2.3 Sterile Technique
Sterile technique is used for long, invasive procedures with high risk of infection.
Sterile technique involves:
• Mask and bonnet (head covering)
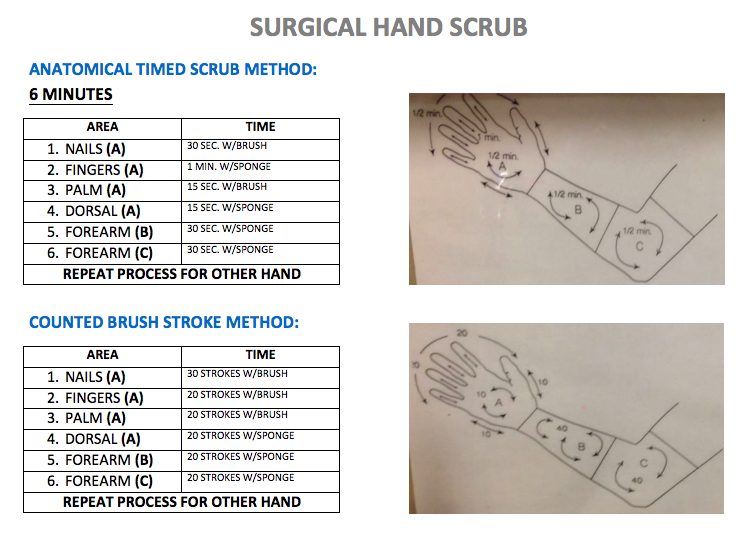
• Surgical hand scrub: A scrub with water and a medicated sponge-brush (4% chlorhexidine) that reaches all 4 anatomical surfaces of the hands, wrists and forearms.
OR
• Surgical hand rub:
• Hands dried with sterile towels
• Sterile gown
• Sterile gloves: REMEMBER that the your STERILE gloves are the LAST things that you don!
DO NOT TOUCH ANYTHING EXCEPT STERILE EQUIPMENT OR ITEMS THAT HAVE A STERILE BARRIER ONCE YOU’VE DONNED YOUR GLOVES!
Sterile technique is indicated for:
• Bone plating
• Bone grafts
• Implant placement
• Orthognathic surgery
• Sinus grafts
• Soft tissue grafts
Sterile Field Work Flow Checklist:
☑️ Clean and disinfect operatory
☑️Place equipment
☑️Arrange personal protective equipment
☑️Arrange hand drying towels
☑️Ensure that staff can move from hand washing to hand drying to separate sterile area without contaminating the sterile field
☑️Plan where and how each item or specimen will be opened, discarded, and processed
Remember:
To prevent contamination:
• Keep clean, dirty, and sterile items separate: sterile can only touch sterile!
• Change gloves and wash hands if going from a contaminated act to an aseptic or sterile act
• The sterile field is considered sterile except for the 2.5 cm border of drape
• Wet items are considered contaminated
Step by step resources:
Surgical Aseptic Technique & the Sterile Field
Video: Wrapping Cassettes for Sterile Technique
Video: Tips for Opening Sterile
Video: Anatomical Surgical Hand Scrub
Video: Surgical Hand Scrub
Video: Gowning & Gloving Yourself (Closed-Glove Method)
Video: Gowning & Gloving Another Person
Video: Gloving Yourself (Open-Glove Method: No Gown)