8 Glenohumeral Arthritis
Glenohumeral arthritis is defined by shoulder pain and stiffness from damage to the articulation between the humeral head and the glenoid process of the scapula. This arthritis may be idiopathic (osteoarthritis), or from autoimmune synovial inflammation (rheumatoid arthritis). Other known causes include trauma (including microtrauma from altered biomechanics or rotator cuff tears), gout, osteonecrosis, neuropathy (Charcot Arthropathy) and infection.
Structure and Function
The glenohumeral joint is a ball and socket joint made by the articulation of the humeral head in the glenoid fossa of the scapula.
With little bony constraint, the joint is the most mobile joint in the body and consequently, inherently unstable. The joint is stabilized by static and dynamic restraints. The static restraints consist of the three glenohumeral ligaments and the glenoid labrum. The dynamic restraints consist of the rotator cuff muscles, the rotator interval, and the tendon of the long head of the biceps.
The glenohumeral joint has three degrees of freedom and functions to perform the following movements at the glenohumeral articulation: flexion/extension; adduction/abduction; and internal and external rotation. Forward flexion is also known as “elevation”, and adduction is also known as “cross body abduction” or “horizontal abduction” (See figures 1 -4).




Glenoid version refers to the relationship between the glenoid cavity and the humeral head. It is a radiographic measurement determined by the angle between the glenoid line and the line perpendicular to the scapular axis. The glenoid is normally slightly retroverted. In addition, the humeral head and neck are also retroverted from the humeral shaft (with the anterior plane defined by the position of the humeral epicondyles at the elbow). Normal humeral version is 20-30° of retroversion. Deviations from normal version can disturb normal mechanics and lead to arthritic changes.
In glenohumeral arthritis, the articular cartilage of the humeral head or glenoid or both is damaged. As in the arthritis of many other joints, glenohumeral arthritis can affect the subchondral bone as well.
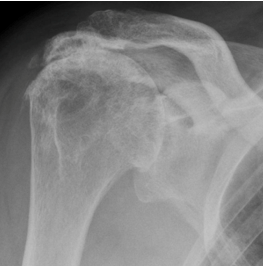
The most common etiology of glenohumeral arthritis is primary osteoarthritis (OA). OA is characterized by progressive degeneration of articular cartilage, dense subchondral bone growth, osteophyte formation, glenoid erosion, and displacement of the humeral head.
Additional Causes of Glenohumeral Arthritis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) – Systemic autoimmune disease of the synovium. Synovial inflammation and soft tissue break down at the shoulder results in wear of the glenoid articular cartilage and medialization of the humeral head.
- Post-traumatic arthritis – Disruption of the articular surface can occur after a humeral fracture or dislocation. The damage with dislocation can be from the impact of the dislocation episode or from microtrauma inflicted by chronic instability.
- Crystalline arthritis – Gout and Calcium Pyrophosphate Dihydrate Deposition Disease (CPPD) result in the deposition of crystals within the joint space which cause synovial inflammation and resultant cartilage damage.
- Osteonecrosis – Morphological and arthritic changes result from loss of blood supply to the humeral head. Osteonecrosis can appear from trauma, use/abuse of alcohol or steroids, hemoglobinopathies, among other causes. It may also be idiopathic (no known cause).
- Charcot Arthropathy – Loss of sensation and proprioception in the joint results in repetitive microtrauma and joint degeneration. Charcot Arthropathy of the shoulder is often related to cervical spine syrinx.
- Rotator cuff arthropathy – Tears of the rotator cuff tendons disturb normal biomechanics (as the rotator cuff is an important shoulder stabilizer). Such tears produce abnormal humeral head contact, leading to breaking down of the articular surfaces.
- Septic Arthritis – The white cell response to infection can damage articular cartilage.
*
Patient Presentation
Patients with glenohumeral arthritis present with shoulder pain and stiffness. Taking a thorough history with these patients is key as it can determine the etiology of the disease.
The clinical presentation depends on the underlying cause of the arthritis.
Patients with glenohumeral osteoarthritis are typically over 50 years old and present with a chief complaint of pain. The pain is usually insidious in onset, progressive, chronic, and worsens with activity. Discomfort may lead to nocturnal awakening, especially when lying on the affected side, and patients typically have functional limitations due to a decreased range of motion. On physical exam, the affected extremity may be atrophic secondary to disuse. Patients have tenderness over the posterior joint line and crepitus with motion of the joint. The most dramatic finding is typically decreased range of motion which is most pronounced with external rotation.
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis present with pain, decreased range of motion, crepitation, and effusions in multiple joints. The effects typically evolve slowly and insidiously. The shoulder is rarely the first joint affected and it is almost never the only affected joint.
In cuff tear arthropathy, patients are usually significantly disabled and are unable to raise their affected arm. Inspection may show hollowing around the scapula secondary to cuff muscle atrophy.
A number of other disease processes, including osteonecrosis, recurrent glenohumeral dislocations, and posttraumatic articular incongruity can lead to destruction of the glenohumeral articular cartilage. In most cases, this results in secondary osteoarthritis and has symptoms similar to primary osteoarthritis although the history will suggest this secondary cause.
Of note, septic arthritis may hurt even without motion, but symptoms are worsened with activity.
Objective Evidence
Imaging of the glenohumeral joint starts with radiographs taken at three views: AP, lateral and scapular (also known as a “Y”) view. Findings on these radiographs often lead to the etiology of the arthritis (Figure 5).
Advanced imaging such as CT and MRI are indicated for pre-operative planning as they provide the surgeon with enhanced imaging of glenoid morphology and rotator cuff pathology.
For the most part, no laboratory tests are necessary for the diagnosis of glenohumeral arthritis. However, if an inflammatory or crystalline arthropathy is suspected, specific labs may be indicated. Namely, ESR, CRP, Rheumatoid factor, and Anti-CCP antibodies for RA and synovial fluid analysis for crystalline arthropathies.
Epidemiology
Arthritis of the glenohumeral joint typically affects patients in the sixth decade of life and on. Of the large joints, the glenohumeral joint trails the hip and knee in the incidence of arthritis–perhaps because a person can avoid using his or her shoulder in a way not possible with the weight bearing joints. Yet because of this relative underuse potential, the true incidence of glenohumeral arthritis remains undetermined.
Differential Diagnosis
Shoulder pain with decreased mobility is a common presentation. After the clinician has determined the shoulder pain to be glenohumeral in origin, the following diagnoses, in the alternative, or in addition to arthritis should be considered:
- Rotator cuff impingement and tendinopathy,
- Rotator cuff tear,
- Adhesive capsulitis,
- Shoulder instability with or without bony or labral damage,
- Locked posterior dislocations in elderly patients.
Clinically, these injuries can appear identical to glenohumeral arthritis and radiographic studies are needed to determine the etiology of the shoulder pain.
Of note, rotator cuff tears have a 5-10% incidence with osteoarthritis of the glenohumeral joint and a 25-50% incidence with rheumatoid arthritis.
Red Flags
Arthritis of the glenohumeral joint is a chronic condition that rarely requires emergency treatment. However, a patient who presents with fever, chills, and fatigue in addition to pain, swelling, warmth, and erythema of the shoulder should be promptly evaluated for a septic shoulder. Exuberant arthritis limited to just the shoulder(s) should prompt a cervical examination for a syrinx.
Shoulder pain might be caused by lung cancers in the superior aspect of the lung (so-called Pancoast tumors). This should not be missed when reviewing the radiographs.
Treatment Options and Outcomes
Mainstays of non-operative treatment for glenohumeral arthritis consist of physical therapy, NSAIDs, activity modification, and injections. NSAIDs reduce pain and inflammation, while physical therapy works to improve range of motion and strengthen the surrounding musculature.
RA can be very well controlled with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARD). Intraarticular injections of corticosteroids act to reduce inflammation. However, arthritis is a progressive disease and medical treatment exhausts quickly.
End stage degenerative joint disease can be treated with joint replacement: Hemiarthroplasty; Total Shoulder Arthroplasty; and Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty.
Hemiarthroplasty
A hemiarthroplasty involves replacing the humeral head with a stemmed prosthesis. It is indicated for patients who have failed non-operative treatment with an intact glenoid and articular damage to the humerus. The best results are seen in patients with concentric glenoids and intact rotator cuffs. This operation is technically easier than adding a glenoid replacement, but usually provides less symptomatic relief. Hemiarthroplasty is also used to treat fracture of the humeral head.
Total Shoulder Arthroplasty
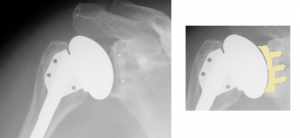
In a total shoulder arthroplasty, the arthritic humeral head is replaced with a metal ball fixed to a stem inserted into the humeral shaft and the glenoid is resurfaced with a polyethylene insert (Figure 6). This procedure is best for patients with a moderate to low activity level. Patients need good bone stock and an intact or repairable rotator cuff. Patients treated with total shoulder arthroplasty see good pain relief and reliable range of motion with a 10-year survival rate of 92-95%. Common complications include component loosening, infection, fracture nerve injury, and rotator cuff tear.
Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty
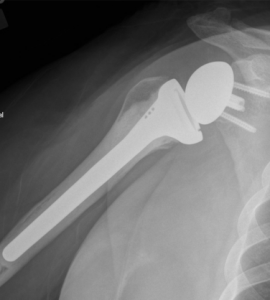
In a reverse shoulder arthroplasty, the glenoid socket is replaced with a metal ball and secured to the scapula and the humeral head is replaced with a cup attached to a stem which functions as a socket (Figure 7). This is the opposite anatomic arrangement of the native glenohumeral joint. This arrangement provides stability in the absence of a functioning rotator cuff. It is indicated for rotator cuff arthropathy, severe proximal humerus fractures, failed total shoulder arthropathy, and glenohumeral deformities that cannot be reconstructed otherwise. This operation can dramatically increase the function of the shoulder and provide excellent pain relief.
Shoulder Arthrodesis
An arthrodesis involves the surgical resection and fusion of the glenohumeral joint. This operation is indicated for laborers unwilling to alter their activities, uncontrolled joint sepsis, recurrent shoulder instability, loss of rotator cuff and deltoid musculature, brachial plexus plexopathies, and salvage for failed total shoulder arthroplasty. Because there is a lot of motion between the scapula and thorax, this operation is tolerated better than an analogous fusion of the hip joint. Nonetheless, most patients are happier with a joint replacement.
Risk Factors and Prevention
Age is one of the primary risks for the development of glenohumeral arthritis. Females display higher incidences of both OA and RA. Glenohumeral arthritis is associated with activities that put high strain on the glenohumeral joint. However, many patients develop arthritis of the shoulder without a decipherable cause.
Lifting heavy weights, either at work or for recreation, increases the chances of developing glenohumeral osteoarthritis.
The incidence of glenohumeral arthritis increase with a history of trauma and prior surgery to the shoulder. Certain studies have shown that over 50% of patients with a primary anterior shoulder dislocation go on to develop some degree of glenohumeral arthritis at 25 years follow-up.
Miscellany
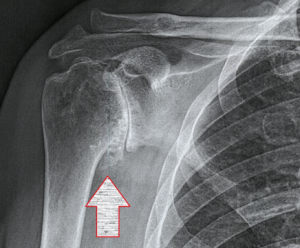
The characteristic osteophyte of glenohumeral arthritis is termed a goat’s beard (Figure 8).
Key Terms
Glenohumeral arthritis, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, articular cartilage, arthroplasty
Skills
Recognize and describe the deformities of the glenohumeral joint caused by arthritis. Recognize the potential etiologies of glenohumeral arthritis. Recognize the clinical and radiographic signs of glenohumeral arthritis. Describe the different treatment modalities for glenohumeral arthritis.
