall manufacturing costs would be lower than projected. However, manufacturing costs were higher than expected at the end of the period. Accordingly, Patty decided to perform a standard cost variance analysis on the manufacturing costs.
The standard quantity and price to make one unit of Lastlock are provided below. The actual costs and quantities are also provided.
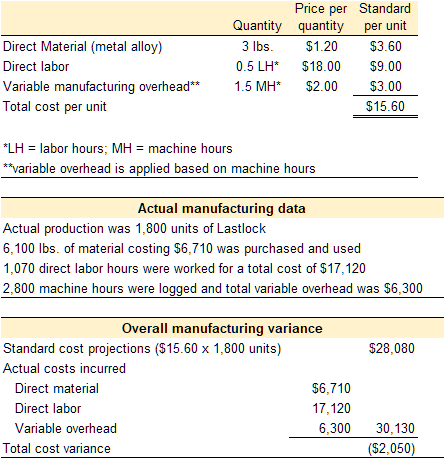

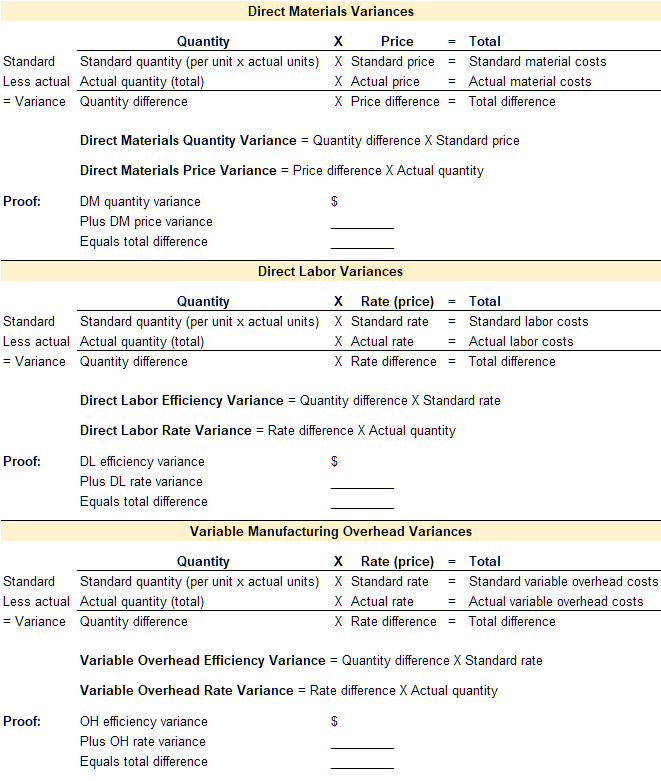
Direct materials variances
Standard costs are established for all direct materials used in the manufacturing process. Direct materials include all materials that can be easily and economically traced to the production of a product. For example, the direct materials necessary to produce a wood desk might include wood and hardware. Indirect materials are materials that are not easily and economically traced to a particular product. Examples of indirect materials are items such as nails, screws, sandpaper, and glue. Indirect materials are included in the manufacturing overhead category and not the direct material category.
Standard costs and quantities are established for each direct material. These standards are then compared to the actual quantities used and the actual price paid for each category of direct material. Any variance between the standard and the actual is caused by a difference in quantity or a difference in price. Therefore, the total variance for direct material is broken down into the direct materials quantity variance and the direct materials price variance.
A template to compute the total variance, direct materials quantity variance, and the direct material price variance is provided below.
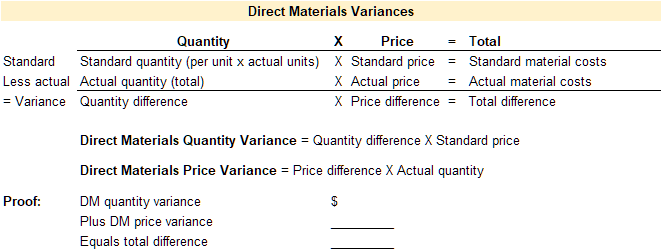
Video Illustration 2: Computing direct materials variances
Using the standard and actual data given for Lastlock and the direct materials variance template, compute the direct materials variances.
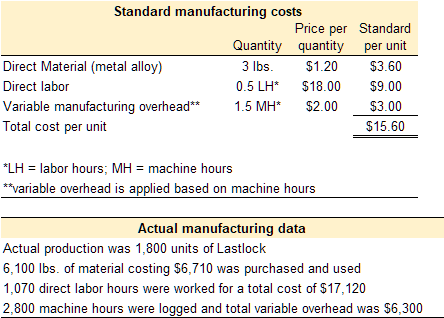


Direct labor variances
Standard costs are established for all direct labor used in the manufacturing process. Direct labor is labor used during the manufacturing process that can be easily and economically traced to the production of a product. For example, the direct labor necessary to produce a wood desk might include the wages paid to the assembly line workers. Indirect labor is labor used in the production process that is not easily and economically traced to a particular product. Examples of indirect labor would be wages paid to the production supervisor or quality control team. While they are a part of the production process, it would be difficult to trace these wages to the production of a single desk. Indirect labor is included in the manufacturing overhead category and not the direct labor category.
Standard costs and quantities are established for each category of direct labor. These standards are then compared to the actual quantities used and the actual price paid for each category of direct labor. Any variance between the standard and the actual is caused by a difference in quantity or a difference in price. When discussing labor, price is referred to as rate instead of price, and quantity is referred to as efficiency instead of quantity. Therefore, the total variance for direct labor is broken down into the direct labor efficiency variance and the direct labor rate variance.
A template to compute the total variance, direct labor efficiency variance, and the direct labor rate variance is provided below.
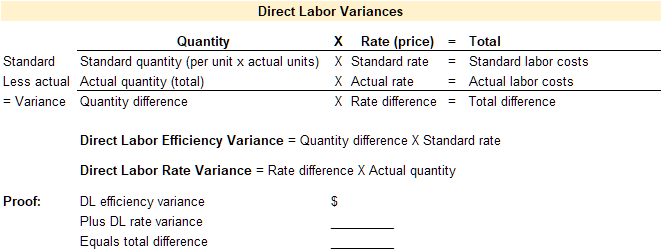
Video Illustration 3: Computing direct labor variances
Using the standard and actual data given for Lastlock and the direct labor variance template, compute the direct labor variances.



Variable manufacturing overhead variances
Standard costs are established for the variable and fixed manufacturing overhead used in the manufacturing process. Manufacturing overhead includes all costs incurred to manufacture a product that are not direct material or direct labor. Examples of manufacturing overhead are indirect materials, e.g. nails and glue; indirect labor, e.g. wages for the production supervisor or quality control; and all other production costs, e.g. costs incurred on the factory such as rent, utilities, and insurance. Variable manufacturing overhead is same amount per unit but the total amount depends on quantity. Fixed manufacturing overhead is the same in total regardless of quantity but the per unit amount changes depending on the quantity. When analyzing fixed manufacturing overhead the actual amount paid is compared to the standard fixed amount. The focus here is on variable manufacturing overhead since it has both a quantity and price element.
Standard costs and quantities are established for variable manufacturing overhead. These standards are then compared to the actual quantities used and the actual price paid for variable manufacturing overhead. Any variance between the standard and the actual is caused by a difference in quantity or a difference in price. When discussing variable overhead, price is referred to as rate instead of price and quantity is referred to as efficiency instead of quantity. Therefore, the total variance for variable manufacturing overhead is broken down into the variable manufacturing overhead efficiency variance and the variable manufacturing overhead rate variance.
A template to compute the total variance, variable manufacturing overhead efficiency variance, and the variable manufacturing overhead rate variance is provided below.
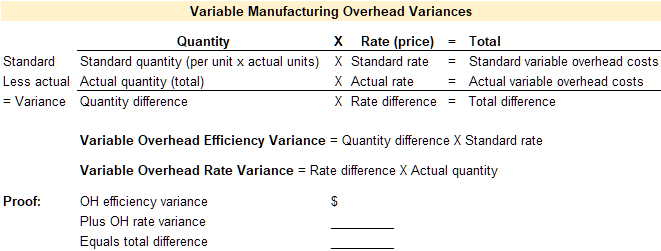
Video Illustration 4: Computing variable manufacturing overhead variances
Using the standard and actual data given for Lastlock and the variable manufacturing overhead variance template, compute the variable manufacturing overhead variances.



Complete standard costing variance template
Practice Video Problems
Practice Video Problem 1: Computing direct materials variances
Kitchen Co. is experiencing production problems with SuddyBuddy, its most profitable product. Management has requested standard cost variances in order to isolate the issue. Standard and actual manufacturing cost data for SuddyBuddy are provided below.
Required 1: Prepare the total direct materials variance, direct materials quantity variance, and direct materials price variance.
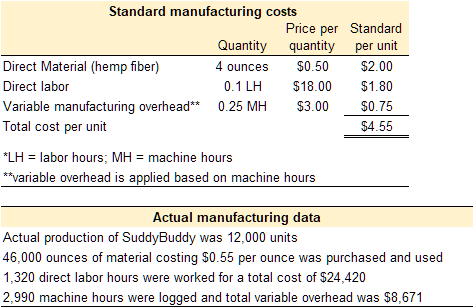


Practice Video Problem 2: Computing direct labor variances
Kitchen Co. is experiencing production problems with SuddyBuddy, its most profitable product. Management has requested standard cost variances in order to isolate the issue. Standard and actual manufacturing cost data for SuddyBuddy are provided below.
Required 1: Prepare the total direct labor variance, direct labor efficiency variance, and direct labor rate variance.



Practice Video Problem 3: Computing manufacturing overhead variances
Kitchen Co. is experiencing production problems with SuddyBuddy, its most profitable product. Management has requested standard cost variances in order to isolate the issue. Standard and actual manufacturing cost data for SuddyBuddy are provided below.
Required 1: Prepare the total manufacturing overhead variance, manufacturing overhead efficiency variance, and manufacturing overhead rate variance.




