98
So far, all the genes we have discussed have had two copies present in all individuals. This is because the individual inherited one from the male parent’s haploid gamete and one from the female parent’s haploid gamete. The two gametes came together during fertilization to produce a diploid individual. There is, however, one exception to this: genes which are present on the sex chromosomes.
In humans, as well as in many other animals and some plants, the sex of the individual is determined by sex chromosomes – one pair of non-homologous chromosomes. Until now, we have only considered inheritance patterns among non-sex chromosomes, or autosomes. In addition to 22 homologous pairs of autosomes, human females have a homologous pair of X chromosomes, whereas human males have an XY chromosome pair. Although the Y chromosome contains a small region of similarity to the X chromosome so that they can pair during meiosis, the Y chromosome is much shorter and contains fewer genes. When a gene being examined is present on the X, but not the Y, chromosome, it is X-linked.
The X chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes. Humans and most mammals have two sex chromosomes, the X and Y. Females have two X chromosomes in their cells, while males have X and Y chromosomes in their cells. Egg cells all contain an X chromosome, while sperm cells contain an X or a Y chromosome. This arrangement means that during fertilization, it is the male that determines the sex of the offspring since the female can only give an X chromosome to the offspring.

Figure 24: A diagram showing the autosomal and sex chromosomes. Remember that in a diploid cell, there would be two copies of each autosomal chromosome present. (Credit: Darryl Lega, NHGRI)
Most sex-linked genes are present on the X chromosome simply because it is much larger than the Y chromosome. The X chromosome spans about 155 million DNA base pairs and represents approximately 5 percent of the total DNA in cells. The X chromosome likely contains 800 to 900 genes. In contrast, the Y chromosome has approximately 59 million base pairs and only 50-60 genes. Sex is determined by the SRY gene, which is located on the Y chromosome and is responsible for the development of a fetus into a male. This means that the presence of a Y chromosome is what causes a fetus to develop as male. Other genes on the Y chromosome are important for male fertility.
Hemophilia is a bleeding disorder that slows the blood clotting process. People with this condition experience prolonged bleeding or oozing following an injury, surgery, or having a tooth pulled. In severe cases of hemophilia, continuous bleeding occurs after minor trauma or even in the absence of injury (spontaneous bleeding). Serious complications can result from bleeding into the joints, muscles, brain, or other internal organs. Milder forms of hemophilia do not necessarily involve spontaneous bleeding, and the condition may not become apparent until abnormal bleeding occurs following surgery or a serious injury.
The major types of this condition are hemophilia A (also known as classic hemophilia or factor VIII deficiency) and hemophilia B (also known as Christmas disease or factor IX deficiency). Although the two types have very similar signs and symptoms, they are caused by mutations in different genes.
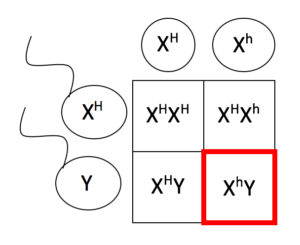
Hemophilia A and hemophilia B are inherited in an X-linked recessive pattern. The genes associated with these conditions are located on the X chromosome, which is one of the two sex chromosomes. In males (who have only one X chromosome), one altered copy of the gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the condition. In females (who have two X chromosomes), a mutation would have to occur in both copies of the gene to cause the disorder. Because it is unlikely that females will have two altered copies of this gene, it is very rare for females to have hemophilia. A characteristic of X-linked inheritance is that fathers cannot pass X-linked traits to their sons.
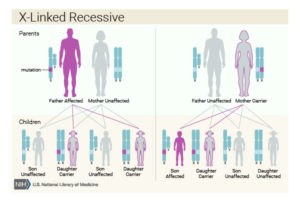
In X-linked recessive inheritance, a female with one altered copy of the gene in each cell is called a carrier. Carrier females have about half the usual amount of coagulation factor VIII or coagulation factor IX, which is generally enough for normal blood clotting. However, about 10 percent of carrier females have less than half the normal amount of one of these coagulation factors; these individuals are at risk for abnormal bleeding, particularly after an injury, surgery, or tooth extraction.
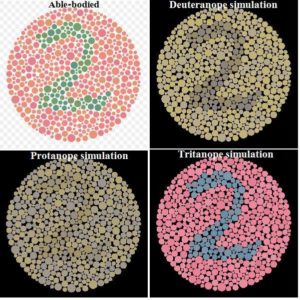
Colorblindness is another example of a sex-linked trait in humans. The genes that produce the photopigments necessary for color vision are located on the X chromosome. If one of these genes is not functional because it contains a harmful mutation, the individual will be colorblind. Men are much more likely than women to be colorblind: up to 100 times more men than women have various types of colorblindness (http://www.colour-blindness.com/general/prevalence/).
References
Unless otherwise noted, images on this page are licensed under CC-BY 4.0 by OpenStax.
OpenStax, Biology. OpenStax CNX. May 27, 2016 http://cnx.org/contents/s8Hh0oOc@9.10:zLLYW2hj@5/Extensions-of-the-Laws-of-Inhe
“X chromosome” by Genetics Home Reference: Your Guide to Understanding Genetic Conditions, National Institutes of Health: U.S> National Library of Medicine is in the Public Domain
“Y chromosome” by Genetics Home Reference: Your Guide to Understanding Genetic Conditions, National Institutes of Health: U.S> National Library of Medicine is in the Public Domain
“Hemophilia” by Genetics Home Reference: Your Guide to Understanding Genetic Conditions, National Institutes of Health: U.S> National Library of Medicine is in the Public Domain
