13

Greek Prepositions
Prepositions in Greek for the most part work as they do in English (S 1636 ff.). The principal difference is that the object of a Greek preposition must be inflected in either the genitive, dative, or accusative case. The preposition together with its object is called a PREPOSITIONAL PHRASE.
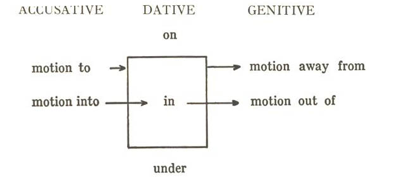
The original or core meaning of Greek prepositions often indicates DIRECTION. This chart shows the directions that each case generally indicates:
Three prepositions illustrate this dynamic. Note that these three have no accent.
- εἰς or ἐς + acc. into
- εἰς τὸ στόμα into the mouth
- ἐν + dat. in
- ἐν τῷ στόματι in the mouth
- ἐκ + gen. from, out of
- ἐκ τοῦ στόματος out of the mouth
- ἐκ becomes ἐξ before a vowel:
- ἐξ αἵματος out of blood
Accents, Elision, and Aspiration
Prepositions – with the exception of εἰς, ἐν, and ἐκ – normally have an ACUTE accent. If the preposition has two syllables, the acute falls on the ULTIMA.
ELISION is common with prepositions; they frequently drop their final vowel before a word beginning with a vowel. In such cases, the preposition has NO ACCENT. There are two important exceptions: περί and πρό. Neither allows for elision.
After a preposition drops its final vowel, if it then ends in a STOP CONSONANT, that consonant becomes ASPIRATED if the following word begins with an aspirated – i.e., marked with a rough breathing – vowel or diphthong.
- ἀπὸ τῆς ἐλπίδος
- from the hope
- ἀπ’ ἐλπίδος
- from hope
- ἀπὸ τοῦ αἵματος
- from the blood
- ἀφ’ αἵματος
- from blood
Prepositions + Accusative Case
- ἀμφί around, about
- ἀνά up, through
- διά because of, through
- εἰς/ἐς into
- ἐπί against
- κατά down, along, according to
- μετά after, behind
- παρά to, throughout, beside
- περί near, around
- πρός toward
- ὑπέρ above, over, beyond
- ὑπό under
Prepositions + Dative Case
- ἀμφί around, near
- ἀνά upon
- ἐν in
- ἐπί on, for the purpose of, because of
- παρά with, near
- περί about
- πρός by, in addition to
- σύν with (the help of)
- ὑπό under
Prepositions + Genitive Case
- ἀμφί around, for the sake of
- ἀντί opposite, instead of, for the sake of
- ἀπό from
- διά through
- ἐκ from
- ἐπί on, at
- κατά down, against
- μετά with
- παρά from
- περί about
- πρό before, in front of
- πρός toward, (swear) by
- ὑπέρ over, on behalf of
- ὑπό under, by
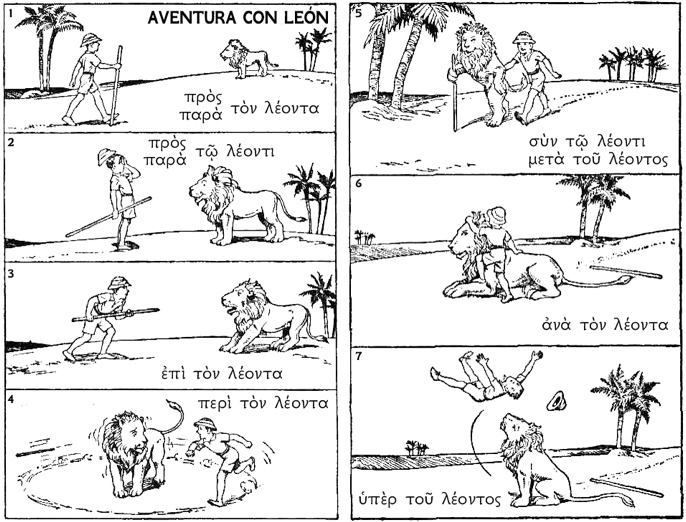
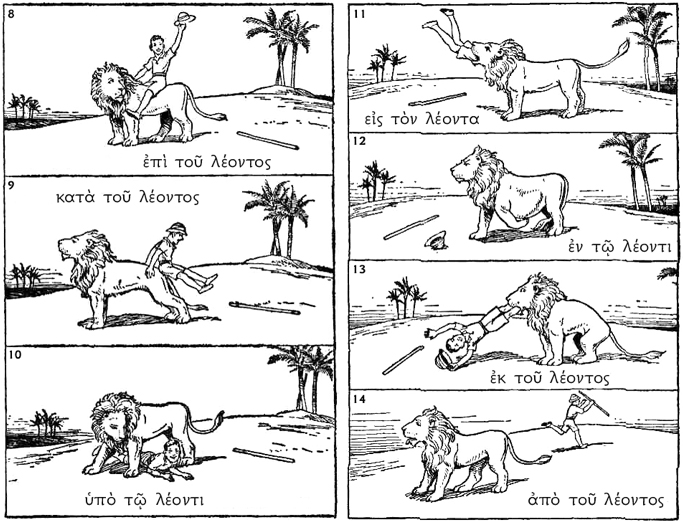
The Man and the Lion
Note the following story of a man and a lion (ὁ λέων, λέοντος), which illustrates well some of the most common prepositions and their cases.
Prepositions as Prefixes
Prepositions often double as prefixes for verbs. The core meanings of the most common prefixes are as follows.
- ἀμφί around
- ἀνά up
- ἀντί back
- ἀπό from
- διά through
- εἰς into
- ἐκ out of
- ἐν in
- ἐπί on
- κατά down
- μετά with
- παρά beside, to
- περί around
- πρό before
- πρός toward
- σύν with
- ὑπέρ above
- ὑπό under
Prefixes, Elision, and Aspiration
When prefixes are attached to verbs, any final vowel drops out – or ELIDES – if the tense stem to which it is added begins with a vowel. As with prepositions, the prefixes περί and πρό are an exception to this rule, and do not elide. If a prefix drops its final vowel, the remaining consonant becomes ASPIRATED if the tense stem begins with an aspirated vowel or diphthong.
We have encountered in earlier lessons some verbs that have prefixes. Note the changes that occur to the prefixes in some of these examples.
- ἀνίστημι (ἀνα + ἵστημι) raise, appoint
- ἀποδίδωμι (ἀπο + δίδωμι) give back
- ἀφίημι (ἀπο + ἵημι) let go, allow, forgive
- ἐπιτίθημι (ἐπι + τίθημι) put on
- καθίστημι (κατα + ἵστημι) set down, establish
- παραδίδωμι (παρα + δίδωμι) hand over, deliver
- πάρειμι (παρα + εἰμί) be present
- παρίστημι (παρα + ἵστημι) present
- προστίθημι (προς + τίθημι) add to
ἐν, ἐγ-, ἐμ- in
σύν, συγ-, συμ-, συλ- with
When the prepositions ἐν and σύν are used as prefixes, they retain these forms when the verb begins with a vowel. When the verb begins with a consonant, they ASSIMILATE with this consonant.
- They retain their form (ἐν– and συν–) before a dental (τ, δ, θ)
- They become ἐμ– and συμ– before a labial (π, β, φ, ψ)
- They become ἐγ– and συγ– before a palatal (κ, γ, χ, ξ)
- συν becomes συλ– before λ.
For example:
- ἐν + βάλλω throw
- ἐμβάλλω throw in; hand in
- σύν + λαμβάνω take
- συλλαμβάνω collect; gather together
- ἐν + ἐργέω work
- ἐνεργέω be in action; be efficient; operate
– τὸ τέλος –
Key Terms and Concepts
- PREPOSITIONAL PHRASE
- THE “DIRECTION” OF CASES
- GENERAL RULES FOR ACCENTS OF PREPOSITIONS
- ELISIONS AND PREPOSITIONS
- ASPIRATION OF PREPOSITIONS
- ELISION OF PREFIXES
- ASPIRATION OF PREFIXES
- CONSONANT ASSIMULATION OF ἐν– AND συν–
Vocabulary List 1
Prepositions + Accusative Case
- ἀμφί around, about
- ἀνά up, through
- διά because of
- εἰς/ἐς into
- ἐπί against
- κατά down, along, according to
- μετά after, behind
- παρά to, throughout, against
- περί near, around
- πρός toward
- ὑπέρ above, over, beyond
- ὑπό under
Vocabulary List 2
Prepositions + Dative Case
- ἀμφί around, near
- ἀνά upon
- ἐν in
- ἐπί on, for the purpose of, because of
- παρά with, near
- περί about
- πρός by, in addition to
- σύν with (the help of)
- ὑπό under
Vocabulary List 3
Prepositions + Genitive Case
- ἀμφί around, for the sake of
- ἀντί opposite, instead of, for the sake of
- ἀπό from
- διά through
- ἐκ from
- ἐπί on, at
- κατά down, against
- μετά with
- παρά from
- περί about
- πρό before, in front of
- πρός toward, (swear) by
- ὑπέρ over, on behalf of
- ὑπό under, by
Vocabulary List 4
Prepositions as Prefixes
- ἀμφί around
- ἀνά up
- ἀντί back
- ἀπό from
- διά through
- εἰς into
- ἐκ out of
- ἐν in
- ἐπί on
- κατά down
- μετά with
- παρά beside, to
- περί around
- πρό before
- πρός toward
- σύν with
- ὑπέρ above
- ὑπό under
Exercises
Ι. Some Greek prepositions can only take one case, some two, others three. Rewrite the Greek preposition vocabulary, this time organized by the number of possible cases each can take. Besides each preposition, list its English definition and the case. In other words, your new list should look as follows.
- Prepositions that take only one case: ἀντί, instead of, for the sake of (genitive), etc.
- Prepositions that take only two cases: διά, because of, through (accusative), through (genitive), etc.
- Prepositions that take three cases: ἐπί, against (accusative), on, for the purpose of, because of (dative), on, at (genitive), etc.
ΙΙ. Using an etymological dictionary (such as this one), list an English derivative for each Greek prefix in Vocabulary List 4. For example: ἀμφί: amphitheater. Note: there is one prefix that does NOT have a common English derivative. Which is it?
III. Practice filling out a blank “Man and the Lion” preposition sheet. A completed one is available here: lion preposition worksheet. A blank one is available here: lion preposition practice.