33
Cross-cultural perspectives
Dr. Evan Freeman
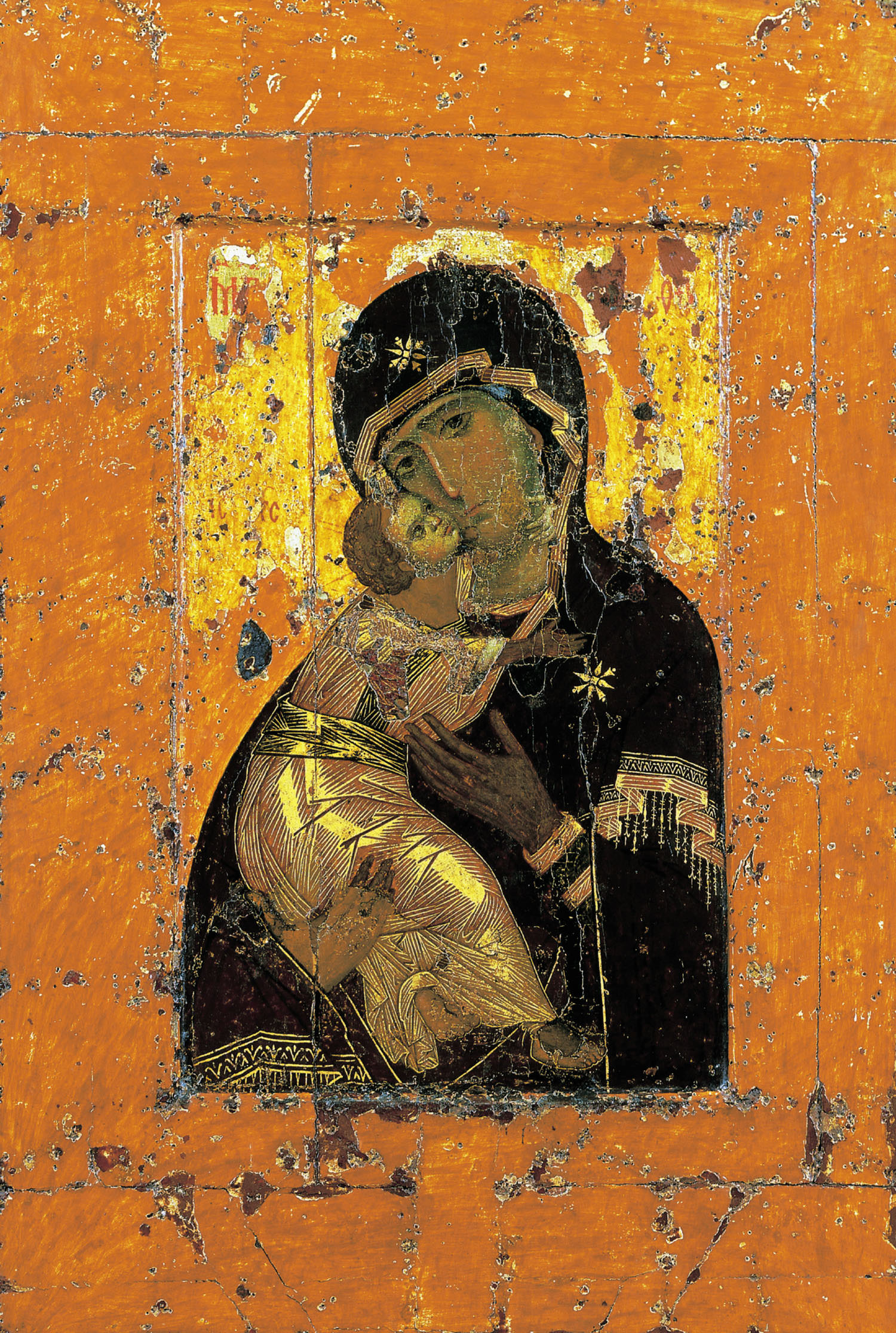

One of the most beloved artworks in Russia is a tempera on wood icon known as the Virgin of Vladimir, or Vladimirskaya. It presents a common composition known as the Virgin eleousa (“compassionate”), which shows Mary and Jesus in tender embrace, their faces pressed together.
The Virgin gazes out at us, commanding our attention, but her hands seem to gesture toward her son, destined to die on the cross and rise from the dead as the savior of humankind. Through the centuries, many miracles have been attributed to this icon, and as a result, numerous patrons and artists have sought to produce copies of it.
But despite the Virgin of Vladimir’s enduring religious and cultural importance in Russia, the icon is not Russian in origin. It was likely painted in the twelfth century in Constantinople (Istanbul), capital of the Eastern Roman “Byzantine” Empire, and brought to Kiev, capital of Kievan Rus’, as a diplomatic gift around 1131. Later, the icon was transferred to the city of Vladimir (hence its name), an important medieval center from the late twelfth to the early fifteenth century, and eventually to the Russian capital of Moscow, where it still remains. The Virgin of Vladimir’s journey from Constantinople to Kiev, and eventually, to Moscow, is part of a larger story of the conversion of Kievan Rus’ to the Orthodox Christianity of the Byzantine Empire in the tenth century and Moscow’s subsequent rise as a new center of power in the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries. While neither the Byzantine Empire nor Kievan Rus’ survive today, works of art and architecture like the Virgin of Vladimir can help us understand the relationship between these medieval states, as well as their contested legacies in today’s world.

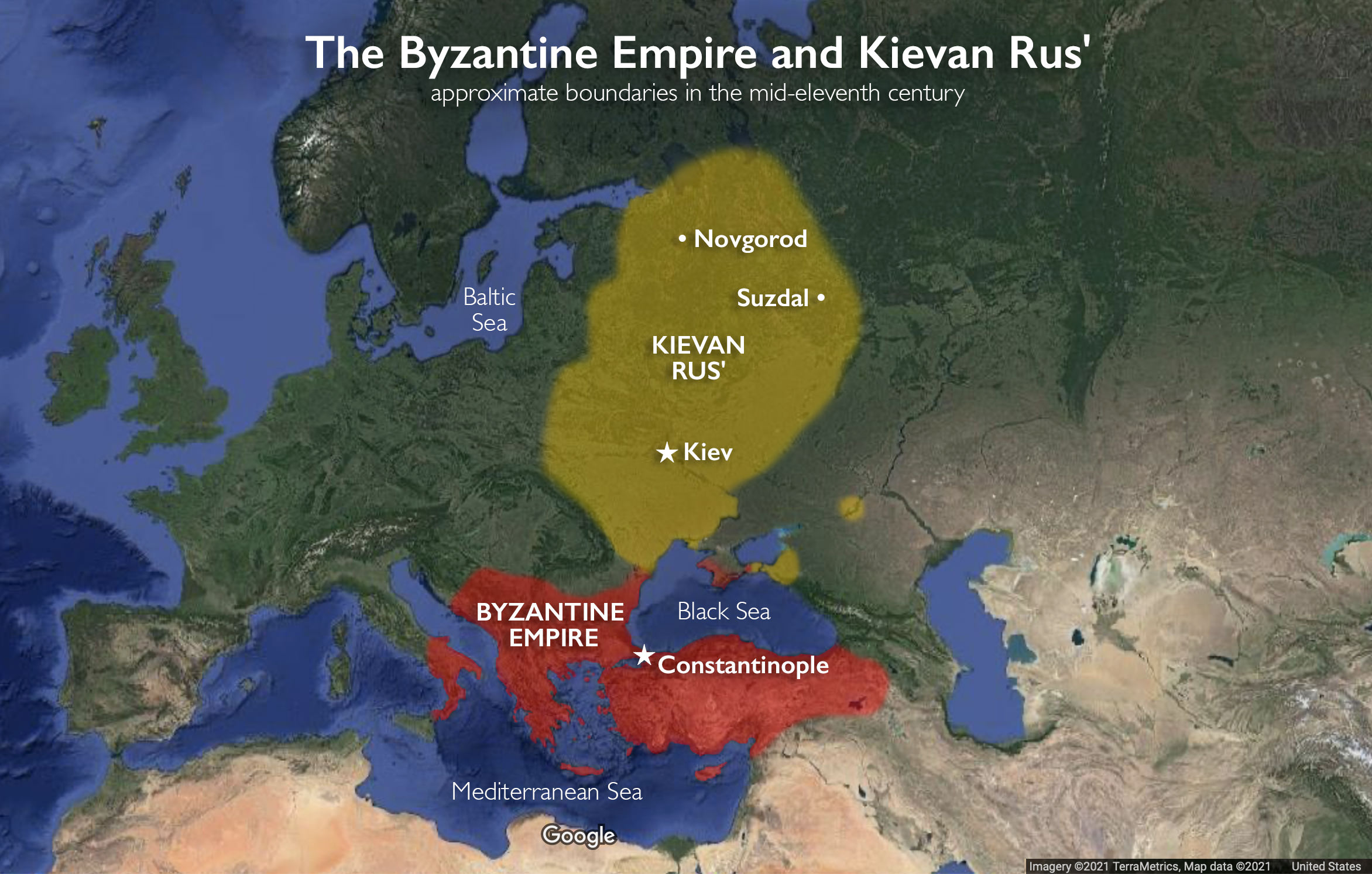
The Byzantine Empire and Kievan Rus’
Kievan Rus’ emerged as a powerful confederation of city-states during the second half of the ninth century in Eastern Europe, where rivers helped link the Baltic Sea (an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that was an important center of trade in the middle ages) with the Black Sea (a sea that lies between Europe and Asia and was of great strategic and commercial importance in the middle ages) and facilitated trade with Constantinople, the wealthy capital of the Byzantine Empire. The capital of Kievan Rus’ was Kiev (today the capital of Ukraine) on the Dnieper River (which flows from central Russia to the Black Sea and was used for travel and trade in the middle ages). The name “Kievan Rus’” refers both to the state and its people.
Kievan Rus’ was sometimes a trading partner and other times an enemy of the Byzantine Empire. But in 987, Prince Vladimir I of Kiev, ruler over Kievan Rus’ from 980–1015, formed an alliance with the Byzantine emperor Basil II (reigned 976–1025), converting from paganism to Christianity and marrying Basil II’s sister Anna in 988. Historical texts describe the subsequent conversion of Vladimir’s formerly pagan subjects by mass baptism in the Dnieper River in Kiev. With its conversion to the Orthodox Christianity of the Byzantines, Kievan Rus’ now began appropriating and adapting Byzantine art and architecture for itself.
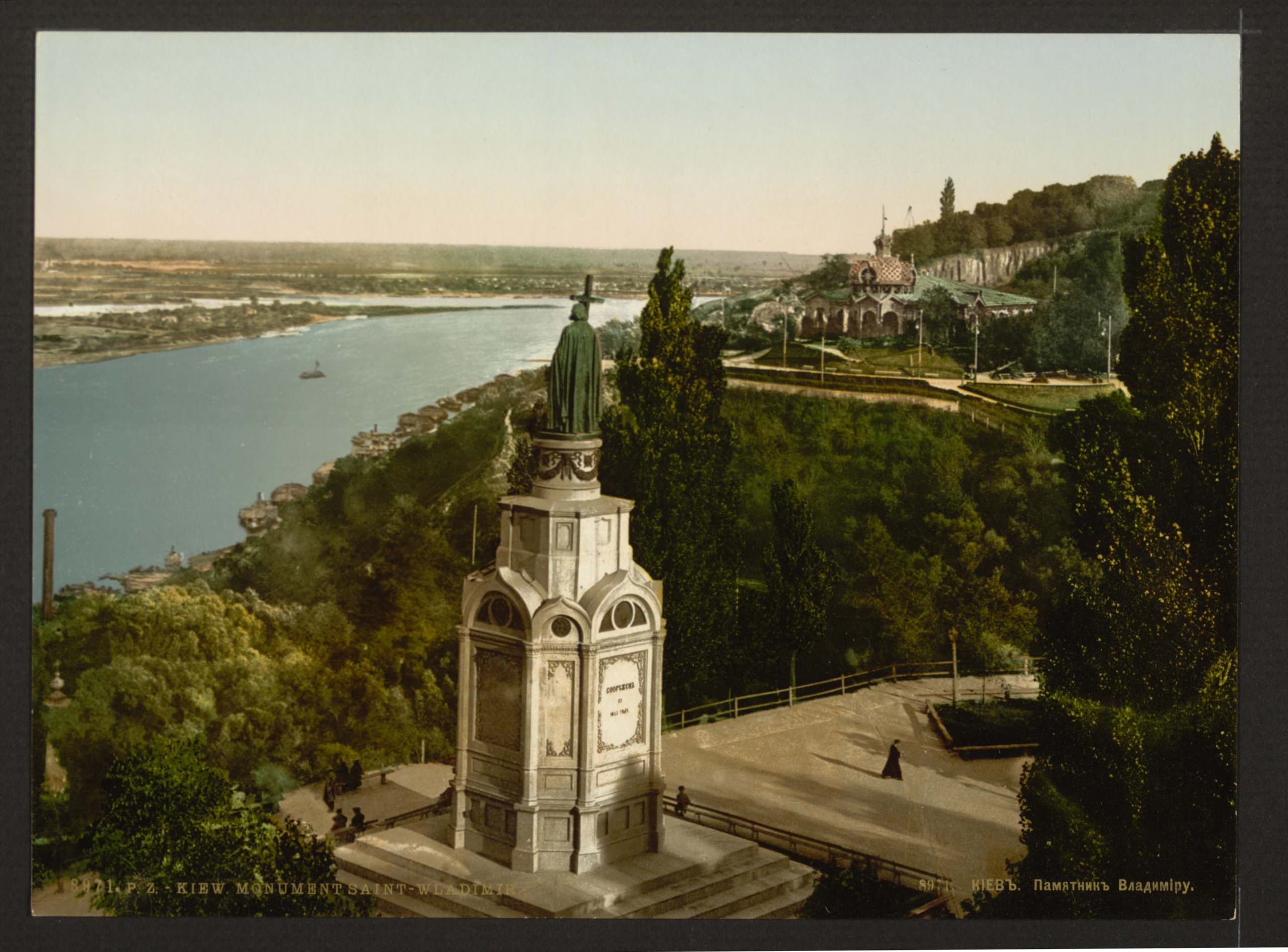
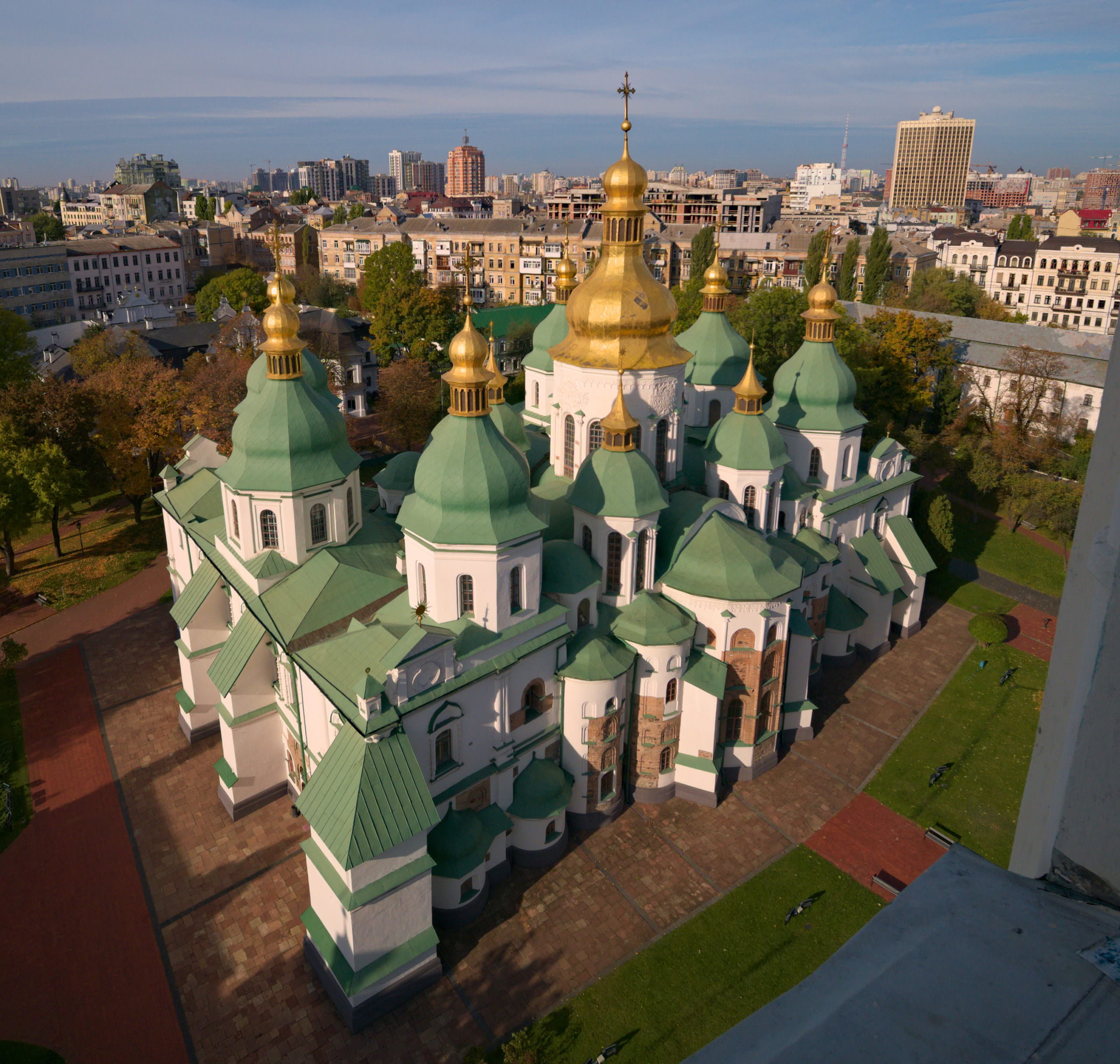


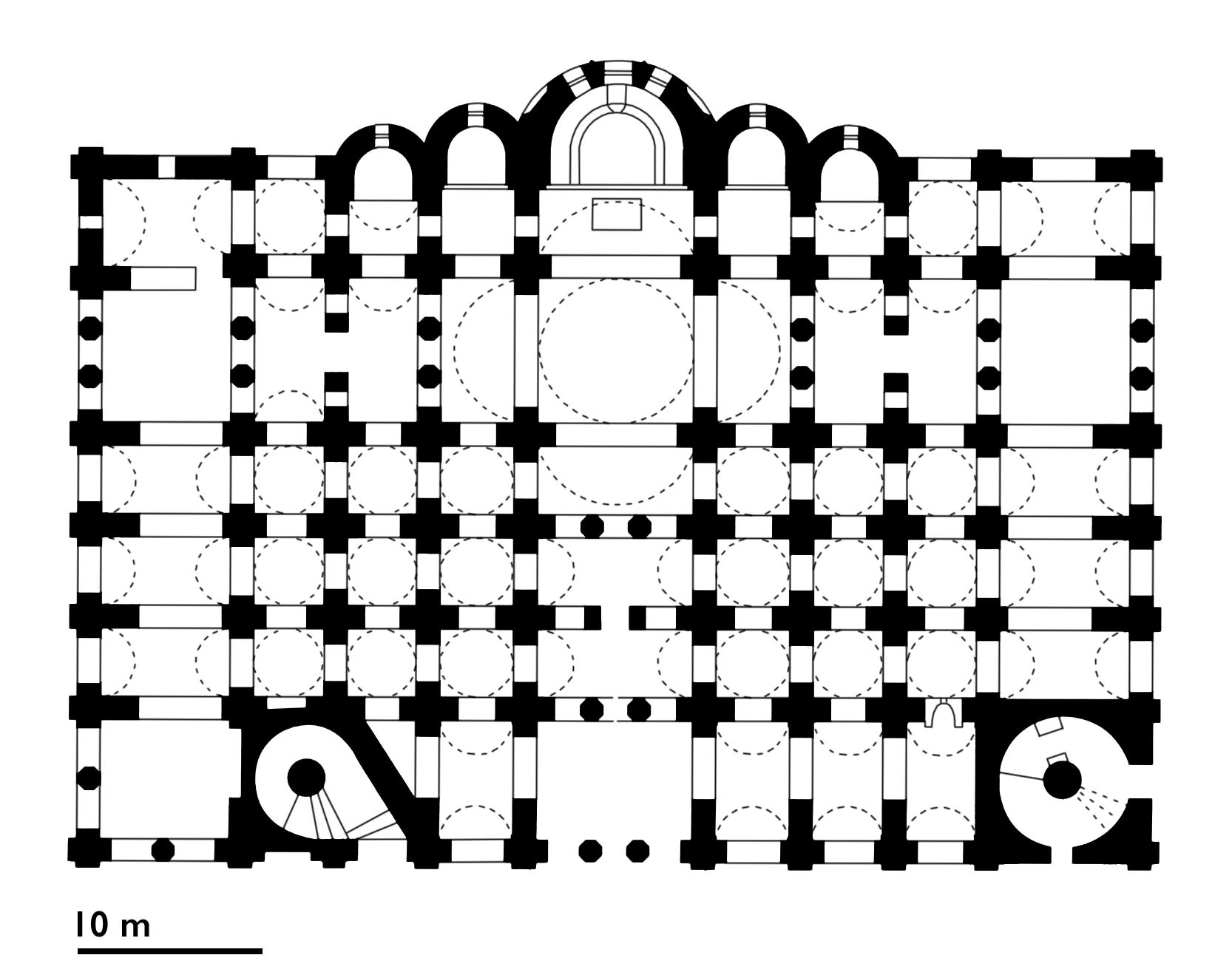
St. Sophia, Kiev
Wishing to emulate the Byzantine capital of Constantinople and its cathedral Hagia Sophia (dedicated to Christ as “Holy Wisdom”), Vladimir’s son Yaroslav (Grand Prince of Kiev from 1019–1054) expanded Kiev and built a magnificent new church to function as the city’s main cathedral, which he likewise dedicated to St. Sophia (“Holy Wisdom”) in imitation of Constantinople’s Hagia Sophia. St. Sophia in Kiev illustrates how Kievan Rus’ appropriated the art and architecture of the Byzantine Empire while also making it their own.
Begun c. 1037, Kiev’s St. Sophia was likely the product of collaboration between Byzantine and local craftsmen. The core of St. Sophia takes the form of a typical Middle Byzantine cross-in-square church, incorporating additional aisles and galleries to accommodate a large cathedral congregation, though still falling short of the astonishing scale of Hagia Sophia in Constantinople. Kiev’s St. Sophia was probably finished in the 1040s and even its first bishop, Theopemptos, came from Constantinople. St. Sophia in Kiev still stands today, albeit with later restorations and additions.
The interior of St. Sophia displays mosaics and frescoes—hallmarks of Byzantine church decoration—though the former are better preserved than the latter. And although church services in Kievan Rus’ were celebrated in Church Slavonic, a language whose written form was first developed by Byzantine missionaries in the ninth century, St. Sophia’s mosaics are labeled in Greek, the language of Byzantium.
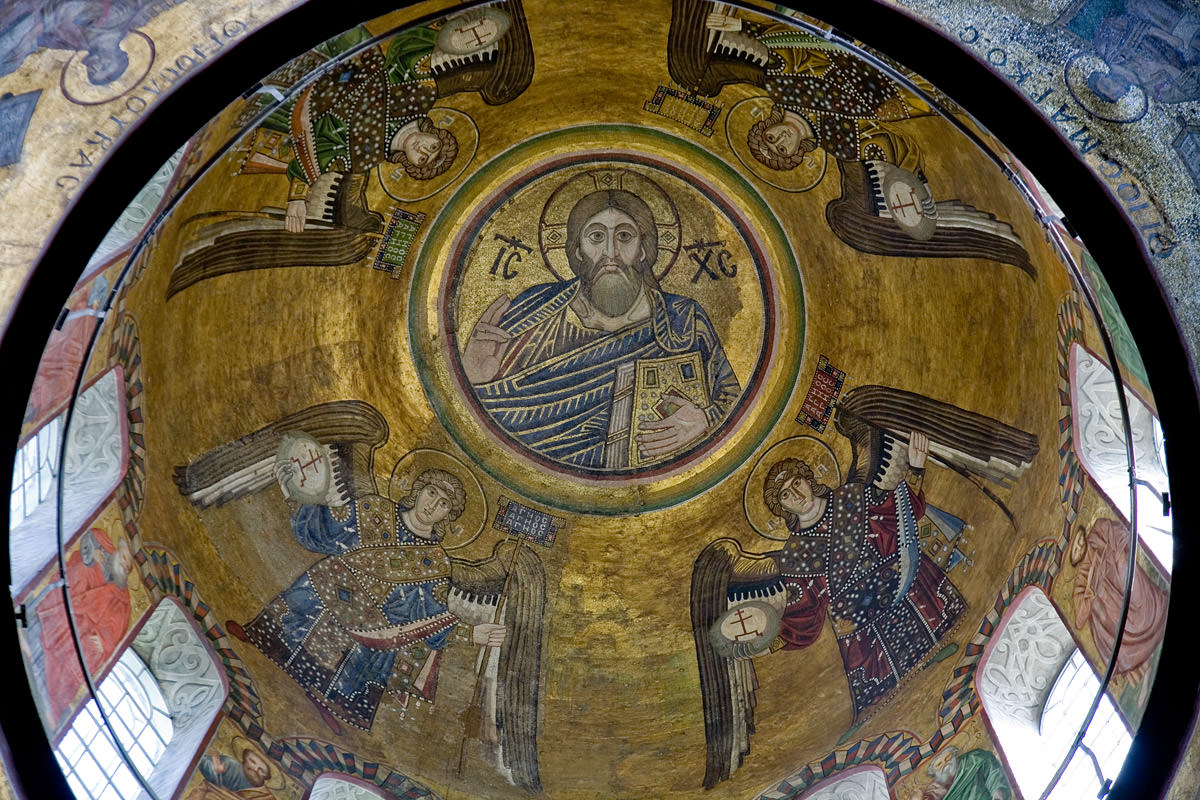
Christ Pantokrator
Byzantine worshippers probably would have found the interior of Kiev’s St. Sophia very familiar. As in contemporary Byzantine churches, such as Daphni monastery, a bearded Christ Pantokrator (“almighty”) reigns over the church from the central dome. Christ is surrounded by angels with large wings in imperial garb. Apostles fill the spaces between the windows in the drum that supports the dome and the four evangelists (authors of the Gospels) appear in the pendentives just below the windows.
The Annunciation
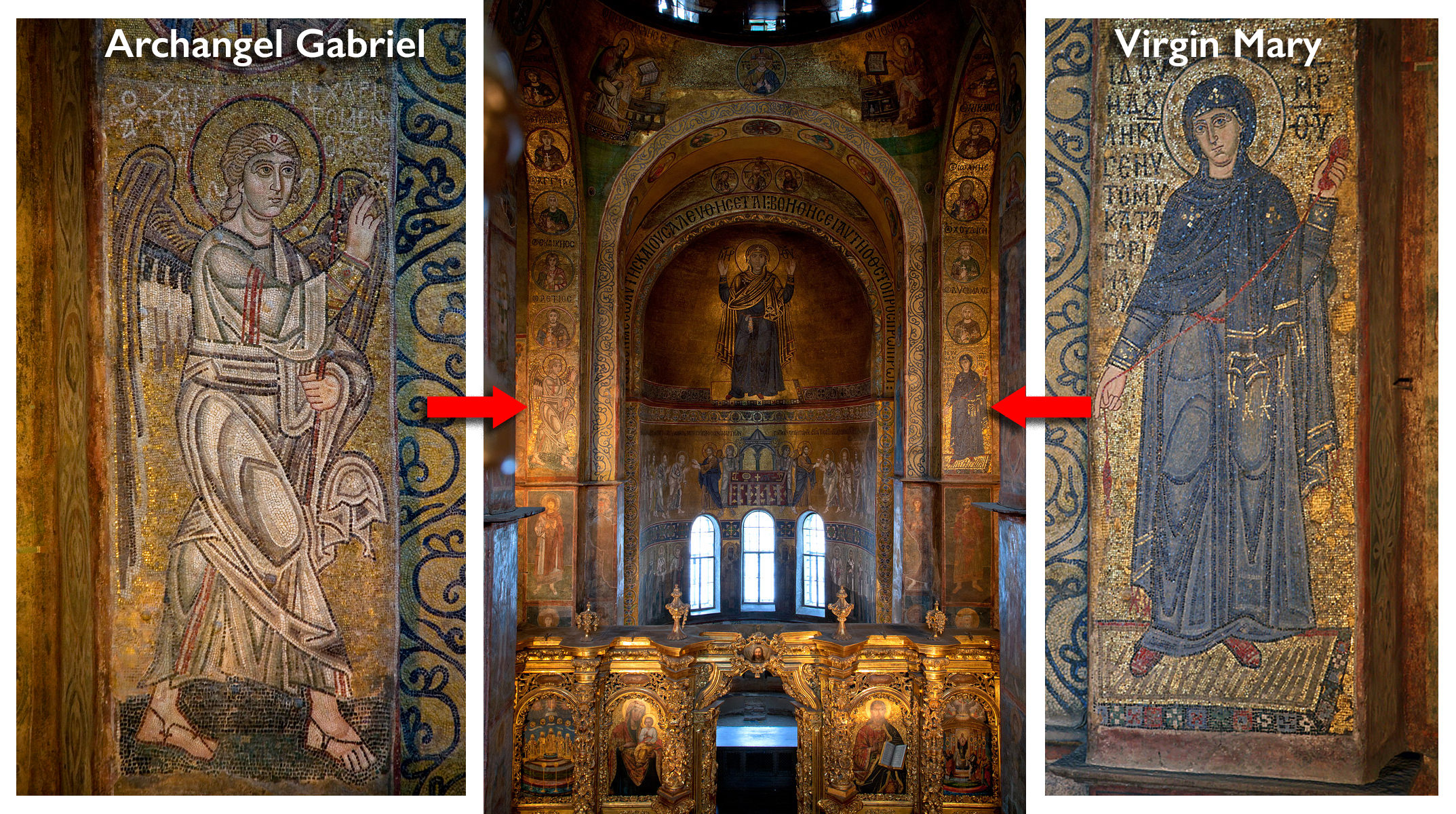
The mosaics in the bema where the altar is located similarly mirror contemporary Byzantine churches and point to the function of this part of the church as the place where the Eucharist was celebrated. (The Eucharist is the Christian offering and blessing of bread and wine, which are then consumed as the body and blood of Christ.)

Gabriel and the Virgin enact the Annunciation from either side of the bema. The angel announces to the Virgin that she will give birth to Jesus, suggesting a parallel between Christ’s incarnation (becoming flesh and blood) through the Virgin and the Eucharistic bread and wine believed to become Christ’s body and blood on the altar below.

A towering Virgin orans (about 5.5 meters tall) looms against the gold ground of the apse. (Orans or orant refers to a gesture of prayer with both hands upraised, commonly used to depict the Virgin Mary in Byzantine art.) She stands on a gold platform and raises her hands in prayer beneath large Greek characters that identify her as the “Mother of God.”
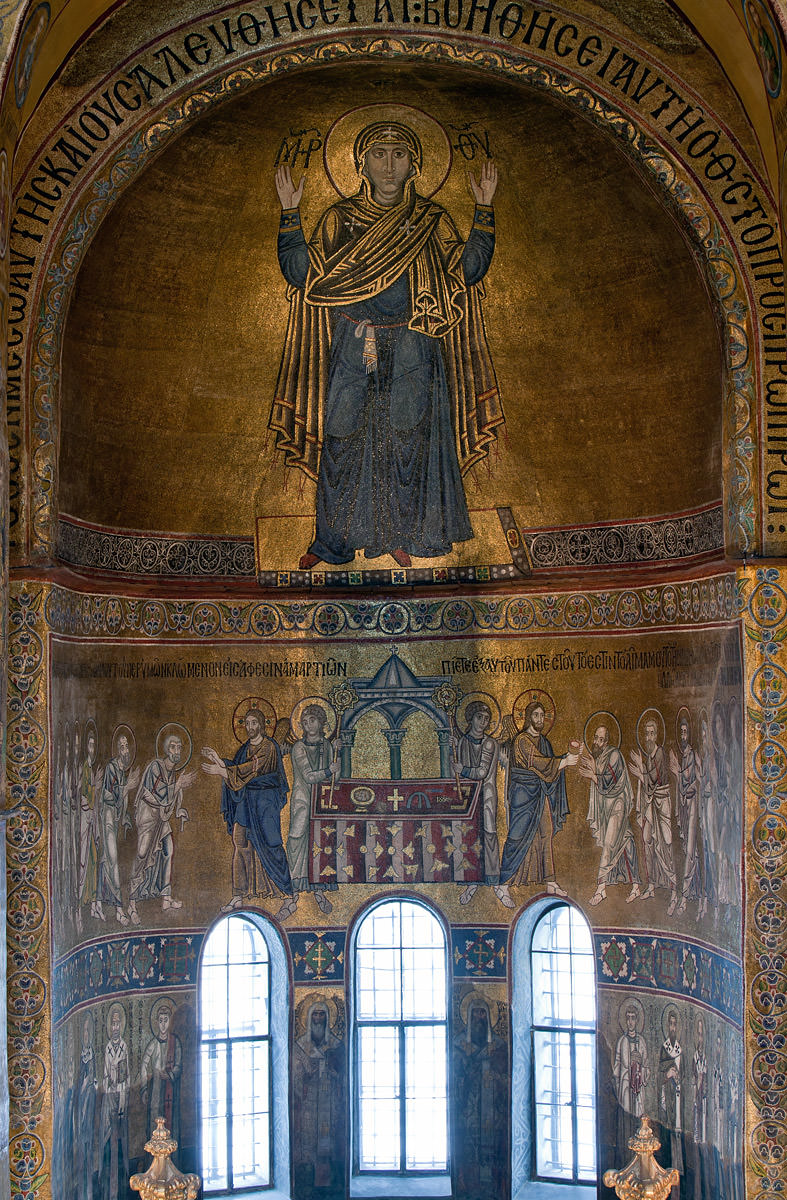
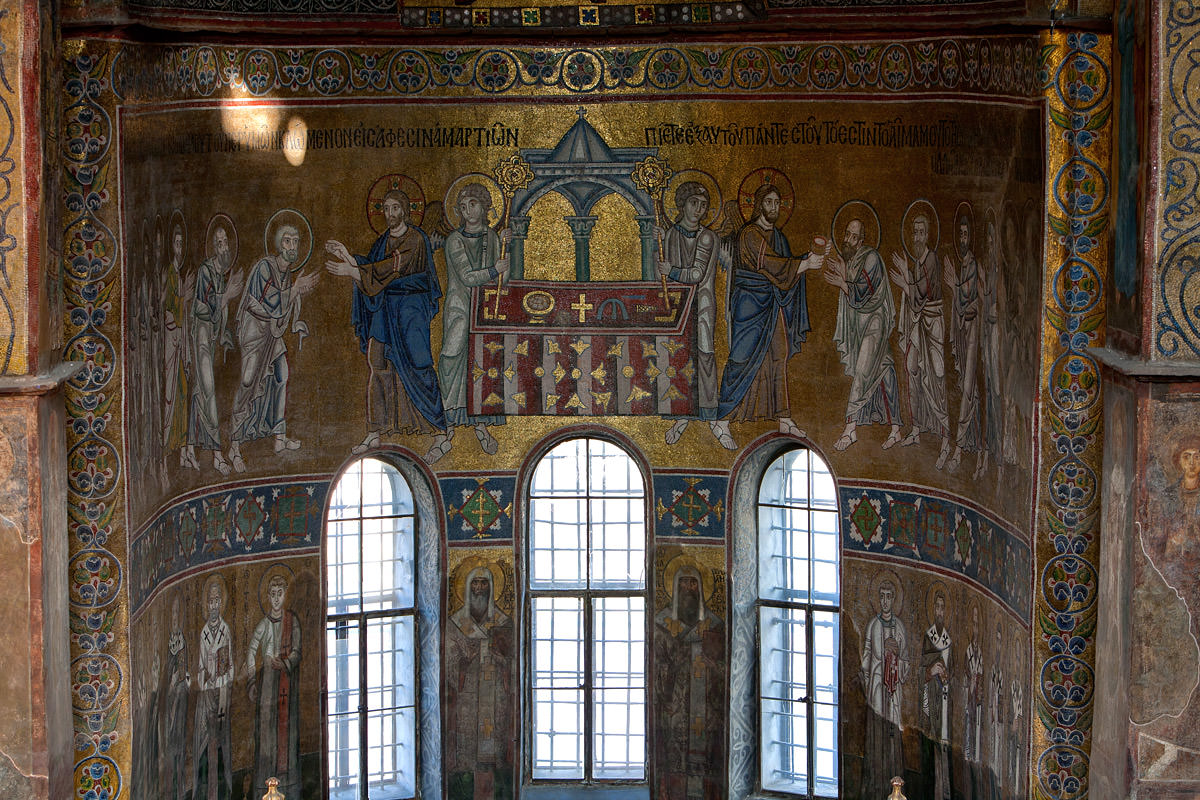


The Communion of the Apostles
Below the Virgin, Christ presides at the celebration of the Eucharist in a scene known as the “Communion of the Apostles,” which became a common feature in Byzantine churches at this time, and which paralleled the celebration of the Eucharist unfolding at the altar below. Although reminiscent of the Last Supper, this image anachronistically depicts Christ presiding at a celebration of the Divine Liturgy like a Byzantine priest with all the trappings of a contemporary church altar. This image must have helped connect the experiences of contemporary worshippers with these holy figures of Christ and his apostles from the past: as worshippers drew near to the altar to receive the Eucharist, they mirrored the apostles who similarly approached Christ in the mosaic above.
Perhaps surprising to modern viewers, Christ actually appears twice in this image. The artists have employed a common medieval visual device known as continuous narration in an attempt to depict two moments within one scene: on the left, Christ offers the Eucharistic bread to six of the apostles; on the right, he offers the Eucharistic wine to six more apostles.
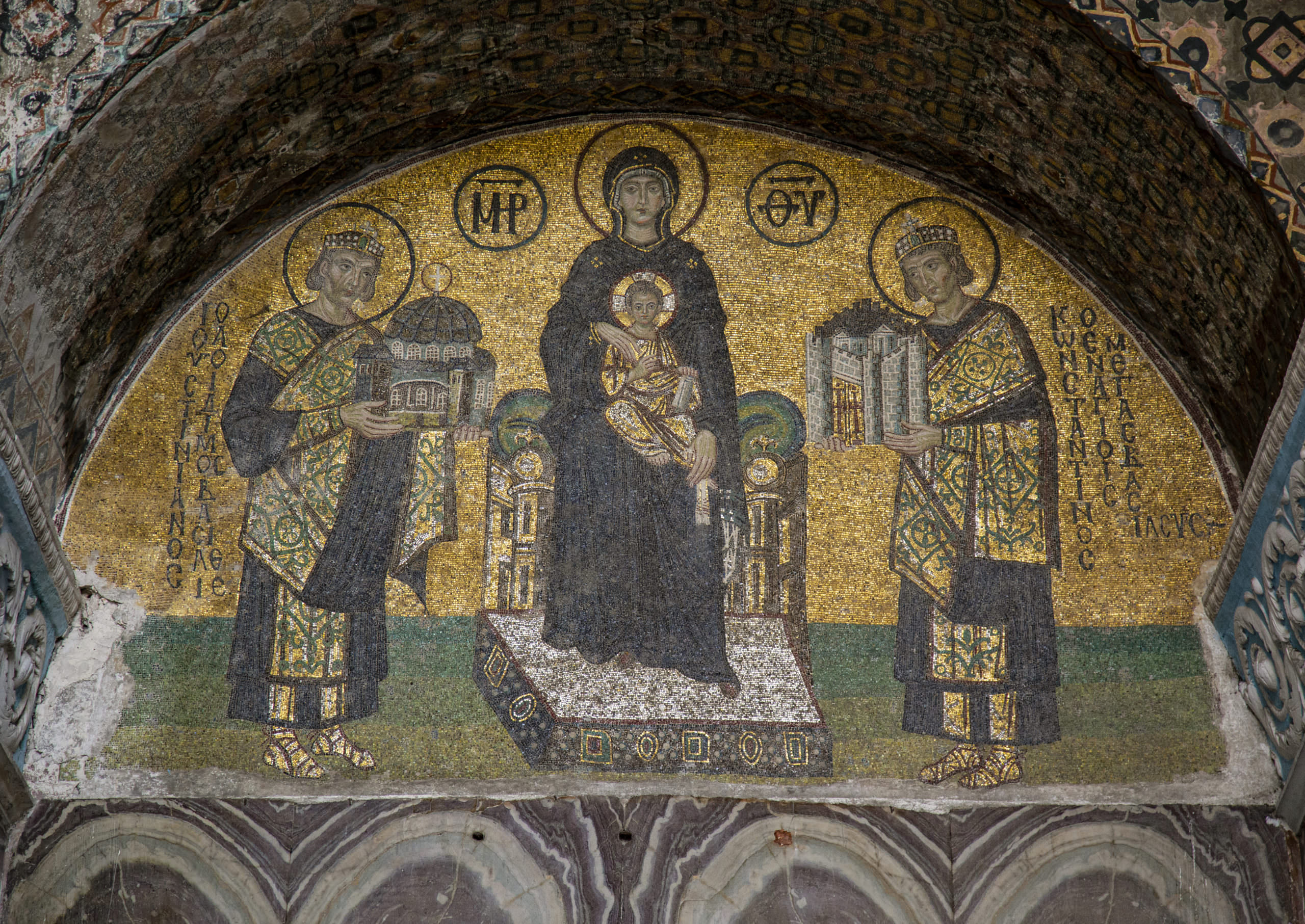

Lost frescoes
Badly damaged frescoes once depicted Vladimir’s son Yarloslav, his wife Irene, and their children. Yaroslav, now lost, was once shown offering a model of St. Sophia cathedral to Christ, much as the Byzantine emperors Constantine and Justinian offer models of Constantinople and Hagia Sophia to the Virgin and Child in a tenth-century mosaic in Hagia Sophia in Constantinople.
The fragmentation of Kievan Rus’
By the middle of the twelfth century, Kiev lost control over its expansive territories, and Kievan Rus’ fragmented into several smaller states, which sometimes fought amongst themselves. This fifteenth-century icon from Novgorod (a powerful city of Kievan Rus’, now located in Russia) depicts a battle in 1170 when forces from Suzdal (a city of Kievan Rus’, now located in Russia) laid siege to Novgorod (see map above). The main subject of this icon is itself another icon—in this case a miracle-working icon of the Virgin orans and Christ Child still preserved in Novgorod’s cathedral of St. Sophia—which, according to legend, played a pivotal role in the battle between Novgorod and Suzdal. This episode illustrates the importance that the holy images, or icons, of the Byzantine Empire came to play in the culture of Kievan Rus’, and later, Russia.
The icon is divided into three registers, in which the narrative of the battle unfolds from top to bottom. The top shows the people of Novgorod processing with the icon of the Virgin orans and Christ Child—a practice inherited from the Byzantines—into the fortified center of their city. The narrative unfolds from right to left. On the right, the clergy retrieve the sacred icon from the Church of the Savior on Elijah Street in the eastern part of the city. The clergy process through the middle of the scene and are received into the fortified center of the city where Novgorod’s cathedral of St. Sophia is located.
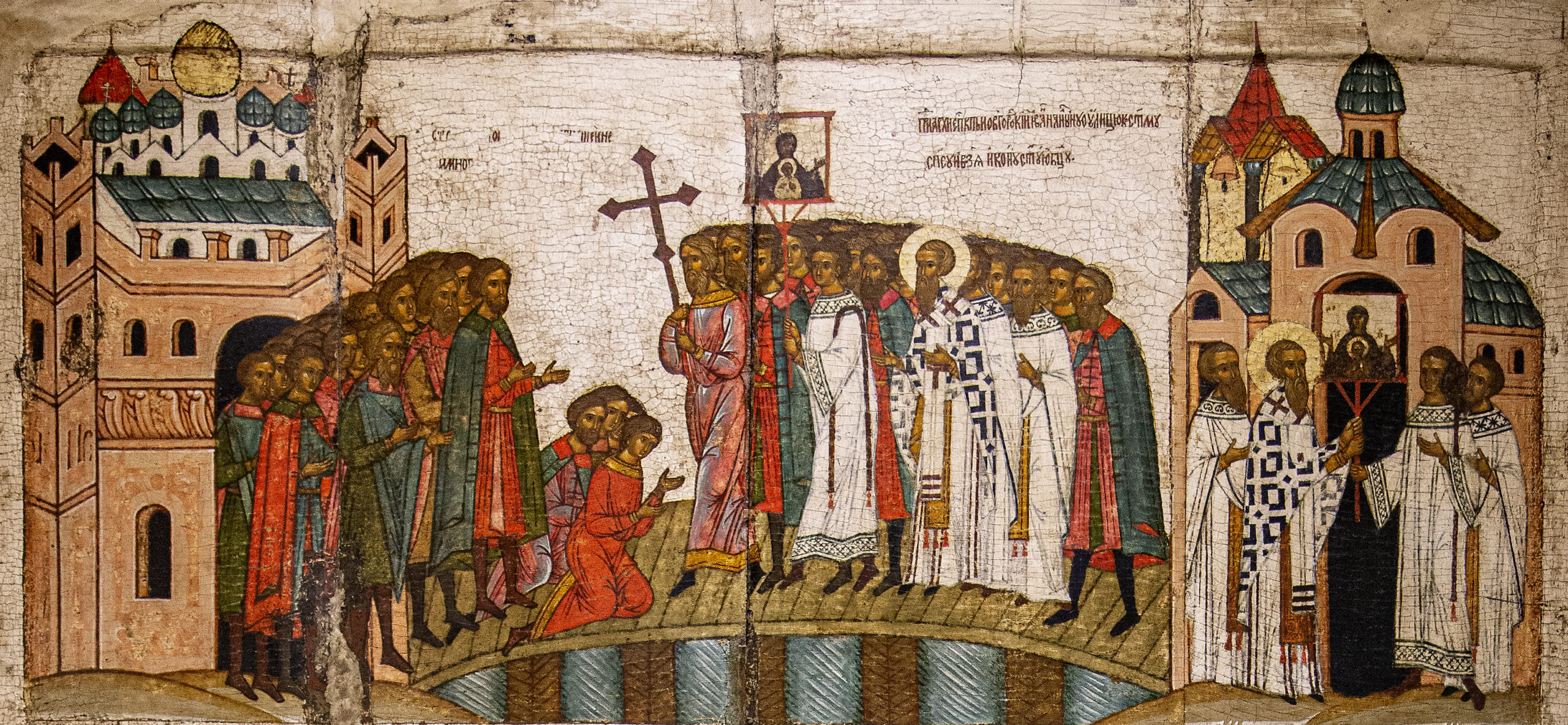
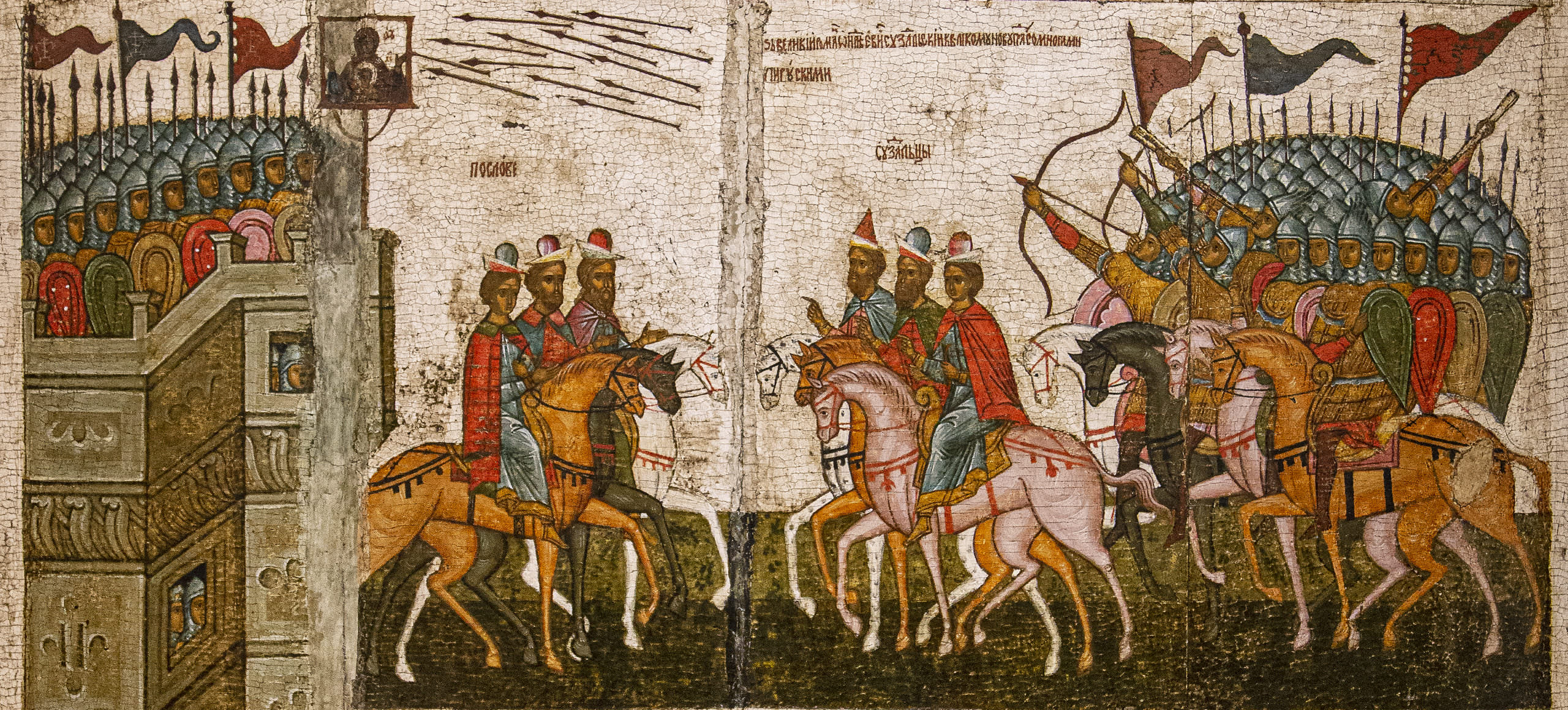




The Novgorodians affixed the icon of the Virgin and Child to the walls of their city as a protection against the army of Suzdal. In the middle register, the army of Suzdal attacks from the right. One of their arrows strikes the icon of the Virgin and Child on the walls of Novgorod, seen in the upper left. According to legend, this prompted the icon of the Virgin to turn inward toward the city of Novgorod and weep. A supernatural darkness then covered the attacking army of Suzdal, and as a result, the attackers began attacking each other.
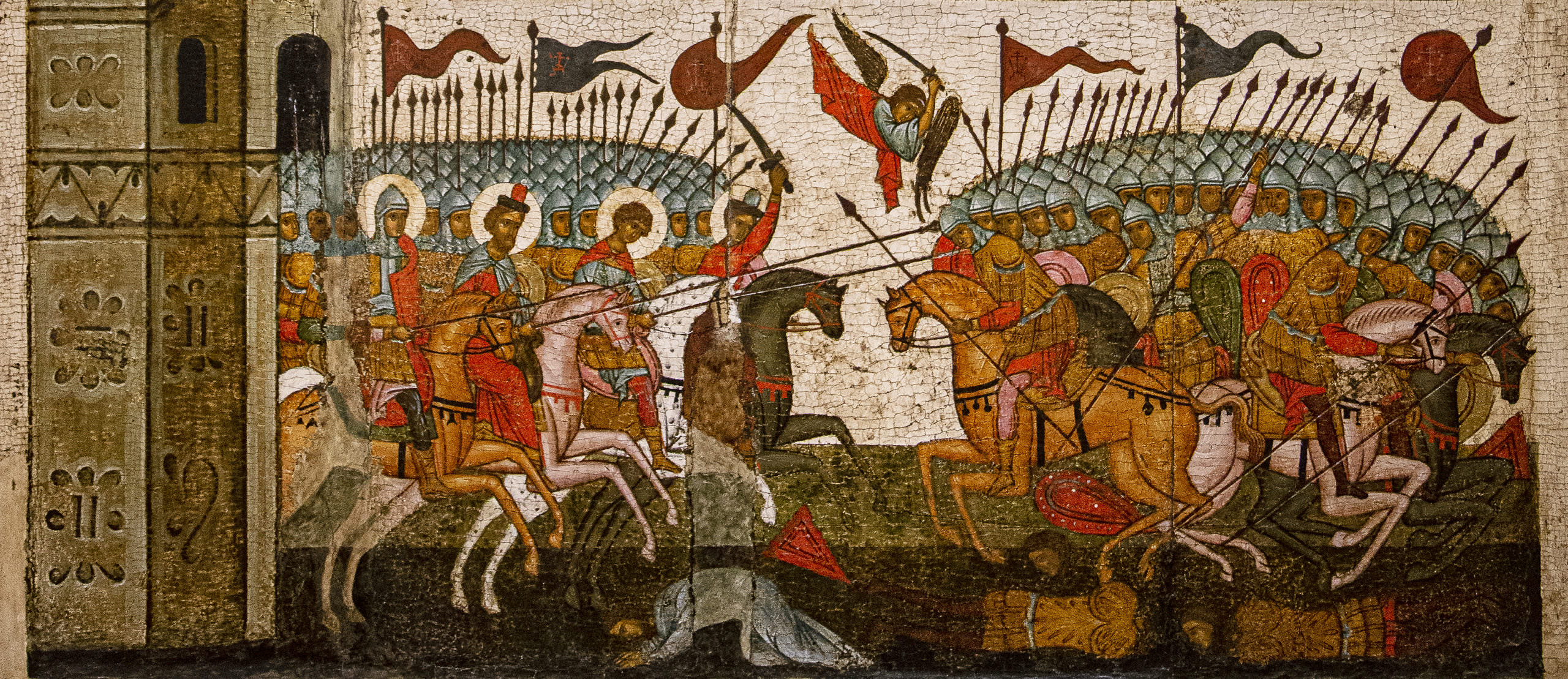

In the bottom register, the soldiers of Novgorod (left) triumphantly counterattack the army of Suzdal (right) with the help of the saints. The Archangel Michael—leader of the heavenly armies—swings his sword as he swoops down into the center of the scene. Additional haloed warrior saints gallop with the soldiers of Novgorod on horseback.
This icon and its subject illustrate the important role that the icons of Byzantium came to play in Kievan Rus’ and Russia. More specifically, the battle between Novgorod and Suzdal illustrates the power ascribed to the Virgin and her miracle-working icons and parallels similar accounts from the Byzantine capital of Constantinople. At the same time, this icon with the Battle of Novgorod and Suzdal illustrates how the people of Novgorod adapted the arts of Byzantium to tell their own stories, in this case, the local miracle of the defense of their city.
The rise of Moscow, “Third Rome”
In the middle of the thirteenth century, Kiev and many of its former territories fell to Mongol invaders, bringing an end to Kievan Rus’. But after two centuries of Mongol rule in the region, the city of Moscow emerged as a new center of power. Moscow was a latecomer among the older cities of Kievan Rus’, emerging in the twelfth century and gaining wealth and power in the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries. The Grand Duke of Moscow Ivan III “the Great,” who reigned as Grand Prince of Moscow from 1462–1505, achieved independence from the Mongols around 1480 and established Moscow as the center of what now became known as “Russia.”
But as Moscow ascended, the Byzantine Empire declined. Constantinople (today Istanbul) fell to the Ottomans (a Turkish dynasty whose name derived from their founder, Osman, and who ruled from the late 13th century until the establishment of the Turkish Republic in 1924) in 1453, ending the long history of the Eastern Roman Empire that had begun when emperor Constantine dedicated the capital city of Constantinople in 330, which he also referred to as “New Rome.” In the years that followed, Moscow increasingly viewed itself as successor to Byzantium and even began referring to itself as the “Third Rome.” [1] In 1472, Ivan III married Sophia Palaiologina, niece of the last Byzantine emperor, symbolically cementing the continuation of Byzantium in Russia.
Rublev’s Trinity
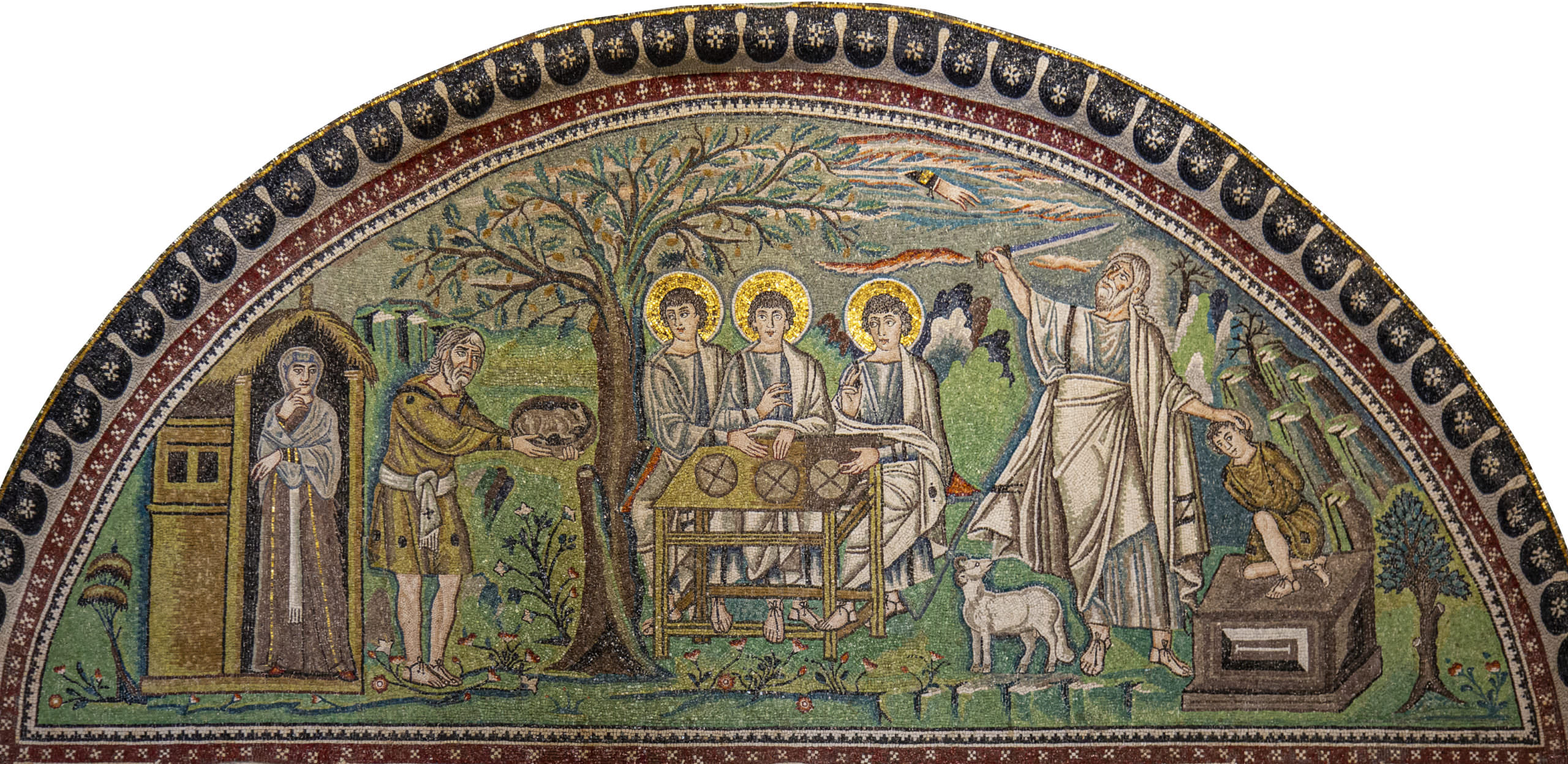
In addition to the Virgin of Vladimir, one of Russia’s best-known artworks—an icon of the Holy Trinity attributed to Andrei Rublev—dates from this period of Moscow’s ascent. Rublev was an influential Russian painter who probably lived from the 1360s until around 1430. Texts describe him painting the Cathedral of the Annunciation of the Moscow Kremlin with the Byzantine painter Theophanes the Greek, although these paintings no longer survive. (The Moscow Kremlin is the fortified historical center of the city of Moscow and contains several palaces and cathedrals. It remains Russia’s center of government today.) Rublev probably painted his icon of the Trinity for the Trinity Lavra of Saint Sergius in Sergiyev Posad, an important monastery near Moscow, where it was part of a church iconostasis (the barrier that separates the sanctuary from the rest of the church).
The harmonious colors and rhythmic contours of the symmetrical composition depict three angels who visited and were served food by the biblical patriarch Abraham and his wife Sarah in Genesis 18 in the Hebrew Bible or “Old Testament.” Christian theologians long interpreted this visitation of the three angels as an image of the Holy Trinity. Byzantine depictions of this event, as seen, for example, in the sixth-century mosaic at San Vitale, typically include both Abraham and Sarah, who play a central role in the biblical episode. But Rublev eliminated Abraham and Sarah from his icon, allowing the viewer to focus on the simplified composition of the three angels seated around an altar-like table. Rublev’s innovative icon reflects new Russian contributions to the Byzantine artistic tradition it inherited.


*
Contested legacies
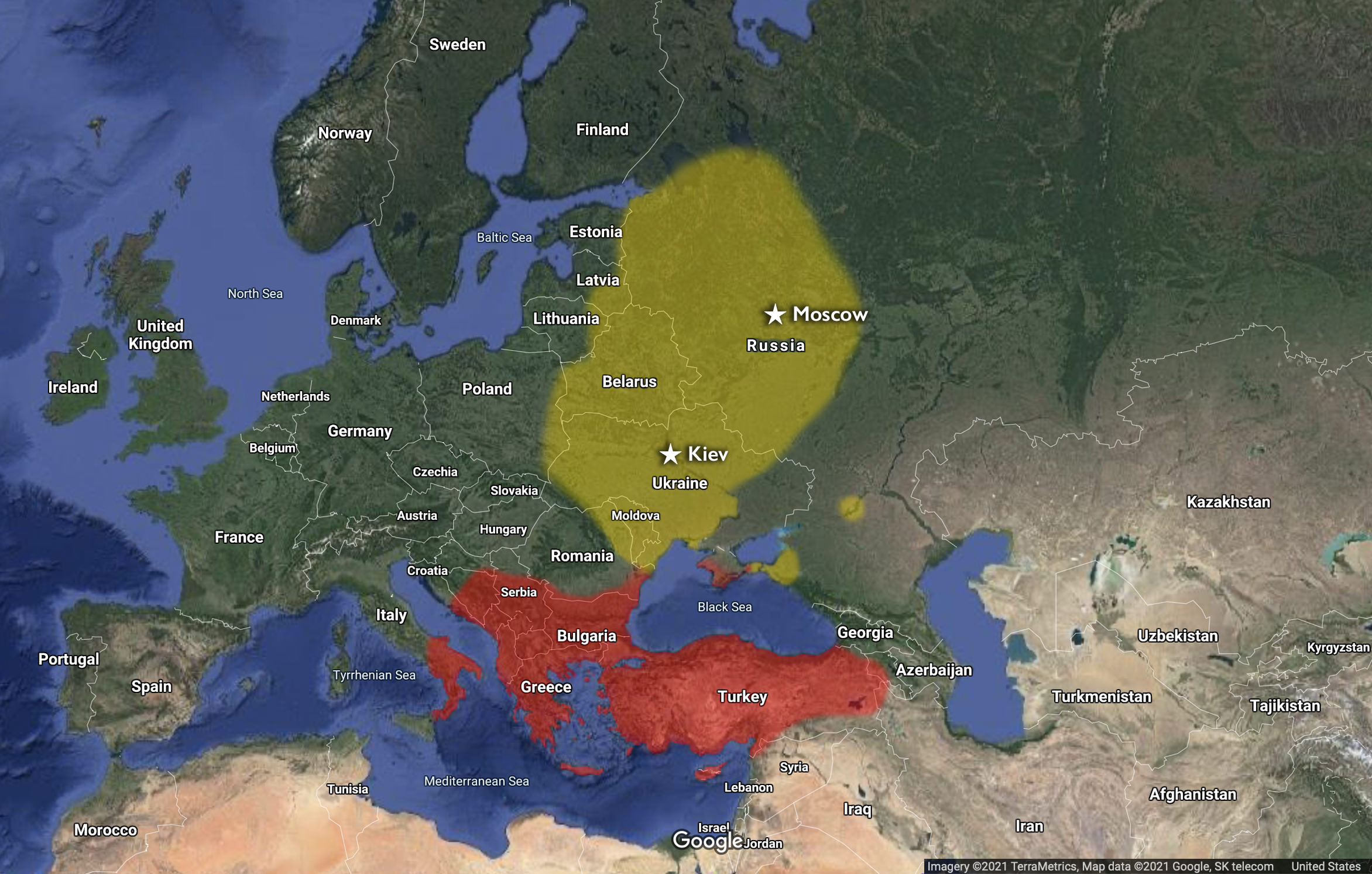
The Byzantine Empire and Kievan Rus’ do not survive, and their former territories are now divided among several states (as seen in the above map). Consequently, the legacies of Byzantium and Kievan Rus’ are often contested among these modern successor states, as the following two competing monuments illustrate.
In Moscow, Russia, the 2016 unveiling of a statue of the tenth-century prince Vladimir I of Kiev caused international consternation. Located in the shadow of the Kremlin—Russia’s center of government—the statue of prince Vladimir towers over Moscow at nearly sixty feet tall. Vladimir holds a monumental cross with his right hand while his left hand clutches a large sword.
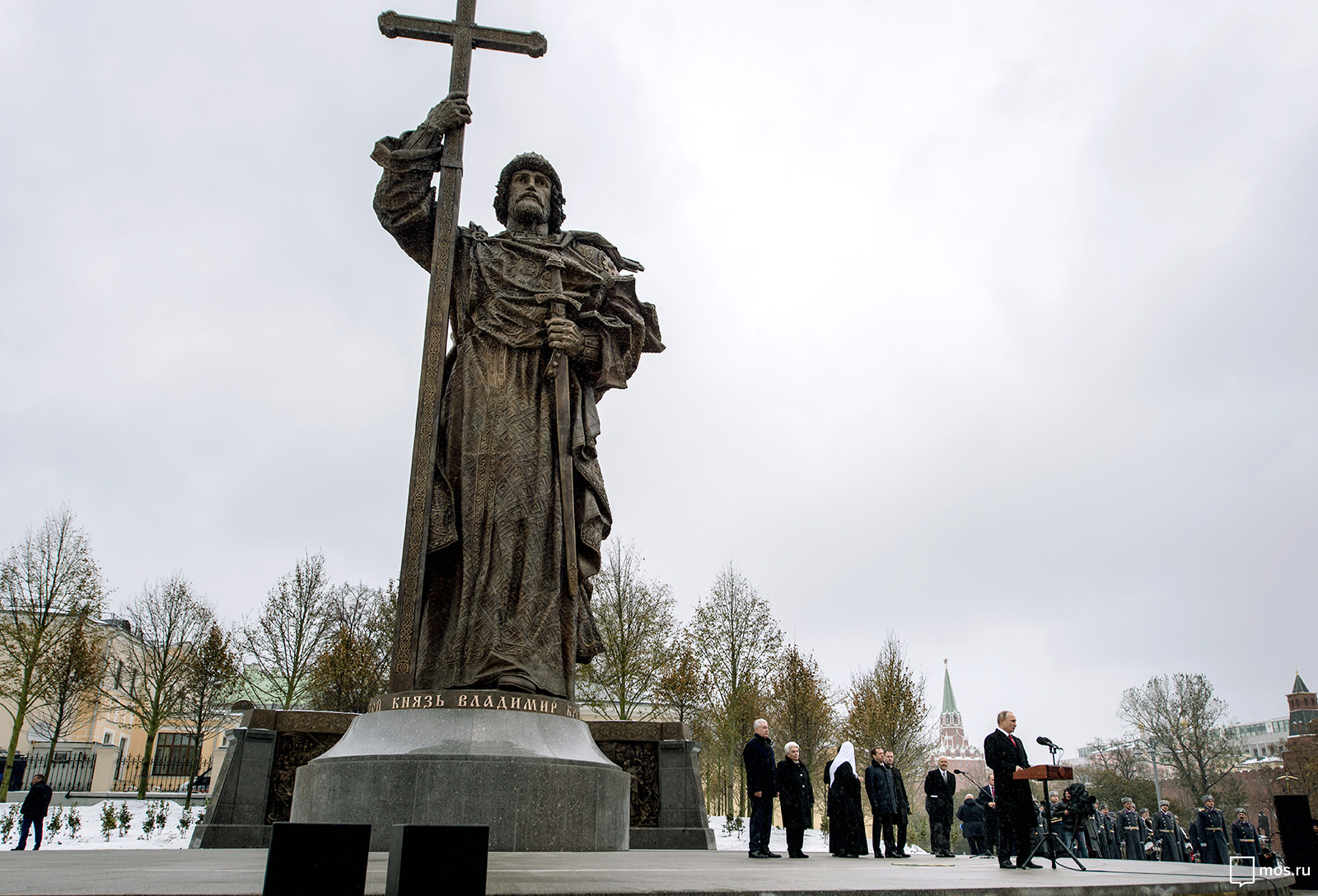

To many, Moscow’s menacing new prince Vladimir statue appears as a thinly veiled reference to the very similar, nineteenth-century statue of prince Vladimir that stands on the banks of the Dnieper River in Kiev, Ukraine, the site of the baptism of Kievan Rus’ into the Christianity of the Byzantines in the tenth century. The timing of Moscow’s installation of the new statue of prince Vladimir in 2016 was also significant: it coincided with Russia’s recent annexation of Crimea and ongoing armed conflict with Ukraine.
By installing the new statue of prince Vladimir in its capital, Russia seemed to lay claim to the historical legacy and perhaps even the former territories of Kievan Rus’, even while some of those territories are part of other states, such as Ukraine.
While the Virgin of Vladimir, St. Sophia in Kiev, and other works of art and architecture tell the story of the conversion of Kievan Rus’ to the Christianity of the Byzantine Empire and the subsequent rise of Moscow as a new center of power, these more recent monuments speak to the enduring, if contested, legacies of Byzantium and Kievan Rus’ in our world today.

Notes:
[1] The monk Philotheus (or Filofei) of Pskov first described Moscow as “third Rome” in a letter in 1510.
Additional resources
TED-Ed, Where did Russia come from? – Alex Gendler <https://youtu.be/lfe1wEQzSzM>
Helen C. Evans, ed., Byzantium: Faith and Power (1261–1557) (New York: The Metropolitan Museum of Art, 2004)
Simon Franklin, “Rus’,” in The Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium, vol. 3, ed. Alexander P. Kazhdan, et al., (Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press, 1991), 1818–1820
Liz James, Mosaics in the Medieval World: From Late antiquity to the Fifteenth Century (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2017)
Martin Gilbert, The Routledge Atlas of Russian History, fourth edition (London and New York: Routledge, 2013)
Neil MacFarquhar, “A New Vladimir Overlooking Moscow,” The New York Times, 4 November 2016.
Neil MacFarquhar, “Another Huge Statue in Russia? Not Rare, but Hugely Divisive,” The New York Times, 28 May 2015.
Janet Martin, Medieval Russia, 980-1584, second edition (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2007)
Olenka Z. Pevny, “Kievan Rus’,” in The Glory of Byzantium: Art and Culture of the Middle Byzantine Era A.D. 843-1261, ed. Helen C. Evans and William D. Wixom (New York: The Metropolitan Museum, 1997), pp. 280–287.
Christian Raffensperger, “Rus: A Brief Overview,” Mapping Eastern Europe <https://mappingeastern europe.princeton.edu/item/rus-a-brief-overview.html>
