Netspeak
Introduction
Netspeak (https://netspeak.org/) is a search engine designed to help you to express yourself in a foreign language by providing you with insight into how common native speakers use certain phrases. Netspeak is a useful tool for increasing lexical diversity and checking accuracy in writing.
Overview of different search functions in Netspeak
Video tutorial
In the following video tutorial, different search functions in Netspeak will be demonstrated step-by-step. Be sure to make use of the bookmark icon at the bottom left of the video to jump to different sections ![]() .
.
Textual tutorial
The following eight examples illustrate how you can use Netspeak to query phrases. Jump to different sections that interest you.
1. Find one word
2. Find two or more words
3. Find any number of words
4. Compare words
5. Compare phrases
6. Find the best synonym
7. Find the best order
8. Advanced search
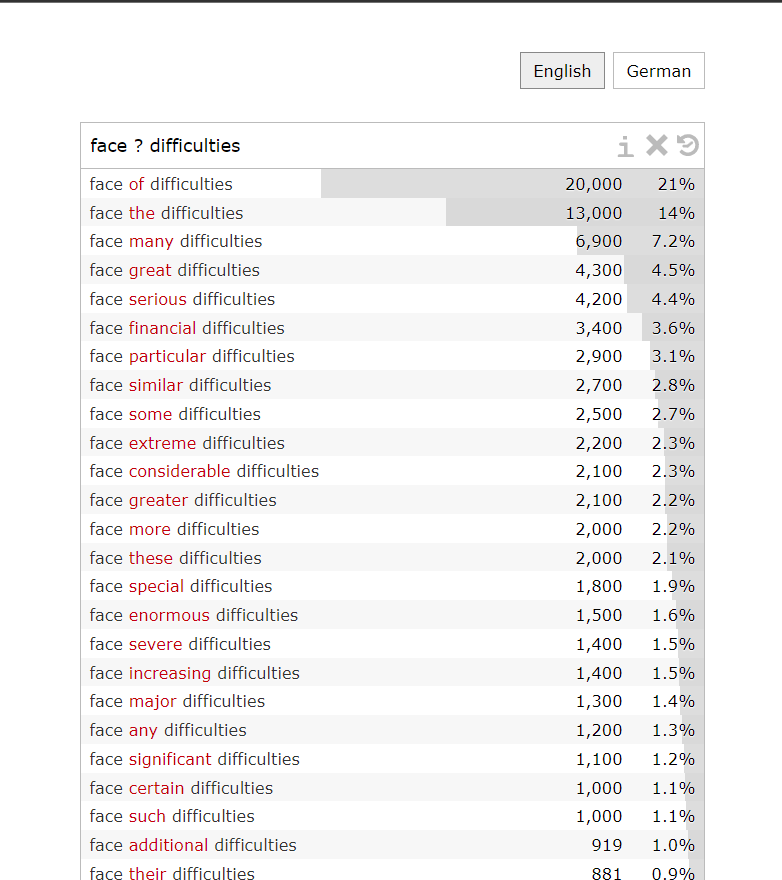
1. Find one word: You can use a question mark “ ? ” in your query to search for a missing word. For example, if you type in “face ? difficulties” (note space), the search results will show the number of times that this phrase appears and the percentage of frequency.
You can also click on the phrase to see the sentences taken from corpora. Take “face increasing difficulties” as an example, you can check the source by clicking [Google Books] to see the target word/phrase in it.
↑ Back to textual tutorial list
2. Find two or more words: You can use two or more question marks “ ? ? ” to find as many words for them. For example, if you type in “face ? ? difficulties” (note space), the search results will show the number of times that this phrase appears and the percentage of frequency.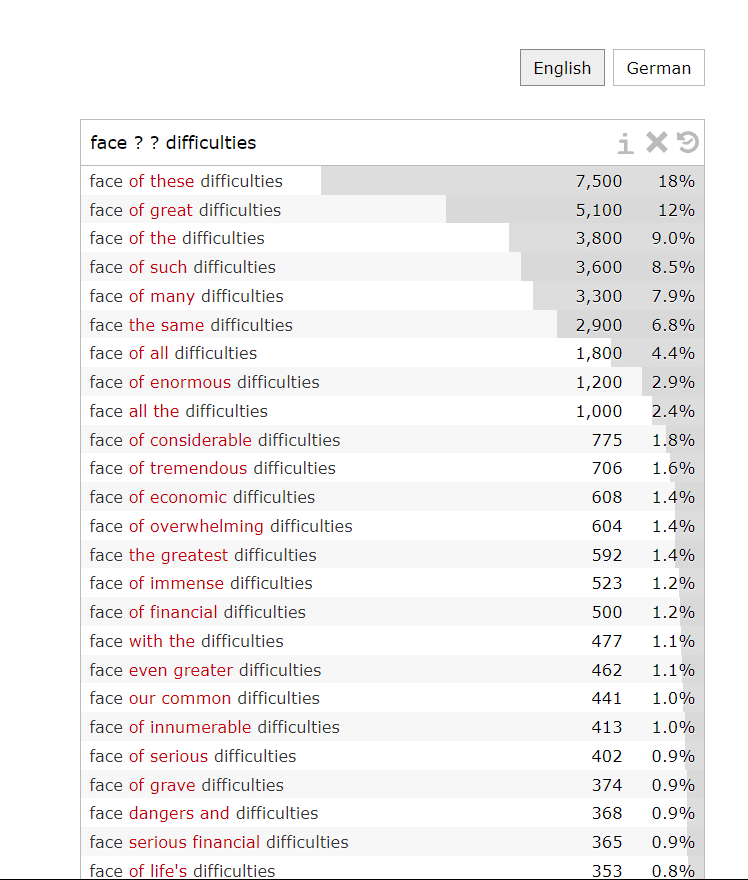 ↑ Back to textual tutorial list
↑ Back to textual tutorial list
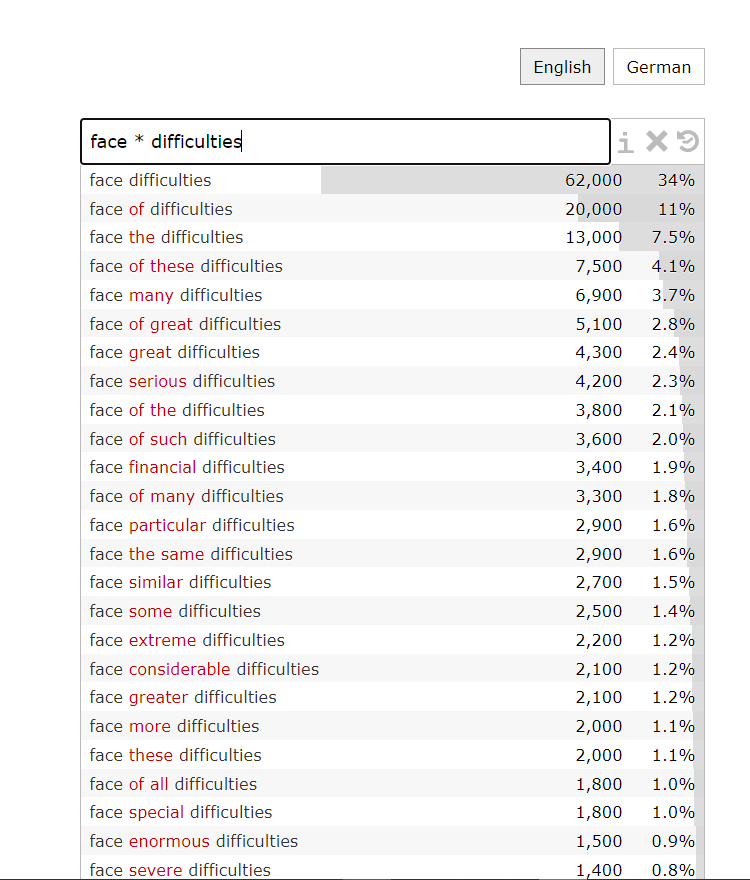
3. Find any number of words: You can use ellipsis dots “ … ” or asterisk “ * ” to find any number of words. For example, you can type in “face … difficulties” (note space) to get phrases such as “face of difficulties”, face of great difficulties” and the percentage of their frequency. You can get the same result by typing in “face * difficulties”.
↑ Back to textual tutorial list
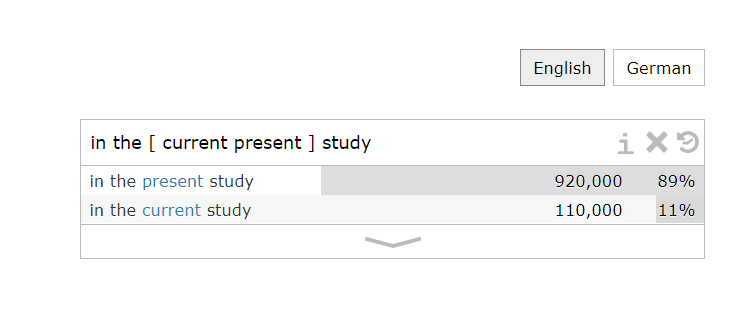
4. Compare words: You can use square brackets “ [ ] ” to compare words or to check which of two or more words is most common. For example, if you want to know “in the current study” and “in the present study” which is more commonly used, you can type in “in the [current present] study”, the search results will show the number of times each phrase appears and the percentage of frequency. We can know that “in the present study” is more commonly used.
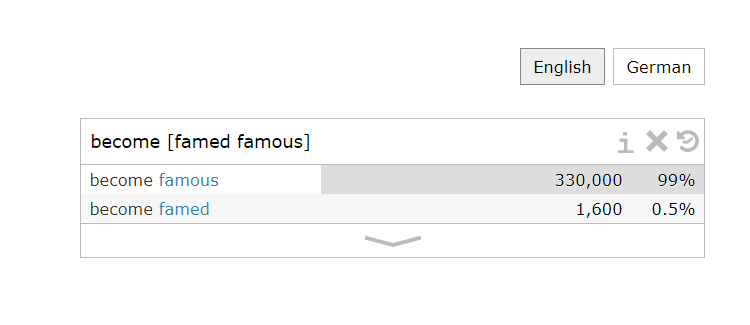
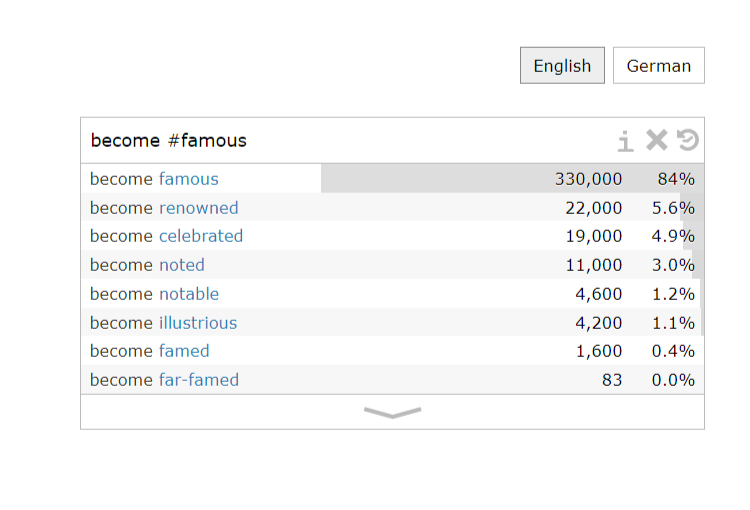
You can also type in “become [famed famous]” to know that the more frequently used one is become famous.
↑ Back to textual tutorial list
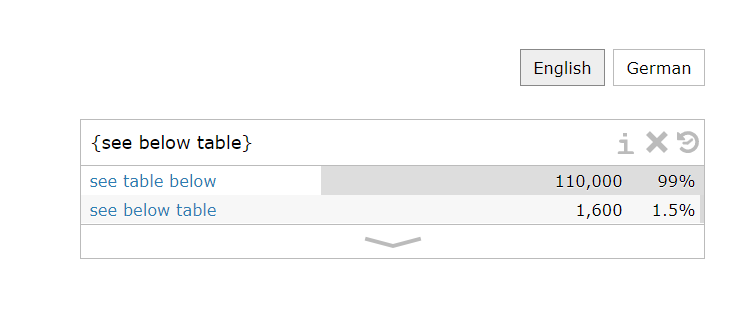
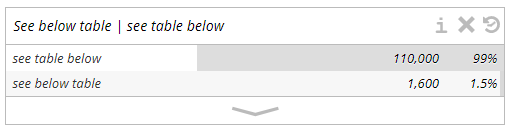
5. Compare phrases: You can use the pipe symbol “ | ” between phrases to get a comparison. For example, if you want to know “see below table” and “see table below” which is more commonly used, you can type in “see below table | see table below”, the search results will show the number of times each phrase appears and the percentage of frequency. From the search result, we can know that “see table below” is more commonly used.
 ↑ Back to textual tutorial list
↑ Back to textual tutorial list
6. Find the best synonym: You can use the hash sign “ # ” in front of a word to check which of its synonyms are commonly written. For example, if you type in “become #famous”, the search results will show the number of times that synonymous phrases appear and the percentage of frequency. From the search result, we know that “become renowned” is the best synonym.
↑ Back to textual tutorial list
You can also use curly brackets “ { } ” to check in which order two or more words are commonly written. For example, just now we used the pipe symbol to see which is more commonly used “see below table” or “see table below”. If we type in “see below table” in curly brackets, we can also get the result that “see table below” is more commonly used. You can also check the frequencies of “to look up something” or “to look something up” by typing in “to look {up something}”.
↑ Back to textual tutorial list
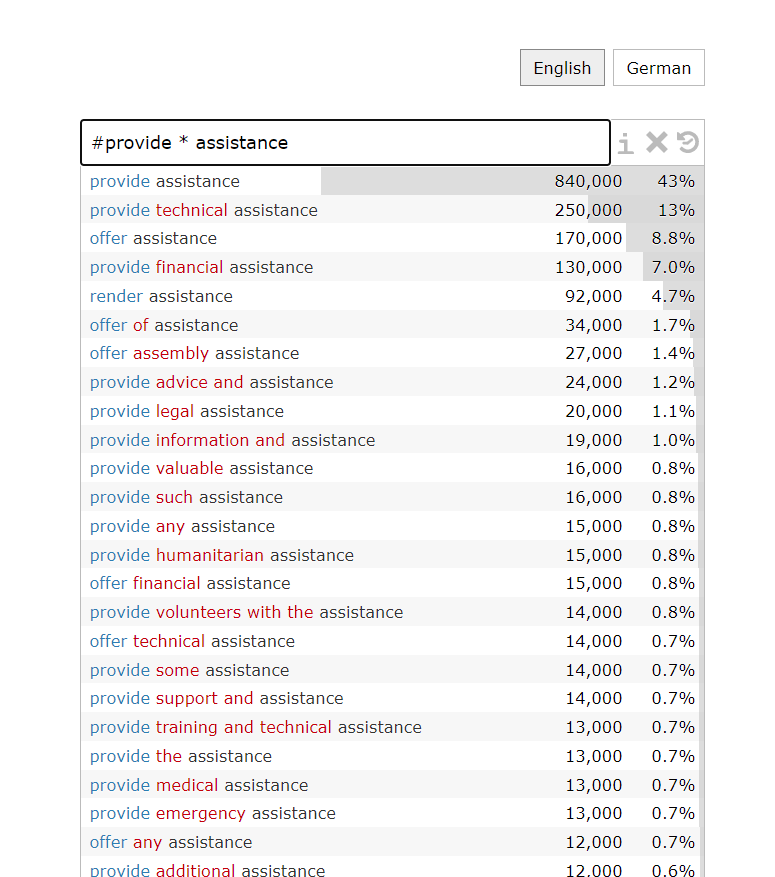
8. Advanced use (Example search: “ #provide * assistance”)
You can also combine different symbols to try the advanced search. For example, you can use the hash sign “ #” in front of “provide” to check which of its synonyms are commonly written in the phrase “provide assistant” and use “ * ” to find any modifiers of “assistance” or missing words in front of “assistance”, then you can get “provide technical assistance”, “offer assistance”, “provide financial assistance”, etc.
↑ Back to textual tutorial list
Try out the exercises below and see how much you have understood.